Kyrgyzstan
Introduction
Background
A Central Asian country of incredible natural beauty and proud nomadic traditions, most of the territory of present-day Kyrgyzstan was formally annexed by the Russian Empire in 1876. The Kyrgyz staged a major revolt against the Tsarist Empire in 1916 in which almost one-sixth of the Kyrgyz population was killed. Kyrgyzstan became a Soviet republic in 1926 and achieved independence in 1991 when the USSR dissolved. Nationwide demonstrations in 2005 and 2010 resulted in the ouster of the country’s first two presidents, Askar AKAEV and Kurmanbek BAKIEV. Interim President Roza OTUNBAEVA led a transitional government and following a nation-wide election, President Almazbek ATAMBAEV was sworn in as president in 2011. In 2017, ATAMBAEV became the first Kyrgyzstani president to step down after serving one full six-year term as required in the country’s constitution. Former prime minister and ruling Social-Democratic Party of Kyrgyzstan member, Sooronbay JEENBEKOV, replaced him after winning the 2017 presidential election, which was the most competitive in the country’s history, although international and local election observers noted cases of vote buying and abuse of public resources. In October 2020, protests against legislative election results spread across Kyrgyzstan, leading to JEENBEKOV’s resignation from the presidency, and catapulting previously imprisoned Sadyr JAPAROV to acting president. In January 2021, Kyrgyzstanis formerly elected JAPAROV as president and approved a referendum to move Kyrgyzstan from a parliamentary to a presidential system. In April 2021, Kyrgyzstanis voted in favor of draft constitutional changes that consolidated power in the presidency. Pro-government parties won a majority in the Jogorku Kenesh (Kyrgyzstan’s legislature) in November 2021 elections. Continuing concerns for Kyrgyzstan include the trajectory of democratization, endemic corruption, a history of tense, and at times violent, interethnic relations, border security vulnerabilities, and potential terrorist threats.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
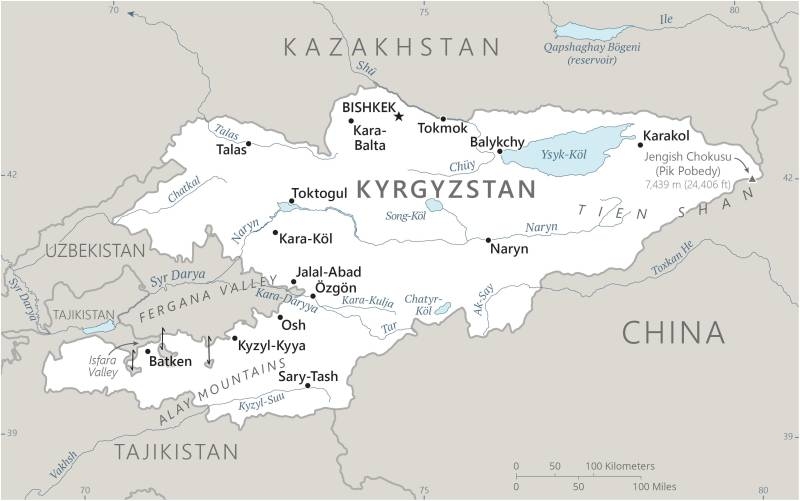
Location
Central Asia, west of China, south of Kazakhstan
Geographic coordinates
41 00 N, 75 00 E
Map references
Asia
Area - comparative
slightly smaller than South Dakota
Land boundaries
total: 4,573 km
border countries (4): China 1,063 km; Kazakhstan 1,212 km; Tajikistan 984 km; Uzbekistan 1,314 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
dry continental to polar in high Tien Shan Mountains; subtropical in southwest (Fergana Valley); temperate in northern foothill zone
Terrain
peaks of the Tien Shan mountain range and associated valleys and basins encompass the entire country
Elevation
highest point: Jengish Chokusu (Pik Pobedy) 7,439 m
lowest point: Kara-Daryya (Karadar'ya) 132 m
mean elevation: 2,988 m
Natural resources
abundant hydropower; gold, rare earth metals; locally exploitable coal, oil, and natural gas; other deposits of nepheline, mercury, bismuth, lead, and zinc
Land use
agricultural land: 55.4% (2018 est.)
