Introduction
Background
The first Austronesian settlers arrived in Samoa around 1000 B.C., and early Samoans traded and intermarried with Fijian and Tongan nobility. The fa’amatai system of titles and nobility developed, which dominates Samoan politics to this day; all but two seats in the legislature are reserved for matai, or heads of families. Dutch explorer Jacob ROGGEVEEN was the first European to spot the islands in 1722. Christian missionaries arrived in the 1830s, converting most of the population. In the 1850s, Apia became a center for Pacific trading and hosted an American commercial agent and British and German consuls. In 1892, American traders convinced the Samoan king to align his country’s date with the US, moving to the east of the International Date Line.
Following the death of the Samoan king in 1841, rival families competed for his titles, devolving into civil war in 1886 with factions getting support from either Germany, the UK, or the US. All three countries sent warships to Apia in 1889, presaging a larger war, but a cyclone destroyed the ships and Malietoa LAUPEPA was installed as king. Upon LAUPEPA’s death in 1898, a second civil war over succession broke out. The war ended in 1899 and the Western powers abolished the monarchy, giving the western Samoan islands to Germany and the eastern Samoan islands to the US. The UK abandoned claims in Samoa and received former German territory in the Solomon Islands.
The Mau, a non-violent popular movement to advocate for Samoan independence, formed in 1908. New Zealand annexed Samoa in 1914 after the outbreak of World War I. Opposition to New Zealand’s rule quickly grew. In 1918, a New Zealand ship introduced the Spanish flu, infecting 90% of the population and killing more than 20%. In 1929, New Zealand police shot into a crowd of peaceful protestors, killing 11, in an event known as Black Sunday. In 1962, Samoa became the first Polynesian nation to reestablish its independence as Western Samoa but dropped the “Western” from its name in 1997. The Human Rights Protection Party has dominated politics since 1982, especially under Prime Minister Sailele TUILAEPA, who has been in power since 1998.
In the late 2000s, Samoa began making efforts to align more closely with Australia and New Zealand. In 2009, Samoa changed its driving orientation to the left side of the road, in line with other Commonwealth countries. In 2011, Samoa jumped forward one day - skipping December 30 - by moving to the west side of the International Date Line so that it was one hour ahead of New Zealand and three hours ahead of the east coast of Australia, rather than 23 and 21 hours behind, respectively.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Oceania, group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand
Geographic coordinates
13 35 S, 172 20 W
Map references
Oceania
Area - comparative
slightly smaller than Rhode Island
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
403 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; rainy season (November to April), dry season (May to October)
Terrain
two main islands (Savaii, Upolu) and several smaller islands and uninhabited islets; narrow coastal plain with volcanic, rugged mountains in interior
Elevation
highest point: Mount Silisili 1,857 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
Natural resources
hardwood forests, fish, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land: 12.4% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.8% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 7.8% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 1.8% (2018 est.)
forest: 60.4% (2018 est.)
other: 27.2% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
0 sq km (2022)
Population distribution
about three-quarters of the population lives on the island of Upolu
Natural hazards
occasional cyclones; active volcanism
volcanism: Savai'I Island (1,858 m), which last erupted in 1911, is historically active
Geography - note
occupies an almost central position within Polynesia
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Samoan(s)
adjective: Samoan
Ethnic groups
Samoan 96%, Samoan/New Zealander 2%, other 1.9% (2011 est.)
note: data represent the population by country of citizenship
Languages
Samoan (Polynesian) (official) 91.1%, Samoan/English 6.7%, English (official) 0.5%, other 0.2%, unspecified 1.6% (2006 est.)
Religions
Protestant 54.9% (Congregationalist 29%, Methodist 12.4%, Assembly of God 6.8%, Seventh Day Adventist 4.4%, other Protestant 2.3%), Roman Catholic 18.8%, Church of Jesus Christ 16.9%, Worship Centre 2.8%, other Christian 3.6%, other 2.9% (includes Baha'i, Muslim), none 0.2% (2016 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 29.31% (male 30,825/female 28,900)
15-24 years: 19.61% (male 20,519/female 19,439)
25-54 years: 37.4% (male 39,011/female 37,200)
55-64 years: 7.5% (male 7,780/female 7,505)
65 years and over: 6.18% (male 5,513/female 7,082) (2020 est.)

Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 74.9
youth dependency ratio: 66
elderly dependency ratio: 8.9
potential support ratio: 11.2 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 25.6 years
male: 25.3 years
female: 26 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
about three-quarters of the population lives on the island of Upolu
Urbanization
urban population: 17.5% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: -0.03% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
36,000 APIA (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.61 male(s)/female
total population: 1.03 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
43 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98Infant mortality rate
total: 18 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 21.76 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 14.05 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 75.19 years
male: 72.28 years
female: 78.25 years (2022 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
16.6% (2019/20)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 98% of population
total: 98.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 2% of population
total: 1.6% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
6.4% of GDP (2019)
Physicians density
0.6 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 99.5% of population
rural: 99.5% of population
total: 99.5% of population
unimproved: urban: 0.5% of population
rural: 0.5% of population
total: 0.5% of population (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: malaria
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 2.18 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 2.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.17 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 25.3% (2020 est.)
male: 36.1% (2020 est.)
female: 14.5% (2020 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 0.9%
women married by age 18: 7.4%
men married by age 18: 2% (2020 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.1%
male: 99%
female: 99.2% (2018)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 19.6%
male: 13.3%
female: 30% (2017 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
soil erosion, deforestation, invasive species, overfishing
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 10.56 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 0.25 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 0.27 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; rainy season (November to April), dry season (May to October)
Land use
agricultural land: 12.4% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.8% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 7.8% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 1.8% (2018 est.)
forest: 60.4% (2018 est.)
other: 27.2% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 17.5% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: -0.03% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.27% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: malaria
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 27,399 tons (2011 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 9,864 tons (2013 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 36% (2013 est.)
Total renewable water resources
0 cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Independent State of Samoa
conventional short form: Samoa
local long form: Malo Sa'oloto Tuto'atasi o Samoa
local short form: Samoa
former: Western Samoa
etymology: the meaning of Samoa is disputed; some modern explanations are that the "sa" connotes "sacred" and "moa" indicates "center," so the name can mean "Holy Center"; alternatively, some assertions state that it can mean "place of the sacred moa bird" of Polynesian mythology; the name, however, may go back to Proto-Polynesian (PPn) times (before 1000 B.C.); a plausible PPn reconstruction has the first syllable as "sa'a" meaning "tribe or people" and "moa" meaning "deep sea or ocean" to convey the meaning "people of the deep sea"
Government type
parliamentary republic
Capital
name: Apia
geographic coordinates: 13 49 S, 171 46 W
time difference: UTC+13 (18 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: name derives from the native village around which the capital was constructed in the 1850s; the village still exists within the larger modern capital
Administrative divisions
11 districts; A'ana, Aiga-i-le-Tai, Atua, Fa'asaleleaga, Gaga'emauga, Gagaifomauga, Palauli, Satupa'itea, Tuamasaga, Va'a-o-Fonoti, Vaisigano
Independence
1 January 1962 (from New Zealand-administered UN trusteeship)
National holiday
Independence Day Celebration, 1 June (1962); note - 1 January 1962 is the date of independence from the New Zealand-administered UN trusteeship, but it is observed in June
Constitution
history: several previous (preindependence); latest 1 January 1962
amendments: proposed as an act by the Legislative Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly membership in the third reading - provided at least 90 days have elapsed since the second reading, and assent of the chief of state; passage of amendments affecting constitutional articles on customary land or constitutional amendment procedures also requires at least two-thirds majority approval in a referendum; amended several times, last in 2020
Legal system
mixed legal system of English common law and customary law; judicial review of legislative acts with respect to fundamental rights of the citizen
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Samoa
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
