Introduction
Background
First explored by the Spaniards in the 16th century and then settled by the English in the mid-17th century, Suriname became a Dutch colony in 1667. With the abolition of African slavery in 1863, workers were brought in from India and Java. The Netherlands granted the colony independence in 1975. Five years later the civilian government was replaced by a military regime that soon declared Suriname a socialist republic. It continued to exert control through a succession of nominally civilian administrations until 1987, when international pressure finally forced a democratic election. In 1990, the military overthrew the civilian leadership, but a democratically elected government - a four-party coalition - returned to power in 1991. The coalition expanded to eight parties in 2005 and ruled until August 2010, when voters returned former military leader Desire BOUTERSE and his opposition coalition to power. President BOUTERSE was reelected unopposed in 2015.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between French Guiana and Guyana
Geographic coordinates
4 00 N, 56 00 W
Map references
South America
Land boundaries
total: 1,907 km
border countries (3): Brazil 515 km, French Guiana 556 km, Guyana 836 km
Coastline
386 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; moderated by trade winds
Terrain
mostly rolling hills; narrow coastal plain with swamps
Elevation
highest point: Juliana Top 1,230 m
lowest point: unnamed location in the coastal plain -2 m
mean elevation: 246 m
Natural resources
timber, hydropower, fish, kaolin, shrimp, bauxite, gold, and small amounts of nickel, copper, platinum, iron ore
Land use
agricultural land: 0.5% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 94.6% (2018 est.)
other: 4.9% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
570 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Amazon (6,145,186 sq km)
Population distribution
population concentrated along the nothern coastal strip; the remainder of the country is sparsely populated
Natural hazards
flooding
Geography - note
smallest independent country on South American continent; mostly tropical rain forest; great diversity of flora and fauna that, for the most part, is increasingly threatened by new development; relatively small population, mostly along the coast
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Surinamer(s)
adjective: Surinamese
Ethnic groups
Hindustani (also known locally as "East Indians"; their ancestors emigrated from northern India in the latter part of the 19th century) 27.4%, Maroon (their African ancestors were brought to the country in the 17th and 18th centuries as slaves and escaped to the interior) 21.7%, Creole (mixed White and Black) 15.7%, Javanese 13.7%, mixed 13.4%, other 7.6%, unspecified 0.6% (2012 est.)
Languages
Dutch (official), English (widely spoken), Sranang Tongo (Surinamese, sometimes called Taki-Taki, is the native language of Creoles and much of the younger population and is lingua franca among others), Caribbean Hindustani (a dialect of Hindi), Javanese
major-language sample(s):
Het Wereld Feitenboek, een omnisbare bron van informatie. (Dutch)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information. (English)
Religions
Protestant 23.6% (includes Evangelical 11.2%, Moravian 11.2%, Reformed .7%, Lutheran .5%), Hindu 22.3%, Roman Catholic 21.6%, Muslim 13.8%, other Christian 3.2%, Winti 1.8%, Jehovah's Witness 1.2%, other 1.7%, none 7.5%, unspecified 3.2% (2012 est.)
Demographic profile
Suriname is a pluralistic society consisting primarily of Creoles (persons of mixed African and European heritage), the descendants of escaped African slaves known as Maroons, and the descendants of Indian and Javanese (Indonesian) contract workers. The country overall is in full, post-industrial demographic transition, with a low fertility rate, a moderate mortality rate, and a rising life expectancy. However, the Maroon population of the rural interior lags behind because of lower educational attainment and contraceptive use, higher malnutrition, and significantly less access to electricity, potable water, sanitation, infrastructure, and health care.
Some 350,000 people of Surinamese descent live in the Netherlands, Suriname's former colonial ruler. In the 19th century, better-educated, largely Dutch-speaking Surinamese began emigrating to the Netherlands. World War II interrupted the outflow, but it resumed after the war when Dutch labor demands grew - emigrants included all segments of the Creole population. Suriname still is strongly influenced by the Netherlands because most Surinamese have relatives living there and it is the largest supplier of development aid. Other emigration destinations include French Guiana and the United States. Suriname's immigration rules are flexible, and the country is easy to enter illegally because rainforests obscure its borders. Since the mid-1980s, Brazilians have settled in Suriname's capital, Paramaribo, or eastern Suriname, where they mine gold. This immigration is likely to slowly re-orient Suriname toward its Latin American roots.
