Introduction
Background
The island was uninhabited when first settled by the British in 1627. African slaves worked the sugar plantations established on the island, which initially dominated the Caribbean sugar industry. By 1720, Barbados was no longer a dominant force within the sugar industry, having been surpassed by the Leeward Islands and Jamaica. Slavery was abolished in 1834. The Barbadian economy remained heavily dependent on sugar, rum, and molasses production through most of the 20th century. The gradual introduction of social and political reforms in the 1940s and 1950s led to complete independence from the UK in 1966. In the 1990s, tourism and manufacturing surpassed the sugar industry in economic importance. Barbados became a republic on 30 November 2021, with the former Governor-General Sandra MASON elected as the first president. Barbados plans to create a new constitution in 2022.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
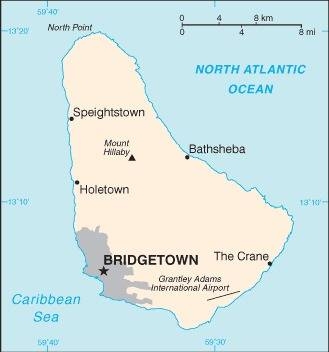
Caribbean, island in the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Venezuela
Geographic coordinates
13 10 N, 59 32 W
Map references
Central America and the Caribbean
Area - comparative
2.5 times the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
97 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; rainy season (June to October)
Terrain
relatively flat; rises gently to central highland region
Elevation
highest point: Mount Hillaby 336 m
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
Natural resources
petroleum, fish, natural gas
Land use
agricultural land: 32.6% (2018 est.)
arable land: 25.6% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 2.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 4.7% (2018 est.)
forest: 19.4% (2018 est.)
other: 48% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
50 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
most densely populated country in the eastern Caribbean; approximately one-third live in urban areas
Natural hazards
infrequent hurricanes; periodic landslides
Geography - note
easternmost Caribbean island
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Barbadian(s) or Bajan (colloquial)
adjective: Barbadian or Bajan (colloquial)
Ethnic groups
African descent 92.4%, mixed 3.1%, White 2.7%, East Indian 1.3%, other 0.2%, unspecified 0.3% (2010 est.)
Languages
English (official), Bajan (English-based creole language, widely spoken in informal settings)
Religions
Protestant 66.4% (includes Anglican 23.9%, other Pentecostal 19.5%, Adventist 5.9%, Methodist 4.2%, Wesleyan 3.4%, Nazarene 3.2%, Church of God 2.4%, Baptist 1.8%, Moravian 1.2%, other Protestant 0.9%), Roman Catholic 3.8%, other Christian 5.4% (includes Jehovah's Witness 2.0%, other 3.4%), Rastafarian 1%, other 1.5%, none 20.6%, unspecified 1.2% (2010 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 17.49% (male 25,762/female 25,764)
15-24 years: 12.34% (male 18,024/female 18,330)
25-54 years: 42.69% (male 62,655/female 63,093)
55-64 years: 13.91% (male 19,533/female 21,430)
65 years and over: 13.57% (male 16,398/female 23,571) (2020 est.)

Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 49
youth dependency ratio: 25.6
elderly dependency ratio: 23.4
potential support ratio: 4.3 (2021 est.)
Median age
total: 39.5 years
male: 38.4 years
female: 40.7 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
most densely populated country in the eastern Caribbean; approximately one-third live in urban areas
Urbanization
urban population: 31.4% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.46% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
89,000 BRIDGETOWN (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.01 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.92 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.55 male(s)/female
total population: 0.93 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
27 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115Infant mortality rate
total: 10 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 11.58 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 8.41 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 78.55 years
male: 75.79 years
female: 81.35 years (2022 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
59.2% (2012)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 98.8% of population
unimproved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 2% of population (2020 est.)
