Introduction
Background
Montevideo, founded by the Spanish in 1726 as a military stronghold, soon became an important commercial center due to its natural harbor. Claimed by Argentina but annexed by Brazil in 1821, Uruguay declared its independence in 1825 and secured its freedom in 1828 after a three-year struggle. The administrations of President Jose BATLLE in the early 20th century launched widespread political, social, and economic reforms that established a statist tradition. A violent Marxist urban guerrilla movement named the Tupamaros (or Movimiento de Liberación Nacional-Tupamaros (MLN-T)), launched in the late 1960s, led Uruguay's president to cede control of the government to the military in 1973. By yearend, the rebels had been crushed, but the military continued to expand its hold over the government. Civilian rule was restored in 1985. In 2004, the left-of-center Frente Amplio Coalition won national elections that effectively ended 170 years of political control previously held by the Colorado and National (Blanco) parties. The left-of-center retained the presidency and control of both chambers of congress until 2019. Uruguay's political and labor conditions are among the freest on the continent.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
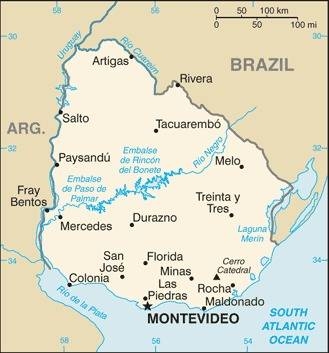
Southern South America, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Argentina and Brazil
Geographic coordinates
33 00 S, 56 00 W
Map references
South America
Area - comparative
about the size of Virginia and West Virginia combined; slightly smaller than the state of Washington

Land boundaries
total: 1,591 km
border countries (2): Argentina 541 km; Brazil 1,050 km
Coastline
660 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or the edge of continental margin
Climate
warm temperate; freezing temperatures almost unknown
Terrain
mostly rolling plains and low hills; fertile coastal lowland
Elevation
highest point: Cerro Catedral 514 m
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 109 m
Natural resources
arable land, hydropower, minor minerals, fish
Land use
agricultural land: 87.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 10.1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.2% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 76.9% (2018 est.)
forest: 10.2% (2018 est.)
other: 2.6% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
2,380 sq km (2012)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Lagoa Mirim (shared with Brazil) - 2,970 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Rio de la Plata/Parana river mouth (shared with Brazil [s], Argentina, Paraguay) - 4,880 km; Uruguay river mouth (shared with Brazil [s] and Argentina) - 1,610 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major aquifers
Guarani Aquifer System
Population distribution
most of the country's population resides in the southern half of the country; approximately 80% of the populace is urban, living in towns or cities; nearly half of the population lives in and around the capital of Montevideo
Natural hazards
seasonally high winds (the pampero is a chilly and occasional violent wind that blows north from the Argentine pampas), droughts, floods; because of the absence of mountains, which act as weather barriers, all locations are particularly vulnerable to rapid changes from weather fronts
Geography - note
second-smallest South American country (after Suriname); most of the low-lying landscape (three-quarters of the country) is grassland, ideal for cattle and sheep raising
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Uruguayan(s)
adjective: Uruguayan
Ethnic groups
White 87.7%, Black 4.6%, Indigenous 2.4%, other 0.3%, none or unspecified 5% (2011 est.)
note: data represent primary ethnic identity
Languages
Spanish (official)
major-language sample(s):
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Roman Catholic 42%, Protestant 15%, other 6%, agnostic 3%, atheist 10%, unspecified 24% (2014 est.)
Demographic profile
Uruguay rates high for most development indicators and is known for its secularism, liberal social laws, and well-developed social security, health, and educational systems. It is one of the few countries in Latin America and the Caribbean where the entire population has access to clean water. Uruguay's provision of free primary through university education has contributed to the country's high levels of literacy and educational attainment. However, the emigration of human capital has diminished the state's return on its investment in education. Remittances from the roughly 18% of Uruguayans abroad amount to less than 1 percent of national GDP. The emigration of young adults and a low birth rate are causing Uruguay's population to age rapidly.
