Introduction
Background
The islands were first populated by voyagers from either Samoa or Tonga in the first millennium A.D., and Tuvalu provided a steppingstone for various Polynesian communities that subsequently settled in Melanesia and Micronesia. Tuvalu eventually came under Samoan and Tongan spheres of influence although proximity to Micronesia allowed some Micronesian communities to flourish in Tuvalu, in particular on Nui Atoll. In the late 1700s and early 1800s, Tuvalu was visited by a series of American, British, Dutch, and Russian ships. The islands were named the Ellice Islands in 1819. The first Christian missionaries arrived in 1861, eventually converting most of the population, and around the same time, several hundred Tuvaluans were kidnapped by people purporting to be missionaries and sent to work on plantations in Peru and Hawaii.
The UK declared a protectorate over the Ellice Islands in 1892 and merged it with the Micronesian Gilbert Islands. The Gilbert and Ellice Islands Protectorate became a colony in 1916. During World War II, the US set up military bases on a few islands, and in 1943, after Japan captured many of the northern Gilbert Islands, the UK transferred administration of the colony southward to Funafuti. After the war, Tarawa in the Gilbert Islands was once again made the colony’s capital and the center of power was firmly in the Gilbert Islands, including the colony’s only secondary school. Amid growing tensions with the Gilbertese, Tuvaluans voted to secede from the colony in 1974, were granted self-rule in 1975, and gained independence in 1978 as Tuvalu. In 1979, the US relinquished its claims to Tuvaluan islands in a treaty of friendship.
The Tuvalu Trust Fund was established in 1987 to provide a longterm economic future for the country. In 2000, Tuvalu negotiated a contract leasing its Internet domain name ".tv" for $50 million in royalties over a 12-year period. The contract was renewed in 2011 for a ten-year period. Tuvalu’s isolation means it sees few tourists; in 2020, Funafuti International Airport had four weekly flights - three to Suva, Fiji, and one to Tarawa. Tuvalu is highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change; in 2018, sea levels in Funafuti were rising twice as fast as global averages.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
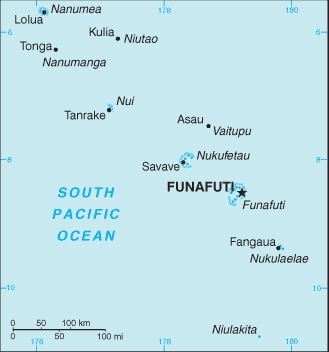
Oceania, island group consisting of nine coral atolls in the South Pacific Ocean, about half way from Hawaii to Australia
Geographic coordinates
8 00 S, 178 00 E
Map references
Oceania
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
24 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; moderated by easterly trade winds (March to November); westerly gales and heavy rain (November to March)
Terrain
low-lying and narrow coral atolls
Elevation
highest point: unnamed location 5 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 2 m
Natural resources
fish, coconut (copra)
Land use
agricultural land: 60% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 60% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0% (2018 est.)
forest: 33.3% (2018 est.)
other: 6.7% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
0 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
over half of the population resides on the atoll of Funafuti
Natural hazards
severe tropical storms are usually rare, but in 1997 there were three cyclones; low levels of islands make them sensitive to changes in sea level
Geography - note
one of the smallest and most remote countries on Earth; six of the nine coral atolls - Nanumea, Nui, Vaitupu, Nukufetau, Funafuti, and Nukulaelae - have lagoons open to the ocean; Nanumaya and Niutao have landlocked lagoons; Niulakita does not have a lagoon
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Tuvaluan(s)
adjective: Tuvaluan
Ethnic groups
Tuvaluan 86.8%, Tuvaluan/I-Kiribati 5.6%, Tuvaluan/other 6.7%, other 0.9% (2012 est.)
Languages
Tuvaluan (official), English (official), Samoan, Kiribati (on the island of Nui)
Religions
Protestant 92.4% (Congregational Christian Church of Tuvalu 85.7%, Brethren 3%, Seventh Day Adventist 2.8%, Assemblies of God .9%), Baha'i 2%, Jehovah's Witness 1.3%, Church of Jesus Christ 1%, other 3.1%, none 0.2% (2012 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 29.42% (male 1,711/female 1,626)
15-24 years: 17.61% (male 1,031/female 966)
25-54 years: 37.17% (male 2,157/female 2,059)
55-64 years: 9.12% (male 427/female 607)
65 years and over: 6.68% (male 289/female 469) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: NA
youth dependency ratio: NA
elderly dependency ratio: NA
potential support ratio: NA
Median age
total: 26.6 years
male: 25.6 years
female: 27.6 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
over half of the population resides on the atoll of Funafuti
Urbanization
urban population: 64.8% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 2.08% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
7,000 FUNAFUTI (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.7 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.62 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Infant mortality rate
total: 29.52 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 33.2 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 25.66 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 68.07 years
male: 65.67 years
female: 70.59 years (2021 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 98.8% of population
total: 99% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 1.2% of population
total: 1% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
19.1% (2018)
Physicians density
0.91 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 91.8% of population
rural: 91% of population
total: 91.5% of population
unimproved: urban: 9.2% of population
rural: 9% of population
total: 8.5% of population (2017 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 20.6%
male: 9.8%
female: 45.9% (2016)
Environment
Environment - current issues
water needs met by catchment systems; the use of sand as a building material has led to beachhead erosion; deforestation; damage to coral reefs from increasing ocean temperatures and acidification; rising sea levels threaten water table; in 2000, the government appealed to Australia and New Zealand to take in Tuvaluans if rising sea levels should make evacuation necessary
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 11.42 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 0.01 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 0.01 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; moderated by easterly trade winds (March to November); westerly gales and heavy rain (November to March)
Land use
agricultural land: 60% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 60% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0% (2018 est.)