arable land: 6.7% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.4% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 48.3% (2018 est.)
forest: 5.1% (2018 est.)
other: 39.5% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
10,043 sq km (2020)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Ozero Issyk-Kul 6,240 sq km
note - second largest saline lake after the Caspian Sea; second highest mountain lake after Lake Titicaca; it is an endorheic mountain basin; although surrounded by snow capped mountains it never freezes
Major rivers (by length in km)
Syr Darya river source (shared with Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan [m] ) - 3,078 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Tarim Basin (1,152,448 sq km), (Aral Sea basin) Amu Darya (534,739 sq km), Syr Darya (782,617 sq km)
Population distribution
the vast majority of Kyrgyzstanis live in rural areas; densest population settlement is to the north in and around the capital, Bishkek, followed by Osh in the west; the least densely populated area is the east, southeast in the Tien Shan mountains
Natural hazards
major flooding during snow melt; prone to earthquakes
Geography - note
landlocked; entirely mountainous, dominated by the Tien Shan range; 94% of the country is 1,000 m above sea level with an average elevation of 2,750 m; many tall peaks, glaciers, and high-altitude lakes
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Kyrgyzstani(s)
adjective: Kyrgyzstani
Ethnic groups
Kyrgyz 73.8%, Uzbek 14.8%, Russian 5.1%, Dungan 1.1%, other 5.2% (includes Uyghur, Tajik, Turk, Kazakh, Tatar, Ukrainian, Korean, German) (2021 est.)
Languages
Kyrgyz (official) 71.4%, Uzbek 14.4%, Russian (official) 9%, other 5.2% (2009 est.)
major-language sample(s):
Дүйнөлүк фактылар китеби, негизги маалыматтын маанилүү булагы. (Kyrgyz)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Muslim 90% (majority Sunni), Christian 7% (Russian Orthodox 3%), other 3% (includes Jewish, Buddhist, Baha'i) (2017 est.)
Demographic profile
Kyrgyzstan is a sparsely populated country whose population is unevenly distributed. More than 50% of the population lives in or around the two cities of Bishkek and Osh and their surrounding districts, which together account for about 12% of the country’s area. Kyrgyzstan’s population continues to grow rapidly owing to its high fertility rate and the traditional preference for larger families, a low mortality rate, a growing share of women of reproductive age, and measures to support families with children. The country has a youthful age structure; over 45% of the population is under the age of 25 as of 2022. Nevertheless, Kyrgyzstan is transitioning from an agricultural society with high fertility and mortality rates to an industrial society with lower fertility and mortality rates.
As part of the USSR, Kyrgyzstan’s rapid population growth was not problematic because its needs were redistributed among the Soviet States. As an independent state, however, population growth became burdensome. International labor migration continues to serve as a safety valve that decreases pressure on the labor market and resources (healthcare, education, and pensions), while also reducing poverty through much-needed remittances. The main destinations for labor migrants are Russia and Kazakhstan, where wages are higher; almost a third of Kyrgyzstan’s working-age population migrates to Russia alone. Outmigration was most pronounced in the 1990s, after the collapse of the USSR, when ethnic Russians, Ukrainians, and Germans left Kyrgyzstan, changing the proportion of ethnic Kyrgyz in the country from barely 50% in 1992 to almost three-quarters today.
While Kyrgyzstan is a net emigration country, it does receive immigrants. The majority of immigrants are from the Commonwealth of Independent States – particularly Kazakhstan, Russia, and Uzbekistan – but more recent arrivals also include persons from China, Turkey, and Turkmenistan. Chinese immigrants work primarily in construction and gold mining, while Turkish immigrants mainly work in construction, trade, education, and services. Border areas between Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan experience irregular migration, but many of these migrants plan to move on to Europe.
