Faroe Islands
Introduction
Background
The population of the Faroe Islands, a self-governing dependency of Denmark, is largely descended from Viking settlers who arrived in the 9th century. The islands have been connected politically to Denmark since the 14th century. The Home Rule Act of 1948 granted a high degree of self-government to the Faroese, who have autonomy over most internal affairs and external trade, while Denmark is responsible for justice, defense, and some foreign affairs. The Faroe Islands are not part of the European Union.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
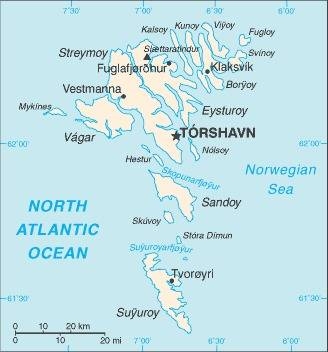
Northern Europe, island group between the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, about halfway between Iceland and Norway
Geographic coordinates
62 00 N, 7 00 W
Map references
Europe
Area
total: 1,393 sq km
land: 1,393 sq km
water: 0 sq km (some lakes and streams)
Area - comparative
eight times the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
1,117 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or agreed boundaries or median line
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm or agreed boundaries or median line
Climate
mild winters, cool summers; usually overcast; foggy, windy
Terrain
rugged, rocky, some low peaks; cliffs along most of coast
Elevation
highest point: Slaettaratindur 882 m
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
Natural resources
fish, whales, hydropower, possible oil and gas
Land use
agricultural land: 2.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0% (2018 est.)
forest: 0.1% (2018 est.)
other: 97.8% (2018 est.)
Population distribution
the island of Streymoy is by far the most populous with over 40% of the population; it has approximately twice as many inhabitants as Eysturoy, the second most populous island; seven of the inhabited islands have fewer than 100 people
Natural hazards
strong winds and heavy rains can occur throughout the year
Geography - note
archipelago of 17 inhabited islands and one uninhabited island, and a few uninhabited islets; strategically located along important sea lanes in northeastern Atlantic; precipitous terrain limits habitation to small coastal lowlands
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Faroese (singular and plural)
adjective: Faroese
Ethnic groups
Faroese 85.3% (Scandinavian and Anglo-Saxon descent), Danish 8.3%, other Nordic 1.4%, other 4.5% (includes Filipino, Poland, Romanian) (2022 est.)
note: data represent respondents by country of birth
Languages
Faroese 93.8% (derived from Old Norse), Danish 3.2%, other 3% (2011 est.)
note: data represent population by primary language
Religions
Christian 89.3% (predominantly Evangelical Lutheran), other 1%, none 3.8%, unspecified 6% (2011 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 19.69% (male 5,247/female 4,920)
15-24 years: 13.89% (male 3,708/female 3,465)
25-54 years: 37.01% (male 10,277/female 8,828)
55-64 years: 12% (male 3,199/female 2,996)
65 years and over: 17.41% (male 4,352/female 4,636) (2020 est.)

Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 62.8
youth dependency ratio: 33.6
elderly dependency ratio: 29.1
potential support ratio: 3.4 (2021)
Median age
total: 37.2 years
male: 36.9 years
female: 37.7 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
the island of Streymoy is by far the most populous with over 40% of the population; it has approximately twice as many inhabitants as Eysturoy, the second most populous island; seven of the inhabited islands have fewer than 100 people
Urbanization
urban population: 43% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.89% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
21,000 TORSHAVN (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.09 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.17 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.09 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/female
total population: 1.08 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Infant mortality rate
total: 5.99 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 6.61 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 5.32 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 81.26 years
male: 78.73 years
female: 83.97 years (2022 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: 0% of population (2020)
Physicians density
2.62 physicians/1,000 population (2016)
Hospital bed density
4.2 beds/1,000 population (2016)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: NA
unimproved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: NA
Literacy
total population: NA
male: NA
female: NA
Environment
Environment - current issues
coastal erosion, landslides and rockfalls, flash flooding, wind storms; oil spills
Air pollutants
carbon dioxide emissions: 0.63 megatons (2016 est.)