In the 1960s, Uruguayans for the first time emigrated en masse - primarily to Argentina and Brazil - because of economic decline and the onset of more than a decade of military dictatorship. Economic crises in the early 1980s and 2002 also triggered waves of emigration, but since 2002 more than 70% of Uruguayan emigrants have selected the US and Spain as destinations because of better job prospects. Uruguay had a tiny population upon its independence in 1828 and welcomed thousands of predominantly Italian and Spanish immigrants, but the country has not experienced large influxes of new arrivals since the aftermath of World War II. More recent immigrants include Peruvians and Arabs.
Age structure
0-14 years: 19.51% (male 336,336/female 324,563)
15-24 years: 15.14% (male 259,904/female 252,945)
25-54 years: 39.86% (male 670,295/female 679,850)
55-64 years: 10.79% (male 172,313/female 193,045)
65 years and over: 14.71% (male 200,516/female 297,838) (2020 est.)

Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 53.6
youth dependency ratio: 29.9
elderly dependency ratio: 23.7
potential support ratio: 4.2 (2021 est.)
Median age
total: 35.5 years
male: 33.8 years
female: 37.3 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
most of the country's population resides in the southern half of the country; approximately 80% of the populace is urban, living in towns or cities; nearly half of the population lives in and around the capital of Montevideo
Urbanization
urban population: 95.8% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.4% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.774 million MONTEVIDEO (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.9 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.55 male(s)/female
total population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
17 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134Infant mortality rate
total: 8.31 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 9.46 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 7.12 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 78.43 years
male: 75.32 years
female: 81.64 years (2022 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
79.6% (2015)
note: percent of women aged 15-44
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
9.4% of GDP (2019)
Physicians density
4.94 physicians/1,000 population (2017)
Hospital bed density
2.4 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 99.2% of population
rural: 99.6% of population
total: 99.2% of population
unimproved: urban: 0.8% of population
rural: 0.4% of population
total: 0.8% of population (2020 est.)
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 5.42 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 1.86 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 2.86 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.71 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 21.5% (2020 est.)
male: 24.4% (2020 est.)
female: 18.5% (2020 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 98.8%
male: 98.5%
female: 99% (2019)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 19 years
male: 17 years
female: 20 years (2019)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 33.1%
male: 29%
female: 38.5% (2020 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
water pollution from meat packing, tannery industries; heavy metal pollution; inadequate solid and hazardous waste disposal; deforestation
Environment - international agreements
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protection, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Life Conservation
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 8.63 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 6.77 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 25.59 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
warm temperate; freezing temperatures almost unknown
Land use
agricultural land: 87.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 10.1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.2% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 76.9% (2018 est.)
forest: 10.2% (2018 est.)
