Introduction
Background
The Philippine Islands became a Spanish colony during the 16th century; they were ceded to the US in 1898 following the Spanish-American War. Led by Emilio AGUINALDO, the Filipinos conducted an insurgency against American rule from 1899-1902, although some fighting continued in outlying islands as late as 1913. In 1935 the Philippines became a self-governing commonwealth. Manuel QUEZON was elected president and was tasked with preparing the country for independence after a 10-year transition. In 1942 the islands fell under Japanese occupation during World War II, and US forces and Filipinos fought together during 1944-45 to regain control. On 4 July 1946 the Republic of the Philippines attained its independence. A 21-year rule by Ferdinand MARCOS ended in 1986, when a "people power" movement in Manila ("EDSA 1") forced him into exile and installed Corazon AQUINO as president. Her presidency was hampered by several coup attempts that prevented a return to full political stability and economic development. Fidel RAMOS was elected president in 1992. His administration was marked by increased stability and by progress on economic reforms. In 1992, the US closed its last military bases on the islands. Joseph ESTRADA was elected president in 1998. He was succeeded by his vice-president, Gloria MACAPAGAL-ARROYO, in January 2001 after ESTRADA's stormy impeachment trial on corruption charges broke down and another "people power" movement ("EDSA 2") demanded his resignation. MACAPAGAL-ARROYO was elected to a six-year term as president in May 2004. Her presidency was marred by several corruption allegations, but the Philippine economy was one of the few to avoid contraction following the 2008 global financial crisis, expanding each year of her administration. Benigno AQUINO III was elected to a six-year term as president in May 2010 and was succeeded by Rodrigo DUTERTE in June 2016. During his six-year term, DUTERTE pursued a controversial drug war that garnered international criticism for alleged human rights abuses. Ferdinand MARCOS Jr., the son of MARCOS Sr., was elected president in May 2022 with the largest popular vote in a presidential election since his father's ouster.
The Philippine Government faces threats from several groups, some of which are on the US Government's Foreign Terrorist Organization list. Manila has waged a decades-long struggle against ethnic Moro insurgencies in the southern Philippines, which led to a peace accord with the Moro National Liberation Front and a separate agreement with a break away faction, the Moro Islamic Liberation Front. The decades-long Maoist-inspired New People's Army insurgency also operates through much of the country. In 2017, Philippine armed forces battled an ISIS-East Asia siege in Marawi City, driving DUTERTE to declare martial law in the region. In 2019, DUTERTE shepherded a landmark peace deal with the Moro Islamic Liberation Front to establish a semi-autonomous region in the southern Philippines, the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region of Muslim Mindanao. The Philippines faces increased tension with China over disputed territorial and maritime claims in the South China Sea.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Philippine Sea and the South China Sea, east of Vietnam
Geographic coordinates
13 00 N, 122 00 E
Map references
Southeast Asia
Area - comparative
slightly less than twice the size of Georgia; slightly larger than Arizona

Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
36,289 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: irregular polygon extending up to 100 nm from coastline as defined by 1898 treaty; since late 1970s has also claimed polygonal-shaped area in South China Sea as wide as 285 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: to the depth of exploitation
Climate
tropical marine; northeast monsoon (November to April); southwest monsoon (May to October)
Terrain
mostly mountains with narrow to extensive coastal lowlands
Elevation
highest point: Mount Apo 2,954 m
lowest point: Philippine Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 442 m
Natural resources
timber, petroleum, nickel, cobalt, silver, gold, salt, copper
Land use
agricultural land: 41% (2018 est.)
arable land: 18.2% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 17.8% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 5% (2018 est.)
forest: 25.9% (2018 est.)
other: 33.1% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
16,270 sq km (2012)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Laguna de Bay - 890 sq km
Population distribution
population concentrated where good farmlands lie; highest concentrations are northwest and south-central Luzon, the southeastern extension of Luzon, and the islands of the Visayan Sea, particularly Cebu and Negros; Manila is home to one-eighth of the entire national population
Natural hazards
astride typhoon belt, usually affected by 15 and struck by five to six cyclonic storms each year; landslides; active volcanoes; destructive earthquakes; tsunamis
volcanism: significant volcanic activity; Taal (311 m), which has shown recent unrest and may erupt in the near future, has been deemed a Decade Volcano by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; Mayon (2,462 m), the country's most active volcano, erupted in 2009 forcing over 33,000 to be evacuated; other historically active volcanoes include Biliran, Babuyan Claro, Bulusan, Camiguin, Camiguin de Babuyanes, Didicas, Iraya, Jolo, Kanlaon, Makaturing, Musuan, Parker, Pinatubo, and Ragang; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Geography - note
note 1: for decades, the Philippine archipelago was reported as having 7,107 islands; in 2016, the national mapping authority reported that hundreds of new islands had been discovered and increased the number of islands to 7,641 - though not all of the new islands have been verified; the country is favorably located in relation to many of Southeast Asia's main water bodies: the South China Sea, Philippine Sea, Sulu Sea, Celebes Sea, and Luzon Strait
note 2: Philippines is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, a belt of active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters bordering the Pacific Ocean; up to 90% of the world's earthquakes and some 75% of the world's volcanoes occur within the Ring of Fire
note 3: the Philippines sits astride the Pacific typhoon belt and an average of 9 typhoons make landfall on the islands each year - with about 5 of these being destructive; the country is the most exposed in the world to tropical storms
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Filipino(s)
adjective: Philippine
Ethnic groups
Tagalog 26%, Bisaya/Binisaya 14.3%, Ilocano 8%, Cebuano 8%, Illonggo 7.9%, Bikol/Bicol 6.5%, Waray 3.8%, Kapampangan 3%, Maguindanao 1.9%, Pangasinan 1.9%, other local ethnicities 18.5%, foreign ethnicities 0.2% (2020 est.)
