Introduction
Background
The Kingdom of Yemen (colloquially known as North Yemen) became independent from the Ottoman Empire in 1918 and in 1962 became the Yemen Arab Republic. The British, who had set up a protectorate area around the southern port of Aden in the 19th century, withdrew in 1967 from what became the People's Republic of Southern Yemen (colloquially known as South Yemen). Three years later, the southern government adopted a Marxist orientation and changed the country's name to the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen. The massive exodus of hundreds of thousands of Yemenis from the south to the north contributed to two decades of hostility between the states. The two countries were formally unified as the Republic of Yemen in 1990. A southern secessionist movement and brief civil war in 1994 was quickly subdued. In 2000, Saudi Arabia and Yemen agreed to delineate their border.
Fighting in the northwest between the government and the Huthis, a Zaydi Shia Muslim minority, continued intermittently from 2004 to 2010, and then again from 2014-present. The southern secessionist movement was revitalized in 2007.
Public rallies in Sana'a against then President Ali Abdallah SALIH - inspired by similar demonstrations in Tunisia and Egypt - slowly built momentum starting in late January 2011 fueled by complaints over high unemployment, poor economic conditions, and corruption. By the following month, some protests had resulted in violence, and the demonstrations had spread to other major cities. By March the opposition had hardened its demands and was unifying behind calls for SALIH's immediate ouster. In April 2011, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), in an attempt to mediate the crisis in Yemen, proposed the GCC Initiative, an agreement in which the president would step down in exchange for immunity from prosecution. SALIH's refusal to sign an agreement led to further violence. The UN Security Council passed Resolution 2014 in October 2011 calling for an end to the violence and completing a power transfer deal. In November 2011, SALIH signed the GCC Initiative to step down and to transfer some of his powers to Vice President Abd Rabuh Mansur HADI. Following HADI's uncontested election victory in February 2012, SALIH formally transferred all presidential powers. In accordance with the GCC Initiative, Yemen launched a National Dialogue Conference (NDC) in March 2013 to discuss key constitutional, political, and social issues. HADI concluded the NDC in January 2014 and planned to begin implementing subsequent steps in the transition process, including constitutional drafting, a constitutional referendum, and national elections.
The Huthis, perceiving their grievances were not addressed in the NDC, joined forces with SALIH and expanded their influence in northwestern Yemen, which culminated in a major offensive against military units and rival tribes and enabled their forces to overrun the capital, Sanaa, in September 2014. In January 2015, the Huthis surrounded the presidential palace, HADI's residence, and key government facilities, prompting HADI and the cabinet to submit their resignations. HADI fled to Aden in February 2015 and rescinded his resignation. He subsequently escaped to Oman and then moved to Saudi Arabia and asked the GCC to intervene militarily in Yemen to protect the legitimate government from the Huthis. In March, Saudi Arabia assembled a coalition of Arab militaries and began airstrikes against the Huthis and Huthi-affiliated forces. Ground fighting between Huthi-aligned forces and anti-Huthi groups backed by the Saudi-led coalition continued through 2016. In 2016, the UN brokered a months-long cessation of hostilities that reduced airstrikes and fighting, and initiated peace talks in Kuwait. However, the talks ended without agreement. The Huthis and SALIH’s political party announced a Supreme Political Council in August 2016 and a National Salvation Government, including a prime minister and several dozen cabinet members, in November 2016, to govern in Sanaa and further challenge the legitimacy of HADI’s government. However, amid rising tensions between the Huthis and SALIH, sporadic clashes erupted in mid-2017, and escalated into open fighting that ended when Huthi forces killed SALIH in early December 2017. In 2018, anti-Huthi forces made the most battlefield