Introduction
Background
As a result of its location at the crossroads of three continents, the area that is modern-day Lebanon is rich in cultural and religious diversity. This region was subject to various foreign conquests for much of its history, including by the Romans, Arabs, and Ottomans. Following World War I, France acquired a mandate over the northern portion of the former Ottoman Empire province of Syria. From it the French demarcated the region of Lebanon in 1920, and it gained independence in 1943. Since then, Lebanon has experienced periods of political turmoil interspersed with prosperity built on its historical position as a regional center for finance and trade, although that status has significantly diminished since the beginning of Lebanon’s economic crisis in 2019, which includes simultaneous currency, debt, and banking crises. The country's 1975-90 civil war, which resulted in an estimated 120,000 fatalities, was followed by years of social and political instability. Sectarianism is a key element of Lebanese political life. Neighboring Syria has historically influenced Lebanon's foreign and domestic policies, and its military occupied Lebanon from 1976 until 2005. Hizballah - a major Lebanese political party, militia, and US-designated foreign terrorist organization - and Israel continued attacks and counterattacks against each other after Syria's withdrawal, and fought a brief war in 2006. Lebanon's borders with Syria and Israel remain unresolved.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
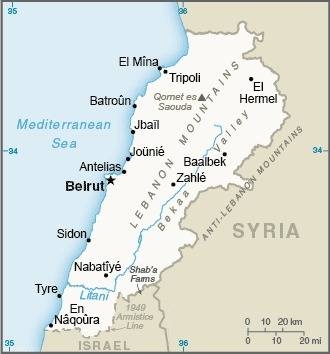
Middle East, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Israel and Syria
Geographic coordinates
33 50 N, 35 50 E
Map references
Middle East
Land boundaries
total: 484 km
border countries (2): Israel 81 km; Syria 403 km
Coastline
225 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
Climate
Mediterranean; mild to cool, wet winters with hot, dry summers; the Lebanon Mountains experience heavy winter snows
Terrain
narrow coastal plain; El Beqaa (Bekaa Valley) separates Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon Mountains
Elevation
highest point: Qornet es Saouda 3,088 m
lowest point: Mediterranean Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 1,250 m
Natural resources
limestone, iron ore, salt, water-surplus state in a water-deficit region, arable land
Land use
agricultural land: 63.3% (2018 est.)
arable land: 11.9% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 12.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 39.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 13.4% (2018 est.)
other: 23.3% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
1,040 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
the majority of the people live on or near the Mediterranean coast, and of these most live in and around the capital, Beirut; favorable growing conditions in the Bekaa Valley, on the southeastern side of the Lebanon Mountains, have attracted farmers and thus the area exhibits a smaller population density
Natural hazards
earthquakes; dust storms, sandstorms
Geography - note
smallest country in continental Asia; Nahr el Litani is the only major river in Near East not crossing an international boundary; rugged terrain historically helped isolate, protect, and develop numerous factional groups based on religion, clan, and ethnicity
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Lebanese (singular and plural)
adjective: Lebanese
Ethnic groups
Arab 95%, Armenian 4%, other 1%
note: many Christian Lebanese do not identify themselves as Arab but rather as descendants of the ancient Canaanites and prefer to be called Phoenicians
Languages
Arabic (official), French, English, Armenian
major-language sample(s):
كتاب حقائق العالم، المصدر الذي لا يمكن الاستغناء عنه للمعلومات الأساسية (Arabic)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Muslim 67.8% (31.9% Sunni, 31.2% Shia, smaller percentages of Alawites and Ismailis), Christian 32.4% (Maronite Catholics are the largest Christian group), Druze 4.5%, very small numbers of Jews, Baha'is, Buddhists, and Hindus (2020 est.)
note: data represent the religious affiliation of the citizen population (data do not include Lebanon's sizable Syrian and Palestinian refugee populations); 18 religious sects recognized
Age structure
0-14 years: 20.75% (male 581,015/female 554,175)
15-24 years: 14.98% (male 417,739/female 401,357)
25-54 years: 46.69% (male 1,296,250/female 1,257,273)
55-64 years: 9.62% (male 250,653/female 275,670)
65 years and over: 7.96% (male 187,001/female 248,479) (2020 est.)

Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 59.3
youth dependency ratio: 44
elderly dependency ratio: 15.3
potential support ratio: 6.5 (2021 est.)
Median age
total: 33.7 years
male: 33.1 years
female: 34.4 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
the majority of the people live on or near the Mediterranean coast, and of these most live in and around the capital, Beirut; favorable growing conditions in the Bekaa Valley, on the southeastern side of the Lebanon Mountains, have attracted farmers and thus the area exhibits a smaller population density
Urbanization
urban population: 89.4% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: -1.23% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
2.421 million BEIRUT (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.93 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.67 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
29 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112Infant mortality rate
total: 7.04 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 7.6 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 6.45 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 78.76 years
male: 77.36 years
female: 80.23 years (2022 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
8.7% of GDP (2019)
Physicians density
2.21 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
Hospital bed density
2.7 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
(2021 est.) <0.1%
Major infectious diseases
note: widespread ongoing transmission of a respiratory illness caused by the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) is occurring throughout Lebanon; as of 9 December 2022, Lebanon has reported a total of 1,220,831 cases of COVID-19 or 17,886.46 cumulative cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 population with a total of 10,740 cumulative deaths or a rate of 157.35 cumulative deaths per 100,000 population; as of 1 December 2022, 49.9% of the population has received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 1.14 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.38 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.21 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.53 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 38.2% (2020 est.)
male: 47.5% (2020 est.)
female: 28.9% (2020 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 1.4%
women married by age 18: 6% (2016 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 95.1%
male: 96.9%
female: 93.3% (2018)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 11 years
male: 12 years
female: 11 years (2014)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 23.3%
male: 24.5%
female: 21.4% (2019)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation; soil deterioration, erosion; desertification; species loss; air pollution in Beirut from vehicular traffic and the burning of industrial wastes; pollution of coastal waters from raw sewage and oil spills; waste-water management
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification, Marine Life Conservation
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 30.67 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 24.8 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 3.37 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
Mediterranean; mild to cool, wet winters with hot, dry summers; the Lebanon Mountains experience heavy winter snows
Land use
agricultural land: 63.3% (2018 est.)
arable land: 11.9% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 12.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 39.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 13.4% (2018 est.)
other: 23.3% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 89.4% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: -1.23% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180Major infectious diseases
note: widespread ongoing transmission of a respiratory illness caused by the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) is occurring throughout Lebanon; as of 9 December 2022, Lebanon has reported a total of 1,220,831 cases of COVID-19 or 17,886.46 cumulative cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 population with a total of 10,740 cumulative deaths or a rate of 157.35 cumulative deaths per 100,000 population; as of 1 December 2022, 49.9% of the population has received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine
Food insecurity
widespread lack of access: due to the ongoing financial and economic crisis - in September 2021, the United Nations estimated that, taking into account multiple factors other than income, such as access to health, education and public utilities, 82% of the population lives in multidimensional poverty in 2021, up from 42% in 2019 (2022)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 2.04 million tons (2014 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 163,200 tons (2014 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 8% (2014 est.)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 240 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 900 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 700 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
4.503 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Lebanese Republic
conventional short form: Lebanon