Languages
Tagalog 39.9%, Bisaya/Binisaya 16%, Hiligaynon/Ilonggo 7.3%, Ilocano 7.1%, Cebuano 6.5%, Bikol/Bicol 3.9%, Waray 2.6%, Kapampangan 2.4%, Maguindanao 1.4%, Pangasinan/Panggalato 1.3%, other languages/dialects 11.2%, unspecified 0.4% (2020 est.)
major-language sample(s):
Ang World Factbook, ang mapagkukunan ng kailangang impormasyon. (Tagalog)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
note: data represent percentage of households; unspecified Filipino (based on Tagalog) and English are official languagesTaga; eight major dialects - Tagalog, Cebuano, Ilocano, Hiligaynon or Ilonggo, Bicol, Waray, Pampango, and Pangasinan
Religions
Roman Catholic 78.8%, Muslim 6.4%, Iglesia ni Cristo 2.6%, other Christian 3.9%, other 8.2%, none/unspecified <0.1 (2020 est.)
Demographic profile
The Philippines is an ethnically diverse country that is in the early stages of demographic transition. Its fertility rate has dropped steadily since the 1950s. The decline was more rapid after the introduction of a national population program in the 1970s in large part due to the increased use of modern contraceptive methods, but fertility has decreased more slowly in recent years. The country’s total fertility rate (TFR) – the average number of births per woman – dropped below 5 in the 1980s, below 4 in the 1990s, and below 3 in the 2010s. TFR continues to be above replacement level at 2.9 and even higher among the poor, rural residents, and the less-educated. Significant reasons for elevated TFR are the desire for more than two children, in part because children are a means of financial assistance and security for parents as they age, particularly among the poor.
The Philippines are the source of one of the world’s largest emigrant populations, much of which consists of legal temporary workers known as Overseas Foreign Workers or OFWs. As of 2019, there were 2.2 million OFWs. They work in a wide array of fields, most frequently in services (such as caregivers and domestic work), skilled trades, and construction but also in professional fields, including nursing and engineering. OFWs most often migrate to Middle Eastern countries, but other popular destinations include Hong Kong, China, and Singapore, as well as employment on ships. Filipino seafarers make up 35-40% of the world’s seafarers, as of 2014. Women OFWs, who work primarily in domestic services and entertainment, have outnumbered men since 1992.
Migration and remittances have been a feature of Philippine culture for decades. The government has encouraged and facilitated emigration, regulating recruitment agencies and adopting legislation to protect the rights of migrant workers. Filipinos began emigrating to the US and Hawaii early in the 20th century. In 1934, US legislation limited Filipinos to 50 visas per year except during labor shortages, causing emigration to plummet. It was not until the 1960s, when the US and other destination countries – Canada, Australia, and New Zealand – loosened their immigration policies, that Filipino emigration expanded and diversified. The government implemented an overseas employment program in the 1970s, promoting Filipino labor to Gulf countries needing more workers for their oil industries. Filipino emigration increased rapidly. The government had intended for international migration to be temporary, but a lack of jobs and poor wages domestically, the ongoing demand for workers in the Gulf countries, and new labor markets in Asia continue to spur Philippine emigration.