progress in Yemen since early 2016, most notably in Al Hudaydah Governorate. In December 2018, the Huthis and Yemeni Government participated in the first UN-brokered peace talks since 2016, agreeing to a limited ceasefire in Al Hudaydah Governorate and the establishment of a UN Mission to monitor the agreement. In April 2019, Yemen’s parliament convened in Say'un for the first time since the conflict broke out in 2014. In August 2019, violence erupted between HADI's government and the pro-secessionist Southern Transition Council (STC) in southern Yemen. In November 2019, HADI's government and the STC signed a power-sharing agreement to end the fighting between them.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
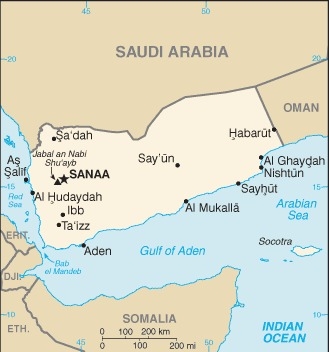
Middle East, bordering the Arabian Sea, Gulf of Aden, and Red Sea, between Oman and Saudi Arabia
Geographic coordinates
15 00 N, 48 00 E
Map references
Middle East
Area
total: 527,968 sq km
land: 527,968 sq km
water: 0 sq km
note: includes Perim, Socotra, the former Yemen Arab Republic (YAR or North Yemen), and the former People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (PDRY or South Yemen)
Area - comparative
almost four times the size of Alabama; slightly larger than twice the size of Wyoming
Land boundaries
total: 1,601 km
border countries (2): Oman 294 km, Saudi Arabia 1307 km
Coastline
1,906 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
Climate
mostly desert; hot and humid along west coast; temperate in western mountains affected by seasonal monsoon; extraordinarily hot, dry, harsh desert in east
Terrain
narrow coastal plain backed by flat-topped hills and rugged mountains; dissected upland desert plains in center slope into the desert interior of the Arabian Peninsula
Elevation
highest point: Jabal an Nabi Shu'ayb 3,666 m
lowest point: Arabian Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 999 m
Natural resources
petroleum, fish, rock salt, marble; small deposits of coal, gold, lead, nickel, and copper; fertile soil in west
Land use
agricultural land: 44.5% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.2% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.6% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 41.7% (2018 est.)
forest: 1% (2018 est.)
other: 54.5% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
6,800 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
the vast majority of the population is found in the Asir Mountains (part of the larger Sarawat Mountain system), located in the far western region of the country
Natural hazards
sandstorms and dust storms in summer
volcanism: limited volcanic activity; Jebel at Tair (Jabal al-Tair, Jebel Teir, Jabal al-Tayr, Jazirat at-Tair) (244 m), which forms an island in the Red Sea, erupted in 2007 after awakening from dormancy; other historically active volcanoes include Harra of Arhab, Harras of Dhamar, Harra es-Sawad, and Jebel Zubair, although many of these have not erupted in over a century
Geography - note
strategic location on Bab el Mandeb, the strait linking the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden, one of world's most active shipping lanes
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Yemeni(s)
adjective: Yemeni
Ethnic groups
predominantly Arab; but also Afro-Arab, South Asian, European
Languages
Arabic (official); note - a distinct Socotri language is widely used on Socotra Island and Archipelago; Mahri is still fairly widely spoken in eastern Yemen
major-language sample(s):
كتاب حقائق العالم، المصدر الذي لا يمكن الاستغناء عنه للمعلومات الأساسية (Arabic)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Muslim 99.1% (official; virtually all are citizens, an estimated 65% are Sunni and 35% are Shia), other 0.9% (includes Jewish, Baha'i, Hindu, and Christian; many are refugees or temporary foreign residents) (2020 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 39.16% (male 5,711,709 /female 5,513,526)
15-24 years: 21.26% (male 3,089,817 /female 3,005,693)
25-54 years: 32.78% (male 4,805,059 /female 4,591,811)
55-64 years: 4% (male 523,769 /female 623,100)
65 years and over: 2.8% (male 366,891 /female 435,855) (2018 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 71.7
youth dependency ratio: 66.7
elderly dependency ratio: 5
potential support ratio: 19.9 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 19.8 years (2018 est.)
