Pakistan
Introduction
Background
The Indus Valley civilization, one of the oldest in the world and dating back at least 5,000 years, spread over much of what is presently Pakistan. During the second millennium B.C., remnants of this culture fused with the migrating Indo-Aryan peoples. The area underwent successive invasions in subsequent centuries from the Persians, Greeks, Scythians, Arabs (who brought Islam), Afghans, and Turks. The Mughal Empire flourished in the 16th and 17th centuries; the British came to dominate the region in the 18th century. The separation in 1947 of British India into the Muslim state of Pakistan (with West and East sections) and largely Hindu India was never satisfactorily resolved, and India and Pakistan fought two wars and a limited conflict - in 1947-48, 1965, and 1999 respectively - over the disputed Kashmir territory. A third war between these countries in 1971 - in which India assisted an indigenous movement reacting to the marginalization of Bengalis in Pakistani politics - resulted in East Pakistan becoming the separate nation of Bangladesh.
In response to Indian nuclear weapons testing, Pakistan conducted its own tests in mid-1998. India-Pakistan relations improved in the mid-2000s but have been rocky since the November 2008 Mumbai attacks and have been further strained by Indian reports of cross-border militancy. Imran KHAN took office as prime minister in 2018 after the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaaf (PTI) party won a plurality of seats in the July 2018 general elections. Pakistan has been engaged in a decades-long armed conflict with militant groups that target government institutions and civilians, including the Tehreek-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP) and other militant networks.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Southern Asia, bordering the Arabian Sea, between India on the east and Iran and Afghanistan on the west and China in the north
Geographic coordinates
30 00 N, 70 00 E
Map references
Asia
Area - comparative
slightly more than five times the size of Georgia; slightly less than twice the size of California

Land boundaries
total: 7,257 km
border countries (4): Afghanistan 2,670 km; China 438 km; India 3,190 km; Iran 959 km
Coastline
1,046 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
Climate
mostly hot, dry desert; temperate in northwest; arctic in north
Terrain
divided into three major geographic areas: the northern highlands, the Indus River plain in the center and east, and the Balochistan Plateau in the south and west
Elevation
highest point: K2 (Mt. Godwin-Austen) 8,611 m
lowest point: Arabian Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 900 m
Natural resources
arable land, extensive natural gas reserves, limited petroleum, poor quality coal, iron ore, copper, salt, limestone
Land use
agricultural land: 35.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 27.6% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.1% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 6.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 2.1% (2018 est.)
other: 62.7% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
193,400 sq km (2020)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Indus river mouth (shared with China [s] and India) - 3,610 km; Sutlej river mouth (shared with China [s] and India) - 1,372 km; Chenab river mouth (shared with India [s]) - 1,086 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Indian Ocean drainage: Indus (1,081,718 sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Tarim Basin (1,152,448 sq km), (Aral Sea basin) Amu Darya (534,739 sq km)
Major aquifers
Indus Basin
Population distribution
the Indus River and its tributaries attract most of the settlement, with Punjab province the most densely populated
Natural hazards
frequent earthquakes, occasionally severe especially in north and west; flooding along the Indus after heavy rains (July and August)
Geography - note
controls Khyber Pass and Bolan Pass, traditional invasion routes between Central Asia and the Indian Subcontinent
People and Society
Population
242,923,845 (2022 est.)
note: results of Pakistan's 2017 national census estimate the country's total population to be 207,684,626
Nationality
noun: Pakistani(s)
adjective: Pakistani
Ethnic groups
Punjabi 44.7%, Pashtun (Pathan) 15.4%, Sindhi 14.1%, Saraiki 8.4%, Muhajirs 7.6%, Balochi 3.6%, other 6.3%
Languages
Punjabi 48%, Sindhi 12%, Saraiki (a Punjabi variant) 10%, Pashto (alternate name, Pashtu) 8%, Urdu (official) 8%, Balochi 3%, Hindko 2%, Brahui 1%, English (official; lingua franca of Pakistani elite and most government ministries), Burushaski, and other 8%
major-language sample(s):
ਸੰਸਾਰ ਦੀ ਤੱਥ ਕਿਤਾਬ, ਆਧਾਰੀ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਲਈ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਸਰੋਤ ਹੈ (Punjabi)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Muslim (official) 96.5% (Sunni 85-90%, Shia 10-15%), other (includes Christian and Hindu) 3.5% (2020 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 36.01% (male 42,923,925/female 41,149,694)
15-24 years: 19.3% (male 23,119,205/female 21,952,976)
25-54 years: 34.7% (male 41,589,381/female 39,442,046)
55-64 years: 5.55% (male 6,526,656/female 6,423,993)
65 years and over: 4.44% (male 4,802,165/female 5,570,595) (2020 est.)