Age structure
0-14 years: 30.49% (male 18,133,279/female 17,366,394)
15-64 years: 64.06% (male 37,667,819/female 36,923,236)
65 years and over: 5.45% (2023 est.) (male 2,516,561/female 3,826,911)
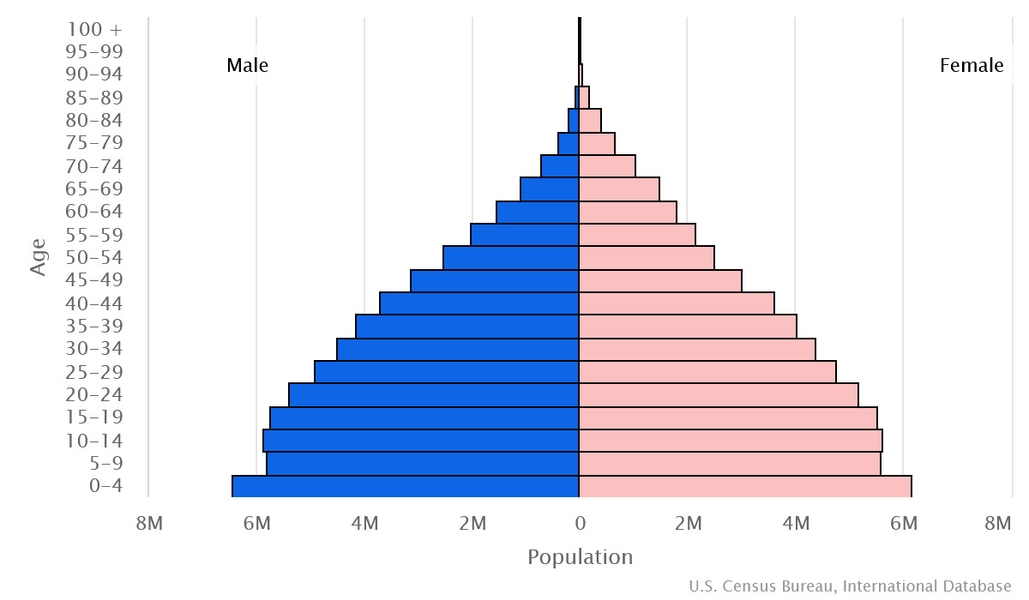
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 56.2
youth dependency ratio: 47.8
elderly dependency ratio: 8.3
potential support ratio: 12 (2021 est.)
Median age
total: 25.4 years (2023 est.)
male: 24.9 years
female: 26 years
comparison ranking: total 165
Population distribution
population concentrated where good farmlands lie; highest concentrations are northwest and south-central Luzon, the southeastern extension of Luzon, and the islands of the Visayan Sea, particularly Cebu and Negros; Manila is home to one-eighth of the entire national population
Urbanization
urban population: 48.3% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.04% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
14.667 million MANILA (capital), 1.949 million Davao, 1.025 million Cebu City, 931,000 Zamboanga, 960,000 Antipolo, 803,000 Cagayan de Oro City, 803,000 Dasmarinas (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.66 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
23.6 years (2022 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
Infant mortality rate
total: 22.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 24.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 19.7 deaths/1,000 live births
comparison ranking: total 74
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 70.5 years (2023 est.)
male: 67 years
female: 74.2 years
comparison ranking: total population 170
Gross reproduction rate
1.35 (2023 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
54.1% (2017)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 99.1% of population
rural: 95% of population
total: 97% of population
unimproved: urban: 0.9% of population
rural: 5% of population
total: 3% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
5.1% of GDP (2020)
Physicians density
0.77 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
Hospital bed density
1 beds/1,000 population (2014)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 96% of population
rural: 91% of population
total: 93.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 4% of population
rural: 9% of population
total: 6.6% of population (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
water contact diseases: leptospirosis
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 4.85 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 1.47 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.03 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 3.34 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
comparison ranking: total 84
Tobacco use
total: 22.9% (2020 est.)
male: 39.3% (2020 est.)
female: 6.5% (2020 est.)
comparison ranking: total 67
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
59.3% (2023 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 2.2%
women married by age 18: 16.5% (2017 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 96.3%
male: 95.7%
female: 96.9% (2019)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 13 years
male: 13 years
female: 13 years (2020)
People - note
one of only two predominantly Christian nations in Southeast Asia, the other being Timor-Leste
Environment
Environment - current issues
uncontrolled deforestation especially in watershed areas; illegal mining and logging; soil erosion; air and water pollution in major urban centers; coral reef degradation; increasing pollution of coastal mangrove swamps that are important fish breeding grounds; coastal erosion; dynamite fishing; wildlife extinction
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Climate
tropical marine; northeast monsoon (November to April); southwest monsoon (May to October)
Land use
agricultural land: 41% (2018 est.)
arable land: 18.2% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 17.8% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 5% (2018 est.)
forest: 25.9% (2018 est.)
