Introduction
Background
An ancient crossroads for various migrations, Uganda has as many as 65 ethnic groups that speak languages from three of Africa’s four major linguistic families. As early as 1200, fertile soils and regular rainfall in the south fostered the formation of several large centralized kingdoms, including Buganda, from which the country derives its name. Muslim traders from Egypt reached northern Uganda in the 1820s, and Swahili merchants from the Indian Ocean coast arrived in the south by the 1840s. The area attracted the attention of British explorers seeking the source of the Nile River in the 1860s, and this influence expanded in subsequent decades with the arrival of Christian missionaries and trade agreements; Uganda was declared a British protectorate in 1894. Buganda and other southern kingdoms negotiated agreements with Britain to secure privileges and a level of autonomy that were rare during the colonial period in Africa. The colonial boundaries demarcating Uganda grouped together a wide range of ethnic groups with different political systems and cultures, and the disparities between how Britain governed southern and northern areas compounded these differences, complicating efforts to establish a cohesive independent country.
Uganda gained independence in 1962 with one of the more developed economies and one of the strongest education systems in Sub-Saharan Africa, but it descended within a few years into political turmoil and internal conflict that lasted more than two decades. In 1966, Prime Minister Milton OBOTE suspended the constitution and violently deposed President Edward MUTESA, who was also the king of Buganda. Idi AMIN seized power in 1971 through a military coup and led the country into economic ruin and rampant mass atrocities that killed as many as 500,000 civilians. AMIN’s annexation of Tanzanian territory in 1979 provoked Tanzania to invade Uganda, depose AMIN, and install a coalition government. In the aftermath, Uganda continued to experience atrocities, looting, and political instability and had four different heads of state between 1979 and 1980. OBOTE regained the presidency in 1980 through a controversial election that sparked renewed guerrilla warfare, killing as an estimated 300,000 civilians. Gen. Tito OKELLO seized power in a coup in 1985, but his rule was short-lived, with Yoweri MUSEVENI becoming president in 1986 after his insurgency captured the capital. MUSEVENI is widely credited with restoring relative stability and economic growth to Uganda but has resisted calls to leave office. In 2017, parliament approved the removal of presidential age limits, making it possible for MUSEVENI to remain in office for life. Uganda faces numerous challenges that could affect future stability, including explosive population growth, power and infrastructure constraints, corruption, underdeveloped democratic institutions, and human rights deficits.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
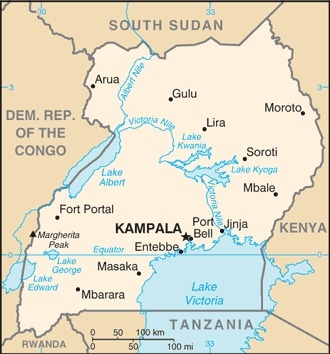
Location
East-Central Africa, west of Kenya, east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Geographic coordinates
1 00 N, 32 00 E
Map references
Africa
Area - comparative
slightly more than two times the size of Pennsylvania; slightly smaller than Oregon
Land boundaries
total: 2,729 km
border countries (5): Democratic Republic of the Congo 877 km, Kenya 814 km, Rwanda 172 km, South Sudan 475 km, Tanzania 391 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
tropical; generally rainy with two dry seasons (December to February, June to August); semiarid in northeast
Terrain
mostly plateau with rim of mountains
Elevation
highest point: Margherita Peak on Mount Stanley 5,110 m
lowest point: Albert Nile 614 m
Natural resources
copper, cobalt, hydropower, limestone, salt, arable land, gold
Land use
agricultural land: 71.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 34.3% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 11.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 25.6% (2018 est.)
forest: 14.5% (2018 est.)
other: 14.3% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
140 sq km (2012)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Victoria (shared with Tanzania and Kenya) - 62,940 sq km; Lake Albert (shared with Democratic Republic of Congo) - 5,590 sq km; Lake Kyoga - 4,430 sq km; Lake Edward (shared with Democratic Republic of Congo) - 2,150 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Nile (shared with Rwanda [s], Tanzania, South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt [m]) - 6,650 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Congo (3,730,881 sq km), (Mediterranean Sea) Nile (3,254,853 sq km)
Population distribution
population density is relatively high in comparison to other African nations; most of the population is concentrated in the central and southern parts of the country, particularly along the shores of Lake Victoria and Lake Albert; the northeast is least populated as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards
droughts; floods; earthquakes; landslides; hailstorms
Geography - note
landlocked; fertile, well-watered country with many lakes and rivers; Lake Victoria, the world's largest tropical lake and the second largest fresh water lake, is shared among three countries: Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda
People and Society
Population
44,712,143 (July 2021 est.)