local long form: Al Jumhuriyah al Lubnaniyah
local short form: Lubnan
former: Greater Lebanon
etymology: derives from the Semitic root "lbn" meaning "white" and refers to snow-capped Mount Lebanon
Government type
parliamentary republic
Capital
name: Beirut
geographic coordinates: 33 52 N, 35 30 E
time difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: derived from the Canaanite or Phoenician word "ber'ot," meaning "the wells" or "fountain," which referred to the site's accessible water table
Administrative divisions
8 governorates (mohafazat, singular - mohafazah); Aakkar, Baalbek-Hermel, Beqaa (Bekaa), Beyrouth (Beirut), Liban-Nord (North Lebanon), Liban-Sud (South Lebanon), Mont-Liban (Mount Lebanon), Nabatiye
Independence
22 November 1943 (from League of Nations mandate under French administration)
National holiday
Independence Day, 22 November (1943)
Constitution
history: drafted 15 May 1926, adopted 23 May 1926
amendments: proposed by the president of the republic and introduced as a government bill to the National Assembly or proposed by at least 10 members of the Assembly and agreed upon by two thirds of its members; if proposed by the National Assembly, review and approval by two-thirds majority of the Cabinet is required; if approved, the proposal is next submitted to the Cabinet for drafting as an amendment; Cabinet approval requires at least two-thirds majority, followed by submission to the National Assembly for discussion and vote; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of a required two-thirds quorum of the Assembly membership and promulgation by the president; amended several times, last in 2004
Legal system
mixed legal system of civil law based on the French civil code, Ottoman legal tradition, and religious laws covering personal status, marriage, divorce, and other family relations of the Jewish, Islamic, and Christian communities
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Lebanon
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: unknown
Suffrage
21 years of age; authorized for all men and women regardless of religion; excludes persons convicted of felonies and other crimes or those imprisoned; excludes all military and security service personnel regardless of rank
Executive branch
chief of state: President Michel AWN (since 31 October 2016)
head of government: Prime Minister Najib MIQATI (since 20 September 2021)
cabinet: Cabinet chosen by the prime minister in consultation with the president and Parliament
elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by Parliament with two-thirds majority vote in the first round and if needed absolute majority vote in a second round for a 6-year term (eligible for non-consecutive terms); last held on 31 October 2016 (next to be held in 2022); prime minister appointed by the president in consultation with Parliament; deputy prime minister determined during cabinet formation
election results:
2022: on 15 December 2022, Parliament in its tenth session failed to elect a president; next vote scheduled in January 2023
2016: Michel AWN elected president in second round; National Assembly vote - Michel AWN (FPM) 83 votes; note - in the initial election held on 23 April 2014, no candidate received the required two-thirds vote, and subsequent attempts failed because Parliament lacked the necessary quorum of 86 members to hold a vote; the president was finally elected in its 46th attempt on 31 October 2016
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Lebanese Parliament or Majlis al-Nuwab in Arabic, Chambre des députés in French (128 seats; members directly elected in multi-member constituencies by open list proportional representation vote, apportioned evenly between Christian and Muslims; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 15 May 2022 (next to be held in May 2026)
election results: percent of vote by coalition/party – NA; seats by party/coalition – FPM 16, LF 14, Amal Movement 13, Hezbollah 13, PSP 9, FM (candidates did not run in 2022; members ran as independents) 8, Kata’ib Party 4, other 30, independent 21; composition - men 120, women 8, percent of women 6.3%
note: Lebanon’s constitution states the Lebanese Parliament cannot conduct regular business until it elects a president when the position is vacant
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Court of Cassation or Supreme Court (organized into 8 chambers, each with a presiding judge and 2 associate judges); Constitutional Council (consists of 10 members)
judge selection and term of office: Court of Cassation judges appointed by Supreme Judicial Council, a 10-member body headed by the chief justice, and includes other judicial officials; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Council members appointed - 5 by the Council of Ministers and 5 by parliament; members serve 5-year terms
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; Courts of First Instance; specialized tribunals, religious courts; military courts
Political parties and leaders
Al-Ahbash or Association of Islamic Charitable Projects or AICP [Shaykh Hussam QARAQIRA]
Amal Movement ("Hope Movement") [Nabih BERRI]
Azm Movement [Najib MIQATI]
Ba’th Arab Socialist Party of Lebanon [leader disputed]
Free Patriotic Movement or FPM [Gibran BASSIL]
Future Movement Bloc or FM [Sa'ad al-HARIRI]
Hizballah [Hassan NASRALLAH]
Islamic Action Front or IAF [Sheikh Zuhayr al-JU’AYD]