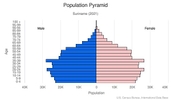
Age structure
0-14 years: 23.38% (male 72,642/female 69,899)
15-24 years: 17.2% (male 53,427/female 51,438)
25-54 years: 44.09% (male 136,889/female 131,868)
55-64 years: 8.78% (male 26,435/female 27,066)
65 years and over: 6.55% (male 17,437/female 22,468) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 51.1
youth dependency ratio: 40.3
elderly dependency ratio: 10.8
potential support ratio: 9.3 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 31 years
male: 30.6 years
female: 31.4 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
population concentrated along the nothern coastal strip; the remainder of the country is sparsely populated
Urbanization
urban population: 66.2% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 0.88% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
239,000 PARAMARIBO (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.78 male(s)/female
total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
120 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65Infant mortality rate
total: 26.6 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 31.72 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 21.23 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 73.57 years
male: 71.09 years
female: 76.16 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
39.1% (2018)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 98.2% of population
rural: 92% of population
total: 96.6% of population
unimproved: urban: 1.8% of population
rural: 8% of population
total: 3.4% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
8% (2018)
Physicians density
1.21 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
Hospital bed density
3 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 98.5% of population
rural: 88.2% of population
total: 95% of population
unimproved: urban: 1.5% of population
rural: 11.8% of population
total: 5% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<200 (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 94.4%
male: 96.1%
female: 92.7% (2018)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 26.5%
male: 18.7%
female: 39.9% (2016 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation as timber is cut for export; pollution of inland waterways by small-scale mining activities
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 23.6 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 1.74 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 2.28 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; moderated by trade winds
Land use
agricultural land: 0.5% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 94.6% (2018 est.)
other: 4.9% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 66.2% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 0.88% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 2.36% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 78,620 tons (2010 est.)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Amazon (6,145,186 sq km)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 49.3 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 135.5 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 431.1 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
99 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Suriname
conventional short form: Suriname
local long form: Republiek Suriname
local short form: Suriname
former: Netherlands Guiana, Dutch Guiana
etymology: name may derive from the indigenous "Surinen" people who inhabited the area at the time of European contact
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Paramaribo
geographic coordinates: 5 50 N, 55 10 W
time difference: UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name may be the corruption of a Carib (Kalina) village or tribe named Parmirbo
Administrative divisions
10 districts (distrikten, singular - distrikt); Brokopondo, Commewijne, Coronie, Marowijne, Nickerie, Para, Paramaribo, Saramacca, Sipaliwini, Wanica
Independence
25 November 1975 (from the Netherlands)
National holiday
Independence Day, 25 November (1975)
Constitution
history: previous 1975; latest ratified 30 September 1987, effective 30 October 1987
amendments: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the total membership; amended 1992
Legal system
civil law system influenced by Dutch civil law; note - a new criminal code was enacted in 2017
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Suriname
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Chandrikapersad SANTOKHI (since 16 July 2020); Vice President Ronnie BRUNSWIJK (since 16 July 2020); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Chandrikapersad SANTOKHI (since 16 July 2020); Vice President Ronnie BRUNSWIJK (since 16 July 2020)
cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president and vice president indirectly elected by the National Assembly; president and vice president serve a 5-year term (no term limits); election last held on 13 July 2020 (next to be held in May 2025)
