Introduction
Background
Colonized by the Portuguese in the 16th century, Macau was the first European settlement in the Far East. Pursuant to an agreement signed by China and Portugal on 13 April 1987, Macau became the Macau Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China on 20 December 1999. In this agreement, China promised that, under its "one country, two systems" formula, China's political and economic system would not be imposed on Macau, and that Macau would enjoy a "high degree of autonomy" in all matters except foreign affairs and defense for the subsequent 50 years.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
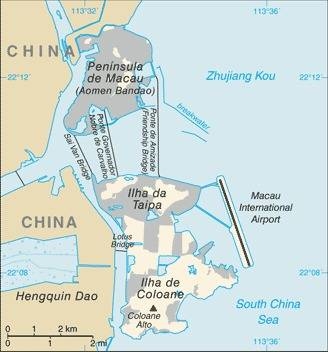
Eastern Asia, bordering the South China Sea and China
Geographic coordinates
22 10 N, 113 33 E
Map references
Southeast Asia
Area - comparative
less than one-sixth the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries
total: 3 km
regional borders (1): China 3 km
Coastline
41 km
Maritime claims
not specified
Climate
subtropical; marine with cool winters, warm summers
Terrain
generally flat
Elevation
highest point: Alto Coloane 172 m
lowest point: South China Sea 0 m
Land use
agricultural land: 0% (2018 est.)
other: 100% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
0 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
population fairly equally distributed
Natural hazards
typhoons
Geography - note
essentially urban; an area of land reclaimed from the sea measuring 5.2 sq km and known as Cotai now connects the islands of Coloane and Taipa; the island area is connected to the mainland peninsula by three bridges
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Chinese
adjective: Chinese
Ethnic groups
Chinese 88.7%, Portuguese 1.1%, mixed 1.1%, other 9.2% (includes Macanese - mixed Portuguese and Asian ancestry) (2016 est.)
Languages
Cantonese 80.1%, Mandarin 5.5%, other Chinese dialects 5.3%, Tagalog 3%, English 2.8%, Portuguese 0.6%, other 2.8%; note - Chinese and Portuguese are official languages; Macanese, a Portuguese-based Creole, is also spoken (2016 est.)
major-language sample(s):
世界概况, 必須擁有的基本資料参考书 (Cantonese)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
folk religion 58.9%, Buddhist 17.3%, Christian 7.2%, other 1.2%, none 15.4% (2020 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 13.43% (male 42,449/female 40,051)
15-24 years: 10.45% (male 33,845/female 30,354)
25-54 years: 49% (male 134,302/female 166,762)
55-64 years: 14.57% (male 44,512/female 45,007)
65 years and over: 12.56% (male 36,223/female 40,953) (2020 est.)

Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 36.9
youth dependency ratio: 20
elderly dependency ratio: 16.9
potential support ratio: 5.9 (2021 est.)
Median age
total: 40.8 years
male: 40.7 years
female: 40.9 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
population fairly equally distributed
Urbanization
urban population: 100% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 1.46% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
682,000 Macau (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.11 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.83 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.74 male(s)/female
total population: 0.9 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Infant mortality rate
total: 4.59 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 4.68 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 4.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 84.98 years
male: 82.09 years
female: 88.02 years (2022 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: NA
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: NA
total: 0% of population (2020)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 96.5%
male: 98.2%
female: 95% (2016)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 18 years
male: 17 years
female: 19 years (2021)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 8.1%
male: 9.9%
female: 6.4% (2020 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
air pollution; coastal waters pollution; insufficient policies in reducing and recycling solid wastes; increasing population density worsening noise pollution
Air pollutants
carbon dioxide emissions: 2.07 megatons (2016 est.)