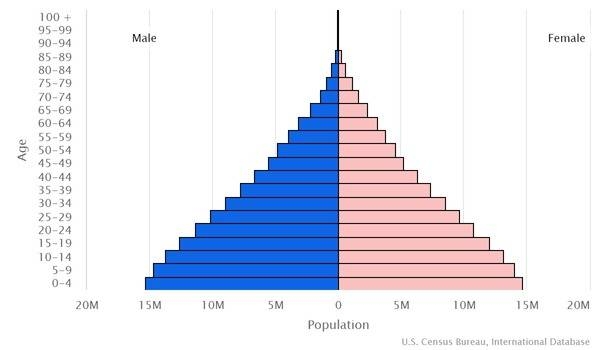
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 70
youth dependency ratio: 62.8
elderly dependency ratio: 7.2
potential support ratio: 13.9 (2021 est.)
Median age
total: 22 years
male: 21.9 years
female: 22.1 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
the Indus River and its tributaries attract most of the settlement, with Punjab province the most densely populated
Urbanization
urban population: 38% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.1% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
17.236 million Karachi, 13.979 million Lahore, 3.711 million Faisalabad, 2.415 million Gujranwala, 2.412 million Peshawar, 1.232 million ISLAMABAD (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.79 male(s)/female
total population: 1.04 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
22.8 years (2017/18 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
Maternal mortality ratio
140 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61Infant mortality rate
total: 53.98 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 58.34 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 49.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 69.67 years
male: 67.62 years
female: 71.82 years (2022 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
34% (2018/19)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 96.5% of population
rural: 92.5% of population
total: 94% of population
unimproved: urban: 3.5% of population
rural: 7.5% of population
total: 6% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
3.4% of GDP (2019)
Physicians density
1.12 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
Hospital bed density
0.6 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 88.6% of population
rural: 73.2% of population
total: 78.9% of population
unimproved: urban: 11.4% of population
rural: 26.8% of population
total: 21.1% of population (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
animal contact diseases: rabies
note 1: widespread ongoing transmission of a respiratory illness caused by the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) is occurring throughout Pakistan; as of 9 December 2022, Pakistan has reported a total of 1,575,382 cases of COVID-19 or 713.19 cumulative cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 population with a total of 30,634 cumulative deaths or a rate of 13.86 cumulative deaths per 100,000 population; as of 8 December 2022, 59.22% of the population has received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine
note 2: Pakistan is one of two countries with endemic wild polio virus (the other is Afghanistan) and considered high risk for international spread of the disease; before any international travel, anyone unvaccinated, incompletely vaccinated, or with an unknown polio vaccination status should complete the routine polio vaccine series; before travel to any high-risk destination, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that adults who previously completed the full, routine polio vaccine series receive a single, lifetime booster dose of polio vaccine
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 0.04 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.04 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 20.2% (2020 est.)
male: 33% (2020 est.)
female: 7.3% (2020 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 3.6%
women married by age 18: 18.3%
men married by age 18: 4.7% (2018 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 58%
male: 69.3%
female: 46.5% (2019)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 9 years
male: 9 years
female: 8 years (2019)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 11.1%
male: 10%
female: 14.4% (2021 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
water pollution from raw sewage, industrial wastes, and agricultural runoff; limited natural freshwater resources; most of the population does not have access to potable water; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; air pollution and noise pollution in urban areas
Environment - international agreements
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protection, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Marine Life Conservation
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 55.21 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 201.15 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 142.12 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
mostly hot, dry desert; temperate in northwest; arctic in north
Land use
agricultural land: 35.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 27.6% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.1% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 6.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 2.1% (2018 est.)
