Papua New Guinea
Introduction
Background
Papua New Guinea (PNG) was first settled between 50,000 and 60,000 years ago. PNG’s harsh geography consisting of mountains, jungles, and numerous river valleys, kept many of the arriving groups isolated, giving rise to PNG’s incredible ethnic and linguistic diversity. Agriculture was independently developed by some of these groups. Around 500 B.C., Austronesian voyagers settled along the coast. Spanish and Portuguese explorers periodically visited the island starting in the 1500s, but none made it into the country’s interior. American and British whaling ships frequented the islands off the coast of New Guinea in the mid-1800s. In 1884, Germany declared a protectorate - and eventually a colony - over the northern part of what would become PNG and named it German New Guinea; days later the UK followed suit on the southern part and nearby islands and called it Papua. Most of their focus was on the coastal regions, leaving the highlands largely unexplored.
The UK put its colony under Australian administration in 1902 and formalized the act in 1906. At the outbreak of World War I, Australia occupied German New Guinea and continued to rule it after the war as a League of Nations Mandate. The discovery of gold along the Bulolo River in the 1920s, led prospectors to venture into the highlands, where they found about 1 million people living in isolated communities. Japan invaded New Guinea in 1941 and reached Papua the following year. Allied victories during the New Guinea campaign pushed out the Japanese, and after the end of the war, Australia combined the two territories into one administration. Sir Michael SOMARE won elections in 1972 on the promise of achieving independence, which was realized in 1975.
A secessionist movement in Bougainville, an island well endowed in copper and gold resources, reignited in 1988 with debates about land use, profits, and an influx of outsiders at the Panguna Copper Mine. Following elections in 1992, the PNG Government took a hardline stance against Bougainville rebels and the resulting civil war led to about 20,000 deaths. In 1997, the PNG Government hired mercenaries to support its troops in Bougainville, sparking an army mutiny and forcing the prime minister to resign. PNG and Bougainville signed a truce in 1997 and a peace agreement in 2001, which granted Bougainville autonomy. An internationally-monitored nonbinding referendum asking Bougainvilleans to chose independence or greater self-rule occurred in November 2019, with 98% of voters opting for independence.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
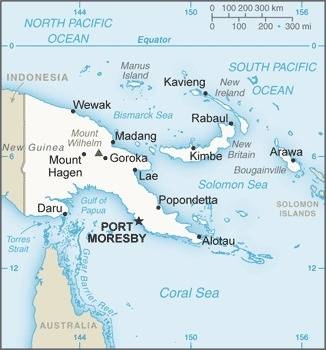
Oceania, group of islands including the eastern half of the island of New Guinea between the Coral Sea and the South Pacific Ocean, east of Indonesia
Geographic coordinates
6 00 S, 147 00 E
Map references
Oceania
Land boundaries
total: 824 km
border countries (1): Indonesia 824 km
Coastline
5,152 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm
measured from claimed archipelagic baselines
Climate
tropical; northwest monsoon (December to March), southeast monsoon (May to October); slight seasonal temperature variation
Terrain
mostly mountains with coastal lowlands and rolling foothills
Elevation
highest point: Mount Wilhelm 4,509 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 667 m
Natural resources
gold, copper, silver, natural gas, timber, oil, fisheries
Land use
agricultural land: 2.6% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0.7% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.5% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0.4% (2018 est.)
forest: 63.1% (2018 est.)