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
Nationality
noun: Ugandan(s)
adjective: Ugandan
Ethnic groups
Baganda 16.5%, Banyankole 9.6%, Basoga 8.8%, Bakiga 7.1%, Iteso 7%, Langi 6.3%, Bagisu 4.9%, Acholi 4.4%, Lugbara 3.3%, other 32.1% (2014 est.)
Languages
English (official language, taught in schools, used in courts of law and by most newspapers and some radio broadcasts), Ganda or Luganda (most widely used of the Niger-Congo languages and the language used most often in the capital), other Niger-Congo languages, Nilo-Saharan languages, Swahili (official), Arabic
Religions
Protestant 45.1% (Anglican 32.0%, Pentecostal/Born Again/Evangelical 11.1%, Seventh Day Adventist 1.7%, Baptist .3%), Roman Catholic 39.3%, Muslim 13.7%, other 1.6%, none 0.2% (2014 est.)
Demographic profile
Uganda has one of the youngest and most rapidly growing populations in the world; its total fertility rate is among the world’s highest at 5.8 children per woman. Except in urban areas, actual fertility exceeds women’s desired fertility by one or two children, which is indicative of the widespread unmet need for contraception, lack of government support for family planning, and a cultural preference for large families. High numbers of births, short birth intervals, and the early age of childbearing contribute to Uganda’s high maternal mortality rate. Gender inequities also make fertility reduction difficult; women on average are less-educated, participate less in paid employment, and often have little say in decisions over childbearing and their own reproductive health. However, even if the birth rate were significantly reduced, Uganda’s large pool of women entering reproductive age ensures rapid population growth for decades to come.
Unchecked, population increase will further strain the availability of arable land and natural resources and overwhelm the country’s limited means for providing food, employment, education, health care, housing, and basic services. The country’s north and northeast lag even further behind developmentally than the rest of the country as a result of long-term conflict (the Ugandan Bush War 1981-1986 and more than 20 years of fighting between the Lord’s Resistance Army (LRA) and Ugandan Government forces), ongoing inter-communal violence, and periodic natural disasters.
Uganda has been both a source of refugees and migrants and a host country for refugees. In 1972, then President Idi AMIN, in his drive to return Uganda to Ugandans, expelled the South Asian population that composed a large share of the country’s business people and bankers. Since the 1970s, thousands of Ugandans have emigrated, mainly to southern Africa or the West, for security reasons, to escape poverty, to search for jobs, and for access to natural resources. The emigration of Ugandan doctors and nurses due to low wages is a particular concern given the country’s shortage of skilled health care workers. Africans escaping conflicts in neighboring states have found refuge in Uganda since the 1950s; the country currently struggles to host tens of thousands from the Democratic Republic of the Congo, South Sudan, and other nearby countries.