Kata'ib Party [Sami GEMAYEL]
Lebanese Democratic Party [Talal ARSLAN]
Lebanese Forces or LF [Samir JA'JA]
Marada Movement [Sulayman FRANJIEH]
Progressive Socialist Party or PSP [Walid JUNBLATT]
Social Democrat Hunshaqian Party [Sabuh KALPAKIAN]
Syrian Social Nationalist Party or SSNP [Rabi BANAT]
Tashnaq or Armenian Revolutionary Federation [Hagop PAKRADOUNIAN]
International organization participation
ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, FAO, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAS (observer), OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Wael HACHEM, Counselor (since 15 March 2021)
chancery: 2560 28th Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 939-6300
FAX: [1] (202) 939-6324
email address and website:
info@lebanonembassyus.org
http://www.lebanonembassyus.org/
consulate(s) general: Detroit, New York, Los Angeles
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Dorothy C. SHEA (since 11 March 2020)
embassy: Awkar-Facing the Municipality, Main Street, Beirut
mailing address: 6070 Beirut Place, Washington DC 20521-6070
telephone: [961] (04) 543-600
FAX: [961] (4) 544-019
email address and website:
BeirutACS@state.gov
https://lb.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three horizontal bands consisting of red (top), white (middle, double width), and red (bottom) with a green cedar tree centered in the white band; the red bands symbolize blood shed for liberation, the white band denotes peace, the snow of the mountains, and purity; the green cedar tree is the symbol of Lebanon and represents eternity, steadiness, happiness, and prosperity
National symbol(s)
cedar tree; national colors: red, white, green
National anthem
name: "Kulluna lil-watan" (All Of Us, For Our Country!)
lyrics/music: Rachid NAKHLE/Wadih SABRA
note: adopted 1927; chosen following a nationwide competition
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 5 (all cultural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Anjar; Baalbek; Byblos; Tyre; Ouadi Qadisha (the Holy Valley) and the Forest of the Cedars of God (Horsh Arz el-Rab)
Economy
Economic overview
Lebanon has a free-market economy and a strong laissez-faire commercial tradition. The government does not restrict foreign investment; however, the investment climate suffers from red tape, corruption, arbitrary licensing decisions, complex customs procedures, high taxes, tariffs, and fees, archaic legislation, and inadequate intellectual property rights protection. The Lebanese economy is service-oriented; main growth sectors include banking and tourism.
The 1975-90 civil war seriously damaged Lebanon's economic infrastructure, cut national output by half, and derailed Lebanon's position as a Middle Eastern banking hub. Following the civil war, Lebanon rebuilt much of its war-torn physical and financial infrastructure by borrowing heavily, mostly from domestic banks, which saddled the government with a huge debt burden. Pledges of economic and financial reforms made at separate international donor conferences during the 2000s have mostly gone unfulfilled, including those made during the Paris III Donor Conference in 2007, following the July 2006 war. The "CEDRE" investment event hosted by France in April 2018 again rallied the international community to assist Lebanon with concessional financing and some grants for capital infrastructure improvements, conditioned upon long-delayed structural economic reforms in fiscal management, electricity tariffs, and transparent public procurement, among many others.
The Syria conflict cut off one of Lebanon's major markets and a transport corridor through the Levant. The influx of nearly one million registered and an estimated 300,000 unregistered Syrian refugees has increased social tensions and heightened competition for low-skill jobs and public services. Lebanon continues to face several long-term structural weaknesses that predate the Syria crisis, notably, weak infrastructure, poor service delivery, institutionalized corruption, and bureaucratic over-regulation. Chronic fiscal deficits have increased Lebanon’s debt-to-GDP ratio, the third highest in the world; most of the debt is held internally by Lebanese banks. These factors combined to slow economic growth to the 1-2% range in 2011-17, after four years of averaging 8% growth. Weak economic growth limits tax revenues, while the largest government expenditures remain debt servicing, salaries for government workers, and transfers to the electricity sector. These limitations constrain other government spending, limiting its ability to invest in necessary infrastructure improvements, such as water, electricity, and transportation. In early 2018, the Lebanese government signed long-awaited contract agreements with an international consortium for petroleum exploration and production as part of the country’s first offshore licensing round. Exploration is expected to begin in 2019.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$79.51 billion (2020 est.)
$99.76 billion (2019 est.)
$106.93 billion (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
1.5% (2017 est.)
1.7% (2016 est.)
0.2% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$11,600 (2020 est.)
$14,600 (2019 est.)
$15,600 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$53.253 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.8% (2019 est.)