Age structure
0-14 years: 30.39% (male 930,455/female 882,137)
15-24 years: 15.7% (male 475,915/female 460,604)
25-54 years: 40.02% (male 1,172,719/female 1,214,624)
55-64 years: 8.09% (male 210,994/female 271,480)
65 years and over: 5.8% (male 132,134/female 213,835) (2020 est.)

Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 63.5
youth dependency ratio: 56.4
elderly dependency ratio: 7.2
potential support ratio: 13.9 (2021 est.)
Median age
total: 27.3 years
male: 26.1 years
female: 28.5 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
the vast majority of Kyrgyzstanis live in rural areas; densest population settlement is to the north in and around the capital, Bishkek, followed by Osh in the west; the least densely populated area is the east, southeast in the Tien Shan mountains
Urbanization
urban population: 37.8% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.05% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.105 million BISHKEK (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.78 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.5 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
22.6 years (2019 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
60 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89Infant mortality rate
total: 25.66 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 29.83 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 21.22 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 72.35 years
male: 68.27 years
female: 76.71 years (2022 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
39.4% (2018)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 89.9% of population
total: 93.6% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 10.1% of population
total: 6.4% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
4.5% of GDP (2019)
Physicians density
2.21 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
Hospital bed density
4.4 beds/1,000 population (2014)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 4.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.43 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.23 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 3.35 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 25.4% (2020 est.)
male: 48% (2020 est.)
female: 2.8% (2020 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 0.3%
women married by age 18: 12.9% (2018 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.6%
male: 99.7%
female: 99.5% (2018)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 14 years
male: 13 years
female: 14 years (2021)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 8.5%
male: 7.6%
female: 10% (2020 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
water pollution; many people get their water directly from contaminated streams and wells; as a result, water-borne diseases are prevalent; increasing soil salinity from faulty irrigation practices; air pollution due to rapid increase of traffic
Environment - international agreements
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 18.12 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 9.79 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 4.47 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
dry continental to polar in high Tien Shan Mountains; subtropical in southwest (Fergana Valley); temperate in northern foothill zone
Land use
agricultural land: 55.4% (2018 est.)
arable land: 6.7% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.4% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 48.3% (2018 est.)
forest: 5.1% (2018 est.)
other: 39.5% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 37.8% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.05% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.01% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1,113,300 tons (2015 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Ozero Issyk-Kul 6,240 sq km
note - second largest saline lake after the Caspian Sea; second highest mountain lake after Lake Titicaca; it is an endorheic mountain basin; although surrounded by snow capped mountains it never freezes
Major rivers (by length in km)
Syr Darya river source (shared with Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan [m] ) - 3,078 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Tarim Basin (1,152,448 sq km), (Aral Sea basin) Amu Darya (534,739 sq km), Syr Darya (782,617 sq km)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 224 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 336 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 7.1 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