Age structure
0-14 years: 48.21% (male 10,548,913/female 10,304,876)
15-24 years: 20.25% (male 4,236,231/female 4,521,698)
25-54 years: 26.24% (male 5,202,570/female 6,147,304)
55-64 years: 2.91% (male 579,110/female 681,052)
65 years and over: 2.38% (male 442,159/female 589,053) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 92.3
youth dependency ratio: 88.5
elderly dependency ratio: 3.8
potential support ratio: 26.2 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 15.7 years
male: 14.9 years
female: 16.5 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
population density is relatively high in comparison to other African nations; most of the population is concentrated in the central and southern parts of the country, particularly along the shores of Lake Victoria and Lake Albert; the northeast is least populated as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization
urban population: 25.6% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 5.41% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
3.470 million KAMPALA (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 0.94 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.85 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.85 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female
total population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
19.4 years (2016 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 20-49
Maternal mortality ratio
375 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30Infant mortality rate
total: 31.49 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 34.98 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 27.88 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 68.58 years
male: 66.34 years
female: 70.9 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
41.8% (2018)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 92.9% of population
rural: 77.2% of population
total: 80.8% of population
unimproved: urban: 7.1% of population
rural: 22.8% of population
total: 19.2% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
6.5% (2018)
Physicians density
0.17 physicians/1,000 population (2017)
Hospital bed density
0.5 beds/1,000 population
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 67.8% of population
rural: 26.6% of population
total: 36.2% of population
unimproved: urban: 32.2% of population
rural: 73.4% of population
total: 63.8% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and Trypanosomiasis-Gambiense (African sleeping sickness)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 76.5%
male: 82.7%
female: 70.8% (2018)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 10 years
male: 10 years
female: 10 years (2011)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 15.6%
male: 13.8%
female: 17.6% (2017 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
draining of wetlands for agricultural use; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; water pollution from industrial discharge and water hyacinth infestation in Lake Victoria; widespread poaching
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 48.41 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 5.68 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 30.24 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; generally rainy with two dry seasons (December to February, June to August); semiarid in northeast
Land use
agricultural land: 71.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 34.3% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 11.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 25.6% (2018 est.)
forest: 14.5% (2018 est.)
other: 14.3% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 25.6% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 5.41% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 7.32% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and Trypanosomiasis-Gambiense (African sleeping sickness)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
Food insecurity
widespread lack of access: due to reduced incomes, and floods - in traditionally food secure urban areas, including the capital, Kampala, more than 600,000 people were food insecure due to the restrictive measures introduced to curb the spread of the COVID-19 virus; the food security situation in urban areas was the most affected by the COVID‑19‑related restrictive measures, as poor households mainly rely on the daily wages obtained through casual labor, petty trading, food vending, construction activities and domestic work; despite the phasing out of some restrictive measures, the food security situation of the urban poor has not significantly improved, as the restrictions still in place on business operations are resulting in a slow recovery of the economic activities; in rural areas, torrential rains in April and May 2020 resulted in localized crop and livelihood losses (2021)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 7,045,050 tons (2016 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 422,703 tons (2017 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 6% (2017 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Victoria (shared with Tanzania and Kenya) - 62,940 sq km; Lake Albert (shared with Democratic Republic of Congo) - 5,590 sq km; Lake Kyoga - 4,430 sq km; Lake Edward (shared with Democratic Republic of Congo) - 2,150 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Nile (shared with Rwanda [s], Tanzania, South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt [m]) - 6,650 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Congo (3,730,881 sq km), (Mediterranean Sea) Nile (3,254,853 sq km)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 328 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 50 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 259 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