male: 19.6 years
female: 19.9 years
Population distribution
the vast majority of the population is found in the Asir Mountains (part of the larger Sarawat Mountain system), located in the far western region of the country
Urbanization
urban population: 38.5% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.71% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)
Major urban areas - population
3.075 million SANAA (capital), 1.012 million Aden (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.84 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.84 male(s)/female
total population: 1.02 male(s)/female (2018 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
20.8 years (2013 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-49
Maternal mortality ratio
164 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54Infant mortality rate
total: 47.56 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 52.95 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 41.91 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 67.18 years
male: 64.89 years
female: 69.59 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
33.5% (2013)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 87.6% of population
total: 92% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 12.4% of population
total: 8% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
5.6% (2015)
Physicians density
0.53 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
Hospital bed density
0.7 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 93.1% of population
rural: 48.5% of population
total: 64.6% of population
unimproved: urban: 6.9% of population
rural: 51.5% of population
total: 35.4% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
<.1% (2020 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<500 (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 70.1%
male: 85.1%
female: 55% (2015)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 9 years
male: 11 years
female: 8 years (2011)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 24.5%
male: 23.5%
female: 34.6% (2014 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
limited natural freshwater resources; inadequate supplies of potable water; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 44.96 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 10.61 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 8.03 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
mostly desert; hot and humid along west coast; temperate in western mountains affected by seasonal monsoon; extraordinarily hot, dry, harsh desert in east
Land use
agricultural land: 44.5% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.2% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.6% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 41.7% (2018 est.)
forest: 1% (2018 est.)
other: 54.5% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 38.5% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.71% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.04% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
Food insecurity
widespread lack of access: due to conflict, poverty, floods, high food and fuel prices - between January and June 2021, the number of food insecure was projected to increase by nearly 3 million to 16.2 million people; out of these, an estimated 11 million people will likely be in "Crisis," 5 million in "Emergency," and the number of those in "Catastrophe" will likely increase to 47,000; economic conditions in the country remain dire; the conflict is further hampering the already constrained livelihood activities and humanitarian access; income earning opportunities have declined due to COVID‑19‑related business disruptions (2021)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 4,836,820 tons (2011 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 386,946 tons (2016 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 8% (2016 est.)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 265 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 65 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 3.235 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
2.1 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Yemen
conventional short form: Yemen
local long form: Al Jumhuriyah al Yamaniyah
local short form: Al Yaman
former: Yemen Arab Republic [Yemen (Sanaa) or North Yemen] and People's Democratic Republic of Yemen [Yemen (Aden) or South Yemen]
etymology: name derivation remains unclear but may come from the Arab term "yumn" (happiness) and be related to the region's classical name "Arabia Felix" (Fertile or Happy Arabia); the Romans referred to the rest of the peninsula as "Arabia Deserta" (Deserted Arabia)
Government type
in transition
Capital
name: Sanaa
geographic coordinates: 15 21 N, 44 12 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name is reputed to mean "well-fortified" in Sabaean, the South Arabian language that went extinct in Yemen in the 6th century A.D.
