Turkmenistan
Introduction
Background
Present-day Turkmenistan covers territory that has been at the crossroads of civilizations for centuries. The area was ruled in antiquity by various Persian empires, and was conquered by Alexander the Great, Muslim armies, the Mongols, Turkic warriors, and eventually the Russians. In medieval times, Merv (located in present-day Mary province) was one of the great cities of the Islamic world and an important stop on the Silk Road. Annexed by Russia in the late 1800s, Turkmen territories later figured prominently in the anti-Bolshevik resistance in Central Asia. In 1924, Turkmenistan became a Soviet republic; it achieved independence upon the dissolution of the USSR in 1991. President for Life Saparmyrat NYYAZOW died in December 2006, and Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW, a deputy chairman under NYYAZOW, emerged as the country's new president. BERDIMUHAMEDOW won Turkmenistan's first multi-candidate presidential election in February 2007, and again in 2012 and in 2017 with over 97% of the vote in both instances, in elections widely regarded as undemocratic.
Turkmenistan has sought new export markets for its extensive hydrocarbon/natural gas reserves, which have yet to be fully exploited. As of late 2021, Turkmenistan exported the majority of its gas to China and smaller levels of gas to Russia. Turkmenistan's reliance on gas exports has made the economy vulnerable to fluctuations in the global energy market, and economic hardships since the drop in energy prices in 2014 have led many Turkmenistanis to emigrate, mostly to Turkey.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
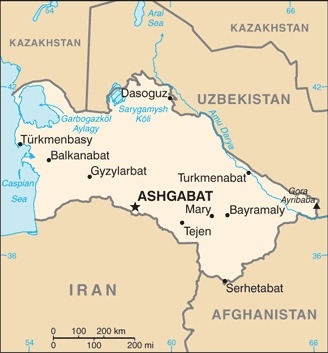
Location
Central Asia, bordering the Caspian Sea, between Iran and Kazakhstan
Geographic coordinates
40 00 N, 60 00 E
Map references
Asia
Area - comparative
slightly more than three times the size of Georgia; slightly larger than California
Land boundaries
total: 4,158 km
border countries (4): Afghanistan 804 km, Iran 1148 km, Kazakhstan 413 km, Uzbekistan 1793 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked); note - Turkmenistan borders the Caspian Sea (1,768 km)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
subtropical desert
Terrain
flat-to-rolling sandy desert with dunes rising to mountains in the south; low mountains along border with Iran; borders Caspian Sea in west
Elevation
highest point: Gora Ayribaba 3,139 m
lowest point: Vpadina Akchanaya (Sarygamysh Koli is a lake in northern Turkmenistan with a water level that fluctuates above and below the elevation of Vpadina Akchanaya, the lake has dropped as low as -110 m) -81 m
mean elevation: 230 m
Natural resources
petroleum, natural gas, sulfur, salt
Land use
agricultural land: 72% (2018 est.)
arable land: 4.1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.1% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 67.8% (2018 est.)
forest: 8.8% (2018 est.)
other: 19.2% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
19,950 sq km (2012)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Salt water lake(s): Caspian Sea (shared with Iran, Azerbaijan, Russia, and Kazakhstan) - 374,000 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Amu Darya (shared with Tajikistan [s], Afghanistan, and Uzbekistan [m]) - 2,620 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: (Aral Sea basin) Amu Darya (534,739 sq km)
Population distribution
the most densely populated areas are the southern, eastern, and northeastern oases; approximately 50% of the population lives in and around the capital of Ashgabat
Natural hazards
earthquakes; mudslides; droughts; dust storms; floods
Geography - note
landlocked; the western and central low-lying desolate portions of the country make up the great Garagum (Kara-Kum) desert, which occupies over 80% of the country; eastern part is plateau
People and Society
Population
5,579,889 (July 2021 est.)
note: some sources suggest Turkmenistan's population could be as much as 1 to 2 million people lower than available estimates because of large-scale emigration during the last 10 years
Nationality
noun: Turkmenistani(s)
adjective: Turkmenistani
Ethnic groups
Turkmen 85%, Uzbek 5%, Russian 4%, other 6% (2003 est.)