forest: 33.3% (2018 est.)
other: 6.7% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 64.8% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 2.08% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 3,989 tons (2011 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 598 tons (2013 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 15% (2013 est.)
Total renewable water resources
0 cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Tuvalu
local long form: none
local short form: Tuvalu
former: Ellice Islands
etymology: "tuvalu" means "group of eight" or "eight standing together" referring to the country's eight traditionally inhabited islands
Government type
parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm
Capital
name: Funafuti; note - the capital is an atoll of some 29 islets; administrative offices are in Vaiaku Village on Fongafale Islet
geographic coordinates: 8 31 S, 179 13 E
time difference: UTC+12 (17 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the atoll is named after a founding ancestor chief, Funa, from the island of Samoa
Administrative divisions
7 island councils and 1 town council*; Funafuti*, Nanumaga, Nanumea, Niutao, Nui, Nukufetau, Nukulaelae, Vaitupu
Independence
1 October 1978 (from the UK)
National holiday
Independence Day, 1 October (1978)
Constitution
history: previous 1978 (at independence); latest effective 1 October 1986
amendments: proposed by the House of Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly membership in the final reading; amended 2007, 2010, 2013; note - in 2016, the United Nations Development Program and the Tuvaluan Government initiated a review of the country's constitution, which was ongoing as of early 2021
Legal system
mixed legal system of English common law and local customary law
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes; for a child born abroad, at least one parent must be a citizen of Tuvalu
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: na
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Acting Governor General Teniku TALESI Honolulu
(since 19 August 2019)
head of government: Prime Minister Kausea NATANO (since 19 September 2019)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the governor general on recommendation of the prime minister
elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch on recommendation of the prime minister; prime minister and deputy prime minister elected by and from members of House of Assembly following parliamentary elections
election results: Kausea NATANO elected prime minister by House of Assembly; House of Assembly vote count on 19 September 2019 - 10 to 6
Legislative branch
description: unicameral House of Assembly or Fale I Fono (16 seats; members directly elected in single- and multi-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 9 September 2019 (next to be held on September 2023)
election results: percent of vote - NA; seats - independent 16 (9 members reelected)
Judicial branch
highest courts: Court of Appeal (consists of the chief justice and not less than 3 appeals judges); High Court (consists of the chief justice); appeals beyond the Court of Appeal are heard by the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London)
judge selection and term of office: Court of Appeal judges appointed by the governor general on the advice of the Cabinet; judge tenure based on terms of appointment; High Court chief justice appointed by the governor general on the advice of the Cabinet; chief justice serves for life; other judges appointed by the governor general on the advice of the Cabinet after consultation with chief justice; judge tenure set by terms of appointment
subordinate courts: magistrates' courts; island courts; land courts
Political parties and leaders
there are no political parties but members of parliament usually align themselves in informal groupings
International organization participation
ACP, ADB, AOSIS, C, FAO, IBRD, IDA, IFAD, IFRCS (observer), ILO, IMF, IMO, IOC, ITU, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: none; the Tuvalu Permanent Mission to the UN serves as the Embassy; it is headed by Samuelu LALONIU (since 21 July 2017); address: 685 Third Avenue, Suite 1104, New York, NY 10017; telephone: [1] (212) 490-0534; FAX: [1] (212) 808-4975; email: tuvalumission.un@gmail.com
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: the US does not have an embassy in Tuvalu; the US Ambassador to Fiji is accredited to Tuvalu
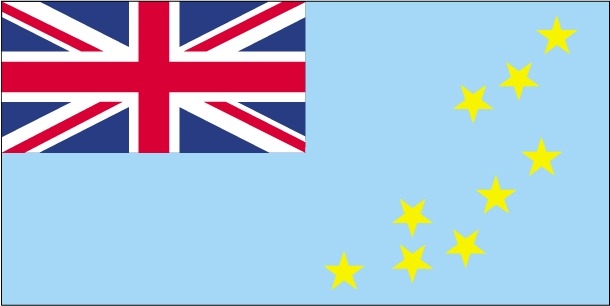
Flag description
light blue with the flag of the UK in the upper hoist-side quadrant; the outer half of the flag represents a map of the country with nine yellow, five-pointed stars on a blue field symbolizing the nine atolls in the ocean
National symbol(s)
maneapa (native meeting house); national colors: light blue, yellow
National anthem
name: "Tuvalu mo te Atua" (Tuvalu for the Almighty)
lyrics/music: Afaese MANOA
note: adopted 1978; the anthem's name is also the nation's motto
Economy
Economic overview
Tuvalu consists of a densely populated, scattered group of nine coral atolls with poor soil. Only eight of the atolls are inhabited. It is one of the smallest countries in the world, with its highest point at 4.6 meters above sea level. The country is isolated, almost entirely dependent on imports, particularly of food and fuel, and vulnerable to climate change and rising sea levels, which pose significant challenges to development.