other: 34.3% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
0 sq km (2022)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Sepik river source and mouth (shared with Indonesia) - 1,126 km; Fly river source and mouth (shared with Indonesia) - 1,050 km
Population distribution
population concentrated in the highlands and eastern coastal areas on the island of New Guinea; predominantly a rural distribution with only about one-fifth of the population residing in urban areas
Natural hazards
active volcanism; the country is subject to frequent and sometimes severe earthquakes; mud slides; tsunamis
volcanism: severe volcanic activity; Ulawun (2,334 m), one of Papua New Guinea's potentially most dangerous volcanoes, has been deemed a Decade Volcano by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; Rabaul (688 m) destroyed the city of Rabaul in 1937 and 1994; Lamington erupted in 1951 killing 3,000 people; Manam's 2004 eruption forced the island's abandonment; other historically active volcanoes include Bam, Bagana, Garbuna, Karkar, Langila, Lolobau, Long Island, Pago, St. Andrew Strait, Victory, and Waiowa; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Geography - note
note 1: shares island of New Guinea with Indonesia; generally east-west trending highlands break up New Guinea into diverse ecoregions; one of world's largest swamps along southwest coast
note 2: two major food crops apparently developed on the island of New Guinea: bananas and sugarcane
note 3: Papua New Guinea is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, a belt of active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters bordering the Pacific Ocean; up to 90% of the world's earthquakes and some 75% of the world's volcanoes occur within the Ring of Fire
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Papua New Guinean(s)
adjective: Papua New Guinean
Ethnic groups
Melanesian, Papuan, Negrito, Micronesian, Polynesian
Languages
Tok Pisin (official), English (official), Hiri Motu (official), some 839 indigenous languages spoken (about 12% of the world's total); many languages have fewer than 1,000 speakers
note: Tok Pisin, a creole language, is widely used and understood; English is spoken by 1%-2%; Hiri Motu is spoken by less than 2%
Religions
Protestant 64.3% (Evangelical Lutheran 18.4%, Seventh Day Adventist 12.9%, Pentecostal 10.4%, United Church 10.3%, Evangelical Alliance 5.9%, Anglican 3.2%, Baptist 2.8%, Salvation Army 0.4%), Roman Catholic 26%, other Christian 5.3%, non-Christian 1.4%, unspecified 3.1% (2011 est.)
note: data represent only the citizen population; roughly 0.3% of the population are non-citizens, consisting of Christian 52% (predominantly Roman Catholic), other 10.7% , none 37.3%
Age structure
0-14 years: 31.98% (male 1,182,539/female 1,139,358)
15-24 years: 19.87% (male 731,453/female 711,164)
25-54 years: 37.68% (male 1,397,903/female 1,337,143)
55-64 years: 5.83% (male 218,529/female 204,717)
65 years and over: 4.64% (male 164,734/female 171,916) (2020 est.)

Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 60.5
youth dependency ratio: 55.5
elderly dependency ratio: 5
potential support ratio: 20.1 (2021 est.)
Median age
total: 24 years
male: 24 years
female: 24 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
population concentrated in the highlands and eastern coastal areas on the island of New Guinea; predominantly a rural distribution with only about one-fifth of the population residing in urban areas
Urbanization
urban population: 13.7% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.91% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
410,000 PORT MORESBY (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 1 male(s)/female
total population: 1.03 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
21.9 years (2016/18)
note: data represents median age a first birth among women 25-49
Maternal mortality ratio
145 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58Infant mortality rate
total: 33.59 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 36.91 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 30.12 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 69.43 years
male: 67.76 years
female: 71.19 years (2022 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
36.7% (2016/18)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 86.2% of population
rural: 41.5% of population
total: 47.5% of population
unimproved: urban: 13.8% of population
rural: 58.5% of population
total: 52.5% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
2.3% of GDP (2019)
Physicians density
0.07 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 57.8% of population
rural: 18.2% of population
total: 23.5% of population
unimproved: urban: 42.2% of population
rural: 81.8% of population
total: 76.5% of population (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 1.26 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.6 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.06 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.6 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 39.3% (2020 est.)
male: 53.5% (2020 est.)
female: 25.1% (2020 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 8%
women married by age 18: 27.3%
men married by age 18: 3.7% (2018 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 64.2%
male: 65.6%
female: 62.8% (2015)
People - note
the indigenous population of Papua New Guinea (PNG) is one of the most heterogeneous in the world; PNG has several thousand separate communities, most with only a few hundred people; divided by language, customs, and tradition, some of these communities have engaged in low-scale tribal conflict with their neighbors for millennia; the advent of modern weapons and modern migrants into urban areas has greatly magnified the impact of this lawlessness
Environment
Environment - current issues
rain forest loss as a result of growing commercial demand for tropical timber; unsustainable logging practices result in soil erosion, water quality degredation, and loss of habitat and biodiversity; large-scale mining projects cause adverse impacts on forests and water quality (discharge of heavy metals, cyanide, and acids into rivers); severe drought; inappropriate farming practices accelerate land degradion (soil erosion, siltation, loss of soil fertility); destructive fishing practices and coastal pollution due to run-off from land-based activities and oil spills
Environment - international agreements
party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 10.91 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 7.54 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 11.05 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; northwest monsoon (December to March), southeast monsoon (May to October); slight seasonal temperature variation
Land use
agricultural land: 2.6% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0.7% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.5% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0.4% (2018 est.)