other: 62.7% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 38% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.1% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.1% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
animal contact diseases: rabies
note 1: widespread ongoing transmission of a respiratory illness caused by the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) is occurring throughout Pakistan; as of 9 December 2022, Pakistan has reported a total of 1,575,382 cases of COVID-19 or 713.19 cumulative cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 population with a total of 30,634 cumulative deaths or a rate of 13.86 cumulative deaths per 100,000 population; as of 8 December 2022, 59.22% of the population has received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine
note 2: Pakistan is one of two countries with endemic wild polio virus (the other is Afghanistan) and considered high risk for international spread of the disease; before any international travel, anyone unvaccinated, incompletely vaccinated, or with an unknown polio vaccination status should complete the routine polio vaccine series; before travel to any high-risk destination, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that adults who previously completed the full, routine polio vaccine series receive a single, lifetime booster dose of polio vaccine
Food insecurity
severe localized food insecurity: due to population displacements, economic constraints, and high prices of the main food staple - according to the latest analysis, about 4.7 million people, 25% of the population, are estimated to be facing high levels of acute food insecurity, between April and June 2022 in 25 districts analyzed in Balochistan, Sindh and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa provinces; prices of wheat flour, the country’s main staple, were at high levels in most markets in May 2022, constraining access to the staple food (2022)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 30.76 million tons (2017 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 2,460,800 tons (2017 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 8% (2017 est.)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Indus river mouth (shared with China [s] and India) - 3,610 km; Sutlej river mouth (shared with China [s] and India) - 1,372 km; Chenab river mouth (shared with India [s]) - 1,086 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Indian Ocean drainage: Indus (1,081,718 sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Tarim Basin (1,152,448 sq km), (Aral Sea basin) Amu Darya (534,739 sq km)
Major aquifers
Indus Basin
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 9.65 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 1.4 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 172.4 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
246.8 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Islamic Republic of Pakistan
conventional short form: Pakistan
local long form: Jamhuryat Islami Pakistan
local short form: Pakistan
former: West Pakistan
etymology: the word "pak" means "pure" in Persian or Pashto, while the Persian suffix "-stan" means "place of" or "country," so the word Pakistan literally means "Land of the Pure"
Government type
federal parliamentary republic
Capital
name: Islamabad
geographic coordinates: 33 41 N, 73 03 E
time difference: UTC+5 (10 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: derived from two words: Islam, an Urdu word referring to the religion of Islam, and -abad, a Persian suffix indicating an "inhabited place" or "city," to render the meaning "City of Islam"
Administrative divisions
4 provinces, 2 Pakistan-administered areas*, and 1 capital territory**; Azad Kashmir*, Balochistan, Gilgit-Baltistan*, Islamabad Capital Territory**, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Punjab, Sindh
Independence
14 August 1947 (from British India)
National holiday
Pakistan Day (also referred to as Pakistan Resolution Day or Republic Day), 23 March (1940); note - commemorates both the adoption of the Lahore Resolution by the All-India Muslim League during its 22-24 March 1940 session, which called for the creation of independent Muslim states, and the adoption of the first constitution of Pakistan on 23 March 1956 during the transition to the Islamic Republic of Pakistan
Constitution
history: several previous; latest endorsed 12 April 1973, passed 19 April 1973, entered into force 14 August 1973 (suspended and restored several times)
amendments: proposed by the Senate or by the National Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of both houses; amended many times, last in 2018
Legal system
common law system with Islamic law influence
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Pakistan
dual citizenship recognized: yes, but limited to select countries
residency requirement for naturalization: 4 out of the previous 7 years and including the 12 months preceding application
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal; note - there are joint electorates and reserved parliamentary seats for women and non-Muslims
Executive branch
chief of state: President Arif ALVI (since 9 September 2018)