Languages
Turkmen (official) 72%, Russian 12%, Uzbek 9%, other 7%
major-language sample(s):
Dünýä Facebooky, esasy maglumat üçin aýrylmaz bir çeşme dir. (Turkmen)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Muslim 93%, Christian 6.4%, Buddhist <1%, folk religion <1%, Jewish <1%, other <1%, unspecified <1% (2020 est.)
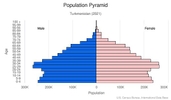
Age structure
0-14 years: 25.44% (male 713,441/female 693,042)
15-24 years: 16.48% (male 458,566/female 452,469)
25-54 years: 44.14% (male 1,214,581/female 1,226,027)
55-64 years: 8.56% (male 221,935/female 251,238)
65 years and over: 5.38% (male 129,332/female 167,996) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 55.2
youth dependency ratio: 47.8
elderly dependency ratio: 7.4
potential support ratio: 13.5 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 29.2 years
male: 28.7 years
female: 29.7 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
the most densely populated areas are the southern, eastern, and northeastern oases; approximately 50% of the population lives in and around the capital of Ashgabat
Urbanization
urban population: 53% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 2.23% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
865,000 ASHGABAT (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.88 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
24.2 years (2019)
Maternal mortality ratio
7 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157Infant mortality rate
total: 38.54 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 46.87 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 29.79 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 71.54 years
male: 68.5 years
female: 74.73 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
49.7% (2019)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
6.6% (2018)
Physicians density
2.23 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
Hospital bed density
4 beds/1,000 population (2014)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.7%
male: 99.8%
female: 99.6% (2015)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 13 years
male: 13 years
female: 13 years (2020)
Environment
Environment - current issues
contamination of soil and groundwater with agricultural chemicals, pesticides; salination, water logging of soil due to poor irrigation methods; Caspian Sea pollution; diversion of a large share of the flow of the Amu Darya into irrigation contributes to that river's inability to replenish the Aral Sea; soil erosion; desertification
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 19.02 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 70.63 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 52.09 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
subtropical desert
Land use
agricultural land: 72% (2018 est.)
arable land: 4.1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.1% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 67.8% (2018 est.)
forest: 8.8% (2018 est.)
other: 19.2% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 53% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 2.23% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 198Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 500,000 tons (2013 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Salt water lake(s): Caspian Sea (shared with Iran, Azerbaijan, Russia, and Kazakhstan) - 374,000 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Amu Darya (shared with Tajikistan [s], Afghanistan, and Uzbekistan [m]) - 2,620 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: (Aral Sea basin) Amu Darya (534,739 sq km)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 755 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 839 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 26.36 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
24.765 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Turkmenistan
local long form: none
local short form: Turkmenistan
former: Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic
etymology: the suffix "-stan" means "place of" or "country," so Turkmenistan literally means the "Land of the Turkmen [people]"
Government type
presidential republic; authoritarian
Capital
name: Ashgabat (Ashkhabad)
geographic coordinates: 37 57 N, 58 23 E
time difference: UTC+5 (10 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: derived from the Persian words "eshq" meaning "love" and "abad" meaning "inhabited place" or "city," and so loosely translates as "the city of love"
Administrative divisions
5 provinces (welayatlar, singular - welayat) and 1 independent city*: Ahal Welayaty (Anew), Ashgabat*, Balkan Welayaty (Balkanabat), Dasoguz Welayaty, Lebap Welayaty (Turkmenabat), Mary Welayaty
note: administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers (exceptions have the administrative center name following in parentheses)
Independence
27 October 1991 (from the Soviet Union)
National holiday
Independence Day, 27 October (1991)
Constitution
history: several previous; latest adopted 14 September 2016
amendments: proposed by the Mejlisi; passage requires two-thirds majority vote or absolute majority approval in a referendum; amended several times, last in 2020 (changed legislature to bicameral)
Legal system
civil law system with Islamic (sharia) law influences
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Turkmenistan
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW (since 14 February 2007); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW (since 14 February 2007)
cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 7-year term (no term limits); election last held on 12 February 2017 (next to be held in February 2024)
election results:
2017: Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW reelected president in the first round; percent of vote - Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW (DPT) 97.7%, other 2.3%
2012: Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW reelected president; percent of vote - Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW 97.1%, Annageldi YAZMYRADOW 1.1%, other candidates 1.8%
Legislative branch
description: bicameral National Council or Milli Genesi consists of:
People's Council or Halk Maslahaty (56 seats; 48 members indirectly elected by provincial councils and 8 members appointed by the president)
Assembly or Mejlisi (125 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by absolute majority vote in 2 rounds if needed to serve 5-year terms)
note: in September 2020, the Turkmenistani legislature (Milli Genesi) adopted a constitutional amendment creating an upper chamber, making the legislature bicameral; the chairperson of the Halk Maslahaty is now designated as the constitutional successor to the presidency; as of April 2021, Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW serves in this position in addition to being president
elections: People's Council - first held on 28 March 2021 for 48 indirectly elected members (next to be held in 2026); first held on 14 April 2021 for 8 presidentially appointed members (next to be held NA)
Assembly - last held on 25 March 2018 (next to be held NA)
election results: People's Council - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - DPT 3, independent 45; composition - men 42, women 14, percent of women 32.3%
Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - DPT 55, APT 11, PIE 11, independent 48 (individuals nominated by citizen groups); composition (as of March 2018) - men 94, women 31, percent of women 24.8%; note - total percent of National Council percent of women 24.9%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court of Turkmenistan (consists of the court president and 21 associate judges and organized into civil, criminal, and military chambers)
judge selection and term of office: judges appointed by the president for 5-year terms
subordinate courts: High Commercial Court; appellate courts; provincial, district, and city courts; military courts
Political parties and leaders
Agrarian Party of Turkmenistan or APT [Basim ANNAGURBANOW]
Democratic Party of Turkmenistan or DPT [Ata SERDAROW]
Party of Industrialists and Entrepreneurs or PIE [Saparmyrat OWGANOW]
note: all of these parties support President BERDIMUHAMEDOW; a law authorizing the registration of political parties went into effect in January 2012; unofficial, small opposition movements exist abroad
International organization participation
ADB, CIS (associate member, has not ratified the 1993 CIS charter although it participates in meetings and held the chairmanship of the CIS in 2012), EAPC, EBRD, ECO, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), ISO (correspondent), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, OSCE, PFP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Meret ORAZOW (since 14 February 2001)
chancery: 2207 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 588-1500
FAX: [1] (202) 588-1500
email address and website:
turkmenembassyus@verizon.net
https://usa.tmembassy.gov.tm/en
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Matthew S. KLIMOW (since 26 June 2019)
embassy: 9 1984 Street (formerly Pushkin Street), Ashgabat 744000
mailing address: 7070 Ashgabat Place, Washington, DC 20521-7070
telephone: [993] (12) 94-00-45
FAX: [993] (12) 94-26-14
email address and website:
ConsularAshgab@state.gov
https://tm.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
green field with a vertical red stripe near the hoist side, containing five tribal guls (designs used in producing carpets) stacked above two crossed olive branches; five white, five-pointed stars and a white crescent moon appear in the upper corner of the field just to the fly side of the red stripe; the green color and crescent moon represent Islam; the five stars symbolize the regions or welayats of Turkmenistan; the guls reflect the national identity of Turkmenistan where carpet-making has long been a part of traditional nomadic life
note: the flag of Turkmenistan is the most intricate of all national flags
National symbol(s)
Akhal-Teke horse; national colors: green, white
National anthem
name: "Garassyz, Bitarap Turkmenistanyn" (Independent, Neutral, Turkmenistan State Anthem)
lyrics/music: collective/Veli MUKHATOV
note: adopted 1997, lyrics revised in 2008, to eliminate references to deceased President Saparmurat NYYAZOW
Economy
Economic overview
Turkmenistan is largely a desert country with intensive agriculture in irrigated oases and significant natural gas and oil resources. The two largest crops are cotton, most of which is produced for export, and wheat, which is domestically consumed. Although agriculture accounts for almost 8% of GDP, it continues to employ nearly half of the country's workforce. Hydrocarbon exports, the bulk of which is natural gas going to China, make up 25% of Turkmenistan’s GDP. Ashgabat has explored two initiatives to bring gas to new markets: a trans-Caspian pipeline that would carry gas to Europe and the Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India gas pipeline. Both face major financing, political, and security hurdles and are unlikely to be completed soon.