other: 33.1% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 48.3% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.04% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 22.45 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 122.29 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 51.32 megatons (2020 est.)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 14,631,923 tons (2016 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 4,096,938 tons (2014 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 28% (2014 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Laguna de Bay - 890 sq km
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 8.16 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
industrial: 9.88 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
agricultural: 67.83 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
Total renewable water resources
479 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of the Philippines
conventional short form: Philippines
local long form: Republika ng Pilipinas
local short form: Pilipinas
etymology: named in honor of King PHILLIP II of Spain by Spanish explorer Ruy LOPEZ de VILLALOBOS, who visited some of the islands in 1543
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Manila
geographic coordinates: 14 36 N, 120 58 E
time difference: UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: derives from the Tagalog "may-nila" meaning "where there is indigo" and refers to the presence of indigo-yielding plants growing in the area surrounding the original settlement
Administrative divisions
81 provinces and 38 chartered cities
provinces: Abra, Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Aklan, Albay, Antique, Apayao, Aurora, Basilan, Bataan, Batanes, Batangas, Biliran, Benguet, Bohol, Bukidnon, Bulacan, Cagayan, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Camiguin, Capiz, Catanduanes, Cavite, Cebu, Cotabato, Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur, Davao de Oro, Davao Occidental, Davao Oriental, Dinagat Islands, Eastern Samar, Guimaras, Ifugao, Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, Iloilo, Isabela, Kalinga, Laguna, Lanao del Norte, Lanao del Sur, La Union, Leyte, Maguindanao, Marinduque, Masbate, Mindoro Occidental, Mindoro Oriental, Misamis Occidental, Misamis Oriental, Mountain, Negros Occidental, Negros Oriental, Northern Samar, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Vizcaya, Palawan, Pampanga, Pangasinan, Quezon, Quirino, Rizal, Romblon, Samar, Sarangani, Siquijor, Sorsogon, South Cotabato, Southern Leyte, Sultan Kudarat, Sulu, Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur, Tarlac, Tawi-Tawi, Zambales, Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur, Zamboanga Sibugay;
chartered cities: Angeles, Bacolod, Baguio, Butuan, Cagayan de Oro, Caloocan, Cebu, Cotabato, Dagupan, Davao, General Santos, Iligan, Iloilo, Lapu-Lapu, Las Pinas, Lucena, Makati, Malabon, Mandaluyong, Mandaue, Manila, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Naga, Navotas, Olongapo, Ormoc, Paranaque, Pasay, Pasig, Puerto Princesa, Quezon, San Juan, Santiago, Tacloban, Taguig, Valenzuela, Zamboanga
Independence
4 July 1946 (from the US)
National holiday
Independence Day, 12 June (1898); note - 12 June 1898 was date of declaration of independence from Spain; 4 July 1946 was date of independence from the US
Constitution
history: several previous; latest ratified 2 February 1987, effective 11 February 1987
amendments: proposed by Congress if supported by three fourths of the membership, by a constitutional convention called by Congress, or by public petition; passage by either of the three proposal methods requires a majority vote in a national referendum; note - the constitution has not been amended since its enactment in 1987
Legal system
mixed legal system of civil, common, Islamic (sharia), and customary law
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; withdrew from the ICCt in March 2019
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the Philippines
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Ferdinand "BongBong" MARCOS, Jr. (since 30 June 2022); Vice President Sara DUTERTE-Carpio (since 30 June 2022); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Ferdinand "BongBong" MARCOS, Jr. (since 30 June 2022); Vice President Sara DUTERTE-Carpio (since 30 June 2022)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president with the consent of the Commission of Appointments, an independent body of 25 Congressional members including the Senate president (ex officio chairman), appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on separate ballots by simple majority popular vote for a single 6-year term; election last held on 9 May 2022 (next to be held on 9 May 2028)
election results:
2022: Ferdinand MARCOS, Jr. elected president; percent of vote - Ferdinand MARCOS, Jr. (PFP) 58.7%, Leni ROBREDO (independent) 27.9%, Manny PACQUIAO (PROMDI) 6.8%, other 6.6%; Sara DUTERTE-Carpio elected vice president; percent of vote Sara DUTERTE-Carpio (Lakas-CMD) 61.5%, Francis PANGILINAN (LP) 17.8%, Tito SOTTO 15.8%, other 4.9%
2016: Rodrigo DUTERTE elected president; percent of vote - Rodrigo DUTERTE (PDP-Laban) 39%, Manuel "Mar" ROXAS (LP) 23.5%, Grace POE (independent) 21.4%, Jejomar BINAY (UNA) 12.7%, Miriam Defensor SANTIAGO (PRP) 3.4%; Leni ROBREDO elected vice president; percent of vote Leni ROBREDO (LP) 35.1%, Bongbong MARCOS (independent) 34.5%, Alan CAYETANO 14.4%, Francis ESCUDERO (independent) 12%, other 4%
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Congress or Kongreso consists of:
Senate or Senado (24 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by majority vote; members serve 6-year terms with one-half of the membership renewed every 3 years)
House of Representatives or Kapulungan Ng Mga Kinatawan (316 seats; 253 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 63 representing minorities directly elected by party-list proportional representation vote; members serve 3-year terms)
elections:
Senate - elections last held on 9 May 2022 (next to be held in May 2025)
House of Representatives - elections last held on 9 May 2022 (next to be held in May 2025)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NPC 5, PDP-Laban 5, NP 4, other 5, independent 5; composition - men 17, women 7, percent of women 29%
House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - PDP-Laban 22.7%, NP 13.7%, NUP 12.6%, NPC 11.7%, Lakas-CMD 9.4%,LP 3.8%, HNP 2.5%, other 19.6% independent 4%; seats by party - PDP-Laban 66, NP, NPC 35, NUP 33, Lakas-CMD 26, LP 10, HNP 6, other 35, independent 6, party-list 63; composition - men 193, women 123, percent of women 38.9%; note - total Congress percent of women 38.2%
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of a chief justice and 14 associate justices)
judge selection and term of office: justices are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial and Bar Council, a constitutionally created, 6-member body that recommends Supreme Court nominees; justices serve until age 70
subordinate courts: Court of Appeals; Sandiganbayan (special court for corruption cases of government officials); Court of Tax Appeals; regional, metropolitan, and municipal trial courts; sharia courts
Political parties and leaders
Democratic Action (Aksyon Demokratiko) [Ernesto RAMEL, Jr]
Alliance for Change (Hugpong ng Pagbabago or HNP) [Claude BAUTISTA]
Lakas ng EDSA-Christian Muslim Democrats or Lakas-CMD [Sara DUTERTE-CARPIO]
Liberal Party or LP [Francis PANGILINAN]
Nacionalista Party or NP [Manuel "Manny" VILLAR]
Nationalist People's Coalition or NPC [Mark COJUANGCO]
National Unity Party or NUP [Ronaldo V. PUNO]
Partido Demokratiko Pilipino-Lakas ng Bayan or PDP-Laban [Rodrigo DUTERTE]
Partido Federal ng Pilipinas or PFP [Ferdinand MARCOS, Jr.]