60.1 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Uganda
conventional short form: Uganda
etymology: from the name "Buganda," adopted by the British as the designation for their East African colony in 1894; Buganda had been a powerful East African state during the 18th and 19th centuries
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Kampala
geographic coordinates: 0 19 N, 32 33 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the site of the original British settlement was referred to by its native name as Akasozi ke'Empala ("hill of the impala" [plural]); over time this designation was shortened to K'empala and finally Kampala
Administrative divisions
134 districts and 1 capital city*; Abim, Adjumani, Agago, Alebtong, Amolatar, Amudat, Amuria, Amuru, Apac, Arua, Budaka, Bududa, Bugiri, Bugweri, Buhweju, Buikwe, Bukedea, Bukomansimbi, Bukwo, Bulambuli, Buliisa, Bundibugyo, Bunyangabu, Bushenyi, Busia, Butaleja, Butambala, Butebo, Buvuma, Buyende, Dokolo, Gomba, Gulu, Hoima, Ibanda, Iganga, Isingiro, Jinja, Kaabong, Kabale, Kabarole, Kaberamaido, Kagadi, Kakumiro, Kalaki, Kalangala, Kaliro, Kalungu, Kampala*, Kamuli, Kamwenge, Kanungu, Kapchorwa, Kapelebyong, Karenga, Kasese, Kasanda, Katakwi, Kayunga, Kazo, Kibaale, Kiboga, Kibuku, Kikuube, Kiruhura, Kiryandongo, Kisoro, Kitagwenda, Kitgum, Koboko, Kole, Kotido, Kumi, Kwania, Kween, Kyankwanzi, Kyegegwa, Kyenjojo, Kyotera, Lamwo, Lira, Luuka, Luwero, Lwengo, Lyantonde, Madi-Okollo, Manafwa, Maracha, Masaka, Masindi, Mayuge, Mbale, Mbarara, Mitooma, Mityana, Moroto, Moyo, Mpigi, Mubende, Mukono, Nabilatuk, Nakapiripirit, Nakaseke, Nakasongola, Namayingo, Namisindwa, Namutumba, Napak, Nebbi, Ngora, Ntoroko, Ntungamo, Nwoya, Obongi, Omoro, Otuke, Oyam, Pader, Pakwach, Pallisa, Rakai, Rubanda, Rubirizi, Rukiga, Rukungiri, Rwampara, Sembabule, Serere, Sheema, Sironko, Soroti, Tororo, Wakiso, Yumbe, Zombo
Independence
9 October 1962 (from the UK)
National holiday
Independence Day, 9 October (1962)
Constitution
history: several previous; latest adopted 27 September 1995, promulgated 8 October 1995
amendments: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly membership in the second and third readings; proposals affecting "entrenched clauses," including the sovereignty of the people, supremacy of the constitution, human rights and freedoms, the democratic and multiparty form of government, presidential term of office, independence of the judiciary, and the institutions of traditional or cultural leaders, also requires passage by referendum, ratification by at least two-thirds majority vote of district council members in at least two thirds of Uganda's districts, and assent ofthe president of the republic; amended several times, last in 2017 (2021)
Legal system
mixed legal system of English common law and customary law
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent or grandparent must be a native-born citizen of Uganda
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: an aggregate of 20 years and continuously for the last 2 years prior to applying for citizenship
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI (since coming to power on 26 January 1986; re-elected for sixth term on 14 January 2021); Vice President Jessica Rose Epel ALUPO (since 21 June 2021); Prime Minister Robinah NABBANJA (since 21 June 2021); First Deputy Prime Minister Rebecca KADAGA (since 24 June 2021); Second Deputy Prime Minister Moses ALI (since 21 June 2021); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI (since coming to power on 26 January 1986; re-elected for sixth term on 14 January 2021); Vice President Jessica Rose Epel ALUPO (since 21 June 2021); Prime Minister Robinah NABBANJA (since 21 June 2021); First Deputy Prime Minister Rebecca KADAGA (since 24 June 2021); Second Deputy Prime Minister Moses ALI (since 21 June 2021)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president from among elected members of the National Assembly or persons who qualify to be elected as members of the National Assembly
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (no term limits); election last held on 14 January 2021 (next to be held in 2026)
election results:
2021: Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI reelected president in the first round; percent of vote - Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI (NRM) 58.6%, Bobi WINE (NUP) 34.8%, Patrick Oboi AMURIAT (FDC) 3.2%, other 3.4%
2016: Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI reelected president in the first round; percent of vote - Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI (NRM) 60.6%, Kizza BESIGYE (FDC) 35.6%, other 3.8%
Legislative branch
description: unicameral National Assembly or Parliament (445 seats; 290 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote, 112 for women directly elected in single-seat districts by simple majority vote, and 25 "representatives" reserved for special interest groups - army 10, disabled 5, youth 5, labor 5; up to 18 ex officio members appointed by the president; members serve 5-year terms)
elections: last held on 18 February 2016 (next to be held in February 2021)
election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NRM 292, FDC 37, DP 5, UPDF 10, UPC 6, independent 66 (excludes 19 ex-officio members)