Current health expenditure
6.3% of GDP (2019)
Physicians density
2.49 physicians/1,000 population (2017)
Hospital bed density
6 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 9.94 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 3.66 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 1.36 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 4.75 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.17 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 8.5% (2020 est.)
male: 15% (2020 est.)
female: 1.9% (2020 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.6%
male: 99.6%
female: 99.6% (2014)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 26%
male: 30.3%
female: 21.2% (2019 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
pollution of coastal waters from waste disposal by ships; soil erosion; illegal solid waste disposal threatens contamination of aquifers
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 22.24 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 1.28 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 2.35 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; rainy season (June to October)
Land use
agricultural land: 32.6% (2018 est.)
arable land: 25.6% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 2.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 4.7% (2018 est.)
forest: 19.4% (2018 est.)
other: 48% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 31.4% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.46% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.01% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 174,815 tons (2011 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 15,733 tons (2015 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 9% (2015 est.)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 20 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 6.2 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 54.8 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
80 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Barbados
etymology: the name derives from the Portuguese "as barbadas," which means "the bearded ones" and can refer either to the long, hanging roots of the island's bearded fig trees or to the alleged beards of the native Carib inhabitants
Government type
parliamentary republic; a Commonwealth realm
Capital
name: Bridgetown
geographic coordinates: 13 06 N, 59 37 W
time difference: UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: named after a bridge constructed over the swampy area (known as the Careenage) around the Constitution River that flows through the center of Bridgetown
Administrative divisions
11 parishes and 1 city*; Bridgetown*, Christ Church, Saint Andrew, Saint George, Saint James, Saint John, Saint Joseph, Saint Lucy, Saint Michael, Saint Peter, Saint Philip, Saint Thomas
Independence
30 November 1966 (from the UK)
National holiday
Independence Day, 30 November (1966)
Constitution
history: adopted 22 November 1966, effective 30 November 1966; Constitution (Amendment) (No. 2) Bill, 2021 establishes Barbados as a republic and revokes the earlier Order in Council
amendments: proposed by Parliament; passage of amendments to constitutional sections such as citizenship, fundamental rights and freedoms, and the organization and authorities of the branches of government requires two-thirds majority vote by the membership of both houses of Parliament; passage of other amendments only requires a majority vote of both houses; amended several times, last in 2021
note: following the transition to a republic in November 2021, the Government of Barbados in February 2022 began the process of establishing a constitution commission to review a new draft constitution
Legal system
English common law; no judicial review of legislative acts
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Sandra MASON (since 30 November 2021)
head of government: Prime Minister Mia MOTTLEY (since 25 May 2018)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president on the advice of the prime minister
elections/appointments: the president is elected by an electoral college of both Houses of Parliament for a four year renewable term; election last held 20 October 2021; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or leader of the majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the president; the prime minister recommends the deputy prime minister
election results: Sandra MASON elected as first president on 20 October 2021
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliament consists of:
Senate (21 seats - 18 for current term; members appointed by the president - 12 on the advice of the prime minister, 2 on the advice of the opposition leader, and 7 at the discretion of the president)
House of Assembly (30 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 5-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last appointments on 4 February 2022 (next appointments in February 2027)
House of Assembly - last held on 19 January 2022 (next to be held in January 2027)
election results:
Senate - appointed; composition as of March 2022- men 10, women 8, percent of women 44.4%
House of Assembly - percent of vote by party - BLP 69%, DLP 26.5%, other 4.5%; seats by party - BLP 30; composition as of March 2022 - men 22, women 8, percent of women 26.7%; note - total Parliament percent of women 33.3%
note: tradition dictates that the election is held within 5 years of the last election, but constitutionally it is 5 years from the first seating of Parliament plus a 90-day grace period
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the High Court with 8 justices) and the Court of Appeal (consists of the High Court chief justice and president of the court and 4 justices; note - in 2005, Barbados acceded to the Caribbean Court of Justice as the final court of appeal, replacing that of the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister and opposition leader of Parliament; other justices appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial and Legal Service Commission, a 5-member independent body consisting of the Supreme Court chief justice, the commission head, and presidential appointees recommended by the prime minister; justices serve until mandatory retirement at age 65
subordinate courts: Magistrates' Courts
Political parties and leaders
Alliance Party for Progress or APP [Joseph ATHERLEY]
Barbados Labor Party or BLP [Mia MOTTLEY]
Democratic Labor Party or DLP [Ronnie YEARWOOD]
International organization participation
ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Noel Anderson LYNCH (since 11 January 2019)
chancery: 2144 Wyoming Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 939-9200
FAX: [1] (202) 332-7467
email address and website:
washington@foreign.gov.bb
consulate(s) general: Miami, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Linda S. TAGLIALATELA (since 1 February 2016) note - also accredited to Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica, Grenada, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
embassy: Wildey Business Park, St. Michael BB 14006, Barbados, W.I.