Administrative divisions
22 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazah); Abyan, 'Adan (Aden), Ad Dali', Al Bayda', Al Hudaydah, Al Jawf, Al Mahrah, Al Mahwit, Amanat al 'Asimah (Sanaa City), 'Amran, Arkhabil Suqutra (Socotra Archipelago), Dhamar, Hadramawt, Hajjah, Ibb, Lahij, Ma'rib, Raymah, Sa'dah, San'a' (Sanaa), Shabwah, Ta'izz
Independence
22 May 1990 (Republic of Yemen was established with the merger of the Yemen Arab Republic [Yemen (Sanaa) or North Yemen] and the Marxist-dominated People's Democratic Republic of Yemen [Yemen (Aden) or South Yemen]); notable earlier dates: North Yemen became independent on 1 November 1918 (from the Ottoman Empire) and became a republic with the overthrow of the theocratic Imamate on 27 September 1962; South Yemen became independent on 30 November 1967 (from the UK)
National holiday
Unification Day, 22 May (1990)
Constitution
history: adopted by referendum 16 May 1991 (following unification); note - after the National Dialogue ended in January 2015, a Constitutional Drafting Committee appointed by the president worked to prepare a new draft constitution that was expected to be put to a national referendum before being adopted; however, the start of the current conflict in early 2015 interrupted the process
amendments: amended several times, last in 2009
Legal system
mixed legal system of Islamic (sharia) law, Napoleonic law, English common law, and customary law
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Yemen; if the father is unknown, the mother must be a citizen
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Abd Rabuh Mansur HADI (since 21 February 2012); Vice President ALI MUHSIN al-Ahmar, Lt. Gen. (since 3 April 2016)
head of government: Prime Minister Maeen Abd al-Malik SAEED (since 15 October 2018)
cabinet: appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 7-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 21 February 2012 (next election NA); note - a special election was held on 21 February 2012 to remove Ali Abdallah SALIH under the terms of a Gulf Cooperation Council-mediated deal during the political crisis of 2011; vice president appointed by the president; prime minister appointed by the president
election results: Abd Rabuh Mansur HADI (GPC) elected as a consensus president with about 50% popular participation; no other candidates
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliament or Majlis consists of:
Shura Council or Majlis Alshoora (111 seats; members appointed by the president; member tenure NA)
House of Representatives or Majlis al Nuwaab (301 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 6-year terms)
elections:
House of Representatives - last held on 27 April 2003 (next scheduled for April 2009 but postponed indefinitely)
election results:
percent of vote by party - GPC 58.0%, Islah 22.6%, YSP 3.8%, Unionist Party 1.9%, other 13.7%; seats by party - GPC 238, Islah 46, YSP 8, Nasserist Unionist Party 3, National Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party 2, independent 4
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of the court president, 2 deputies, and nearly 50 judges; court organized into constitutional, civil, commercial, family, administrative, criminal, military, and appeals scrutiny divisions)
judge selection and term of office: judges appointed by the Supreme Judicial Council, which is chaired by the president of the republic and includes 10 high-ranking judicial officers; judges serve for life with mandatory retirement at age 65
subordinate courts: appeal courts; district or first instance courts; commercial courts
Political parties and leaders
General People’s Congress or GPC (3 factions: pro-Hadi [Abdrabbi Mansur HADI], pro-Houthi [Sadeq Ameen Abu RAS], pro-Saleh [Ahmed SALEH]
National Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party [Qassem Salam SAID]
Nasserist Unionist People's Organization [Abdulmalik al-MEKHLAFI]
Southern Transitional Council or STC [Aidarus al-ZOUBAIDA]
Yemeni Reform Grouping or Islah [Muhammed Abdallah al-YADUMI]
Yemeni Socialist Party or YSP [Dr. Abd al-Rahman Umar al-SAQQAF]
(
International organization participation
AFESD, AMF, CAEU, CD, EITI (temporarily suspended), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAS, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS (observer), OIC, OPCW, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Ahmad Awadh BIN MUBARAK (since 3 August 2015)
chancery: 2319 Wyoming Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 965-4760
FAX: [1] (202) 337-2017
email address and website:
Information@yemenembassy.org
https://www.yemenembassy.org/
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: ambassador (vacant); Chargé d’Affaires Cathy WESTLEY (since 23 May 2021); note - the embassy closed in March 2015; Yemen Affairs Unit currently operates out of US Embassy Riyadh
embassy: previously - Sa'awan Street, Sanaa
mailing address: 6330 Sanaa Place, Washington DC 20521-6330
telephone: US Embassy Riyadh [966] 11-488-3800
previously - [967] 1 755-2000
FAX: US Embassy Riyadh [966] 11-488-7360
email address and website:
YemenEmergencyUSC@state.gov
https://ye.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and black; the band colors derive from the Arab Liberation flag and represent oppression (black), overcome through bloody struggle (red), to be replaced by a bright future (white)
note: similar to the flag of Syria, which has two green stars in the white band, and of Iraq, which has an Arabic inscription centered in the white band; also similar to the flag of Egypt, which has a heraldic eagle centered in the white band
National symbol(s)
golden eagle; national colors: red, white, black
National anthem
name: "al-qumhuriyatu l-muttahida" (United Republic)
lyrics/music: Abdullah Abdulwahab NOA'MAN/Ayyoab Tarish ABSI
note: adopted 1990; the music first served as the anthem for South Yemen before unification with North Yemen in 1990
Economy
Economic overview
Yemen is a low-income country that faces difficult long-term challenges to stabilizing and growing its economy, and the current conflict has only exacerbated those issues. The ongoing war has halted Yemen’s exports, pressured the currency’s exchange rate, accelerated inflation, severely limited food and fuel imports, and caused widespread damage to infrastructure. The conflict has also created a severe humanitarian crisis - the world’s largest cholera outbreak currently at nearly 1 million cases, more than 7 million people at risk of famine, and more than 80% of the population in need of humanitarian assistance.