other: 2.6% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 95.8% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.4% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 1.56% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1,260,140 tons (2012 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 100,811 tons (2011 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 8% (2011 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Lagoa Mirim (shared with Brazil) - 2,970 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Rio de la Plata/Parana river mouth (shared with Brazil [s], Argentina, Paraguay) - 4,880 km; Uruguay river mouth (shared with Brazil [s] and Argentina) - 1,610 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major aquifers
Guarani Aquifer System
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 410 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 80 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 3.17 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
172.2 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Oriental Republic of Uruguay
conventional short form: Uruguay
local long form: Republica Oriental del Uruguay
local short form: Uruguay
former: Banda Oriental, Cisplatine Province
etymology: name derives from the Spanish pronunciation of the Guarani Indian designation of the Uruguay River, which makes up the western border of the country and whose name later came to be applied to the entire country
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Montevideo
geographic coordinates: 34 51 S, 56 10 W
time difference: UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name "Montevidi" was originally applied to the hill that overlooked the bay upon which the city of Montevideo was founded; the earliest meaning may have been "[the place where we] saw the hill"
Administrative divisions
19 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento); Artigas, Canelones, Cerro Largo, Colonia, Durazno, Flores, Florida, Lavalleja, Maldonado, Montevideo, Paysandu, Rio Negro, Rivera, Rocha, Salto, San Jose, Soriano, Tacuarembo, Treinta y Tres
Independence
25 August 1825 (from Brazil)
National holiday
Independence Day, 25 August (1825)
Constitution
history: several previous; latest approved by plebiscite 27 November 1966, effective 15 February 1967, reinstated in 1985 at the conclusion of military rule
amendments: initiated by public petition of at least 10% of qualified voters, proposed by agreement of at least two fifths of the General Assembly membership, or by existing "constitutional laws" sanctioned by at least two thirds of the membership in both houses of the Assembly; proposals can also be submitted by senators, representatives, or by the executive power and require the formation of and approval in a national constituent convention; final passage by either method requires approval by absolute majority of votes cast in a referendum; amended many times, last in 2004
Legal system
civil law system based on the Spanish civil code
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 3-5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
Executive branch
chief of state: President Luis Alberto LACALLE POU (since 1 March 2020); Vice President Beatriz ARGIMON Cedeira (since 1 March 2020); the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Luis Alberto LACALLE POU (since 1 March 2020); Vice President Beatriz ARGIMON Cedeira (since 1 March 2020)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president with approval of the General Assembly
elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by absolute majority vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for nonconsecutive terms); election last held on 27 October 2019 with a runoff election on 24 November 2019 (next to be held in October 2024, and a runoff if needed in November 2024)
election results:
2019: Luis Alberto LACALLE POU elected president - results of the first round of presidential elections: percent of vote - Daniel MARTINEZ (FA) 40.7%, Luis Alberto LACALLE POU (Blanco) 29.7%, Ernesto TALVI (Colorado Party) 12.8%, and Guido MANINI RIOS (Open Cabildo) 11.3%, other 5.5%; results of the second round: percent of vote - Luis Alberto LACALLE POU (Blanco) 50.6%, Daniel MARTINEZ (FA) 49.4%
2014: Tabare VAZQUEZ elected president in second round; percent of vote - Tabare VAZQUEZ (Socialist Party) 56.5%, Luis Alberto LACALLE Pou (Blanco) 43.4%
Legislative branch
description: bicameral General Assembly or Asamblea General consists of:
Chamber of Senators or Camara de Senadores (30 seats; members directly elected in a single nationwide constituency by proportional representation vote; the vice-president serves as the presiding ex-officio member; elected members serve 5-year terms)
Chamber of Representatives or Camara de Representantes (99 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by party-list proportional representation vote using the D'Hondt method; members serve 5-year terms)
elections:
Chamber of Senators - last held on 27 October 2019 (next to be held in October 2024)
Chamber of Representatives - last held on 27 October 2019 (next to be held in October 2024)
election results:
Chamber of Senators - percent of vote by coalition/party - NA; seats by coalition/party - Frente Amplio 13, National Party 10, Colorado Party 4, Open Cabildo 3; composition - men 21, women 10, percent of women 25.3%%
Chamber of Representatives - percent of vote by coalition/party - NA; seats by coalition/party - Frente Amplio 42, National Party 30, Colorado Party 13, Open Cabildo 11, Independent Party 1, other 2; composition - men 74, women 25, percent of women 25.3%; note - total General Assembly percent of women 26.9%
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court of Justice (consists of 5 judges)
judge selection and term of office: judges nominated by the president and appointed by two-thirds vote in joint conference of the General Assembly; judges serve 10-year terms, with reelection possible after a lapse of 5 years following the previous term
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; District Courts (Juzgados Letrados); Peace Courts (Juzgados de Paz); Rural Courts (Juzgados Rurales)
Political parties and leaders
Broad Front or FA (Frente Amplio) [Fernando PEREIRA] - (a broad governing coalition that comprises 34 factions including Uruguay Assembly [Danilo ASTORI], Progressive Alliance [Rodolfo NIN NOVOA], New Space [Rafael MICHELINI], Socialist Party [Gonzalo CIVILA], Vertiente Artiguista [Enrique RUBIO], Christian Democratic Party [Jorge RODRIGUEZ], For the People’s Victory [Luis PUIG], Popular Participation Movement or MPP [Jose MUJICA], Big House [Constanza MOREIRA], Communist Party [Juan CASTILLO], The Federal League [Sergio LIER], Fuerza Renovadora [Mario BERGARA])
Colorado Party (including Batllistas [Julio Maria SANGUINETTI] and Ciudadanos [Adrian PENA])
Independent Party [Pablo MIERES]
National Party or Blanco (including Todos (Everyone) [Luis LACALLE POU] and National Alliance [Carlos CAMY])
Open Cabildo [Guido MANINI RIOS]
Popular Unity [Gonzalo ABELLA]
International organization participation
CAN (associate), CD, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, Mercosur, MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM (observer), OAS, OIF (observer), OPANAL, OPCW, Pacific Alliance (observer), PCA, SICA (observer), UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Andres Augusto DURAN HAREAU (since 23 December 2020)
chancery: 1913 I Street NW, Washington, DC 20006
telephone: [1] (202) 331-1313
FAX: [1] (202) 331-8142
email address and website:
urueeuu@mrree.gub.uy
consulate(s) general: Miami, New York, San Francisco
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Jennifer SAVAGE (since 20 January 2021)
embassy: Lauro Muller 1776, Montevideo 11200
mailing address: 3360 Montevideo Place, Washington DC 20521-3360
telephone: (+598) 1770-2000
FAX: [+598] 1770-2128
email address and website:
MontevideoACS@state.gov
https://uy.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
nine equal horizontal stripes of white (top and bottom) alternating with blue; a white square in the upper hoist-side corner with a yellow sun bearing a human face (delineated in black) known as the Sun of May with 16 rays that alternate between triangular and wavy; the stripes represent the nine original departments of Uruguay; the sun symbol evokes the legend of the sun breaking through the clouds on 25 May 1810 as independence was first declared from Spain (Uruguay subsequently won its independence from Brazil); the sun features are said to represent those of Inti, the Inca god of the sun
note: the banner was inspired by the national colors of Argentina and by the design of the US flag
National symbol(s)
Sun of May (a sun-with-face symbol); national colors: blue, white, yellow
National anthem
name: "Himno Nacional" (National Anthem of Uruguay)
lyrics/music: Francisco Esteban ACUNA de Figueroa/Francisco Jose DEBALI
note: adopted 1848; the anthem is also known as "Orientales, la Patria o la tumba!" ("Uruguayans, the Fatherland or Death!"); it is the world's longest national anthem in terms of music (105 bars; almost five minutes); generally only the first verse and chorus are sung
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 3 (all cultural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Historic City of Colonia del Sacramento; Fray Bentos Industrial Landscape; The work of engineer Eladio Dieste: Church of Atlántida
Economy
Economic overview
Uruguay has a free market economy characterized by an export-oriented agricultural sector, a well-educated workforce, and high levels of social spending. Uruguay has sought to expand trade within the Common Market of the South (Mercosur) and with non-Mercosur members, and President VAZQUEZ has maintained his predecessor's mix of pro-market policies and a strong social safety net.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$75.06 billion (2020 est.)
$79.73 billion (2019 est.)
$79.45 billion (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
2.7% (2017 est.)
1.7% (2016 est.)
0.4% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$21,600 (2020 est.)
$23,000 (2019 est.)
$23,000 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$56.108 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
7.8% (2019 est.)
7.5% (2018 est.)