head of government: Prime Minister Shehbaz SHARIF (since 11 April 2022); former Prime Minister Imran KHAN on 10 April lost a no-confidence vote in the National Assembly
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president upon the advice of the prime minister
elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by the Electoral College consisting of members of the Senate, National Assembly, and provincial assemblies for a 5-year term (limited to 2 consecutive terms); election last held on 4 September 2018 (next to be held in 2023); prime minister elected by the National Assembly on 17 August 2018
election results: 2018: Arif ALVI elected president; Electoral College vote - Arif ALVI (PTI) 352, Fazl-ur-REHMAN (MMA) 184, Aitzaz AHSAN (PPP) 124; Imran KHAN elected prime minister; National Assembly vote - Imran KHAN (PTI) 176, Shehbaz SHARIF (PML-N) 96
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliament or Majlis-e-Shoora consists of:
Senate (100 seats; members indirectly elected by the 4 provincial assemblies and the territories' representatives by proportional representation vote; members serve 6-year terms with one-half of the membership renewed every 3 years)
National Assembly (342 seats; 272 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 70 members - 60 women and 10 non-Muslims - directly elected by proportional representation vote; all members serve 5-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last held on 3 March 2021 (next to be held in March 2024)
National Assembly - last held on 25 July 2018 (next to be held on 25 July 2023)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PTI 25, PPP 21, PML-N 18, BAP 13, JU-F 5, other 13, independent 5; composition - men 81, women 19, percent of women 19%
National Assembly - percent of votes by party - NA; seats by party - PTI 156, PML-N 83, PPP 55, MMA 16, MQM-P 7, BAP 5, PML-Q 5, BNP 4, GDA 3, AML 1, ANP 1, JWP 1, independent 4; composition - men 272, women 70, percent of women 20.2%; note - total Parliament percent of women 20.1%
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court of Pakistan (consists of the chief justice and 16 judges)
judge selection and term of office: justices nominated by an 8-member parliamentary committee upon the recommendation of the Judicial Commission, a 9-member body of judges and other judicial professionals, and appointed by the president; justices can serve until age 65
subordinate courts: High Courts; Federal Shariat Court; provincial and district civil and criminal courts; specialized courts for issues, such as taxation, banking, and customs
Political parties and leaders
Awami National Party or ANP [Asfandyar Wali KHAN]
Awami Muslim League or AML [Sheikh Rashid AHMED]
Balochistan Awami Party or BAP [Jam Kamal KHAN]
Balochistan National Party-Awami or BNP-A [Mir Israr Ullah ZEHRI]
Balochistan National Party-Mengal or BNP-M [Sardar Akhtar Jan MENGAL]
Grand Democratic Alliance or GDA [Pir PAGARO] (includes F, NPP, PML-Q, PTI, QAT)
Jamaat-i Islami or JI [Sirajul HAQ]
Jamhoori Wattan Party or JWP [Shahzain BUGTI]
Jamiat Ulema-e-Islam or JUI-F [Maulana Fazal-ur-REHMAN]
Muttahida Majlis-e-Amal or MMA [Maulana Fazal-ur-REHMAN] (alliance of several parties)
Muttahida Qaumi Movement-London or MQM-L [Altaf HUSSAIN] (MQM split into two factions in 2016)
Muttahida Qaumi Movement-Pakistan or MQM-P [Dr. Khalid Maqbool SIDDIQUI] (MQM split into two factions in 2016)
National Party or NP [Abdul Malik BALOCH]
Pak Sarzameen Party or PSP [Mustafa KAMAL]
Pakhtunkhwa Milli Awami Party or PMAP or PkMAP [Mahmood Khan ACHAKZAI]
Pakhtunkhwa Milli Awami Party or PML-F [Pir PAGARO or Syed Shah Mardan SHAH-II]
Pakistan Muslim League-Nawaz or PML-N [Shehbaz SHARIF]
Pakistan Muslim League – Quaid-e-Azam Group or PML-Q [Chaudhry Shujaat HUSSAIN]
Pakistan Muslim League or PML-F [Pir PAGARO]
Pakistan Peoples Party or PPP [Bilawal BHUTTO ZARDARI, Asif Ali ZARDARI]
Pakistan Tehrik-e Insaaf or PTI (Pakistan Movement for Justice) [Imran KHAN]
Qaumi Awami Tehreek or AT [Sajjad Ahmed CHANDIO]
Qaumi Awami Tehreek or QAT [Ayaz Latif PALIJO]
Qaumi Watan Party or QWP [Aftab Ahmed Khan SHERPAO]
note: political alliances in Pakistan shift frequently
International organization participation
ADB, AIIB, ARF, ASEAN (sectoral dialogue partner), C, CERN (associate member), CICA, CP, D-8, ECO, FAO, G-11, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURCAT, MINURSO, MINUSCA, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS (observer), OIC, OPCW, PCA, SAARC, SACEP, SCO, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNHRC, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNSOS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Sardar Masood KHAN (since 24 March 2022)
chancery: 3517 International Court NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 243-6500
FAX: [1] (202) 686-1534
email address and website:
consularsection@embassyofpakistanusa.org
https://embassyofpakistanusa.org/
consulate(s) general: Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Angela AGGELER
embassy: Diplomatic Enclave, Ramna 5, Islamabad
mailing address: 8100 Islamabad Place, Washington, DC 20521-8100
telephone: [92] 051-201-4000
FAX: [92] 51-2338071
email address and website:
ACSIslamabad@state.gov
https://pk.usembassy.gov/
consulate(s) general: Karachi, Lahore, Peshawar
Flag description