Prior to the start of the conflict in 2014, Yemen was highly dependent on declining oil and gas resources for revenue. Oil and gas earnings accounted for roughly 25% of GDP and 65% of government revenue. The Yemeni Government regularly faced annual budget shortfalls and tried to diversify the Yemeni economy through a reform program designed to bolster non-oil sectors of the economy and foreign investment. In July 2014, the government continued reform efforts by eliminating some fuel subsidies and in August 2014, the IMF approved a three-year, $570 million Extended Credit Facility for Yemen.
However, the conflict that began in 2014 stalled these reform efforts and ongoing fighting continues to accelerate the country’s economic decline. In September 2016, President HADI announced the move of the main branch of Central Bank of Yemen from Sanaa to Aden where his government could exert greater control over the central bank’s dwindling resources. Regardless of which group controls the main branch, the central bank system is struggling to function. Yemen’s Central Bank’s foreign reserves, which stood at roughly $5.2 billion prior to the conflict, have declined to negligible amounts. The Central Bank can no longer fully support imports of critical goods or the country’s exchange rate. The country also is facing a growing liquidity crisis and rising inflation. The private sector is hemorrhaging, with almost all businesses making substantial layoffs. Access to food and other critical commodities such as medical equipment is limited across the country due to security issues on the ground. The Social Welfare Fund, a cash transfer program for Yemen’s neediest, is no longer operational and has not made any disbursements since late 2014.
Yemen will require significant international assistance during and after the protracted conflict to stabilize its economy. Long-term challenges include a high population growth rate, high unemployment, declining water resources, and severe food scarcity.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$73.63 billion (2017 est.)
$78.28 billion (2016 est.)
$90.63 billion (2015 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
-5.9% (2017 est.)
-13.6% (2016 est.)
-16.7% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$2,500 (2017 est.)
$2,700 (2016 est.)
$3,200 (2015 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$54.356 billion (2018 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
24.7% (2017 est.)
-12.6% (2016 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 20.3% (2017 est.)
industry: 11.8% (2017 est.)
services: 67.9% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 116.6% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 17.6% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 2.2% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 7.5% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -43.9% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
mangoes/guavas, potatoes, sorghum, onions, milk, poultry, watermelons, grapes, oranges, bananas
Industries
crude oil production and petroleum refining; small-scale production of cotton textiles, leather goods; food processing; handicrafts; aluminum products; cement; commercial ship repair; natural gas production
Labor force - by occupation
note: most people are employed in agriculture and herding; services, construction, industry, and commerce account for less than one-fourth of the labor force
Population below poverty line
48.6% (2014 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
36.7 (2014 est.)
37.3 (1999 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2.6%
highest 10%: 30.3% (2008 est.)
Budget
revenues: 2.821 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 4.458 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$1.236 billion (2017 est.)
-$1.868 billion (2016 est.)
Exports - partners
China 53%, Saudi Arabia 10%, United Arab Emirates 7%, Australia 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
crude petroleum, gold, fish, industrial chemical liquids, scrap iron (2019)
Imports - partners
China 25%, Turkey 10%, United Arab Emirates 9%, Saudi Arabia 8%, India 7% (2019)
Imports - commodities
wheat, refined petroleum, iron, rice, cars (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$245.4 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$592.6 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$6.805 billion (2018 est.)