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court of Uganda (consists of the chief justice and at least 6 justices)
judge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the president of the republic in consultation with the Judicial Service Commission, an 8-member independent advisory body, and approved by the National Assembly; justices serve until mandatory retirement at age 70
subordinate courts: Court of Appeal (also acts as the Constitutional Court); High Court (includes 12 High Court Circuits and 8 High Court Divisions); Industrial Court; Chief Magistrate Grade One and Grade Two Courts throughout the country; qadhis courts; local council courts; family and children courts
Political parties and leaders
Alliance for National Transformation or ANT [Ms. Alice ALASO, acting national coordinator]; note - Mugisha MUNTU resigned his position as ANT national coordinator in late June 2020 to run in the 2021 presidential election
Activist Party [Stephen BAMPIGGA]
Democratic Party or DP [Norbert MAO]
Conservative Party [Walyemera Daniel MASUMBA]
Forum for Democratic Change or FDC [Patrick Oboi AMURIAT]
Justice Forum or JEEMA [Asuman BASALIRWA]
National Resistance Movement or NRM [Yoweri MUSEVENI]
Uganda People's Congress or UPC [James AKENA]
National Unity Platform [Nkonge KIBALAMA]
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, COMESA, EAC, EADB, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Mull Sebujja KATENDE (since 8 September 2017)
chancery: 5911 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20011
telephone: [1] (202) 726-7100
FAX: [1] (202) 726-1727
email address and website:
washington@mofa.go.ug; info@ugandaembassysus.org; ambauganda@aol.com
https://washington.mofa.go.ug/
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Natalie E. BROWN (since 17 November 2020)
embassy: 1577 Ggaba Road, Kampala
mailing address: 2190 Kampala Place, Washington DC 20521-2190
telephone: [256] (0) 312-306-001
FAX: [256] (0) 414-259-794
email address and website:
KampalaUScitizen@state.gov
https://ug.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
six equal horizontal bands of black (top), yellow, red, black, yellow, and red; a white disk is superimposed at the center and depicts a grey crowned crane (the national symbol) facing the hoist side; black symbolizes the African people, yellow sunshine and vitality, red African brotherhood; the crane was the military badge of Ugandan soldiers under the UK
National symbol(s)
grey crowned crane; national colors: black, yellow, red
National anthem
name: Oh Uganda, Land of Beauty!
lyrics/music: George Wilberforce KAKOMOA
note: adopted 1962
Economy
Economic overview
Uganda has substantial natural resources, including fertile soils, regular rainfall, substantial reserves of recoverable oil, and small deposits of copper, gold, and other minerals. Agriculture is one of the most important sectors of the economy, employing 72% of the work force. The country’s export market suffered a major slump following the outbreak of conflict in South Sudan, but has recovered lately, largely due to record coffee harvests, which account for 16% of exports, and increasing gold exports, which account for 10% of exports. Uganda has a small industrial sector that is dependent on imported inputs such as refined oil and heavy equipment. Overall, productivity is hampered by a number of supply-side constraints, including insufficient infrastructure, lack of modern technology in agriculture, and corruption.
Uganda’s economic growth has slowed since 2016 as government spending and public debt has grown. Uganda’s budget is dominated by energy and road infrastructure spending, while Uganda relies on donor support for long-term drivers of growth, including agriculture, health, and education. The largest infrastructure projects are externally financed through concessional loans, but at inflated costs. As a result, debt servicing for these loans is expected to rise.
Oil revenues and taxes are expected to become a larger source of government funding as oil production starts in the next three to 10 years. Over the next three to five years, foreign investors are planning to invest $9 billion in production facilities projects, $4 billion in an export pipeline, as well as in a $2-3 billion refinery to produce petroleum products for the domestic and East African Community markets. Furthermore, the government is looking to build several hundred million dollars’ worth of highway projects to the oil region.
Uganda faces many economic challenges. Instability in South Sudan has led to a sharp increase in Sudanese refugees and is disrupting Uganda's main export market. Additional economic risks include: poor economic management, endemic corruption, and the government’s failure to invest adequately in the health, education, and economic opportunities for a burgeoning young population. Uganda has one of the lowest electrification rates in Africa - only 22% of Ugandans have access to electricity, dropping to 10% in rural areas.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$99.61 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$96.84 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$90.67 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
4.8% (2017 est.)
2.3% (2016 est.)
5.7% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$2,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$2,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$2,100 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$34.683 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.8% (2019 est.)
2.6% (2018 est.)