Progressive Movement for the Devolution of Initiatives or PROMDI [Mariano "Mimo" OSMENA]
International organization participation
ADB, APEC, ARF, ASEAN, BIS, CD, CICA (observer), CP, EAS, FAO, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSTAH, NAM, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, PIF (partner), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNMIL, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Jose Manuel del Gallego ROMUALDEZ (since 29 November 2017)
chancery: 1600 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone: [1] (202) 467-9300
FAX: [1] (202) 328-7614
email address and website:
info@phembassy-us.org; consular@phembassy-us.org
The Embassy of the Republic of the Philippines in Washington D.C. (philippineembassy-dc.org)
consulate(s) general: Chicago, Honolulu, Los Angeles, New York, Saipan (Northern Mariana Islands), San Francisco, Tamuning (Guam)
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador MaryKay Loss CARLSON (since 22 July 2022)
embassy: 1201 Roxas Boulevard, Manila 1000
mailing address: 8600 Manila Place, Washington DC 20521-8600
telephone: [63] (2) 5301-2000
FAX: [63] (2) 5301-2017
email address and website:
acsinfomanila@state.gov
https://ph.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
two equal horizontal bands of blue (top) and red; a white equilateral triangle is based on the hoist side; the center of the triangle displays a yellow sun with eight primary rays; each corner of the triangle contains a small, yellow, five-pointed star; blue stands for peace and justice, red symbolizes courage, the white equal-sided triangle represents equality; the rays recall the first eight provinces that sought independence from Spain, while the stars represent the three major geographical divisions of the country: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao; the design of the flag dates to 1897
note: in wartime the flag is flown upside down with the red band at the top
National symbol(s)
three stars and sun, Philippine eagle; national colors: red, white, blue, yellow

National anthem
name: "Lupang Hinirang" (Chosen Land)
lyrics/music: Jose PALMA (revised by Felipe PADILLA de Leon)/Julian FELIPE
note: music adopted 1898, original Spanish lyrics adopted 1899, Filipino (Tagalog) lyrics adopted 1956; although the original lyrics were written in Spanish, later English and Filipino versions were created; today, only the Filipino version is used
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 6 (3 cultural, 3 natural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Baroque Churches of the Philippines (c); Tubbataha Reefs Natural Park (n); Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras (c); Historic Vigan (c); Puerto-Princesa Subterranean River National Park (n); Mount Hamiguitan Range Wildlife Sanctuary (n)
Economy
Economic overview
diversified, growing East Asian economy; major semiconductor, ship-building, and electronics exporter; significant remittances; COVID-19 hit consumption and investments hard; regional tensions with China; major geothermal energy user
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$921.826 billion (2021 est.)
$872.09 billion (2020 est.)
$963.83 billion (2019 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
comparison ranking: 30
Real GDP per capita
$8,100 (2021 est.)
$7,800 (2020 est.)
$8,700 (2019 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
comparison ranking: 155
GDP (official exchange rate)
$377.205 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
3.93% (2021 est.)
2.39% (2020 est.)