The public sector dominates economic activity. Tuvalu has few natural resources, except for its fisheries. Earnings from fish exports and fishing licenses for Tuvalu’s territorial waters are a significant source of government revenue. In 2013, revenue from fishing licenses doubled and totaled more than 45% of GDP.
Official aid from foreign development partners has also increased. Tuvalu has substantial assets abroad. The Tuvalu Trust Fund, an international trust fund established in 1987 by development partners, has grown to $104 million (A$141 million) in 2014 and is an important cushion for meeting shortfalls in the government's budget. While remittances are another substantial source of income, the value of remittances has declined since the 2008-09 global financial crisis, but has stabilized at nearly $4 million per year. The financial impact of climate change and the cost of climate related adaptation projects is one of many concerns for the nation.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$50 million note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$50 million note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$50 million note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
3.2% (2017 est.)
3% (2016 est.)
9.1% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$4,400 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$4,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$3,900 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$40 million (2017 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
4.1% (2017 est.)
3.5% (2016 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 24.5% (2012 est.)
industry: 5.6% (2012 est.)
services: 70% (2012 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 87% (2016 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 24.3% (2016 est.)
exports of goods and services: 43.7% (2016 est.)
imports of goods and services: -66.1% (2016 est.)
Agricultural products
coconuts, vegetables, tropical fruit, bananas, roots/tubers nes, pork, poultry, eggs, pig fat, pig offals
Industries
fishing
Labor force - by occupation
note: most people make a living through exploitation of the sea, reefs, and atolls - and through overseas remittances (mostly from workers in the phosphate industry and sailors)
Population below poverty line
26.3% (2010 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
39.1 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 42.68 million (2013 est.)
expenditures: 32.46 million (2012 est.)
note: revenue data include Official Development Assistance from Australia
Taxes and other revenues
106.7% (of GDP) (2013 est.)
note: revenue data include Official Development Assistance from Australia
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
$2 million (2017 est.)
$8 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$10 million note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$10 million note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
Thailand 50%, Indonesia 40% (2019)
Exports - commodities
fish, ships, coins, metal-clad products, electrical power accessories (2019)
Imports
$70 million note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$60 million note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
China 32%, Japan 29%, Fiji 23%, New Zealand 6% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, fishing ships, tug boats, other ships, iron structures (2019)
Exchange rates
Tuvaluan dollars or Australian dollars (AUD) per US dollar -
1.311 (2017 est.)
1.3442 (2016 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 20.6%
male: 9.8%
female: 45.9% (2016)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - from fossil fuels
96% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2014)
country comparison to the world: 202Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
0% of total installed capacity (2014)
country comparison to the world: 209Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 2,000 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 17.59 (2018 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 8,000 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 70.36 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: internal communications needs met; small global scale of over 11,000 people on 9 inhabited islands; mobile subscriber penetration about 40% and broadband about 10% penetration; govt. owned and sole provider of telecommunications services; 2G widespread; the launch in 2019 of the Kacific-1 satellite will improve the telecommunication sector for the Asia Pacific region (2020)
domestic: radiotelephone communications between islands; fixed-line 18 per 100 and mobile-cellular 70 per 100 (2019)
international: country code - 688; international calls can be made by satellite
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
no TV stations; many households use satellite dishes to watch foreign TV stations; 1 government-owned radio station, Radio Tuvalu, includes relays of programming from international broadcasters (2019)
Internet users
total: 5,849 (2021 est.)
percent of population: 49.32% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 450 (2017 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3.96 (2019 est.)
Transportation
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2013)
Merchant marine
total: 245
by type: bulk carrier 22, container ship 3, general cargo 32, oil tanker 21, other 167 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Funafuti
Military and Security
Military and security forces
no regular military forces; Tuvalu Police Force (Ministry of Justice, Communications, and Foreign Affairs)
Military - note
Australia provides support to the Tuvalu Police Force, including donations of patrol boats