$7.181 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Yemeni rials (YER) per US dollar -
275 (2017 est.)
214.9 (2016 est.)
214.9 (2015 est.)
228 (2014 est.)
214.89 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 24.5%
male: 23.5%
female: 34.6% (2014 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
population without electricity: 16 million (2019)
electrification - total population: 47% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 72% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 31% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
1.819 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116Electricity - from fossil fuels
79% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 212Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214Electricity - from other renewable sources
21% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36Refined petroleum products - production
20,180 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89Refined petroleum products - consumption
104,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78Natural gas - proved reserves
478.5 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 1.19 million (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4.28 (2018 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 15,297,789 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 55.18 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: large percent of the population is in need of humanitarian assistance and telecom services are vital but disrupted; mobile towers are often deliberately targeted; maintenance is dangerous to staff; aid organizations rely on satellite and radio communications; scarcity of telecom equipment in rural areas; ownership of telecom services and the related revenues and taxes have become a political issue; Chinese company Huawei helping to rebuild some equipment (2020)
domestic: the national network consists of microwave radio relay, cable, tropospheric scatter, GSM and CDMA mobile-cellular telephone systems; fixed-line teledensity remains low by regional standards at 4 per 100 but mobile cellular use expanding at 55 per 100 (2019)
international: country code - 967; landing points for the FALCON, SeaMeWe-5, Aden-Djibouti, and the AAE-1 international submarine cable connecting Europe, Africa, the Middle East, Asia and Southeast Asia; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (2 Indian Ocean and 1 Atlantic Ocean), 1 Intersputnik (Atlantic Ocean region), and 2 Arabsat; microwave radio relay to Saudi Arabia and Djibouti (2020)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
state-run TV with 2 stations; state-run radio with 2 national radio stations and 5 local stations; stations from Oman and Saudi Arabia can be accessed
Internet users
total: 8.06 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 26.72% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 386,330 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1.68 (2019 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 8
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 336,310 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 3.27 million mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 17
over 3,047 m: 4
2,438 to 3,047 m: 9
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2013)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 40
over 3,047 m: 3
2,438 to 3,047 m: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m: 7
914 to 1,523 m: 16
under 914 m: 9 (2013)
Pipelines
641 km gas, 22 km liquid petroleum gas, 1370 km oil (2013)
Roadways
total: 71,300 km (2005)
paved: 6,200 km (2005)
unpaved: 65,100 km (2005)
Merchant marine
total: 34
by type: general cargo 2, oil tanker 4, other 28 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Aden, Al Hudaydah, Al Mukalla
Military and Security
Military and security forces
as of 2021, military and security forces operating in Yemen consists of a patchwork of government, non-state, and foreign-backed regular, semi-regular/militia, and paramilitary forces, often with informal command organizations and conflicting, fluid, or overlapping agendas, loyalties, and relationships; in addition, the Huthis maintain opposition military and security forces
Republic of Yemen Government (ROYG) forces; Ministry of Defense: Yemeni National Army, Air Force and Air Defense, Navy and Coastal Defense Forces, Border Guard, Strategic Reserve Forces (includes Special Forces and Presidential Protection Brigades, which are under the Ministry of Defense but responsible to the president), Popular Committee Forces (government-backed tribal militia); Ministry of Interior: Special Security Forces (paramilitary; formerly known as Central Security Forces), Political Security Organization (state security), National Security Bureau (intelligence), Counterterrorism Unit
Saudi-backed forces: paramilitary/militia border security brigades based largely on tribal or regional affiliation (deployed along the Saudi-Yemen border, especially the areas bordering the governorates of Saada and Al-Jawf)