6.2% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: BBB- (2013)
Moody's rating: Baa2 (2014)
Standard & Poors rating: BBB (2015)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 6.2% (2017 est.)
industry: 24.1% (2017 est.)
services: 69.7% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 66.8% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 14.3% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 16.7% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: -1% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 21.6% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -18.4% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
soybeans, milk, rice, maize, wheat, barley, beef, sugar cane, sorghum, oranges
Industries
food processing, electrical machinery, transportation equipment, petroleum products, textiles, chemicals, beverages
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 13%
industry: 14%
services: 73% (2010 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 33.1%
male: 29%
female: 38.5% (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
8.8% (2019 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
39.7 (2018 est.)
41.9 (2013)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 1.9%
highest 10%: 30.8% (2014 est.)
Budget
revenues: 17.66 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 19.72 billion (2017 est.)
Public debt
65.7% of GDP (2017 est.)
61.6% of GDP (2016 est.)
note: data cover general government debt and include debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intragovernmental debt; intragovernmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions.
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
$879 million (2017 est.)
$410 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$13.55 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$16.99 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$17.04 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Exports - partners
China 29%, Brazil 12%, United States 5%, Netherlands 5%, Argentina 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
sulfate wood pulp, beef, soybeans, concentrated milk, rice (2019)
Imports
$11.29 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$13.31 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$13.82 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Imports - partners
Brazil 25%, China 15%, United States 11%, Argentina 11% (2019)
Imports - commodities
crude petroleum, packaged medicines, cars, broadcasting equipment, delivery trucks (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$15.96 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$13.47 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$43.705 billion (2019 est.)
$42.861 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
Uruguayan pesos (UYU) per US dollar -
42.645 (2020 est.)
37.735 (2019 est.)
32.2 (2018 est.)
27.52 (2014 est.)
23.25 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 5.348 million kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 11,461,960,000 kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 1.148 billion kWh (2020 est.)
imports: 515 million kWh (2020 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1,329,700,000 kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 3.6% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 42.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 30.6% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 21.6% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 400 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 50,200 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 41,500 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 0 barrels (2021 est.)
Refined petroleum products - production
42,220 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81Natural gas
production: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
consumption: 96.872 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
exports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
imports: 96.872 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
proven reserves: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
6.45 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 6.259 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 190,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
66.909 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 1,224,600 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 35 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 4,779,790 (2019)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 138.08 (2019)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Uruguay has an advanced telecom market, with excellent infrastructure and one of the highest broadband penetration rates in Latin America; fixed-line teledensity is also particularly high for the region, while mobile penetration is the second highest after Panama; in terms of computer penetration, Uruguay tops all other countries in the region by a considerable margin, and this has facilitated growth in fixed-line broadband adoption; the government and telecom regulator have introduced a range of measures to help develop the deployment of fiber infrastructure, partly in a bid to encourage economic growth and stimulate e-commerce; fiber accounted for about 77% of all fixed and fixed-wireless broadband connections as of June 2020; with investment projected to reach $800 million, the state-owned incumbent Antel is expected to provide national FttP coverage by early 2022; together with the FttP network, the opening of the submarine cable system in early 2012 and August 2017 have helped boost Uruguay’s internet bandwidth, and increase the data rate available to end-users; Uruguay is one of the very few Latin American countries where the local fixed-line market is neither privatized nor liberalized; other segments of the telecom market have been opened to competition, including international long-distance telephony, mobile telephony, and fixed-wireless broadband; Uruguay is also one of the few countries in the world where broadband access via cable modem does not exist; although cable networks are well equipped technologically, and digital cable TV is widely available, telecom legislation prohibits data transmission over pay TV networks; the government announced in December 2020 that it intended to introduce changes to the law to permit pay TV providers to offer internet and telephony packages over their own networks; all three operators offer mobile broadband through 3G and LTE networks; operators have achieved nationwide 3G coverage and the number of mobile broadband subscribers continues to grow; at the end of 2019, spectrum in the 5G-suitable range was auctioned, enabling operators to launch 5G services; the regulator is working on a spectrum and connectivity policy that emphasizes 5G (2021)
domestic: most modern facilities concentrated in Montevideo; nationwide microwave radio relay network; overall fixed-line roughly 35 per 100 and mobile-cellular teledensity 131 per 100 persons (2020)
international: country code - 598; landing points for the Unisor, Tannat, and Bicentenario submarine cable system providing direct connectivity to Brazil and Argentina; Bicentenario 2012 and Tannat 2017 cables helped end-users with Internet bandwidth; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2020)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Broadcast media
mixture of privately owned and state-run broadcast media; more than 100 commercial radio stations and about 20 TV channels; cable TV is available; many community radio and TV stations; adopted the hybrid Japanese/Brazilian HDTV standard (ISDB-T) in December 2010 (2019)
Internet users
total: 2,987,405 (2020 est.)