23.618 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Kyrgyz Republic
conventional short form: Kyrgyzstan
local long form: Kyrgyz Respublikasy
local short form: Kyrgyzstan
former: Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic
etymology: a combination of the Turkic words "kyrg" (forty) and "-yz" (tribes) with the Persian suffix "-stan" (country) creating the meaning "Land of the Forty Tribes"; the name refers to the 40 clans united by the mythic Kyrgyz hero, MANAS
Government type
parliamentary republic
Capital
name: Bishkek
geographic coordinates: 42 52 N, 74 36 E
time difference: UTC+6 (11 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: founded in 1868 as a Russian settlement on the site of a previously destroyed fortress named "Pishpek"; the name was retained and overtime became "Bishkek"
Administrative divisions
7 provinces (oblustar, singular - oblus) and 2 cities* (shaarlar, singular - shaar); Batken Oblusu, Bishkek Shaary*, Chuy Oblusu (Bishkek), Jalal-Abad Oblusu, Naryn Oblusu, Osh Oblusu, Osh Shaary*, Talas Oblusu, Ysyk-Kol Oblusu (Karakol)
note: administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers (exceptions have the administrative center name following in parentheses)
Independence
31 August 1991 (from the Soviet Union)
National holiday
Independence Day, 31 August (1991)
Constitution
history: previous 1993, 2007, 2010; latest approved by referendum in April 2021 that transitioned Kyrgyzstan from a parliamentary to a presidential system, and implemented changes that allow the president to serve for two 5-year terms rather that one 6-year term, reduced the number of seats in Kyrgyzstan's legislature from 120 to 90, and established a Kurultay - a public advisory council
amendments: proposed as a draft law by the majority of the Supreme Council membership or by petition of 300,000 voters; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Council membership in each of at least three readings of the draft two months apart; the draft may be submitted to a referendum if approved by two thirds of the Council membership; adoption requires the signature of the president
Legal system
civil law system, which includes features of French civil law and Russian Federation laws
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Kyrgyzstan
dual citizenship recognized: yes, but only if a mutual treaty on dual citizenship is in force
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Sadyr JAPAROV (since 28 January 2021)
head of government: President Sadyr JAPAROV (since 28 January 2021)
cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 10 January 2021 (next to be held in 2027)
election results: 2021: Sadyr JAPAROV elected president in first round; percent of vote - Sadyr JAPAROV (Mekenchil) 79.2%, Adakhan MADUMAROV (United Kyrgyzstan) 6.8%, other 14%
2017: Sooronbay JEENBEKOV elected president; Sooronbay JEENBEKOV (Social Democratic Party of Kosovo) 54.7%, Omurbek BABANOV (independent) 33.8%, Adakhan MADUMAROV (United Kyrgyzstan) 6.6%, and other 4.9%
note: the President is both Chief of State and Head of Government.
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Supreme Council or Jogorku Kenesh (90 seats statutory, current 88; 54 seats allocated for proportional division among political party lists from the national vote and 36 seats allocated for candidates running in single-seat constituencies; members serve 5-year terms; parties must receive 5% of the vote to win seats in the Council)
elections: last held on 28 November 2021 (next to be held in 2026)
election results: percent of vote by party - AJK 19.1%, Ishenim 15%, Yntymak 12.1%, Alliance 9.2%, Butun Kyrgyzstan 7.8%, Yiman Nuru 6.8%, other 30%; seats by party - AJK 15, Ishenim 12, Yntymak 9, Alliance 7, Butun Kyrgyzstan 6, Yiman Nuru 5, other 36; composition - men 70, women 18, percent of women 20.5%
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of 25 judges); Constitutional Chamber of the Supreme Court (consists of the chairperson, deputy chairperson, and 9 judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court and Constitutional Court judges appointed by the Supreme Council on the recommendation of the president; Supreme Court judges serve for 10 years, Constitutional Court judges serve for 15 years; mandatory retirement at age 70 for judges of both courts
subordinate courts: Higher Court of Arbitration; oblast (provincial) and city courts
Political parties and leaders
Alliance [Mirlan JEENCHOROEV]
Ata-Jurt Kyrgyzstan (Homeland) or AJK [Aybek MATKERIMOV]
Butun Kyrgyzstan (All Kyrgyzstan) [Adakhan MADUMAROV]
Ishenim (Trust in Kyrgyz) [Rysbat AMATOV]
Mekenchil (Patriotic Party) [Sadyr JAPAROV]