green with a vertical white band (symbolizing the role of religious minorities) on the hoist side; a large white crescent and star are centered in the green field; the crescent, star, and color green are traditional symbols of Islam
National symbol(s)
five-pointed star between the horns of a waxing crescent moon, jasmine; national colors: green, white
National anthem
name: "Qaumi Tarana" (National Anthem)
lyrics/music: Abu-Al-Asar Hafeez JULLANDHURI/Ahmed Ghulamali CHAGLA
note: adopted 1954; also known as "Pak sarzamin shad bad" (Blessed Be the Sacred Land)
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 6 (all cultural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Archaeological Ruins at Moenjodaro; Buddhist Ruins of Takht-i-Bahi; Taxila; Fort and Shalamar Gardens in Lahore; Historical Monuments at Makli, Thatta; Rohtas Fort
Economy
Economic overview
Decades of internal political disputes and low levels of foreign investment have led to underdevelopment in Pakistan. Pakistan has a large English-speaking population, with English-language skills less prevalent outside urban centers. Despite some progress in recent years in both security and energy, a challenging security environment, electricity shortages, and a burdensome investment climate have traditionally deterred investors. Agriculture accounts for one-fifth of output and two-fifths of employment. Textiles and apparel account for more than half of Pakistan's export earnings; Pakistan's failure to diversify its exports has left the country vulnerable to shifts in world demand. Pakistan’s GDP growth has gradually increased since 2012, and was 5.3% in 2017. Official unemployment was 6% in 2017, but this fails to capture the true picture, because much of the economy is informal and underemployment remains high. Human development continues to lag behind most of the region.
In 2013, Pakistan embarked on a $6.3 billion IMF Extended Fund Facility, which focused on reducing energy shortages, stabilizing public finances, increasing revenue collection, and improving its balance of payments position. The program concluded in September 2016. Although Pakistan missed several structural reform criteria, it restored macroeconomic stability, improved its credit rating, and boosted growth. The Pakistani rupee has remained relatively stable against the US dollar since 2015, though it declined about 10% between November 2017 and March 2018. Balance of payments concerns have reemerged, however, as a result of a significant increase in imports and weak export and remittance growth.
Pakistan must continue to address several longstanding issues, including expanding investment in education, healthcare, and sanitation; adapting to the effects of climate change and natural disasters; improving the country’s business environment; and widening the country’s tax base. Given demographic challenges, Pakistan’s leadership will be pressed to implement economic reforms, promote further development of the energy sector, and attract foreign investment to support sufficient economic growth necessary to employ its growing and rapidly urbanizing population, much of which is under the age of 25.
In an effort to boost development, Pakistan and China are implementing the "China-Pakistan Economic Corridor" (CPEC) with $60 billion in investments targeted towards energy and other infrastructure projects. Pakistan believes CPEC investments will enable growth rates of over 6% of GDP by laying the groundwork for increased exports. CPEC-related obligations, however, have raised IMF concern about Pakistan’s capital outflows and external financing needs over the medium term.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$1,021,130,000,000 (2020 est.)
$1,015,800,000,000 (2019 est.)
$1,005,850,000,000 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
data are for fiscal years
Real GDP growth rate
5.4% (2017 est.)
4.6% (2016 est.)
4.1% (2015 est.)
note: data are for fiscal years
Real GDP per capita
$4,600 (2020 est.)
$4,700 (2019 est.)
$4,700 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$253.183 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
9.3% (2019 est.)
5.2% (2018 est.)
4.2% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: B- (2018)
Moody's rating: B3 (2015)
Standard & Poors rating: B- (2019)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 24.4% (2016 est.)
industry: 19.1% (2016 est.)
services: 56.5% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 82% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 11.3% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 14.5% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 1.6% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 8.2% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -17.6% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
sugar cane, buffalo milk, wheat, milk, rice, maize, potatoes, cotton, fruit, mangoes/guavas
Industries
textiles and apparel, food processing, pharmaceuticals, surgical instruments, construction materials, paper products, fertilizer, shrimp
Labor force
61.71 million (2017 est.)
note: extensive export of labor, mostly to the Middle East, and use of child labor
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 42.3%
industry: 22.6%
services: 35.1% (FY2015 est.)