Climate
mild winters, cool summers; usually overcast; foggy, windy
Land use
agricultural land: 2.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0% (2018 est.)
forest: 0.1% (2018 est.)
other: 97.8% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 43% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.89% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0% of GDP (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 61,000 tons (2014 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 40,870 tons (2012 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 67% (2012 est.)
Total renewable water resources
0 cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Faroe Islands
local long form: none
local short form: Foroyar
etymology: the archipelago's name may derive from the Old Norse word "faer," meaning sheep
Government type
parliamentary democracy (Faroese Parliament); part of the Kingdom of Denmark
Dependency status
part of the Kingdom of Denmark; self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark since 1948
Capital
name: Torshavn
geographic coordinates: 62 00 N, 6 46 W
time difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: the meaning in Danish is "Thor's harbor"
Administrative divisions
part of the Kingdom of Denmark; self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark; there are 29 first-order municipalities (kommunur, singular - kommuna) Eidhi, Eystur, Famjin, Fuglafjordhur, Fugloy, Hov, Husavik, Hvalba, Hvannasund, Klaksvik, Kunoy, Kvivik, Nes, Porkeri, Runavik, Sandur, Sjovar, Skalavik, Skopun, Skuvoy, Sorvagur, Sumba, Sunda, Torshavn, Tvoroyri, Vagar, Vagur, Vestmanna, Vidhareidhi
Independence
none (part of the Kingdom of Denmark; self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark)
National holiday
Olaifest (Olavsoka) (commemorates the death in battle of King OLAF II of Norway, later St. OLAF), 29 July (1030)
Constitution
history: 5 June 1953 (Danish Constitution), 23 March 1948 (Home Rule Act), and 24 June 2005 (Takeover Act) serve as the Faroe Islands' constitutional position in the Unity of the Realm
amendments: see entry for Denmark
Legal system
the laws of Denmark apply where applicable
Citizenship
see Denmark
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: Queen MARGRETHE II of Denmark (since 14 January 1972), represented by High Commissioner Lene Moyell JOHANSEN, chief administrative officer (since 15 May 2017)
head of government: Prime Minister Bardur A STEIG NIELSEN (since 16 September 2019)
cabinet: Landsstyri appointed by the prime minister
elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; high commissioner appointed by the monarch; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually elected prime minister by the Faroese Parliament; election last held on 31 August 2019 (next to be held in 2023)
election results: 2019: Bardur A STEIGNIELSEN elected prime minister; Parliament vote - NA
2015: Aksel V. JOHANNESEN elected prime minister; Parliament vote - NA
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Faroese Parliament or Logting (33 seats; members directly elected in a single nationwide constituency by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)
the Faroe Islands elect 2 members to the Danish Parliament to serve 4-year terms
elections: Faroese Parliament - last held on 8 December 2022 (next to be held in 2023)
Faroese seats in the Danish Parliament last held on 5 June 2019 (next to be held no later than June 2023)
election results: Faroese Parliament percent of vote by party - JF 27.3%, B 21.2%, A 18.2%, E 18.2%, F 9.1%, H 6.0%, seats by party - JF 9, B 7, A 6, E 6, F 3, H 2; composition - men 27, women 6; percent of women 18.2%
Faroese seats in Danish Parliament - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - JF 1, B 1; composition - men 2
2019: Faroese Parliament percent of vote by party - People's Party 24.2%, JF 21.2%, Union Party 21.2%, Republic 18.2%, Center Party 6%, Progress Party 6%, Self-Government Party 3%, seats by party - People's Party 8, JF 7, Union Party 7, Republic 6, Center Party 2, Progress Party 2, Self-Government Party 1, composition - men 25, women 8; percent of women 24.2%
Faroese seats in Danish Parliament - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - JF 1, Republic 1; composition - men 2
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Faroese Court or Raett (Rett - Danish) decides both civil and criminal cases; the Court is part of the Danish legal system