Social Democratic Party of Kosovo or SDPK (dissolved in 2020)
Social Democrats or SDK [Temirlan SULTANBEKOV]
United Kyrgyzstan [Adakhan Kumsanbayevich MADUMAROV]
Yntymak (Unity) [Marlen MAMATALIEV]
Yyman Nuru (Light of Faith) [Nurjigit KADYRBEKOV]
International organization participation
ADB, CICA, CIS, CSTO, EAEC, EAEU, EAPC, EBRD, ECO, EITI (compliant country), FAO, GCTU, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM (observer), OIC, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, SCO, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Baktybek AMANBAYEV (since 7 July 2021)
chancery: 2360 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 449-9822
FAX: [1] (202) 449-8275
email address and website:
kgembassy.usa@mfa.gov.kg; kgconsulate.washington@mfa.gov.kg
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Sonata COULTER (since September 2021)
embassy: 171 Prospect Mira, Bishkek 720016
mailing address: 7040 Bishkek Place, Washington DC 20521-7040
telephone: [996] (312) 597-000
FAX: [996] (312) 597-744
email address and website:
ConsularBishkek@state.gov
https://kg.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
red field with a yellow sun in the center having 40 rays representing the 40 Kyrgyz tribes; on the obverse side the rays run counterclockwise, on the reverse, clockwise; in the center of the sun is a red ring crossed by two sets of three lines, a stylized representation of a "tunduk" - the crown of a traditional Kyrgyz yurt; red symbolizes bravery and valor, the sun evinces peace and wealth
National symbol(s)
white falcon; national colors: red, yellow
National anthem
name: "Kyrgyz Respublikasynyn Mamlekettik Gimni" (National Anthem of the Kyrgyz Republic)
lyrics/music: Djamil SADYKOV and Eshmambet KULUEV/Nasyr DAVLESOV and Kalyi MOLDOBASANOV
note: adopted 1992
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 3 (2 cultural, 1 natural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Sulaiman-Too Sacred Mountain (c); Silk Roads: the Chang'an-Tianshan Corridor (c); Western Tien Shan (n)
Economy
Economic overview
Kyrgyzstan is a landlocked, mountainous, lower middle income country with an economy dominated by minerals extraction, agriculture, and reliance on remittances from citizens working abroad. Cotton, wool, and meat are the main agricultural products, although only cotton is exported in any quantity. Other exports include gold, mercury, uranium, natural gas, and - in some years - electricity. The country has sought to attract foreign investment to expand its export base, including construction of hydroelectric dams, but a difficult investment climate and an ongoing legal battle with a Canadian firm over the joint ownership structure of the nation’s largest gold mine deter potential investors. Remittances from Kyrgyz migrant workers, predominantly in Russia and Kazakhstan, are equivalent to more than one-quarter of Kyrgyzstan’s GDP.
Following independence, Kyrgyzstan rapidly implemented market reforms, such as improving the regulatory system and instituting land reform. In 1998, Kyrgyzstan was the first Commonwealth of Independent States country to be accepted into the World Trade Organization. The government has privatized much of its ownership shares in public enterprises. Despite these reforms, the country suffered a severe drop in production in the early 1990s and has again faced slow growth in recent years as the global financial crisis and declining oil prices have dampened economies across Central Asia. The Kyrgyz government remains dependent on foreign donor support to finance its annual budget deficit of approximately 3 to 5% of GDP.
Kyrgyz leaders hope the country’s August 2015 accession to the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) will bolster trade and investment, but slowing economies in Russia and China and low commodity prices continue to hamper economic growth. Large-scale trade and investment pledged by Kyrgyz leaders has been slow to develop. Many Kyrgyz entrepreneurs and politicians complain that non-tariff measures imposed by other EAEU member states are hurting certain sectors of the Kyrgyz economy, such as meat and dairy production, in which they have comparative advantage. Since acceding to the EAEU, the Kyrgyz Republic has continued harmonizing its laws and regulations to meet EAEU standards, though many local entrepreneurs believe this process as disjointed and incomplete. Kyrgyzstan’s economic development continues to be hampered by corruption, lack of administrative transparency, lack of diversity in domestic industries, and difficulty attracting foreign aid and investment.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$31.02 billion (2020 est.)