5.6% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: B+ (2015)
Moody's rating: B2 (2016)
Standard & Poors rating: B (2014)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 28.2% (2017 est.)
industry: 21.1% (2017 est.)
services: 50.7% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 74.3% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 8% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 23.9% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.3% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 18.8% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -25.1% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
sugar cane, plantains, cassava, maize, sweet potatoes, milk, vegetables, beans, bananas, sorghum
Industries
sugar processing, brewing, tobacco, cotton textiles; cement, steel production
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 71%
industry: 7%
services: 22% (2013 est.)
Population below poverty line
21.4% (2016 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
42.8 (2016 est.)
45.7 (2002)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2.4%
highest 10%: 36.1% (2009 est.)
Budget
revenues: 3.848 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 4.928 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
1 July - 30 June
Current account balance
-$1.212 billion (2017 est.)
-$707 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$6.12 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$5.63 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$5.958 billion (2017 est.)
Exports - partners
United Arab Emirates 58%, Kenya 9% (2019)
Exports - commodities
gold, coffee, milk, fish and fish products, tobacco (2019)
Imports
$9.54 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$8.65 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$7.44 billion (2017 est.)
Imports - partners
China 19%, India 17%, Kenya 16%, United Arab Emirates 7%, Japan 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
packaged medicines, aircraft, delivery trucks, cars, wheat (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$3.654 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$3.034 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
note: excludes gold
Debt - external
$13.85 billion (2019 est.)
$12.187 billion (2018 est.)
$6.241 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Ugandan shillings (UGX) per US dollar -
3,680 (2020 est.)
3,685 (2019 est.)
3,735 (2018 est.)
3,234.1 (2014 est.)
2,599.8 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 15.6%
male: 13.8%
female: 17.6% (2017 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 29% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 66% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 17% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
1.02 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127Electricity - from fossil fuels
19% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
68% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19Electricity - from other renewable sources
12% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74Refined petroleum products - consumption
32,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119Natural gas - proved reserves
14.16 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 90,774 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 27,688,987 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 60.53 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: telecom infrastructure has developed through private partnerships; as of 2018, fixed-fiber backbone infrastructure is available in over half of Uganda’s districts; mobile phone companies now provide 4G networks across all major cities and national parks, while offering 3G coverage in small cities and most rural areas with road access; price of commercial Internet services dropped substantially in 2019; consumers rely on mobile infrastructure to provide voice and broadband services as fixed-line infrastructure is poor; 5G migration is developing slowly; government commissioned broadband satellite services for rural areas in 2019 (2020)
domestic: fixed-line 1 per 100 and mobile- cellular systems teledensity about 57 per 100 persons; intercity traffic by wire, microwave radio relay, and radiotelephone communication stations (2019)
international: country code - 256; satellite earth stations - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) and 1 Inmarsat; analog and digital links to Kenya and Tanzania
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
public broadcaster, Uganda Broadcasting Corporation (UBC), operates radio and TV networks; 31 Free-To-Air (FTA) TV stations, 2 digital terrestrial TV stations, 3 cable TV stations, and 5 digital satellite TV stations; 258 operational FM stations
Internet users
total: 12.16 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 23.71% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 34,596 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 6 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 26
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 21,537 (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 5
over 3,047 m: 3
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2019)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 42
over 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 8
914 to 1,523 m: 26
under 914 m: 7 (2013)
Railways
total: 1,244 km (2014)
narrow gauge: 1,244 km 1.000-m gauge (2014)
Roadways
total: 20,544 km (excludes local roads) (2017)
paved: 4,257 km (2017)
unpaved: 16,287 km (2017)
Waterways
(there are no long navigable stretches of river in Uganda; parts of the Albert Nile that flow out of Lake Albert in the northwestern part of the country are navigable; several lakes including Lake Victoria and Lake Kyoga have substantial traffic; Lake Albert is navigable along a 200-km stretch from its northern tip to its southern shores) (2011)
Ports and terminals
lake port(s): Entebbe, Jinja, Port Bell (Lake Victoria)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Uganda People's Defense Force (UPDF): Land Forces, Air Forces, Marine Forces, Special Forces Command, Reserve Force (2021)
Military expenditures
2.5% of GDP (2020 est.)