subordinate courts: Court of the First Instance or Tribunal de Premiere Instance; Court of Administrative Law or Tribunal Administratif; Mixed Commercial Court; Land Court
Political parties and leaders
Center Party or H (Midflokkurin) [Jenis av RANA]
People's Party or A (Folkaflokkurin) [Benir JOHANNESEN]
Progress Party or F (Framsokn) [Ruth VANG]
Republic or E (Tjodveldi) [Hogni HOYDAL] (formerly the Republican Party)
Self-Government Party or D (Sjalvstyri or Sjalvstyrisflokkurin) [Jogvan SKORHEIM]
Social Democratic Party or JF (Javnadarflokkurin) or JF [Aksel V. JOHANNESEN]
Union Party or B (Sambandsflokkurin) [Bardur A STEIG NIELSEN]
International organization participation
Arctic Council, IMO (associate), NC, NIB, UNESCO (associate), UPU
Diplomatic representation in the US
none (self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark)
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: none (self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark)
Flag description
white with a red cross outlined in blue extending to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted toward the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog (Danish flag); referred to as Merkid, meaning "the banner" or "the mark," the flag resembles those of neighboring Iceland and Norway, and uses the same three colors - but in a different sequence; white represents the clear Faroese sky, as well as the foam of the waves; red and blue are traditional Faroese colors
note: the blue on the flag is a lighter blue (azure) than that found on the flags of Iceland or Norway
National symbol(s)
ram; national colors: red, white, blue
National anthem
name: "Mitt alfagra land" (My Fairest Land)
lyrics/music: Simun av SKAROI/Peter ALBERG
note: adopted 1948; the anthem is also known as "Tu alfagra land mitt" (Thou Fairest Land of Mine); as a self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark, the Faroe Islands are permitted their own national anthem
Economy
Economic overview
The Faroese economy has experienced a period of significant growth since 2011, due to higher fish prices and increased salmon farming and catches in the pelagic fisheries. Fishing has been the main source of income for the Faroe Islands since the late 19th century, but dependence on fishing makes the economy vulnerable to price fluctuations. Nominal GDP, measured in current prices, grew 5.6% in 2015 and 6.8% in 2016. GDP growth was forecast at 6.2% in 2017, slowing to 0.5% in 2018, due to lower fisheries quotas, higher oil prices and fewer farmed salmon combined with lower salmon prices. The fisheries sector accounts for about 97% of exports, and half of GDP. Unemployment is low, estimated at 2.1% in early 2018. Aided by an annual subsidy from Denmark, which amounts to about 11% of Faroese GDP , Faroese have a standard of living equal to that of Denmark. The Faroe Islands have bilateral free trade agreements with the EU, Iceland, Norway, Switzerland, and Turkey.
For the first time in 8 years, the Faroe Islands managed to generate a public budget surplus in 2016, a trend which continued in 2017. The local government intends to use this to reduce public debt, which reached 38% of GDP in 2015. A fiscal sustainability analysis of the Faroese economy shows that a long-term tightening of fiscal policy of 5% of GDP is required for fiscal sustainability.
Increasing public infrastructure investments are likely to lead to continued growth in the short term, and the Faroese economy is becoming somewhat more diversified. Growing industries include financial services, petroleum-related businesses, shipping, maritime manufacturing services, civil aviation, IT, telecommunications, and tourism.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$2.001 billion (2014 est.)
$1.89 billion (2013 est.)
$1.608 billion (2012 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
5.9% (2017 est.)
7.5% (2016 est.)
2.4% (2015 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$2.765 billion (2014 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 18% (2013 est.)
industry: 39% (2013 est.)
services: 43% (2013 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 52% (2013)
government consumption: 29.6% (2013)
investment in fixed capital: 18.4% (2013)
Agricultural products
potatoes, mutton, sheep skins, sheep offals, beef, sheep fat, cattle offals, cattle hides, cattle fat
Industries
fishing, fish processing, tourism, small ship repair and refurbishment, handicrafts
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 15%
industry: 15%
services: 70% (December 2016 est.)