mailing address: 3120 Bridgetown Place, Washington DC 20521-3120
telephone: (246) 227-4000
FAX: (246) 431-0179
email address and website:
BridgetownACS@state.gov
https://bb.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal vertical bands of ultramarine blue (hoist side), gold, and ultramarine blue with the head of a black trident centered on the gold band; the band colors represent the blue of the sea and sky and the gold of the beaches; the trident head represents independence and a break with the past (the colonial coat of arms contained a complete trident)
National symbol(s)
Neptune's trident, pelican, Red Bird of Paradise flower (also known as Pride of Barbados); national colors: blue, yellow, black
National anthem
name: "The National Anthem of Barbados"
lyrics/music: Irving BURGIE/C. Van Roland EDWARDS
note: adopted 1966; the anthem is also known as "In Plenty and In Time of Need"
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 1 (cultural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Historic Bridgetown and its Garrison
Economy
Economic overview
Barbados is the wealthiest and one of the most developed countries in the Eastern Caribbean and enjoys one of the highest per capita incomes in the region. Historically, the Barbadian economy was dependent on sugarcane cultivation and related activities. However, in recent years the economy has diversified into light industry and tourism. Offshore finance and information services are important foreign exchange earners, boosted by being in the same time zone as eastern US financial centers and by a relatively highly educated workforce. Following the 2008-09 recession, external vulnerabilities such as fluctuations in international oil prices have hurt economic growth, raised Barbados' already high public debt to GDP ratio - which stood at 105% of GDP in 2016 - and cut into its international reserves.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$3.7 billion (2020 est.)
$4.49 billion (2019 est.)
$4.49 billion (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
-0.2% (2017 est.)
2.3% (2016 est.)
2.2% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$12,900 (2020 est.)
$15,600 (2019 est.)
$15,700 (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$4.99 billion (2017 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
4.4% (2017 est.)
1.5% (2016 est.)
Credit ratings
Moody's rating: Caa1 (2019)
Standard & Poors rating: B- (2019)
note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 1.5% (2017 est.)
industry: 9.8% (2017 est.)
services: 88.7% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 84.2% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 13.4% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 17.6% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.2% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 31.6% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -47% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
sugar cane, poultry, vegetables, milk, eggs, pork, coconuts, pulses, sweet potatoes, tropical fruit
Industries
tourism, sugar, light manufacturing, component assembly for export
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 10%
industry: 15%
services: 75% (1996 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 26%
male: 30.3%
female: 21.2% (2019 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 1.466 billion (2017 est.) (2013 est.)
expenditures: 1.664 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
1 April - 31 March
Current account balance
-$189 million (2017 est.)
-$206 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$485.4 million (2017 est.)
$516.9 million (2016 est.)
note: Data are in current year dollars and do not include illicit exports or re-exports.
Exports - partners
US 21%, Poland 14%, Jamaica 8%, Guyana 6%,Trinidad and Tobago 6% (2019)
Exports - commodities
rums and other hard liquor, ships, orthopedic appliances, cement, packaged medicines (2019)
Imports - partners
United States 35%, Trinidad and Tobago 14%, China 9%, Netherlands 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, ships, cars, shipping containers, packaged medicines (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$264.5 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$341.8 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$4.49 billion (2010 est.)
$668 million (2003 est.)
Exchange rates
Barbadian dollars (BBD) per US dollar -
2 (2017 est.)
2 (2016 est.)
2 (2015 est.)