6% (2018 est.)
4.4% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: RD (2020)
Moody's rating: C (2020)
Standard & Poors rating: D (2020)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 3.9% (2017 est.)
industry: 13.1% (2017 est.)
services: 83% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 87.6% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 13.3% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 21.8% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.5% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 23.6% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -46.4% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
potatoes, milk, tomatoes, apples, oranges, olives, wheat, cucumbers, poultry, lemons
Industries
banking, tourism, real estate and construction, food processing, wine, jewelry, cement, textiles, mineral and chemical products, wood and furniture products, oil refining, metal fabricating
Labor force
2.166 million (2016 est.)
note: excludes as many as 1 million foreign workers and refugees
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 39% (2009 est.) NA
industry: NA
services: NA
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 23.3%
male: 24.5%
female: 21.4% (2019)
Population below poverty line
27.4% (2011 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
31.8 (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 11.62 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 15.38 billion (2017 est.)
Public debt
146.8% of GDP (2017 est.)
145.5% of GDP (2016 est.)
note: data cover central government debt and exclude debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intragovernmental debt; intragovernmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$12.37 billion (2017 est.)
-$11.18 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$18.17 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$19.16 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Exports - partners
Switzerland 27%, United Arab Emirates 15%, South Korea 11%, Saudi Arabia 7%, Kuwait 6% (2019)
Exports - commodities
gold, jewelry, shotguns, diamonds, scrap copper (2019)
Imports
$31.34 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$32.78 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Imports - partners
United Arab Emirates 11%, China 10%, Italy 8%, Greece 8%, Turkey 7%, United States 6% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, cars, packaged medicines, jewelry, gold (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$55.42 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$54.04 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$33.077 billion (2019 est.)
$33.655 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
Lebanese pounds (LBP) per US dollar -
1,517.5 (2020 est.)
1,513 (2019 est.)
1,506.5 (2018 est.)
1,507.5 (2014 est.)
1,507.5 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 3.768 million kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 18,715,620,000 kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 0 kWh (2019 est.)
imports: 900 million kWh (2019 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 2.219 billion kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 94.3% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 0.5% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 5% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 268,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 268,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 0 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 168,500 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 0 barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
production: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
consumption: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
exports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
imports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
proven reserves: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
25.838 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 563,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 25.275 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
53.528 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 875,480 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 13 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 4,288,221 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 63 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Lebanon’s economic crisis has had a dire effect on the country’s telecom services; although some progress has been made with developing 5G, the poor economic conditions have contributed to an erratic electricity supply and a lack of fuel to maintain generators; this has meant that internet services to areas of the country are not available on a regular basis, frustrating all those who depend on stable connectivity, and stalling business growth; adding to the difficulties are the combined stresses of the pandemic and the political crisis; a caretaker cabinet in September 2021 made way for a new government though there is little confidence on the ground that sectarian-based political horse-trading will give way to responsible governing to improve the lot of the stressed populace (2022)
domestic: fixed-line nearly 13 per 100 and nearly 63 per 100 for mobile-cellular subscriptions (2020)
international: country code - 961; landing points for the IMEWE, BERYTAR AND CADMOS submarine cable links to Europe, Africa, the Middle East and Asia; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean and 1 Atlantic Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Broadcast media
7 TV stations, 1 of which is state owned; more than 30 radio stations, 1 of which is state owned; satellite and cable TV services available; transmissions of at least 2 international broadcasters are accessible through partner stations (2019)
Internet users
total: 6,825,442 (2020 est.)