forest: 63.1% (2018 est.)
other: 34.3% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 13.7% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.91% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 2.08% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1 million tons (2014 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 20,000 tons (2016 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 2% (2016 est.)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Sepik river source and mouth (shared with Indonesia) - 1,126 km; Fly river source and mouth (shared with Indonesia) - 1,050 km
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 223.5 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 167.6 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 1 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
801 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Independent State of Papua New Guinea
conventional short form: Papua New Guinea
local short form: Papuaniugini
former: German New Guinea, British New Guinea, Territory of Papua and New Guinea
abbreviation: PNG
etymology: the word "papua" derives from the Malay "papuah" describing the frizzy hair of the Melanesians; Spanish explorer Ynigo ORTIZ de RETEZ applied the term "Nueva Guinea" to the island of New Guinea in 1545 after noting the resemblance of the locals to the peoples of the Guinea coast of Africa
Government type
parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm
Capital
name: Port Moresby
geographic coordinates: 9 27 S, 147 11 E
time difference: UTC+10 (15 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
time zone note: Papua New Guinea has two time zones, including Bougainville (UTC+11)
etymology: named in 1873 by Captain John MORESBY (1830-1922) in honor of his father, British Admiral Sir Fairfax MORESBY (1786-1877)
Administrative divisions
20 provinces, 1 autonomous region*, and 1 district**; Bougainville*, Central, Chimbu, Eastern Highlands, East New Britain, East Sepik, Enga, Gulf, Hela, Jiwaka, Madang, Manus, Milne Bay, Morobe, National Capital**, New Ireland, Northern, Southern Highlands, Western, Western Highlands, West New Britain, West Sepik
Independence
16 September 1975 (from the Australia-administered UN trusteeship)
National holiday
Independence Day, 16 September (1975)
Constitution
history: adopted 15 August 1975, effective at independence 16 September 1975
amendments: proposed by the National Parliament; passage has prescribed majority vote requirements depending on the constitutional sections being amended – absolute majority, two-thirds majority, or three-fourths majority; amended many times, last in 2016
Legal system
mixed legal system of English common law and customary law
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Papua New Guinea
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 8 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: King CHARLES III (since 8 September 2022); represented by Governor General Grand Chief Sir Bob DADAE (since 28 February 2017)
head of government: Prime Minister James MARAPE (since 30 May 2019); Deputy Prime Minister Sam BASIL (since 20 December 2020)
cabinet: National Executive Council appointed by the governor general on the recommendation of the prime minister
elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general nominated by the National Parliament and appointed by the chief of state; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the governor general pending the outcome of a National Parliament vote
election results: James MARAPE elected prime minister; National Parliament vote - 101 to 8
Legislative branch
description: unicameral National Parliament (111 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies - 89 local, 20 provinicial, the autonomous province of Bouganville, and the National Capital District - by majority preferential vote; members serve 5-year terms); note - the constitution allows up to 126 seats
elections: last held from 4-22 July 2022 (next to be held in June 2027)
election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PANGU PATI - 38, PNC - 17, URP - 11, NAP - 5, PNC - 4, SDP - 4, PFP - 3, ULP - 3, Advance PNG - 2, National Party - 2, AP - 1, Destiny Party - 1, Greens - 1, Liberal Party - 1, MAP - 1, NGP - 1, ODP - 1, PLP - 1, PMC - 1, PPP - 1, PRP - 1, THE - 1, independents - 9; composition - NA
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice, deputy chief justice, 35 justices, and 5 acting justices); National Courts (consists of 13 courts located in the provincial capitals, with a total of 19 resident judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the governor general upon advice of the National Executive Council (cabinet) after consultation with the National Justice Administration minister; deputy chief justice and other justices appointed by the Judicial and Legal Services Commission, a 5-member body that includes the Supreme Court chief and deputy chief justices, the chief ombudsman, and a member of the National Parliament; full-time citizen judges appointed for 10-year renewable terms; non-citizen judges initially appointed for 3-year renewable terms and after first renewal can serve until age 70; appointment and tenure of National Court resident judges NA