Turkmenistan’s autocratic governments under presidents NIYAZOW (1991-2006) and BERDIMUHAMEDOW (since 2007) have made little progress improving the business climate, privatizing state-owned industries, combatting corruption, and limiting economic development outside the energy sector. High energy prices in the mid-2000s allowed the government to undertake extensive development and social spending, including providing heavy utility subsidies.
Low energy prices since mid-2014 are hampering Turkmenistan’s economic growth and reducing government revenues. The government has cut subsidies in several areas, and wage arrears have increased. In January 2014, the Central Bank of Turkmenistan devalued the manat by 19%, and downward pressure on the currency continues. There is a widening spread between the official exchange rate (3.5 TMM per US dollar) and the black market exchange rate (approximately 14 TMM per US dollar). Currency depreciation and conversion restrictions, corruption, isolationist policies, and declining spending on public services have resulted in a stagnate economy that is nearing crisis. Turkmenistan claims substantial foreign currency reserves, but non-transparent data limit international institutions’ ability to verify this information.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$92.33 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$86.86 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
$81.787 billion (2017 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
6.5% (2017 est.)
6.2% (2016 est.)
6.5% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$15,500 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$14,800 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
$14,205 (2017 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$40.819 billion (2018 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 7.5% (2017 est.)
industry: 44.9% (2017 est.)
services: 47.7% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 50% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 10% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 28.2% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 26.2% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -14.3% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
milk, wheat, cotton, tomatoes, potatoes, watermelons, grapes, sugar beet, beef, rice
Industries
natural gas, oil, petroleum products, textiles, food processing
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 48.2%
industry: 14%
services: 37.8% (2004 est.)
Population below poverty line
0.2% (2012 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
40.8 (1998)
country comparison to the world: 58Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2.6%
highest 10%: 31.7% (1998)
Budget
revenues: 5.657 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 6.714 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$4.359 billion (2017 est.)
-$7.207 billion (2016 est.)
Exports - partners
China 82% (2019)
Exports - commodities
natural gas, refined petroleum, crude petroleum, cotton fibers, fertilizers (2019)
Imports - partners
Turkey 25%, Russia 18%, China 14%, Germany 6% (2019)
Imports - commodities
iron products, harvesting machinery, packaged medicines, broadcasting equipment, tractors (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$24.91 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$25.05 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$539.4 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$425.3 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Turkmenistani manat (TMM) per US dollar -
4.125 (2017 est.)
3.5 (2016 est.)
3.5 (2015 est.)
3.5 (2014 est.)
2.85 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
4.001 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88Electricity - from fossil fuels
100% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 207Electricity - from other renewable sources
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 210Refined petroleum products - production
191,100 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52Refined petroleum products - consumption
160,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63Natural gas - proved reserves
7.504 trillion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 682,000 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 11.85 (2018 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 9.377 million (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 162.9 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: stagnant economy, rural geography, and authoritarian rule limit development of the telecom sector; in cooperation with Russian-based partners, operators have installed high-speed fiber-optic lines and upgraded most of the country's telephone switch centers with digital technology; some rural areas lack fixed-line coverage; mobile broadband is in the early stages of development; services are extremely slow, though Trans-Caspian cable will provide international Internet capacity and improvement in services; freedom of press and expression restricted through monitoring, media interruption, and removal of receivers from households; importer of broadcasting equipment from UAE (2020)
domestic: fixed-line 12 per 100 and mobile-cellular teledensity is about 163 per 100 persons; first telecommunication satellite was launched in 2015 (2019)
international: country code - 993; linked by fiber-optic cable and microwave radio relay to other CIS republics and to other countries by leased connections to the Moscow international gateway switch; an exchange in Ashgabat switches international traffic through Turkey via Intelsat; satellite earth stations - 1 Orbita and 1 Intelsat (2018)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
broadcast media is government controlled and censored; 7 state-owned TV and 4 state-owned radio networks; satellite dishes and programming provide an alternative to the state-run media; officials sometimes limit access to satellite TV by removing satellite dishes
Internet users
total: 2.01 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 21.25% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 5,000 (2017 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2019 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 27
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 2,457,474 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 16.92 million mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 21
over 3,047 m: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 9
1,524 to 2,437 m: 9
914 to 1,523 m: 2 (2013)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
under 914 m: 4 (2013)
Heliports
1 (2013)
Pipelines
7500 km gas, 1501 km oil (2013)
Railways
total: 5,113 km (2017)
broad gauge: 5,113 km 1.520-m gauge (2017)
Roadways
total: 58,592 km (2002)
paved: 47,577 km (2002)
unpaved: 11,015 km (2002)
Waterways
1,300 km (Amu Darya River and Kara Kum Canal are important inland waterways) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 55Merchant marine
total: 73
by type: general cargo 6, oil tanker 8, other 59 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Caspian Sea - Turkmenbasy
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Armed Forces of Turkmenistan: Land Forces, Navy, Air and Air Defense Forces; Federal Border Guard Service (2021)
Military expenditures
0.9% of GDP (2020 est.)