2.39% (2019 est.)
comparison ranking: 97
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: BBB (2017)
Moody's rating: Baa2 (2014)
Standard & Poors rating: BBB+ (2019)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 9.6% (2017 est.)
industry: 30.6% (2017 est.)
services: 59.8% (2017 est.)
comparison rankings: services 130; industry 74; agriculture 93
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 73.5% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 11.3% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 25.1% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.1% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 31% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -40.9% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
sugar cane, rice, coconuts, maize, bananas, vegetables, tropical fruit, plantains, pineapples, cassava
Industries
semiconductors and electronics assembly, business process outsourcing, food and beverage manufacturing, construction, electric/gas/water supply, chemical products, radio/television/communications equipment and apparatus, petroleum and fuel, textile and garments, non-metallic minerals, basic metal industries, transport equipment
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 7.3% (2021 est.)
male: 6.3%
female: 9%
comparison ranking: total 175
Population below poverty line
16.7% (2018 est.)
Average household expenditures
on food: 42% of household expenditures (2018 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 1.4% of household expenditures (2018 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 3.2%
highest 10%: 29.5% (2015 est.)
Budget
revenues: $71.173 billion (2020 est.)
expenditures: $90.953 billion (2020 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$6.009 billion (2021 est.)
$11.578 billion (2020 est.)
-$3.047 billion (2019 est.)
comparison ranking: 192
Exports
$87.79 billion (2021 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$80.034 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$94.741 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
comparison ranking: 47
Exports - partners
China 16%, United States 14%, Japan 12%, Hong Kong 12%, Singapore 7% (2021)
Exports - commodities
integrated circuits, office machinery/parts, insulated wiring, transformers, semiconductors (2021)
Imports
$126.508 billion (2021 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$99.943 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$131.013 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
comparison ranking: 39
Imports - partners
China 29%, Japan 8%, South Korea 7%, United States 6%, Singapore 6%, Indonesia 6%, Thailand 5%, Taiwan 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
integrated circuits, refined petroleum, cars, crude petroleum, broadcasting equipment (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$108.755 billion (31 December 2021 est.)
$109.99 billion (31 December 2020 est.)
$89.515 billion (31 December 2019 est.)
comparison ranking: 28
Exchange rates
Philippine pesos (PHP) per US dollar -
Exchange rates:
49.255 (2021 est.)
49.624 (2020 est.)
51.796 (2019 est.)
52.661 (2018 est.)
50.404 (2017 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
population without electricity: 3 million (2020)
electrification - total population: 97.4% (2021)
electrification - urban areas: 98.6% (2021)
electrification - rural areas: 96.4% (2021)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 27.885 million kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 90,926,990,000 kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 0 kWh (2020 est.)
imports: 0 kWh (2020 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 9.994 billion kWh (2019 est.)
comparison rankings: imports 209; exports 209; installed generating capacity 38; transmission/distribution losses 32; consumption 35
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 77.6% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 1.3% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 1.1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 8% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 11% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 1.1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 13.752 million metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 32.855 million metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 7.554 million metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 28.358 million metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 361 million metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 10,300 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 527,400 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 12,400 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 232,500 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 138.5 million barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
production: 3,632,507,000 cubic meters (2019 est.)
consumption: 3,632,507,000 cubic meters (2019 est.)
exports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
imports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
proven reserves: 98.542 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
142.282 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 70.82 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 64.418 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 7.044 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
comparison ranking: total emissions 36
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 5,028,018 (2021 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4 (2021 est.)
comparison ranking: total subscriptions 27
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 163,345,244 (2021 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 143 (2021 est.)
comparison ranking: total subscriptions 11
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: the Covid-19 pandemic had a relatively minor impact on the Philippine’s telecom sector in 2020; subscriber numbers fell in some areas, but this was offset by strong growth in mobile data and broadband usage since a significant proportion of the population transitioned to working or studying from home; major investment programs covering LTE, 5G, and fiber broadband networks suffered slight delays due to holdups in supply chains, but activity has since ramped up in an attempt to complete the roll outs as per the original schedule; the major telecom operators had mixed financial results for the past year; overall, the number of mobile subscribers is expected to grow to 153 million by the end of 2021, with the penetration rate approaching 144%; the government remains keen, and committed, to seeing strong competition, growth, and service excellence in the telecom sector, so there is likely to be continued support (financially as well as through legislation such as enabling mobile tower sharing and number portability) to ensure that the sector remains viable for emerging players; the mobile sector will remain the Philippines’ primary market for telecommunications well into the future; the unique terrain and resulting challenges associated with accessing remote parts of the archipelago means that in many areas fixed networks are neither cost-effective nor logistically viable; the bulk of telecoms investment over the coming years will continue to be in 5G and 5G-enabled LTE networks; coverage of LTE and 5G networks extends to over 95% of the population, and for the vast majority of people mobile will likely remain their only platform for telecom services (2021)
domestic: fixed-line nearly 4 per 100 and mobile-cellular nearly 143 per 100 (2021)
international: country code - 63; landing points for the NDTN, TGN-IA, AAG, PLCN, EAC-02C, DFON, SJC, APCN-2, SeaMeWe, Boracay-Palawan Submarine Cable System, Palawa-Illoilo Cable System, NDTN, SEA-US, SSSFOIP, ASE and JUPITAR submarine cables that together provide connectivity to the US, Southeast Asia, Asia, Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and Australia (2019)
Broadcast media
multiple national private TV and radio networks; multi-channel satellite and cable TV systems available; more than 400 TV stations; about 1,500 cable TV providers with more than 2 million subscribers, and some 1,400 radio stations; the Philippines adopted Japan’s Integrated Service Digital Broadcast – Terrestrial standard for digital terrestrial television in November 2013 and is scheduled to complete the switch from analog to digital broadcasting by the end of 2023 (2019)
Internet users
total: 58.3 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 53% (2021 est.)