subordinate courts: district, village, and juvenile courts, military courts, taxation courts, coronial courts, mining warden courts, land courts, traffic courts, committal courts, grade five courts
Political parties and leaders
Advance PNG [Muglua DILU]
Allegiance Party or AP [Bryan KRAMER]
Destiny Party [Marsh NARAWEC]
Liberal Party [John PUNDARI]
Melanesian Alliance Party or MAP [Joseph YOPYYOPY]
National Alliance Party or NAP [Allan BIRD]
New Generation Party or NGP [Keith IDUHU]
Our Development Party or ODP [Puka TEMU]
Papua and Niugini Union Party or PANGU PATI [vacant]
Papua New Guinea Greens Party [Richard MASERE]
Papua New Guinea National Party [Kerenga KUA]
Papua New Guinea Party or PNGP [Belden NAMAH]
People's First Party or PFP [Richard MARU]
People's Labor Party or PLP [Luther WENGE]
People's Movement for Change or PMC [Gary JAFFA]
People's National Congress Party or PNC [Peter Paire O'NEILL]
People's Party or PP [Peter IPATAS]
People's Progress Party or PPP [Sir Julius CHAN]
People's Reform Party or PRP [James DONALD]
Social Democratic Party or SDP [Powes PARKOP]
Triumph Heritage Empowerment Party or THE [Don POLYE]
United Labor Party or PLP [vacant]
United Resources Party or URP [William DUMA]
International organization participation
ACP, ADB, AOSIS, APEC, ARF, ASEAN (observer), C, CD, CP, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d’Affaires Cephas KAYO, Minister (since 31 January 2018)
chancery: 1825 K Street NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20006
telephone: [1] (202) 745-3680
FAX: [1] (202) 745-3679
email address and website:
info@pngembassy.org
http://www.pngembassy.org/
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Joe ZADROZNY (since 14 April 2022); note - also accredited to the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu
embassy: P.O. Box 1492, Port Moresby
mailing address: 4240 Port Moresby Place, Washington DC 20521-4240
telephone: [675] 308-2100
email address and website:
ConsularPortMoresby@state.gov
https://pg.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
divided diagonally from upper hoist-side corner; the upper triangle is red with a soaring yellow bird of paradise centered; the lower triangle is black with five, white, five-pointed stars of the Southern Cross constellation centered; red, black, and yellow are traditional colors of Papua New Guinea; the bird of paradise - endemic to the island of New Guinea - is an emblem of regional tribal culture and represents the emergence of Papua New Guinea as a nation; the Southern Cross, visible in the night sky, symbolizes Papua New Guinea's connection with Australia and several other countries in the South Pacific
National symbol(s)
bird of paradise; national colors: red, black
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 1 (cultural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Kuk Early Agricultural Site
Economy
Economic overview
Papua New Guinea (PNG) is richly endowed with natural resources, but exploitation has been hampered by rugged terrain, land tenure issues, and the high cost of developing infrastructure. The economy has a small formal sector, focused mainly on the export of those natural resources, and an informal sector, employing the majority of the population. Agriculture provides a subsistence livelihood for 85% of the people. The global financial crisis had little impact because of continued foreign demand for PNG's commodities.
Mineral deposits, including copper, gold, and oil, account for nearly two-thirds of export earnings. Natural gas reserves amount to an estimated 155 billion cubic meters. Following construction of a $19 billion liquefied natural gas (LNG) project, PNG LNG, a consortium led by ExxonMobil, began exporting liquefied natural gas to Asian markets in May 2014. The project was delivered on time and only slightly above budget. The success of the project has encouraged other companies to look at similar LNG projects. French supermajor Total is hopes to begin construction on the Papua LNG project by 2020. Due to lower global commodity prices, resource revenues of all types have fallen dramatically. PNG’s government has recently been forced to adjust spending levels downward.
Numerous challenges still face the government of Peter O'NEILL, including providing physical security for foreign investors, regaining investor confidence, restoring integrity to state institutions, promoting economic efficiency by privatizing moribund state institutions, and maintaining good relations with Australia, its former colonial ruler. Other socio-cultural challenges could upend the economy including chronic law and order and land tenure issues. In August, 2017, PNG launched its first-ever national trade policy, PNG Trade Policy 2017-2032. The policy goal is to maximize trade and investment by increasing exports, to reduce imports, and to increase foreign direct investment (FDI).
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$36.69 billion (2020 est.)
$38.17 billion (2019 est.)
$36.06 billion (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
2.5% (2017 est.)
1.6% (2016 est.)