percent of population: 86% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 1,063,701 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 31 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 5
Airports - with paved runways
total: 11
over 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 4
under 914 m: 2 (2021)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 122
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 40
under 914 m: 79 (2021)
Pipelines
257 km gas, 160 km oil (2013)
Railways
total: 1,673 km (2016) (operational; government claims overall length is 2,961 km)
standard gauge: 1,673 km (2016) 1.435-m gauge
Roadways
total: 77,732 km (2010)
paved: 7,743 km (2010)
unpaved: 69,989 km (2010)
Merchant marine
total: 61
by type: container ship 1, general cargo 4, oil tanker 4, other 52 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Montevideo
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Armed Forces of Uruguay (Fuerzas Armadas del Uruguay): National Army (Ejercito Nacional), National Navy (Armada Nacional, includes Coast Guard (Prefectura Nacional Naval)), Uruguayan Air Force (Fuerza Aerea); Ministry of Interior: National Police (2022)
note: the National Police includes the paramilitary National Republican Guard or Guardia Nacional Republicana
Military expenditures
2.3% of GDP (2021 est.)
2% of GDP (2020 est.)
2.1% of GDP (2019 est.) (approximately $1.47 billion)
2.1% of GDP (2018 est.) (approximately $1.51 billion)
2% of GDP (2017 est.) (approximately $1.38 billion)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 22,000 active duty personnel (14,000 Army; 5,000 Navy; 3,000 Air Force) (2022)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the military's inventory includes a wide variety of older or second-hand equipment; since 2010, it has imported limited amounts of military hardware from about 10 countries with Spain as the leading supplier (2022)
Military service age and obligation
18-30 years of age (18-22 years of age for Navy) for voluntary military service for men and women; up to 40 years of age for specialists; enlistment is voluntary in peacetime, but the government has the authority to conscript in emergencies (2022)
note: as of 2017, women comprised about 19% of the active military
Military deployments
830 Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO); 210 Golan Heights (UNDOF) (May 2022)
Military - note
the military has some domestic responsibilities, including perimeter security for a number of prisons and border security; in 2020, the military deployed more than 1,000 troops to assist the National Police in securing the land border with Brazil and the riverine border with Argentina as part of a border control law passed in 2018 (2022)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Uruguay-Argentina: in 2010, the ICJ ruled in favor of Uruguay's operation of two paper mills on the Uruguay River, which forms the border with Argentina; the two countries formed a joint pollution monitoring regime, which ended the dispute
Uruguay-Brazil: uncontested boundary dispute between Brazil and Uruguay over Braziliera/Brasiliera Island in the Quarai/Cuareim River leaves the tripoint with Argentina in question; smuggling of firearms and narcotics continues to be an issue along the Uruguay-Brazil border
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 19,000 (Venezuela) (economic and political crisis; includes Venezuelans who have claimed asylum or have received alternative legal stay) (2022)
stateless persons: 5 (mid-year 2021)
Illicit drugs
transit country for drugs mainly bound for Europe, often through sea-borne containers; limited law enforcement corruption; money laundering; weak border control along Brazilian frontier; increasing consumption of cocaine base and synthetic drugs