2 (2014 est.)
2 (2013 est.)
note: the Barbadian dollar is pegged to the US dollar
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 311,000 kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 1 billion kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 0 kWh (2019 est.)
imports: 0 kWh (2019 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 20 million kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 95.9% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 4.1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 1,000 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 10,800 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 700 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 2 million barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
production: 14.923 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
consumption: 20.954 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
exports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
imports: 6.031 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
proven reserves: 113 million cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
1.703 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 1.662 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 41,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
83.723 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 128,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 45 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 295,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 103 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: the telecom sector has seen a decline in subscriber numbers (particularly for prepaid mobile services the mainstay of short term visitors) and revenue; fixed and mobile broadband services are two areas that have benefited from the crisis as employees and students have resorted to working from home; one area of the telecom market that is not prepared for growth is 5G mobile; governments, regulators, and even the mobile network operators have shown that they have not been investing in 5G opportunities at the present time; network expansion and enhancements remain concentrated around improving LTE coverage (2021)
domestic: fixed-line teledensity of roughly 45 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular telephone density about 103 per 100 persons (2020)
international: country code - 1-246; landing points for the ECFS and Southern Caribbean Fiber submarine cable with links to 15 other islands in the eastern Caribbean extending from the British Virgin Islands to Trinidad and Puerto Ricco; satellite earth stations - 1 (Intelsat - Atlantic Ocean); tropospheric scatter to Trinidad and Saint Lucia (2019)
Broadcast media
government-owned Caribbean Broadcasting Corporation (CBC) operates the lone terrestrial TV station; CBC also operates a multi-channel cable TV subscription service; roughly a dozen radio stations, consisting of a CBC-operated network operating alongside privately owned radio stations (2019)
Internet users
total: 235,357 (2019 est.)
percent of population: 82% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 128,000 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 45 (2020 est.)
Transportation
Airports - with paved runways
total: 1
over 3,047 m: 1 (2021)
Pipelines
33 km gas, 64 km oil, 6 km refined products (2013)
Merchant marine
total: 165
by type: bulk carrier 46, general cargo 103, other 16 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Bridgetown
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Barbados Defense Force: The Barbados Regiment, The Barbados Coast Guard (2022)
Military expenditures
0.8% of GDP (2022 est.)
0.9% of GDP (2021 est.)
0.9% of GDP (2020 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2019 est.) (approximately $35 million)
0.8% of GDP (2018 est.) (approximately $40 million)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 600 active personnel (2022)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Netherlands provide the BDF's major equipment inventory (maritime patrol boats) (2022)
Military service age and obligation
voluntary service only (men and women); 17 years, 9 months to 17 years, 11 months with letter of consent from a parent or guardian, or be in the age range of 18-25 years at the start of recruit training; citizens of Barbados by descent or naturalization (2022)
Military - note
Barbados has been a member of the Caribbean Regional Security System (RSS) since its creation in 1982; RSS signatories (Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica, Grenada, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines) agreed to prepare contingency plans and assist one another, on request, in national emergencies, prevention of smuggling, search and rescue, immigration control, fishery protection, customs and excise control, maritime policing duties, protection of off-shore installations, pollution control, national and other disasters, and threats to national security; the RSS is headquartered in Barbados (2022)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Barbados-Venezuela (Maritime Boundary): Barbados joins other Caribbean states and the United Kingdom to counter Venezuela's claim that Aves Island, a large sandbar with some vegetation, sustains human habitation or economic life, the criteria under the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), Article 121, which would permit Venezuela to extend its EEZ/continental shelf over a large portion of the eastern Caribbean Sea. The dispute hampers hydrocarbon prospecting and creation of exploration blocks.
Barbados-Trinidad and Tobago (Maritime Boundary): Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago abide by the April 2006 Permanent Court of Arbitration decision delimiting a maritime boundary and limiting catches of flying fish in Trinidad and Tobago's exclusive economic zone.
Illicit drugs
a transit point for cocaine and marijuana destined for North America, Europe, and elsewhere in the Caribbean