21 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: TUIMALEALI'IFANO Va’aletoa Sualauvi II (since 21 July 2017)
head of government: Prime Minister FIAME Naomi Mata’afa (since 24 May 2021)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the chief of state on the prime minister's advice
elections/appointments: chief of state indirectly elected by the Legislative Assembly to serve a 5-year term (2-term limit); election last held on 23 August 2022 (next to be held in 2027); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party is usually appointed prime minister by the chief of state, approved by the Legislative Assembly
election results: TUIMALEALI'IFANO Va’aletoa Sualauvi unanimously reelected by the Legislative Assembly on 23 August 2022
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Legislative Assembly or Fono (53 seats for 2021-2026 term); members from 51 single-seat constituencies directly elected by simple majority vote, with a minimum 10% representation of women in the Assembly required; members serve 5-year terms)
elections: election last held on 9 April 2021 (next election to be held in 2026)
election results: percent of vote by party - HRPP 55%, FAST 37%, TSP 3%, independents 5%; seats by party – FAST 30, HRPP 22, independents 1; composition - men 47, women 6, percent of women 11.3%
note: on 29 November 2021, the Election Commissioner added two women seats to parliament, bringing the HRPP’s total from 20 to 22 seats
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Court of Appeal (consists of the chief justice and 2 Supreme Court judges and meets once or twice a year); Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and several judges)
judge selection and term of office: chief justice appointed by the chief of state upon the advice of the prime minister; other Supreme Court judges appointed by the Judicial Service Commission, a 3-member body chaired by the chief justice and includes the attorney general and an appointee of the Minister of Justice; judges normally serve until retirement at age 68
subordinate courts: District Court; Magistrates' Courts; Land and Titles Courts; village fono or village chief councils
Political parties and leaders
Fa'atuatua i le Atua Samoa ua Tasi or FAST [FIAME Naomi Mata'afa]
Human Rights Protection Party or HRPP [TUILA'EPA Sailele Malielegaoi]
Tautua Samoa Party or TSP [Afualo Wood Uti SALELE]
International organization participation
ACP, ADB, AOSIS, C, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Pa’olelei LUTERU (since 7 July 2021)
chancery: 685 Third Avenue, 44th Street, 11th Floor, Suite 1102, New York, NY 10017
telephone: [1] (212) 599-6196
FAX: [1] (212) 599-0797
email address and website:
samoanymission@outlook.com
https://www.un.int/samoa/samoa/embassy-independent-state-samoa-united-states-america
consulate(s) general: Pago Pago (American Samoa)
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: the US Ambassador to New Zealand is accredited to Samoa
embassy: 5th Floor, Accident Corporation Building, Matafele Apia
mailing address: 4400 Apia Place, Washington DC 20521-4400
telephone: [685] 21-436
FAX: [685] 22-030
email address and website:
ApiaConsular@state.gov
https://ws.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
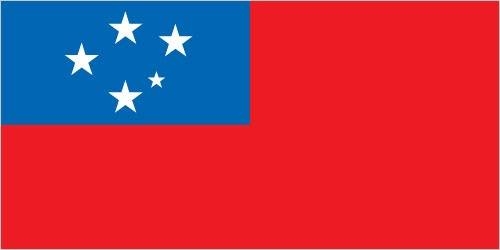
red with a blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side quadrant bearing five white, five-pointed stars representing the Southern Cross constellation; red stands for courage, blue represents freedom, and white signifies purity
note: similar to the flag of Taiwan
National symbol(s)
Southern Cross constellation (five, five-pointed stars); national colors: red, white, blue
National anthem
name: "O le Fu'a o le Sa'olotoga o Samoa" (The Banner of Freedom)
lyrics/music: Sauni Liga KURESA
note: adopted 1962; also known as "Samoa Tula'i" (Samoa Arise)
Economy
Economic overview
The economy of Samoa has traditionally been dependent on development aid, family remittances from overseas, tourism, agriculture, and fishing. It has a nominal GDP of $844 million. Agriculture, including fishing, furnishes 90% of exports, featuring fish, coconut oil, nonu products, and taro. The manufacturing sector mainly processes agricultural products. Industry accounts for nearly 22% of GDP while employing less than 6% of the work force. The service sector accounts for nearly two-thirds of GDP and employs approximately 50% of the labor force. Tourism is an expanding sector accounting for 25% of GDP; 132,000 tourists visited the islands in 2013.
The country is vulnerable to devastating storms. In September 2009, an earthquake and the resulting tsunami severely damaged Samoa and nearby American Samoa, disrupting transportation and power generation, and resulting in about 200 deaths. In December 2012, extensive flooding and wind damage from Tropical Cyclone Evan killed four people, displaced over 6,000, and damaged or destroyed an estimated 1,500 homes on Samoa's Upolu Island.
The Samoan Government has called for deregulation of the country's financial sector, encouragement of investment, and continued fiscal discipline, while at the same time protecting the environment. Foreign reserves are relatively healthy and inflation is low, but external debt is approximately 45% of GDP. Samoa became the 155th member of the WTO in May 2012, and graduated from least developed country status in January 2014.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$1.25 billion (2020 est.)
$1.28 billion (2019 est.)
$1.24 billion (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
2.5% (2017 est.)
7.1% (2016 est.)
1.6% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$6,300 (2020 est.)
$6,500 (2019 est.)