2.1% of GDP (2019)
1.4% of GDP (2018)
1.5% of GDP (2017)
1.6% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; approximately 45-50,000 troops, including about 1,000-1,500 air and marine personnel (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the UPDF's inventory is mostly older Russian/Soviet-era equipment with a limited mix of more modern Russian- and Western-origin arms; since 2010, the leading suppliers of arms to the UPDF are Russia and Ukraine (2021)
Military deployments
6,200 Somalia (AMISOM); 620 Somalia (UNSOM); 250 Equatorial Guinea (2021)
Military service age and obligation
18-25 years of age for voluntary military duty (must be single, no children); 9-year service obligation (2021)
Military - note
the UPDF, which is constitutionally granted seats in parliament, is widely viewed as a key constituency for MUSEVENI; it has been used by MUSEVENI and the NRM to break up rallies, raid opposition offices, and surveil rival candidates
the UPDF has conducted operations in the Democratic Republic of the Congo against a Congo-based Ugandan rebel group, the Allied Democratic Forces (ADF), which was designated as a Foreign Terrorist Organization by the US State Department in March 2021 as the Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (ISIS-DRC; see the Terrorist Group Appendix); beginning in 2012, the UPDF also led regional efforts to pursue the Lord’s Resistance Army (LRA), a small, violent group of Ugandan origin that conducted widespread attacks against civilians in much of Central Africa; the UPDF withdrew from the mission in 2017 after declaring that the LRA no longer posed a security threat
Uganda intervened in the South Sudan civil war in 2013-2016 and UPDF forces have clashed with South Sudanese forces along the border as recently as 2020
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
al-Shabaab; Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham - Democratic Republic of Congo (ISIS-DRC)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Uganda is subject to armed fighting among hostile ethnic groups, rebels, armed gangs, militias, and various government forces that extend across its borders; Ugandan refugees as well as members of the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA) seek shelter in southern Sudan and the Democratic Republic of the Congo's Garamba National Park; LRA forces have also attacked Kenyan villages across the border
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 953,630 (South Sudan) (refugees and asylum seekers), 449,863 (Democratic Republic of the Congo), 51,775 (Burundi), 51,321 (Somalia) (refugees and asylum seekers), 25,507 (Rwanda), 19,468 (Eritrea) (2021)
Trafficking in persons
current situation: human traffickers exploit domestic and foreign victims in Uganda, and traffickers exploit victims from Uganda abroad; young Ugandan children are exploited in forced labor in agriculture, fishing, forestry, cattle herding, mining, stone quarrying, brick making, carpentry, steel manufacturing, street vending, bars, restaurants, gold mining, and domestic service; traffickers exploit girls and boys in commercial sex; most are children from the northeastern region and are exploited in forced begging, commercial sex in brothels, or sold in markets; traffickers compel children from the Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda, Burundi, Kenya, Tanzania, and South Sudan into forced agricultural labor and sex trafficking in Uganda; young women most at risk for transnational trafficking seek employment as domestic workers in the Middle East and then are exploited in sex trafficking; traffickers subject Ugandans to forced labor and sex trafficking in UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait, Iraq, Iran, Egypt, Turkey, Algeria, Malaysia, Thailand, Bahrain, Jordan, China, Kenya, and India; traffickers are often relatives, friends of victims, or religious leaders who receive a fee per worker from recruiters
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch list — Uganda does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking but is making significant efforts to do so; efforts include investigating allegations of complicit officials, implementing the protection and prevention provisions of the 2009 anti-trafficking act, convicting alleged traffickers, developing a plan for an anti-trafficking department within the police force; however, the government reported the lowest number of investigations in the past five years and a substantial decrease in prosecutions; authorities provided no training for law enforcement and immigration officials and identified fewer victims; the Coordination Office for Prevention of Trafficking in Persons is severely underfunded, stifling efforts to coordinate and combat trafficking; no systematic procedures to refer or assist victims have been developed, and the government provides no resources to NGOs for protective services; Uganda was downgraded to Tier 2 Watch List (2020)