Unemployment rate
6% (2017 est.)
6% (2016 est.)
note: Pakistan has substantial underemployment
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 11.1%
male: 10%
female: 14.4% (2021 est.)
Population below poverty line
24.3% (2015 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
33.5 (2015 est.)
30.9 (FY2011)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 4%
highest 10%: 26.1% (FY2013)
Budget
revenues: 46.81 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 64.49 billion (2017 est.)
note: data are for fiscal years
Fiscal year
1 July - 30 June
Current account balance
-$7.143 billion (2019 est.)
-$19.482 billion (2018 est.)
Exports
$27.3 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$30.67 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$30.77 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Exports - partners
United States 14%, China 8%, Germany 7%, United Kingdom 6% (2019)
Exports - commodities
textiles, clothing and apparel, rice, leather goods, surgical instruments (2019)
Imports
$51.07 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$57.98 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$68.42 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Imports - partners
China 28%, United Arab Emirates 11%, United States 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, crude petroleum, natural gas, palm oil, scrap iron (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$18.46 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$22.05 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$107.527 billion (2019 est.)
$95.671 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
Pakistani rupees (PKR) per US dollar -
160.425 (2020 est.)
155.04 (2019 est.)
138.8 (2018 est.)
102.769 (2014 est.)
101.1 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 79% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 91% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 72% (2019)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 39.925 million kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 103,493,520,000 kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 0 kWh (2019 est.)
imports: 487 million kWh (2019 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 17.389 billion kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 55.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 8.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 2.8% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 31.9% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.8% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 4.855 million metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 21.012 million metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 1,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 17.239 million metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 3.064 billion metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 100,700 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 493,400 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 7,800 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 198,400 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 540 million barrels (2021 est.)
Refined petroleum products - production
291,200 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43Natural gas
production: 38,056,250,000 cubic meters (2019 est.)
consumption: 48,391,627,000 cubic meters (2019 est.)
exports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
imports: 10,743,167,000 cubic meters (2019 est.)
proven reserves: 592.218 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
193.869 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 47.468 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 67.789 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 78.611 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
15.859 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 2,876,794 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 175,624,364 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 80 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Pakistan’s telecom market transitioned from a regulated state-owned monopoly to a deregulated competitive structure in 2003, now aided by foreign investment; moderate growth over the last six years, supported by a young population and a rising use of mobile services; telecom infrastructure is improving, with investments in mobile-cellular networks, fixed-line subscriptions declining; system consists of microwave radio relay, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, cellular, and satellite networks; 4G mobile services broadly available; 5G tests ongoing; data centers in major cities; mobile and broadband doing well and dominate over fixed-broadband sector; future growth (in market size as well as revenue) is likely to come from the wider availability of value-added services on top of the expansion of 4G LTE and (from 2023) 5G mobile networks; the Universal Service Fund (USF) continues to direct investment towards the development of mobile broadband (and, to a lesser extent, fiber-based networks) in under-served and even under served areas of the country, with multiple projects being approved to start in 2021 and 2022 (2021)
domestic: mobile-cellular subscribership has increased; more than 90% of Pakistanis live within areas that have cell phone coverage; fiber-optic networks are being constructed throughout the country to increase broadband access and broadband penetration in Pakistan is increasing--by the end of 2021, 50% of the population had access to broadband services; fixed-line teledensity is a little over 1 per 100 and mobile-cellular roughly 84 per 100 persons (2021)
international: country code - 92; landing points for the SEA-ME-WE-3, -4, -5, AAE-1, IMEWE, Orient Express, PEACE Cable, and TW1 submarine cable systems that provide links to Europe, Africa, the Middle East, Asia, Southeast Asia, and Australia; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Indian Ocean); 3 operational international gateway exchanges (1 at Karachi and 2 at Islamabad); microwave radio relay to neighboring countries (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Broadcast media
television is the most popular and dominant source of news in Pakistan with over 120 satellite tv stations licensed by the country’s electronic media regulatory body, PEMRA ,and 40 media companies/channels with landing rights permission; state-run Pakistan Television Corporation (PTV) is the largest television network in the country and serves over 90% of the population with the largest terrestrial infrastructure of the country; PTV consists of nine TV Channels and PTV networks give special coverage to Kashmir; Pakistanis have access to over 100 private cable and satellite channels; 6 channels are considered the leaders for news reporting and current affairs programing in the country; state-owned Pakistan Broadcasting Corporation (PBC or Radio Pakistan) has the largest radio audience in the country, particularly in the rural areas; Radio Pakistan’s AM/SW/FM stations cover 98 percent of the population and 80 percent of the total area in the country; all major newspapers have online editions and all major print publications operate websites; freedom of the press and freedom of speech in the country are fragile (2021)
Internet users
total: 55,223,083 (2020 est.)