Climate
subtropical; marine with cool winters, warm summers
Land use
agricultural land: 0% (2018 est.)
other: 100% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 100% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 1.46% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 377,942 tons (2016 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 75,588 tons (2014 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 20% (2014 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Macau Special Administrative Region
conventional short form: Macau
official long form: Aomen Tebie Xingzhengqu (Chinese)/ Regiao Administrativa Especial de Macau (Portuguese)
official short form: Aomen (Chinese)/ Macau (Portuguese)
etymology: name is thought to derive from the A-Ma Temple - built in 1488 and dedicated to Mazu, the goddess of seafarers and fishermen - which is referred to locally as "Maa Gok" - and in Portuguese became "Macau"; the Chinese name Aomen means "inlet gates"
Government type
executive-led limited democracy; a special administrative region of the People's Republic of China
Dependency status
special administrative region of the People's Republic of China
Administrative divisions
none (special administrative region of the People's Republic of China)
Independence
none (special administrative region of China)
National holiday
National Day (anniversary of the Founding of the People's Republic of China), 1 October (1949); note - 20 December (1999) is celebrated as Macau Special Administrative Region Establishment Day
Constitution
history: previous 1976 (Organic Statute of Macau, under Portuguese authority); latest adopted 31 March 1993, effective 20 December 1999 (Basic Law of the Macau Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China serves as Macau's constitution)
amendments: proposed by the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress (NPC), the People’s Republic of China State Council, and the Macau Special Administrative Region; submittal of proposals to the NPC requires two-thirds majority vote by the Legislative Assembly of Macau, approval by two thirds of Macau's deputies to the NPC, and consent of the Macau chief executive; final passage requires approval by the NPC; amended 2005, 2012
Legal system
civil law system based on the Portuguese model
Citizenship
see China
Suffrage
18 years of age in direct elections for some legislative positions, universal for permanent residents living in Macau for the past 7 years; note - indirect elections are limited to organizations registered as "corporate voters" and an election committee for the chief executive drawn from broad regional groupings, municipal organizations, central government bodies, and elected Macau officials
Executive branch
chief of state: President of China XI Jinping (since 14 March 2013)
head of government: Chief Executive HO lat Seng (since 20 December 2019)
cabinet: Executive Council appointed by the chief executive
elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by National People's Congress for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 17 March 2018 (next to be held in March 2023); chief executive chosen by a 400-member Election Committee for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 24 August 2019 (next to be held in 2024)
election results: 2019: HO Iat Seng (unopposed; received 392 out of 400 votes)
2014: Fernando CHUI Sai (unopposed; received 380 of 396 votes)
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Legislative Assembly or Regiao Administrativa Especial de Macau (33 seats; 14 members directly elected by proportional representation vote, 12 indirectly elected by an electoral college of professional and commercial interest groups, and 7 appointed by the chief executive; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 12 September 2021 (next to be held in September 2025)
election results: percent of vote - ACUM 20.1%, UPD 18%, NE 13.8%, UMG 12.7%, UPP 11.4%, ABL 10.8%, PS 6.6%, other 6.6%; seats by political group - ACUM 3, UPD 2, UMG 2, UPP 2, ABL 2, NE 2, PS 1; composition NA
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Court of Final Appeal of Macau Special Administrative Region (consists of the court president and 2 associate justices)
judge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the Macau chief executive upon the recommendation of an independent commission of judges, lawyers, and "eminent" persons; judge tenure NA
subordinate courts: Court of Second Instance; Court of First instance; Lower Court; Administrative Court
Political parties and leaders
Alliance for Change or APM [Melinda CHAN Mei-yi]
Alliance for a Happy Home or ABL [WONG Kit-cheng] (an electoral list of UPP)
Macau Civic Power [Agnes LAM Iok-fong]
Macau-Guangdong Union or UMG [MAK Soi-kun]
Macau Citizens' Development Association or ACDM [Becky SONG Pek-kei]
New Democratic Macau Association or ANMD [AU Kam-san]
New Hope or NE [Jose Maria Pereira COUTINHO]
New Macau Association (New Macau Progressives) or AMN or ANPM [Sulu SOU Ka-hou]
New Union for Macau's Development or NUDM [Angela LEONG On-kei]
Progress Promotion Union
Prosperous Democratic Macau Association or APMD (an electoral list of AMN)
Union for Development or UPD [HO Sut Heng]
Union for Promoting Progress or UPP [HO Ion-sang]
United Citizens Association of Macau or ACUM [CHAN Meng-kam]
note: there is no political party ordinance, so there are no registered political parties; politically active groups register as societies or companies
International organization participation
ICC (national committees), IHO, IMF, IMO (associate), Interpol (subbureau), ISO (correspondent), UNESCO (associate), UNWTO (associate), UPU, WCO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
none (Special Administrative Region of China)
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: the US has no offices in Macau; US Consulate General in Hong Kong is accredited to Macau
Flag description
green with a lotus flower above a stylized bridge and water in white, beneath an arc of five gold, five-pointed stars: one large in the center of the arc and two smaller on either side; the lotus is the floral emblem of Macau, the three petals represent the peninsula and two islands that make up Macau; the five stars echo those on the flag of China
National symbol(s)
lotus blossom; national colors: green, white, yellow
National anthem
note: as a Special Administrative Region of China, "Yiyongjun Jinxingqu" is the official anthem (see China)
Economy
Economic overview
Since opening up its locally-controlled casino industry to foreign competition in 2001, Macau has attracted tens of billions of dollars in foreign investment, transforming the territory into one of the world's largest gaming centers. Macau's gaming and tourism businesses were fueled by China's decision to relax travel restrictions on Chinese citizens wishing to visit Macau. In 2016, Macau's gaming-related taxes accounted for more than 76% of total government revenue.