5.3% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$4,100 (2020 est.)
$4,300 (2019 est.)
$4,200 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$19.82 billion (2017 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
5.4% (2017 est.)
6.7% (2016 est.)
Credit ratings
Moody's rating: B2 (2016)
Standard & Poors rating: B- (2020)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 22.1% (2017 est.)
industry: 42.9% (2017 est.)
services: 35% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 43.7% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 19.7% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 10% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.4% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 49.3% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -22.3% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
oil palm fruit, bananas, coconuts, fruit, sweet potatoes, game meat, yams, roots/tubers nes, vegetables, taro
Industries
copra crushing, palm oil processing, plywood production, wood chip production; mining (gold, silver, copper); crude oil and petroleum products; construction, tourism, livestock (pork, poultry, cattle), dairy products, spice products (turmeric, vanilla, ginger, cardamom, chili, pepper, citronella, and nutmeg), fisheries products
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 85%
industry: NA
services: NA
Population below poverty line
37% (2002 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
50.9 (1996)
country comparison to the world: 13Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 1.7%
highest 10%: 40.5% (1996)
Budget
revenues: 3.638 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 4.591 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
$4.859 billion (2017 est.)
$4.569 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$10.6 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$9.224 billion (2016 est.)
Exports - partners
Australia 26%, China 26%, Japan 22%, Taiwan 7% (2019)
Exports - commodities
natural gas, gold, copper, lumber, crude petroleum, nickel, palm oil, fish, coffee (2019)
Imports
$4.84 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$2.077 billion (2016 est.)
Imports - partners
Australia 33%, China 19%, Singapore 14%, Malaysia 9% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, excavation machinery, crude petroleum, foodstuffs, delivery trucks (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$1.735 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$1.656 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$17.94 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$18.28 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
kina (PGK) per US dollar -
3.5131 (2020 est.)
3.4042 (2019 est.)
3.36915 (2018 est.)
2.7684 (2014 est.)
2.4614 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 58.9% (2018)
electrification - urban areas: 82% (2018)
electrification - rural areas: 55.4% (2018)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 1.139 million kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 3,701,693,000 kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 0 kWh (2019 est.)
imports: 0 kWh (2019 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 340 million kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 80.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 18.9% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 37,200 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 38,200 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 60,300 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 27,400 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 159.7 million barrels (2021 est.)
Refined petroleum products - production
22,170 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88Natural gas
production: 11,784,065,000 cubic meters (2020 est.)
consumption: 166.984 million cubic meters (2020 est.)
exports: 11,764,498,000 cubic meters (2020 est.)
imports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
proven reserves: 183.125 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
6.491 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 5.965 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 526,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
11.316 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 166,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 4.818 million (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 54 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: fixed-line teledensity in Papua New Guinea has seen little change over the past two decades; progress in the country’s telecom sector has come primarily from mobile networks, where accessibility has expanded considerably in recent years, with population coverage increasing from less than 3% in 2006 to more than 90% by early 2021; the MNOs operate networks offering services based on GSM, 3G, and LTE, depending on location; GSM is prevalent in many rural and remote areas, while 3G and LTE are centered more on urban areas; MNOs’ investments in 4G are growing, though GSM still represents the bulk of all mobile connections owing to the low penetration of smartphones and the concentration of high-speed data networks predominantly in high value urban areas; a lack of sufficient competition and investment in the wire line segment has driven up prices and hampered network coverage and quality; infrastructure deployment costs are high, partly due to the relatively low subscriber base, the difficult terrain, and the high proportion of the population living in rural areas; fixed telecom infrastructure is almost non-existent outside urban centers, leaving most of the population under served; PNG is the Pacific region’s largest poorly developed telecom market, with only around 22% of its people connected to the internet; this falls far behind the recommended targets set in the country’s National Broadband Policy drafted in 2013, which aimed to provide broadband access to 90% of the total population by 2018; the existing submarine cable infrastructure is insufficient to serve the country’s needs; low international capacity has meant that internet services are expensive and slow; the cable links PNG to the Solomon Islands and Australia (landing at Sydney); despite the improvement in recent years, the country is still impacted by a connectivity infrastructure deficit, making it reliant on more expensive alternatives such as satellites, also weighing on the affordability of services for end-users (2022)
domestic: access to telephone services is not widely available; fixed-line nearly 2 per 100 and mobile-cellular nearly 54 per 100 persons (2020)
international: country code - 675; landing points for the Kumul Domestic Submarine Cable System, PNG-LNG, APNG-2, CSCS and the PPC-1 submarine cables to Australia, Guam, PNG and Solomon Islands; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Broadcast media
4 TV stations: 1 commercial station operating since 1987, 1 state-run station launched in 2008, 1 digital free-to-view network launched in 2014, and 1 satellite network Click TV (PNGTV) launched in 2015; the state-run National Broadcasting Corporation operates 3 radio networks with multiple repeaters and about 20 provincial stations; several commercial radio stations with multiple transmission points as well as several community stations; transmissions of several international broadcasters are accessible (2018)
Internet users
total: 965,373 (2019 est.)