0.9% of GDP (2019 est.)
1% of GDP (2018 est.)
1.8% of GDP (2017 est.)
1.7% of GDP (2016 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; estimated 30,000 active troops (est. 25,000 National Army; 1,000 Navy; 4,000 Air and Air Defense Forces) (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the inventory for Turkmenistan's military is comprised almost entirely of older Russian and Soviet-era weapons systems, although in recent years, Turkmenistan has purchased some equipment, including aircraft and air defense systems, from other countries; since 2010, China, Russia, and Turkey are the leading arms suppliers to Turkmenistan (2021)
Military service age and obligation
18-30 years of age for compulsory male military service; 2-year conscript service obligation (2.5 years for the Navy); 20 years of age for voluntary service; males may enroll in military schools from age 15 (2021)
Military - note
as of 2021, Turkmenistan continued to pursue a nationalist and isolationist security policy and has declined to participate in post-Soviet military groupings such as the Collective Security Treaty Organization military alliance (CSTO) and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO); however, in September 2020, it participated in a Russian-led multinational military exercise held in southern Russia’s Astrakhan region alongside Russian, Chinese, Pakistani, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Tajik, Uzbek, Mongolian, Syrian, Iranian, Egyptian, Belarusian, Turkish, Armenian, and Azerbaijani contingents
as of 2021, Turkmenistan was trying to improve its naval capabilities on the Caspian Sea by expanding ship building capabilities and adding larger vessels to the Navy’s inventory; in 2018, it opened its first naval shipyard and in August 2021, the Navy commissioned its largest warship, a corvette that was jointly constructed with Turkey
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
cotton monoculture in Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan creates water-sharing difficulties for Amu Darya river states; field demarcation of the boundaries with Kazakhstan commenced in 2005; bilateral talks continue with Azerbaijan on dividing the seabed and contested oilfields in the middle of the Caspian
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 3,924 (2020)
Trafficking in persons
current situation: Turkmenistan is a source, and to a much lesser degree, destination country for men, women, and children who are subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; Turkmen in search of work in other countries are forced to work in textile sweatshops, construction, and domestic service; some Turkmen women and girls are sex trafficked abroad; Turkey is the primary trafficking destination, followed by Russia, India, and other countries in the Middle East, South and Central Asia, and Europe; labor trafficking occurs within Turkmenistan, particularly in the construction industry; government officials require employees in private sector institutions, soldiers, and public sector workers to pick cotton without payment under the threat of penalty, such as dismissal, reduced work hours, or salary deductions to meet government-imposed quotas for the cotton harvest
tier rating: Tier 3 — Turkmenistan does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; the government approved the 2020-2022 national action plan, continued anti-trafficking awareness campaigns, worked with international organizations on combating trafficking, provided training to its diplomatic corps on human trafficking, and identified potential trafficking victims at the international airport; however, the government used forced labor in the cotton harvest and public works projects; no officials were held accountable for their role in trafficking crimes; authorities did not prosecute or convict any traffickers; no victims were identified and offered protection or assistance programs (2020)
Illicit drugs
transit country for Afghan opiates to Turkish, Russian, and European markets, either directly from Afghanistan or through Iran; not a major producer or source country for illegal drugs or precursor chemicals