Macau's economy slowed dramatically in 2009 as a result of the global economic slowdown, but strong growth resumed in the 2010-13 period, largely on the back of tourism from mainland China and the gaming sectors. In 2015, this city of 646,800 hosted nearly 30.7 million visitors. Almost 67% came from mainland China. Macau's traditional manufacturing industry has slowed greatly since the termination of the Multi-Fiber Agreement in 2005. Services export — primarily gaming — increasingly has driven Macau’s economic performance. Mainland China’s anti-corruption campaign brought Macau’s gambling boom to a halt in 2014, with spending in casinos contracting 34.3% in 2015. As a result, Macau's inflation-adjusted GDP contracted 21.5% in 2015 and another 2.1% in 2016 - down from double-digit expansion rates in the period 2010-13 - but the economy recovered handsomely in 2017.
Macau continues to face the challenges of managing its growing casino industry, risks from money-laundering activities, and the need to diversify the economy away from heavy dependence on gaming revenues. Macau's currency, the pataca, is closely tied to the Hong Kong dollar, which is also freely accepted in the territory.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$35.58 billion (2020 est.)
$81.44 billion (2019 est.)
$83.64 billion (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
9.1% (2017 est.)
-0.9% (2016 est.)
-21.6% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$54,800 (2020 est.)
$127,200 (2019 est.)
$132,400 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$53.841 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.7% (2019 est.)
3% (2018 est.)
1.2% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: AA (2018)
Moody's rating: Aa3 (2016)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 0% (2016 est.)
industry: 6.3% (2017 est.)
services: 93.7% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 24.2% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 9.9% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 18.5% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.8% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 79.4% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -32% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
pork, poultry, beef, pig fat, pig offals, eggs, pepper, cattle offals, cattle hides, goose/guinea fowl meat
Industries
tourism, gambling, clothing, textiles, electronics, footwear, toys
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 2.5%
industry: 9.8%
services: 4.4%
industry and services: 12.4%
agriculture/fishing/forestry/mining: 15%
manufacturing: 25.9%
construction: 7.1%
transportation and utilities: 2.6%
commerce: 20.3% (2013 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 8.1%
male: 9.9%
female: 6.4% (2020 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
35 (2013)
38 (2008)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 14.71 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 9.684 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
$16.75 billion (2017 est.)
$12.22 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$45.35 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$45.62 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
note: includes reexports
Exports - partners
Hong Kong 66%, China 9% (2019)
Exports - commodities
broadcasting equipment, jewelry, watches, trunks/cases, telephones (2019)
Imports
$17.35 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$18.28 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Imports - partners
China 33%, Hong Kong 31%, France 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
jewelry, watches, electricity, aircraft, cars (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$20.17 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$18.89 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
note: the Fiscal Reserves Act that came into force on 1 January 2012 requires the fiscal reserves to be separated from the foreign exchange reserves and to be managed separately; the transfer of assets took place in February 2012
Exchange rates
patacas (MOP) per US dollar -
8 (2017 est.)
7.9951 (2016 est.)
7.9951 (2015 est.)
7.985 (2014 est.)