Population below poverty line
10% (2015 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
22.7 (2013 est.)
21.6 (2011 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 835.6 million (2014 est.)
expenditures: 883.8 million (2014)
note: Denmark supplies the Faroe Islands with almost one-third of its public funds
Fiscal year
calendar year
Exports - partners
Russia 26.4%, UK 14.1%, Germany 8.4%, China 7.9%, Spain 6.8%, Denmark 6.2%, US 4.7%, Poland 4.4%, Norway 4.1% (2017)
Exports - commodities
fish and fish products (97%) (2017 est.)
Imports - partners
Denmark 33%, China 10.7%, Germany 7.6%, Poland 6.8%, Norway 6.7%, Ireland 5%, Chile 4.3% (2017)
Imports - commodities
goods for household consumption, machinery and transport equipment, fuels, raw materials and semi-manufactures, cars
Exchange rates
Danish kroner (DKK) per US dollar -
6.586 (2017 est.)
6.7269 (2016 est.)
6.7269 (2015 est.)
6.7236 (2014 est.)
5.6125 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 128,000 kW (2020 est.)
consumption: 358.64 million kWh (2019 est.)
exports: 0 kWh (2020 est.)
imports: 0 kWh (2020 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 23.16 million kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 58.9% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
nuclear: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
solar: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
wind: 15.1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
hydroelectricity: 26% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
tide and wave: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
geothermal: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
biomass and waste: 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Coal
production: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
consumption: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
exports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
imports: 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
proven reserves: 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 0 bbl/day (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 5,500 bbl/day (2019 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate exports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil and lease condensate imports: 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 0 barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
production: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
consumption: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
exports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
imports: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
proven reserves: 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
870,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 870,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 15,341 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 31 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 59,213 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 121 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: the Faroe Islands have a highly developed communication network, which covers the whole country; from telecommunication and mobile phones to the internet and media, the Faroe Islands are at the forefront of modern communications technology; working within the special geographic circumstances of the Faroe Islands; companies have become world experts in providing digital communication solutions to remote and sparsely populated areas (2022)
domestic: roughly 31 per 100 teledensity for fixed-line and nearly 121 per 100 for mobile-cellular; both NMT (analog) and GSM (digital) mobile telephone systems are installed (2020)
international: country code - 298; landing points for the SHEFA-2, FARICE-1, and CANTAT-3 fiber-optic submarine cables from the Faroe Islands, to Denmark, Germany, UK and Iceland; satellite earth stations - 1 Orion; (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Broadcast media
1 publicly owned TV station; the Faroese telecommunications company distributes local and international channels through its digital terrestrial network; publicly owned radio station supplemented by 3 privately owned stations broadcasting over multiple frequencies
Internet users
total: 47,703 (2019 est.)
percent of population: 98% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 18,443 (2020 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 38 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020) (registered in Denmark)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 3 (registered in Denmark)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2021)
Roadways
total: 960 km (2017)
paved: 500 km (2017)
unpaved: 460 km (2017)
note: those islands not connected by roads (bridges or tunnels) are connected by seven different ferry links operated by the nationally owned company SSL; 28 km of tunnels
Merchant marine
total: 101
by type: container ships 6, general cargo 48, oil tanker 1, other 46 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Fuglafjordur, Torshavn, Vagur
Military and Security
Military and security forces
no regular military forces or conscription
Military - note
the Government of Denmark has responsibility for defense; as such, the Danish military’s Joint Arctic Command in Nuuk, Greenland is responsible for territorial defense of the Faroe Islands; the Joint Arctic Command has a contact element in the capital of Torshavn
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
because anticipated offshore hydrocarbon resources have not been realized, earlier Faroese proposals for full independence have been deferred; Iceland, the UK, and Ireland dispute Denmark's claim to UNCLOS that the Faroe Islands' continental shelf extends beyond 200 nm