$33.95 billion (2019 est.)
$32.46 billion (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
4.6% (2017 est.)
4.3% (2016 est.)
3.9% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$4,700 (2020 est.)
$5,300 (2019 est.)
$5,100 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$8.442 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
1.1% (2019 est.)
1.5% (2018 est.)
3.1% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Moody's rating: B2 (2015)
Standard & Poors rating: NR (2016)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 14.6% (2017 est.)
industry: 31.2% (2017 est.)
services: 54.2% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 85.4% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 18.9% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 33.2% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 1.8% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 39.7% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -79% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
milk, potatoes, sugar beet, maize, wheat, barley, tomatoes, watermelons, onions, carrots/turnips
Industries
small machinery, textiles, food processing, cement, shoes, lumber, refrigerators, furniture, electric motors, gold, rare earth metals
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 48%
industry: 12.5%
services: 39.5% (2005 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 8.5%
male: 7.6%
female: 10% (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
20.1% (2019 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
27.7 (2018 est.)
29 (2001)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 4.4%
highest 10%: 22.9% (2014 est.)
Budget
revenues: 2.169 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 2.409 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$306 million (2017 est.)
-$792 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$3.11 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$2.73 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$2.352 billion (2017 est.)
Exports - partners
United Kingdom 56%, Kazakhstan 13%, Russia 13%, Uzbekistan 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
gold, precious metals, various beans, refined petroleum, scrap copper (2019)
Imports
$5.67 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$5.86 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
$4.953 billion (2017 est.)
Imports - partners
China 53%, Russia 17%, Kazakhstan 7%, Uzbekistan 7%, Turkey 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, footwear, clothing and apparel, broadcasting equipment, walnuts (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$2.177 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$1.97 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$8.372 billion (2019 est.)
$8.066 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
soms (KGS) per US dollar -
68.35 (2017 est.)
69.914 (2016 est.)
69.914 (2015 est.)
64.462 (2014 est.)
53.654 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 4.626 million kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 12,324,140,000 kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 271 million kWh (2019 est.)
imports: 269 million kWh (2019 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 2.514 billion kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 8.5% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 91.5% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 2.287 million metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 1.717 million metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 984,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 481,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 971 million metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 700 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 32,100 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 1,400 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 8,200 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 40 million barrels (2021 est.)
Refined petroleum products - production
6,996 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102Natural gas
production: 25.542 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
consumption: 207.845 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
exports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
imports: 191.478 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
proven reserves: 5.663 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
7.88 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 2.967 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 4.505 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 408,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
35.059 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 299,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 5 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 8.511 million (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 130 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: the country’s telecom sector (specifically the mobile segment) has likewise been able to prosper; ongoing political tension, increasing repression of the media and information, and continuing problems with corporate governance may be putting a strain on further growth by reducing the country’s appeal to much-needed foreign investors; Kyrgyzstan has been reasonably successful in its attempts to liberalize its economy and open up its telecom market to competition; the mobile market has achieved high levels of penetration (140% in 2021) along with a fairly competitive operating environment with four major players; mobile broadband has come along strongly, reaching over 125% penetration in 2019 before falling back slightly during the Covid-19 crisis; slow-to-moderate growth is expected for both segments in coming years, supported by the anticipated rollout of 5G services starting from late 2022 (2022)
domestic: fixed-line penetration at nearly 5 per 100 persons remains low and concentrated in urban areas; mobile-cellular subscribership up to over 130 per 100 persons (2020)
international: country code - 996; connections with other CIS (Commonwealth of Independent States, 9 members post-Soviet Republics in EU) countries by landline or microwave radio relay and with other countries by leased connections with Moscow international gateway switch and by satellite; satellite earth stations - 2 (1 Intersputnik, 1 Intelsat) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Broadcast media
state-funded public TV broadcaster KTRK has nationwide coverage; also operates Ala-Too 24 news channel which broadcasts 24/7 and 4 other educational, cultural, and sports channels; ELTR and Channel 5 are state-owned stations with national reach; the switchover to digital TV in 2017 resulted in private TV station growth; approximately 20 stations are struggling to increase their own content up to 50% of airtime, as required by law, instead of rebroadcasting primarily programs from Russian channels or airing unlicensed movies and music; 3 Russian TV stations also broadcast; state-funded radio stations and about 10 significant private radio stations also exist (2019)
Internet users
total: 3,683,700 (July 2022 est.)