United Arab Emirates-backed forces include tribal and regionally-based militia and paramilitary forces (concentrated in the southern governates): Southern Transitional Council (STC) forces, including the Security Belt Forces, the Shabwani and Hadrami “Elite” Forces, the Support and Backup Forces (aka Logistics and Support Forces), Facilities Protection Forces, and Anti-Terrorism Forces; Republican Forces; Joint Forces; note – under the 2019 Riyadh Agreement, the STC forces are to be incorporated into Yemen’s Ministries of Defense and Interior under the authority of the HADI government
Huthi: ground, air/air defense, coastal defense, presidential protection, special operations, missile, and tribal militia forces
note – a considerable portion--up to 70 percent by some estimates--of Yemen’s military and security forces defected in whole or in part to former president SALAH and the Huthi opposition in 2011-2015
Military expenditures
4.3% of GDP (2014)
4.3% of GDP (2013)
4.7% of GDP (2012)
5% of GDP (2011)
4.8% of GDP (2010)
note - no reliable information exists following the start of renewed conflict in 2015
Military and security service personnel strengths
information limited and widely varied; ROYG: up to 300,000 estimated military, paramilitary, and militia forces; UAE- and Saudi-backed forces: 150-200,000 estimated trained fighters; Huthis: up to 200,000 estimated fighters (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the inventory of the Yemeni Government forces consists primarily of Russian and Soviet-era equipment, although much of it has been lost in the current conflict; since the start of the civil war in 2014, it has received limited amounts of donated equipment from some Gulf States, including Saudi Arabia and UAE (2021)
Maritime threats
the Maritime Administration of the US Department of Transportation has issued Maritime Advisory 2020-017 (Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, Arabian Sea, and Indian Ocean-Violence Due to Regional Conflict and Piracy) effective 14 December 2020, which states in part the "Conflict in Yemen continues to pose potential risk to US flagged commercial vessels transiting the southern Red Sea, Bab al Mandeb Strait, and Gulf of Aden. Threats may come from a variety of different sources including, but not limited to, missiles, rockets, projectiles, mines, small arms, unmanned aerial vehicles, unmanned surface vessels, or waterborne improvised explosive devices. These threat vectors continue to pose a direct or collateral risk to US flagged commercial vessels operating in the region. Additionally, piracy poses a threat in the Gulf of Aden, Western Arabian Sea, and Western Indian Ocean."
Military service age and obligation
18 is the legal minimum age for voluntary military service; conscription abolished in 2001; 2-year service obligation (note - limited information since the start of the civil war) (2021)
Military - note
in 2015, a Saudi-led coalition of Arab states intervened militarily in Yemen in support of the Republic of Yemen Government (ROYG) against the separatist Huthis; as of late 2021, the conflict had become largely stalemated, but the coalition (consisting largely of Saudi forces), ROYG forces, and the Huthis continued to engage in fighting, mostly with air and missile forces, although heavy ground fighting was also taking place over the key oil-rich province of Marib; the Saudis have conducted numerous air strikes in northern Yemen, while the Huthis have launched attacks into Saudi territory with ballistic missiles and unmanned aerial vehicles armed with explosives; Saudi Arabia also has raised and equipped paramilitary/militia security forces in Yemen based largely on tribal or regional affiliation to deploy along the Saudi-Yemen border, especially the areas bordering the governorates of Saada and Al-Jawf; as of late 2021, the Saudi-led coalition continued to control Yemen’s airspace and the port of Hodeida
the United Arab Emirates (UAE) intervened in Yemen in 2015 as part of the Saudi-led coalition with about 3,500 troops, as well as supporting air and naval forces; UAE withdrew its main military force from Yemen in 2019, but has retained a small military presence while working with proxies in southern Yemen, most notably the Southern Transitional Council (STC); as of 2021, UAE had recruited, trained, and equipped an estimated 150-200,000 Yemeni fighters and formed them into dozens of militia and paramilitary units
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps/Qods Force; Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham - Yemen; al-Qa'ida in the Arabian Peninsula
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Saudi Arabia has reinforced its concrete-filled security barrier along sections of the fully demarcated border with Yemen to stem illegal cross-border activities
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 113,869 (Somalia), 17,306 (Ethiopia) (2021)
IDPs: 4,002,012 (conflict in Sa'ada Governorate; clashes between al-Qa'ida in the Arabian Peninsula and government forces) (2020)