percent of population: 25% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 2,523,027 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 5 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 52
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 6,880,637 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 217.53 million (2018) mt-km
Airports - with paved runways
total: 108
over 3,047 m: 15
2,438 to 3,047 m: 20
1,524 to 2,437 m: 43
914 to 1,523 m: 20
under 914 m: 10 (2021)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 43
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 9
914 to 1,523 m: 9
under 914 m: 24 (2021)
Heliports
23 (2021)
Pipelines
13,452 km gas transmission and 177,029 km gas distribution, 3,663 km oil, 1,150 km refined products (2022)
Railways
total: 11,881 km (2021)
narrow gauge: 389 km (2021) 1.000-m gauge
broad gauge: 11,492 km (2021) 1.676-m gauge (286 km electrified)
Roadways
total: 264,175 km (2021)
paved: 185,463 km (2021) (includes 708 km of expressways)
unpaved: 78,712 km (2021)
Merchant marine
total: 57
by type: bulk carrier 5, oil tanker 7, other 45 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Karachi, Port Muhammad Bin Qasim
container port(s) (TEUs): Karachi (2,097,855) (2019)
LNG terminal(s) (import): Port Qasim
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Pakistan Army (includes National Guard), Pakistan Navy (includes marines, Maritime Security Agency), Pakistan Air Force (Pakistan Fizaia); Ministry of Interior: Frontier Corps, Pakistan Rangers (2022)
note 1: the National Guard is a paramilitary force and one of the Army's reserve forces, along with the Pakistan Army Reserve, the Frontier Corps, and the Pakistan Rangers
note 2: the Frontier Corps is a paramilitary force manned mostly by individuals from the tribal areas and commanded by officers from the Pakistan Army; it manages security duties in the tribal areas and on the border with Afghanistan (Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa provinces, including the former Federally Administered Tribal Areas)
note 3: the Pakistan Rangers is a paramilitary force operating in Sindh and Punjab
Military expenditures
4% of GDP (2022 est.)
4% of GDP (2021 est.)
4% of GDP (2020 est.)
4.1% of GDP (2019) (approximately $21.6 billion)
4.1% of GDP (2018) (approximately $21.6 billion)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; approximately 630,000 active duty personnel (550,000 Army; 30,000 Navy; 50,000 Air Force); approximately 150,000 Frontier Corps and Pakistan Rangers (2022)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Pakistan military inventory includes a broad mix of equipment, primarily from China, France, Russia, Turkey, Ukraine, the UK, and the US; since 2010, China has been the leading supplier of arms to Pakistan; Pakistan also has a large domestic defense industry (2022)
Military service age and obligation
16 (or 17 depending on service) to 23 years of age for voluntary military service; soldiers cannot be deployed for combat until age 18; women serve in all three armed forces; reserve obligation to age 45 for enlisted men, age 50 for officers (2022)
Military deployments
1,300 Central African Republic (MINUSCA); 1,970 Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO); 220 Mali (MINUSMA); 290 South Sudan (UNMISS); 220 Sudan (UNISFA) (May 2022)
Military - note
the military has carried out three coups since Pakistan's independence in 1947 and as of 2022 remained a dominant force in the country’s political arena; its chief external focus was on the perceived threat from India, as well as implications of the fall of the government in Kabul, but over the past 15 years, the military also has increased its role in internal security missions, including counterinsurgency and counterterrorism; it is the lead security agency in many areas of the former Federally Administered Tribal Areas
the military establishment also has a large stake in the country's economic sector; through two large conglomerates, it is involved in a diverse array of commercial activities, including banking, construction of public projects, employment services, energy and power generation, fertilizer, food, housing, real estate, and security services