comparison ranking: total 18
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 7,936,574 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 7 (2020 est.)
comparison ranking: total 25
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 13 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 200
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 43,080,118 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 835.9 million (2018) mt-km
Airports - with paved runways
89
civil airports: 11
military airports: 4
joint use (civil-military) airports: 2
other airports: 72
note: paved runways have a concrete or asphalt surface but not all have facilities for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control; the length of a runway required for aircraft to safely operate depends on a number of factors including the type of aircraft, the takeoff weight (including passengers, cargo, and fuel), engine types, flap settings, landing speed, elevation of the airport, and average maximum daily air temperature; paved runways can reach a length of 5,000 m (16,000 ft.), but the “typical” length of a commercial airline runway is between 2,500-4,000 m (8,000-13,000 ft.)
Airports - with unpaved runways
158
note: unpaved runways have a surface composition such as grass or packed earth and are most suited to the operation of light aircraft; unpaved runways are usually short, often less than 1,000 m (3,280 ft.) in length; airports with unpaved runways often lack facilities for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control
Heliports
2 (2021)
Pipelines
530 km gas, 138 km oil (non-operational), 185 km refined products (2017)
Railways
total: 77 km (2017)
standard gauge: 49 km (2017) 1.435-m gauge
narrow gauge: 28 km (2017) 1.067-m gauge
comparison ranking: total 130
Roadways
total: 216,387 km (2014)
paved: 61,093 km (2014)
unpaved: 155,294 km (2014)
comparison ranking: total 25
Merchant marine
total: 1,853 (2022)
by type: bulk carrier 59, container ship 43, general cargo 749, oil tanker 210, other 792
comparison ranking: total 14
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Batangas, Cagayan de Oro, Cebu, Davao, Liman, Manila
container port(s) (TEUs): Manila (4,976,014) (2021)
LNG terminal(s) (import): Batangas
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP): Army, Navy (includes Marine Corps), Air Force
Department of Transportation: Philippine Coast Guard (PCG)
Department of the Interior: Philippine National Police Force (PNP) (2023)
note 1: the PCG is an armed and uniformed service that would be attached to the AFP during a conflict
note 2: the Philippine Government also arms and supports civilian militias; the AFP controls Civilian Armed Force Geographical Units, while the Civilian Volunteer Organizations fall under PNP command
Military expenditures
1.2% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2020)
1.1% of GDP (2019)
1% of GDP (2018)
comparison ranking: 107
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 140,000 active-duty personnel (100,000 Army; 25,000 Navy, including about 8,000 Marine Corps; 15,000 Air Force) (2023)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the AFP is equipped with a wide mix of imported weapons systems; in recent years, it has received equipment from more than a dozen countries led by Israel, South Korea, and the US (2023)
Military service age and obligation
18-27 years of age for voluntary military service for men and women; no conscription (2023)
note: as of 2020, women made up about 6% of the active military; women were allowed to enter the Philippine Military Academy and train as combat soldiers in 1993
Military - note
the Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP) were formally organized during the American colonial period as the Philippine Army; they were established by the National Defense Act of 1935 and were comprised of both Filipinos and Americans
the US and Philippines agreed to a mutual defense treaty in 1951; in 2014, the two governments signed an Enhanced Defense Cooperation Agreement (EDCA) that established new parameters for military cooperation; under the EDCA, the Philippine Government may grant US troops access to Philippine military bases on a rotational basis “for security cooperation exercises, joint and combined military training activities, and humanitarian assistance and disaster relief activities”; the Philippines has Major Non-NATO Ally (MNNA) status with the US, a designation under US law that provides foreign partners with certain benefits in the areas of defense trade and security cooperation
the Philippine Government faces a number of internal threats from several armed separatists, terrorists, and criminal groups; as such, much of the AFP's operational focus is internal security, particularly in the south, where several separatist Islamic insurgent and terrorist groups operate and up to 60% of the armed forces are deployed; additional combat operations are conducted against the Communist People’s Party/New People’s Army, which is active mostly on Luzon, the Visayas, and areas of Mindanao; prior to a peace deal in 2014, the AFP fought a decades-long conflict against the Moro Islamic Liberation Front (MILF), a separatist organization based mostly on the island of Mindanao; the MILF's armed wing, the Bangsamoro Islamic Armed Forces (BIAF), had up to 40,000 fighters under arms
the AFP’s air and ground forces are experienced with and largely configured for counterinsurgency and counterterrorist operations; a majority of the Air Force’s combat aircraft are ground attack capable and organized in mixed fixed-wing and helicopter squadrons or combat groups formed for mobile operations against insurgents and terrorists; similarly, 10 of the Army’s 11 divisions are light infantry, and the AFP has a joint-service special operations command comprised of rangers, scouts, special forces, counterterrorism, quick reaction, marine, naval, and air units