election results: Chandrikapersad SANTOKHI elected president unopposed; National Assembly vote - NA
Legislative branch
description: unicameral National Assembly or Nationale Assemblee (51 seats; members directly elected in 10 multi-seat constituencies by party-list proportional representation vote using the D'Hondt method to serve 5-year terms)
elections: last held on 25 May 2020 (next to be held in May 2025)
election results: percent of vote by party - VHP 41.1%, NDP 29.4%, ABOP 17.6%, NPS 7.8%, other 3.9%; seats by party - VHP 21, NDP 15, ABOP 9, NPS 4, other 2; composition - men 35, women 16, percent of women 31.4%
Judicial branch
highest courts: High Court of Justice of Suriname (consists of the court president, vice president, and 4 judges); note - appeals beyond the High Court are referred to the Caribbean Court of Justice; human rights violations can be appealed to the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights with judgments issued by the Inter-American Court on Human Rights
judge selection and term of office: court judges appointed by the national president in consultation with the National Assembly, the State Advisory Council, and the Order of Private Attorneys; judges serve for life
subordinate courts: cantonal courts
Political parties and leaders
Alternative Combination or A-Com (coalition includes ABOP, KTPI, Party for Democracy and Development)
Brotherhood and Unity in Politics or BEP [Celsius WATERBERG]
Democratic Alternative '91 or DA91 [Angelique DEL CASTILLO]
General Liberation and Development Party or ABOP [Ronnie BRUNSWIJK}
National Democratic Party or NDP [Desire Delano BOUTERSE]
National Party of Suriname or NPS [Gregory RUSLAND]
Party for Democracy and Development in Unity or DOE [Carl BREEVELD]
Party for National Unity and Solidarity or KTPI [Willy SOEMITA]
People's Alliance (Pertjaja Luhur) or PL [Paul SOMOHARDJO]
Progressive Workers' and Farmers' Union or PALU [Jim HOK]
Progressive Reform Party or VHP [Chandrikapersad SANTOKHI]
Reform and Renewal Movement or HVB
Surinamese Labor Party or SPA [Guno CASTELEN]
International organization participation
ACP, AOSIS, Caricom, CD, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OIC, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Niermala Sakoentala BADRISING (since 21 July 2017)
chancery: 4301 Connecticut Avenue NW, Suite 400, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 629-4302
FAX: [1] (202) 629-4769
email address and website:
amb.vs@gov.sr
https://www.surinameembassy.org/
consulate(s) general: Miami
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Karen Lynn WILLIAMS (since 20 November 2018)
embassy: 165 Kristalstraat, Paramaribo
mailing address: 3390 Paramaribo Place, Washington DC 20521-3390
telephone: [597] 556-700
FAX: [597] 551-524
email address and website:
caparamar@state.gov
https://sr.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
five horizontal bands of green (top, double width), white, red (quadruple width), white, and green (double width); a large, yellow, five-pointed star is centered in the red band; red stands for progress and love, green symbolizes hope and fertility, white signifies peace, justice, and freedom; the star represents the unity of all ethnic groups; from its yellow light the nation draws strength to bear sacrifices patiently while working toward a golden future
National symbol(s)
royal palm, faya lobi (flower); national colors: green, white, red, yellow
National anthem
name: "God zij met ons Suriname!" (God Be With Our Suriname)
lyrics/music: Cornelis Atses HOEKSTRA and Henry DE ZIEL/Johannes Corstianus DE PUY
note: adopted 1959; originally adapted from a Sunday school song written in 1893 and contains lyrics in both Dutch and Sranang Tongo
Economy
Economic overview
Suriname’s economy is dominated by the mining industry, with exports of oil and gold accounting for approximately 85% of exports and 27% of government revenues. This makes the economy highly vulnerable to mineral price volatility. The worldwide drop in international commodity prices and the cessation of alumina mining in Suriname significantly reduced government revenue and national income during the past few years. In November 2015, a major US aluminum company discontinued its mining activities in Suriname after 99 years of operation. Public sector revenues fell, together with exports, international reserves, employment, and private sector investment.
Economic growth declined annually from just under 5% in 2012 to -10.4% in 2016. In January 2011, the government devalued the currency by 20% and raised taxes to reduce the budget deficit. Suriname began instituting macro adjustments between September 2015 and 2016; these included another 20% currency devaluation in November 2015 and foreign currency interventions by the Central Bank until March 2016, after which time the Bank allowed the Surinamese dollar (SRD) to float. By December 2016, the SRD had lost 46% of its value against the dollar. Depreciation of the Surinamese dollar and increases in tariffs on electricity caused domestic prices in Suriname to rise 22.0% year-over-year by December 2017.