Pakistan and India have fought several conflicts since 1947, including the Indo-Pakistan War of 1965 and the Indo-Pakistan and Bangladesh War of Independence of 1971, as well as two clashes over the disputed region of Kashmir (First Kashmir War of 1947 and the Kargil Conflict of 1999); a fragile cease-fire in Kashmir was reached in 2003, revised in 2018, and reaffirmed in 2021, although the Line of Control remained contested as of 2022, and India has accused Pakistan of backing armed separatists and terrorist organizations in Jammu and Kashmir; in addition, India and Pakistan have battled over the Siachen Glacier of Kashmir, which was seized by India in 1984 with Pakistan attempting to retake the area in 1985, 1987, and 1995; despite a cease-fire, as of 2022 both sides continued to maintain a permanent military presence there with outposts at altitudes above 20,000 feet (over 6,000 meters) where most casualties were due to extreme weather or the hazards of operating in the high mountain terrain of the world’s highest conflict, including avalanches, exposure, and altitude sickness
Pakistan has Major Non-NATO Ally (MNNA) status with the US; MNNA is a designation under US law that provides foreign partners with certain benefits in the areas of defense trade and security cooperation; while MNNA status provides military and economic privileges, it does not entail any security commitments (2022)
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Haqqani Network; Harakat ul-Jihad-i-Islami; Harakat ul-Mujahidin; Hizbul Mujahideen; Indian Mujahedeen; Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham-Khorasan (ISIS-K); Islamic State of ash-Sham – India; Islamic State of ash-Sham – Pakistan; Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan; Jaish-e-Mohammed; Jaysh al Adl (Jundallah); Lashkar i Jhangvi; Lashkar-e Tayyiba; Tehrik-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP); al-Qa’ida; al-Qa’ida in the Indian Subcontinent (AQIS)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Pakistan-Afghanistan: since 2002, with UN assistance, Pakistan has repatriated about 5.3 million Afghan refugees, leaving about 2.74-3 million; Pakistan has sent troops across and built fences along some remote tribal areas of its treaty-defined Durand Line border with Afghanistan, which serve as bases for foreign terrorists and other illegal activities; in February 2022, amid skirmishes between Taliban and Pakistani forces, Pakistan announced its intent to finish constructing the barbed wire fence along the Durand Line and bring nearby areas under its control; Afghan, Coalition, and Pakistan military meet periodically to clarify the alignment of the boundary on the ground and on maps
Pakistan-China: none identified
Pakistan-India: Kashmir remains the site of the world's largest and most militarized territorial dispute with portions under the de facto administration of China (Aksai Chin), India (Jammu and Kashmir), and Pakistan (Azad Kashmir and Northern Areas); UN Military Observer Group in India and Pakistan has maintained a small group of peacekeepers since 1949; India does not recognize Pakistan's ceding historic Kashmir lands to China in 1964; India and Pakistan have initiated discussions on defusing the armed standoff in the Siachen glacier region; the Siachen glacier is claimed by both countries and militarily occupied by India: Pakistan opposed India's fencing the highly militarized Line of Control (completed in 2004) and the construction of the Baglihar Dam on the Chenab River (opened in 2008) in Jammu and Kashmir, which is part of the larger dispute on water sharing of the Indus River and its tributaries; to defuse tensions and prepare for discussions on a maritime boundary, India and Pakistan seek technical resolution of the disputed boundary in Sir Creek estuary at the mouth of the Rann of Kutch in the Arabian Sea; Pakistani maps continue to show Junagadh in India's Gujarat State as part of Pakistan
Pakistan-Iran: none identified
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 2.62-2.88 million (1.28 million registered, 1.34-1.6 million undocumented or otherwise categorized) (Afghanistan) (2022)
IDPs: 104,000 (primarily those who remain displaced by counter-terrorism and counter-insurgency operations and violent conflict between armed non-state groups in the Federally Administered Tribal Areas and Khyber-Paktunkwa Province; more than 1 million displaced in northern Waziristan in 2014; individuals also have been displaced by repeated monsoon floods) (2021)
stateless persons: 47 (mid-year 2021)
Illicit drugs
minor cultivator of opium poppy and cannabis with 1,400 hectares of poppy cultivated 2016; one of the world’s top transit corridors for opiates and cannabis products along with Afghanistan and Iran; precursor chemicals also pass through Pakistan as a major transit point for global distribution