$6,300 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$841 million (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 10.4% (2017 est.)
industry: 23.6% (2017 est.)
services: 66% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: NA
government consumption: NA
investment in fixed capital: NA
investment in inventories: NA
exports of goods and services: 27.2% (2015 est.)
imports of goods and services: -50.5% (2015 est.)
Agricultural products
coconuts, taro, bananas, yams, tropical fruit, pineapples, mangoes/guavas, papayas, roots/tubers nes, pork
Industries
food processing, building materials, auto parts
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 65%
industry: 6%
services: 29% (2015 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 19.6%
male: 13.3%
female: 30% (2017 est.)
Population below poverty line
20.3% (2013 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
38.7 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 237.3 million (2017 est.)
expenditures: 276.8 million (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
June 1 - May 31
Current account balance
-$19 million (2017 est.)
-$37 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$310 million (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
country comparison to the world: 199Exports - partners
American Samoa 21%, United States 13%, New Zealand 12%, Australia 10%, Tokelau 6%, Taiwan 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
refined petroleum, fish, fruit juice, coconut oil, beer (2019)
Imports
$430 million (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$312.6 million (2016 est.)
Imports - partners
New Zealand 22%, China 16%, Singapore 13%, United States 10%, Australia 9%, South Korea 8%, Fiji 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, iron products, poultry meats, cars, insulated wiring (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$133 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$122.5 million (31 December 2015 est.)
Exchange rates
tala (SAT) per US dollar -
2.54712 (2020 est.)
2.65534 (2019 est.)
2.57069 (2018 est.)
2.5609 (2014 est.)
2.3318 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 50,000 kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 120.13 million kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 0 kWh (2020 est.)
imports: 0 kWh (2020 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 15 million kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 72.7% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 27.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 0 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 2,500 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 0 barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
production: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
consumption: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
exports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
imports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
proven reserves: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
355,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 355,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
27.111 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 6,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 69,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 35 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Samoa was one of the first Pacific Island countries to establish a regulatory infrastructure and to liberalize its telecom market; the advent of competition in the mobile market saw prices fall by around 50% and network coverage increase to more than 90% of the population; Samoa also boasts one of the highest rates of mobile phone coverage in the Pacific region; the growth of fixed-line internet has been impeded by factors including the high costs for bandwidth, under investment in fixed-line infrastructure; Samoa’s telecoms sector has been inhibited by a lack of international connectivity; Samoa has had access to the Samoa-America-Samoa (SAS) cable laid in 2009, this cable has insufficient capacity to meet the country’s future bandwidth needs; this issue was addressed with two new submarine cables that became available in 2018 and 2019; combined with the Samoa National Broadband Highway (SNBH), have improved internet data rates and reliability, and have helped to reduce the high costs previously associated with internet access in Samoa; in April 2022, the Samoan government announced its decision to take over control of the Samoa Submarine Cable Company, looking to the cable to generate additional revenue for the state (2022)
domestic: fixed-line roughly 3 per 100 and mobile-cellular teledensity nearly 35 telephones per 100 persons (2020)
international: country code - 685; landing points for the Tui-Samo, Manatua, SAS, and Southern Cross NEXT submarine cables providing connectivity to Samoa, Fiji, Wallis & Futuna, Cook Islands, Niue, French Polynesia, American Samoa, Australia, New Zealand, Kiribati, Los Angeles (US), and Tokelau; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Broadcast media
state-owned TV station privatized in 2008; 4 privately owned television broadcast stations; about a half-dozen privately owned radio stations and one state-owned radio station; TV and radio broadcasts of several stations from American Samoa are available (2019)
Internet users
total: 67,012 (2019 est.)
percent of population: 34% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 1,692 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 4
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 137,770 (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2021)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 3
under 914 m: 3 (2021)
Merchant marine
total: 12
by type: general cargo 3, oil tanker 3, other 6 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Apia
Military and Security
Military and security forces
no regular military forces; Samoa Police Force (Ministry of Police, Prisons, and Correction Services) (2022)
Military - note
informal defense ties exist with NZ, which is required to consider any Samoan request for assistance under the 1962 Treaty of Friendship
Samoa has a "shiprider" agreement with the US, which allows local maritime law enforcement officers to embark on US Coast Guard (USCG) and US Navy (USN) vessels, including to board and search vessels suspected of violating laws or regulations within Somoa's designated exclusive economic zone (EEZ) or on the high seas; "shiprider" agreements also enable USCG personnel and USN vessels with embarked USCG law enforcement personnel to work with host nations to protect critical regional resources (2022)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
none identified