percent of population: 84% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 432,070 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 6 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 21
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 2,981,937 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 56.57 million (2018) mt-km
Airports - with paved runways
total: 5
over 3,047 m: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
under 914 m: 1 (2021)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 2
under 914 m: 1 (2021)
Heliports
1 (2021)
Pipelines
88 km gas (2013)
Railways
total: 401 km (2017)
standard gauge: 319 km (2017) 1.435-m gauge
narrow gauge: 82 km (2017) 1.050-m gauge
note: rail system is still unusable due to damage sustained from fighting in the 1980s and in 2006
Merchant marine
total: 48
by type: bulk carrier 2, general cargo 31, oil tanker 1, other 14 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Beirut, Tripoli
container port(s) (TEUs): Beirut (1,229,100) (2019)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Lebanese Armed Forces (LAF): Army Command (includes Presidential Guard Brigade, Land Border Regiments), Naval Forces, Air Forces; Ministry of Interior: Internal Security Forces Directorate (law enforcement; includes Mobile Gendarmerie), Directorate for General Security (DGS; border control, some domestic security duties) (2022)
note: the commander of the LAF is also the commander of the Army; the LAF patrols external borders, while official border checkpoints are under the authority of Directorate for General Security
Military expenditures
3.2% of GDP (2021 est.)
3% of GDP (2020 est.)
4.7% of GDP (2019 est.) (approximately $3.6 billion)
5.1% of GDP (2018 est.) (approximately $4.1 billion)
4.6% of GDP (2017 est.) (approximately $3.95 billion)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 80,000 active troops (77,000 Army; 1,500 Navy; 1,500 Air Force) (2022)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the LAF inventory includes a wide mix of mostly older equipment from a diverse array of countries; since 2010, the US has been the leading supplier of armaments (mostly second-hand equipment) to Lebanon (2022)
Military service age and obligation
17-25 years of age for men and women for voluntary military service; no conscription (2022)
note: as of 2020, women comprised about 5% of the active duty military
Military - note
as of 2022, the Lebanese military faced multiple challenges, including securing parts of the border with war-torn Syria from infiltrations of militants linked to the Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (ISIS) and al-Qa’ida terrorist groups and maintaining stability along its volatile border with Israel, where the Iranian-backed and Lebanon-based terrorist group Hizballah conducted a war with Israel in 2006 and tensions remained high, including occasional armed skirmishes; the military also faced a financial crisis as government debt and national economic difficulties undercut its ability to fully pay and supply personnel, which has sparked domestic and international fears that the armed forces may disintegrate
the United Nations Interim Force In Lebanon (UNIFIL) has operated in the country since 1978, originally under UNSCRs 425 and 426 to confirm Israeli withdrawal from Lebanon, restore international peace and security, and assist the Lebanese Government in restoring its effective authority in the area; following the July-August 2006 war, the UN Security Council adopted resolution 1701 enhancing UNIFIL and deciding that in addition to the original mandate, it would, among other things, monitor the cessation of hostilities, support the Lebanese Armed Forces as they deployed throughout the south of Lebanon, and provide assistance for humanitarian access for civilians and the return of displaced persons; UNIFIL had approximately 9,500 personnel deployed in the country as of mid-2022 (2022)
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Abdallah Azzam Brigades; al-Aqsa Martyrs Brigade; Asbat al-Ansar; HAMAS; Hizballah; Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps/Qods Force; Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (ISIS); al-Nusrah Front (Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham); Palestine Liberation Front; Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP); PFLP-General Command
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Lebanon-Syria: lacking a treaty or other documentation describing the boundary, portions of the Lebanon-Syria boundary are unclear with several sections in dispute; in March 2021, Syria signed a contract with a Russian company for oil and gas exploration in a maritime area Lebanon claims as its own based on a 2011 map sent to the UN
Lebanon-Israel: Lebanon has claimed Shab'a Farms area in the Israeli-controlled Golan Heights; Lebanon and Israel resumed negotiations over their maritime border in 2020, but their efforts were derailed when Lebanon argued that the map the UN was using needed modifications
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 479,537 (Palestinian refugees) (2020); 825,081 (Syria) (2022)
IDPs: 7,000 (2020)
stateless persons: undetermined (2016); note - tens of thousands of persons are stateless in Lebanon, including many Palestinian refugees and their descendants, Syrian Kurds denaturalized in Syria in 1962, children born to Lebanese women married to foreign or stateless men; most babies born to Syrian refugees, and Lebanese children whose births are unregistered
Illicit drugs
source country for amphetamine tablets destined for Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Libya and Sudan; in 2021 authorities in various Near Eastern countries seized millions of captagon tablets that originated in or transited to Lebanon, prompting Lebanese authorities to conduct raids on captagon production facilities and trafficking rings within the country