percent of population: 11% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 21,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 0.2 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 6 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 48
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 964,713 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 30.93 million (2018) mt-km
Airports - with paved runways
total: 21
over 3,047 m: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 12
914 to 1,523 m: 5
under 914 m: 1 (2021)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 540
1,524 to 2,437 m: 11
914 to 1,523 m: 53
under 914 m: 476 (2021)
Heliports
2 (2021)
Pipelines
264 km oil (2013)
Roadways
total: 9,349 km (2011)
paved: 3,000 km (2011)
unpaved: 6,349 km (2011)
Merchant marine
total: 177
by type: container ship 6, general cargo 81, oil tanker 3, other 87 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Kimbe, Lae, Madang, Rabaul, Wewak
LNG terminal(s) (export): Port Moresby
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Papua New Guinea Defense Force (PNGDF; includes land, maritime, and air elements); Ministry of Police: Royal Papua New Guinea Constabulary (2022)
Military expenditures
0.4% of GDP (2021 est.)
0.4% of GDP (2020 est.)
0.3% of GDP (2019) (approximately $100 million)
0.3% of GDP (2018) (approximately $100 million)
0.3% of GDP (2017) (approximately $110 million)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 3,000 active duty troops (2022)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the PNGDF has a limited inventory consisting of a diverse mix of foreign-supplied weapons and equipment; Papua New Guinea has received most of its military assistance from Australia (2021)
Military service age and obligation
18-27 for a general enlistee or 18-30 for an officer cadet; no conscription (2022)
Military - note
as of 2022, Australia and the US were assisting Papua New Guinea with expanding and improving the Defense Force naval base at Lombrum on Manus Island; the US first established a Lombrum base in 1944 during World War II
the PNGDF was established in 1973; its infantry regiment and primary unit, the Royal Pacific Islands Regiment (RPIR), is descended from Australian Army infantry battalions comprised of native soldiers and led by Australian officers and non-commissioned officers formed during World War II to help fight the Japanese; the RPIR was disbanded after the war, but reestablished in 1951 as part of the Australian Army where it continued to serve until Papua New Guinea gained its independence in 1975, when it became part of the PNGDF (2022)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Papua New Guinea-Australia: relies on assistance from Australia to keep out illegal cross-border activities from primarily Indonesia, including goods smuggling, illegal narcotics trafficking, and squatters and secessionists
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 11,601 (Indonesia) (mid-year 2021)
IDPs: 24,000 (natural disasters, tribal conflict, inter-communal violence, development projects) (2021)
stateless persons: 9 (mid-year 2021)
Trafficking in persons
tier rating: Tier 3 — Papua New Guinea does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; despite remaining at Tier 3, the government continued to identify some trafficking victims and a prominent trafficking case was advanced; however, the government did not provide protective services for victims and did not systematically implement its victim identification procedures; corruption among officials in the logging sector remains a problem, and they continue to facilitate sex trafficking and forced labor; no alleged traffickers were convicted; the government dedicates little financial and human resources to combat trafficking, and awareness of trafficking is low among government officials (2020)
trafficking profile: Papua New Guinea is a source, destination, and transit country for men, women, and children subjected to sex trafficking and forced labor; women and children are subjected to sex trafficking and domestic servitude; families may sell girls into forced marriages to settle debts, leaving them vulnerable to forced domestic service; local and Chinese men are forced to labor in logging and mining camps; migrant women from Malaysia, Thailand, China, and the Philippines are subjected to sex trafficking and domestic servitude at logging and mining camps, fisheries, and entertainment sites
Illicit drugs
transit point for smuggling drugs such as methamphetamine and cocaine; major consumer of cannabis