in addition to its typical roles of patrolling the country's territorial waters, the Navy conducts interdiction operations against terrorist, insurgent, and criminal groups around the southern islands, including joint maritime patrols with Indonesia and Malaysia, particularly in the Sulu Sea; the Navy has commands for offshore, littoral, and amphibious operations; most of its surface fleet consists of coastal patrol vessels and fast attack craft, although in response to maritime and territorial disputes with China in the South China Sea over the past decade the Navy has acquired some larger warships, including frigates, a corvette, offshore patrol vessels (OPVs), and landing platform dock (LPD) amphibious assault ships, and has plans to acquire additional corvettes and OPVs in the next few years; the Marine Corps consists of four infantry brigades and also conducts counterinsurgency operations
the Philippines National Police (PNP) also has an active role in counterinsurgency and counter-terrorism operations alongside the AFP, particularly the Special Action Force, a PNP commando unit that specializes in urban counter-terrorism operations (2023)
Space
Space agency/agencies
Philippine Space Agency (PhilSA; established 2019); Philippine Space Council (PSC; established in 2019 as an advisory body responsible for coordinating and integrating policies, programs and resources affecting space science and technology applications); prior to PhilSA’s establishment, the Philippine’s space program was decentralized under several organizations, including the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical, and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA), the National Mapping and Resource Information Authority (NAMRIA), and the National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council (NDRRMC) (2023)
Space launch site(s)
none; reviewing the possibility of establishing a commercial launchpad, possibly in Mindanao given its proximity to the Equator (2023)
Space program overview
has a small and ambitious space program focused on acquiring satellites and related technologies, largely for the areas of climate studies, national security, and risk management; also prioritizing development of the country’s space expertise and industry; manufactures and operates satellites (mostly micro- and nano-sized), including remote sensing (RS) and scientific/experimental; has relations with a variety of foreign space agencies and industries, including those of China, the European Space Agency and some of its member states, Japan, Russia, and the US (2023)
note: further details about the key activities, programs, and milestones of the country’s space program, as well as government spending estimates on the space sector, appear in Appendix S
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Terrorist group(s): Abu Sayyaf Group; Communist Party of the Philippines/New People's Army (CPP/NPA); Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham – East Asia (ISIS-EA) in the Philippines
note 1: ISIS-EA factions include Daulah Islamiya-Lanao (aka Maute Group), Daulah Islamiya-Maguindanao, Daulah Islamiya-Socsargen, ISIS-aligned elements of the Abu Sayyaf Group (ASG), ISIS-aligned elements of the Bangsamoro Islamic Freedom Fighters (BIFF), and rogue elements of the Moro Islamic Liberation Front (MILF)
note 2: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Philippines-Taiwan-China-Malaysia-Vietnam: Philippines claims sovereignty over Scarborough Reef (also claimed by China together with Taiwan) and over certain of the Spratly Islands, known locally as the Kalayaan (Freedom) Islands, also claimed by China, Malaysia, Taiwan, and Vietnam; the 2002 "Declaration on the Conduct of Parties in the South China Sea," has eased tensions in the Spratly Islands but falls short of a legally binding "code of conduct" desired by several of the disputants; in March 2005, the national oil companies of China, the Philippines, and Vietnam signed a joint accord to conduct marine seismic activities in the Spratly Islands
Philippines-Malaysia: Philippines retains a dormant claim to Malaysia's Sabah State in northern Borneo based on the Sultanate of Sulu's granting the Philippines Government power of attorney to pursue a sovereignty claim on his behalf; the disagreement resurfaced in September 2020 , when Malaysia’s submission to the UN about extending its continental shelf was sharply countered by the Philippines because it included the disputed territory
Philippines-Palau: maritime delimitation negotiations continue with Palau, as of March 2022
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 102,000 (government troops fighting the Moro Islamic Liberation Front, the Abu Sayyaf Group, and the New People's Army; clan feuds; armed attacks, political violence, and communal tensions in Mindanao) (2022)
stateless persons: 261 (2022); note - stateless persons are descendants of Indonesian migrants
Illicit drugs
Illegal drugs, including methamphetamine hydrochloride, cannabis, and methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MMDA, or "ecstasy") enter the Philippines from the Golden Triangle (Thailand, Laos, and Burma); drugs entering the Philippines are used locally and transported to other countries in Southeast Asia and Oceania; Chinese transnational organizations are the principal supplier of methamphetamine; not a significant source or transit country for drugs entering the United States