7.9871 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 478,000 kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 5,278,600,000 kWh (2020 est.)
exports: 0 kWh (2020 est.)
imports: 4,852,600,000 kWh (2020 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 136 million kWh (2020 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 66.4% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 33.6% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 0 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 14,300 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 0 barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
production: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
consumption: 136.714 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
exports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
imports: 133.712 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
proven reserves: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
2.012 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 1.744 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 268,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
81.407 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 110,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 17 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 2.793 million (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 430 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Macau’s economy and GDP have been on a roller coaster ride since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020; the Special Administrative Region (SAR) of China is heavily dependent on tourists coming from the mainland and Hong Kong to play in Macau’s many casinos, but the ensuing lock downs contributed to a dramatic fall in visitor numbers as well as income; this too, has had a major effect on the telecom sector (particularly in the mobile segment) with short-stay visitors as well as foreign workers on temporary-stay visas being forced to stay away.; total mobile subscription numbers are estimated to have dropped from a high of 2.8 million in 2019 (representing a whopping 442% penetration rate in a region with a population of just 700,000) to less than half that by the end of 2021: 1.3 million subscribers; Macau had almost the highest mobile penetration rate in the world; it is now sitting at a more ‘reasonable’ level of 200%; a significant bounce back can be expected to follow the easing of travel restrictions, although perhaps not up to the same lofty heights achieved in 2019; asecond factor behind the steep fall in 2020 was the introduction of a Cyber Security Law that required all prepaid SIM cards to become registered or face being deactivated in October 2020; the combined effect of the pandemic and the new restrictions meant that prepaid subscriber numbers fell by more than 80%; postpaid accounts, largely the domain of Macau’s permanent residents, were barely affected by the external upheaval; they continued to increase in number, year-on-year, and provided better returns to the operators thanks to substantially increased data usage during the lock downs; the mobile broadband market has experienced the same dramatic fluctuations as the broader mobile segment over the last two years, at least in terms of subscriber numbers; but this is largely because mobile broadband uptake is inextricably tied to the base mobile offering in Macau; with total mobile broadband data traffic going up, not down, between 2019 and 2021, that again points to the strength of the contract segment helping to drive future growth in Macau’s telecom sector (2022)
domestic: fixed-line nearly 17 per 100 and mobile-cellular roughly 430 per 100 persons (2020)
international: country code - 853; landing point for the SEA-ME-WE-3 submarine cable network that provides links to Asia, Africa, Australia, the Middle East, and Europe; HF radiotelephone communication facility; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Broadcast media
local government dominates broadcast media; 2 television stations operated by the government with one broadcasting in Portuguese and the other in Cantonese and Mandarin; 1 cable TV and 4 satellite TV services available; 3 radio stations broadcasting, of which 2 are government-operated (2019)
Internet users
total: 571,421 (2020 est.)
percent of population: 88% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 208,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 32 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020) (registered in China)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 21 (registered in China)
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 3,157,724 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 31.84 million (2018) mt-km
Airports - with paved runways
total: 1
over 3,047 m: 1 (2021)
Heliports
2 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Macau
Military and Security
Military and security forces
no regular indigenous military forces; Macau Public Security Police Force (includes the Police Intervention Tactical Unit or UTIP for counterterrorism operations)
Military - note
defense is the responsibility of China; the Chinese People's Liberation Army (PLA) maintains a garrison in Macau
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
none identified
Trafficking in persons
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List — Macau does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking but is making significant efforts to do so; the government trained police, customs, and social welfare officials on human trafficking, funded an awareness campaign, and provided services to victims; authorities convicted three sex traffickers but did not sentence anyone to significant prison terms; authorities investigated only one potential trafficking case and made no prosecutions; the government provided no assistance to any victims, and officials did not initiate any prosecutions or sentence convicted traffickers to significant terms of imprisonment; Macau was downgraded to Tier 2 Watch List (2020)
trafficking profile: Macau is a destination and, to a much lesser extent, source for women and children subjected to sex trafficking and possibly forced labor; most victims come from the Chinese mainland, but others are trafficked from China, Russia, and Southeast Asia; victims are lured in by false job offers and forced into prostitution, often being confined to massage parlors and illegal brothels where their identity documents are confiscated and they are threatened with violence; Chinese, Russian, and Thai criminal organizations are believed to be involved in recruiting women for Macau’s commercial sex industry
Illicit drugs
asian organized crime groups involved in drug trafficking and money laundering