percent of population: 55% (July 2022 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 289,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 5 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 17
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 709,198 (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 18
over 3,047 m: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 3
1,524 to 2,437 m: 11
under 914 m: 3 (2021)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 10
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 1
under 914 m: 8 (2021)
Pipelines
4,195 km gas (2022), 16 km oil (2022) (2022)
Railways
total: 424 km (2022)
broad gauge: 424 km (2018) 1.520-m gauge
Ports and terminals
lake port(s): Balykchy (Ysyk-Kol or Rybach'ye)(Lake Ysyk-Kol)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Armed Forces of the Kyrgyz Republic: Land Forces, Air Defense Forces, National Guard; Internal Troops; State Committee for National Security (GKNB): Border Service (2022)
Military expenditures
1.7% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.8% of GDP (2020 est.)
2.3% of GDP (2019 est.) (approximately $410 million)
2.3% of GDP (2018 est.) (approximately $400 million)
2.3% of GDP (2017 est.) (approximately $390 million)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 12,000 active duty troops (8,500 Land Forces; 2,500 Air Force/Air Defense; 1,000 National Guard) (2022)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Kyrgyz military inventory is comprised of mostly older Russian and Soviet-era equipment; Kyrgyzstan relies on donations of military equipment, which come mostly from Russia under a 2013 agreement between Bishkek and Moscow (2022)
Military service age and obligation
18-27 years of age for compulsory or voluntary male military service in the Armed Forces or Interior Ministry; 12-month service obligation (9 months for university graduates), with optional fee-based 3-year service in the call-up mobilization reserve; women may volunteer at age 19; 16-17 years of age for military cadets, who cannot take part in military operations (2022)
Military - note
Kyrgyzstan has been a member of the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) since 1994 and contributes troops to CSTO's rapid reaction force (2022)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Kyrgyzstan-China: a 2009 treaty settled a border dispute, with Kyrgyzstan receiving the Khan Tengri Peak and Kyrgyzstan ceding to China the Uzengi-Kush area
Kyrgyzstan-Kazakhstan: in January 2019, Kyrgyzstan ratified the 2017 agreement on the demarcation of the Kyrgyzstan-Kazakhstan border
Kyrgyzstan-Tajikistan: as the last major Central Asian boundary dispute with lengthy undelimited sections, the lowland (NE part) of the Kyrgz-Tajik line seems intractable despite recent Kyrgyz-Uzbek compromises and agreements on delimitation and demarcation
Kyrgyzstan-Uzbekistan: delimitation of approximately 15% or 200 km of border with Uzbekistan is hampered by serious disputes over enclaves and other areas; Kyrgyz and Uzbek officials signed an agreement in March 2021 on the final delimitation and demarcation of the Kyrgyzstan-Uzbekistan border; the accord included several land swaps that gave Kyrgyzstan more territory but was offset by Uzbekistan retaining use of reservoirs on Kyrgyz land; although a Kyrgyz official returned from the March 2021 meetings and said the decades-old border dispute was 100% resolved, his talks with residents in some affected areas showed that agreement had not been reached on all border segments
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 16 (mid-year 2021)
Illicit drugs
a prime transshipment location; illegal drugs move from Afghanistan to Russia, and sometimes into Europe