Suriname's economic prospects for the medium-term will depend on its commitment to responsible monetary and fiscal policies and on the introduction of structural reforms to liberalize markets and promote competition. The government's over-reliance on revenue from the extractive sector colors Suriname's economic outlook. Following two years of recession, the Fitch Credit Bureau reported a positive growth of 1.2% in 2017 and the World Bank predicted 2.2% growth in 2018. Inflation declined to 9%, down from 55% in 2016 , and increased gold production helped lift exports. Yet continued budget imbalances and a heavy debt and interest burden resulted in a debt-to-GDP ratio of 83% in September 2017. Purchasing power has fallen rapidly due to the devalued local currency. The government has announced its intention to pass legislation to introduce a new value-added tax in 2018. Without this and other measures to strengthen the country’s fiscal position, the government may face liquidity pressures.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$9.46 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$11.07 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$10.95 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
1.9% (2017 est.)
-5.1% (2016 est.)
-2.6% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$16,100 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$19,000 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$19,000 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$3.419 billion (2017 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
22% (2017 est.)
55.5% (2016 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: C (2020)
Moody's rating: Caa3 (2020)
Standard & Poors rating: SD (2020)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 11.6% (2017 est.)
industry: 31.1% (2017 est.)
services: 57.4% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 27.6% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 11.7% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 52.5% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 26.5% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 68.9% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -60.6% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
rice, sugar cane, bananas, oranges, vegetables, plantains, coconuts, poultry, cassava, eggs
Industries
gold mining, oil, lumber, food processing, fishing
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 11.2%
industry: 19.5%
services: 69.3% (2010)
Population below poverty line
70% (2002 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 560.7 million (2017 est.)
expenditures: 827.8 million (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$2 million (2017 est.)
-$169 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$2.29 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$2.24 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
Switzerland 39%, United Arab Emirates 31%, Belgium 10% (2019)
Exports - commodities
gold, lumber, refined petroleum, fish, cigarettes (2019)
Imports
$2.41 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$2.07 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
United States 22%, Netherlands 14%, China 13%, Trinidad and Tobago 7%, Antigua and Barbuda 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, delivery trucks, excavation machinery, cars, construction vehicles (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$424.4 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$381.1 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$1.7 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$1.436 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Surinamese dollars (SRD) per US dollar -
7.53 (2017 est.)
6.229 (2016 est.)
6.229 (2015 est.)
3.4167 (2014 est.)
3.3 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 26.5%
male: 18.7%
female: 39.9% (2016 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 97.4% (2018)
electrification - urban areas: 99% (2018)
electrification - rural areas: 94.3% (2018)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
504,000 kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149Electricity - from fossil fuels
61% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
38% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56Electricity - from other renewable sources
2% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144Crude oil - proved reserves
84.2 million bbl (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70Refined petroleum products - production
7,571 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101Refined petroleum products - consumption
13,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 103,240 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 17.6 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 899,339 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 153.3 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: smallest nation in South America with low population and client base; state-owned fixed-line tele-density rates and broadband services below regional average for Latin America and Caribbean; operator building out fiber network; mobile penetration is above regional average; fixed-line effective along the coastline yet poor in the interior; competition in the mobile sector; launch of 5G in Paramaribo; importer of broadcasting equipment from USA (2020)
domestic: fixed-line 16 per 100 and mobile-cellular teledensity 140 telephones per 100 persons; microwave radio relay network is in place (2019)
international: country code - 597; landing point for the SG-SCS submarine cable linking South America with the Caribbean; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
2 state-owned TV stations; 1 state-owned radio station; multiple private radio and TV stations (2019)
Internet users
total: 352,100 (2021 est.)
percent of population: 48.95% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 92,270 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 15.73 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 4 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 20
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 272,347 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 33.2 million mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 6
over 3,047 m: 1
under 914 m: 5 (2019)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 49
914 to 1,523 m: 4
under 914 m: 45 (2013)
Pipelines
50 km oil (2013)
Roadways
total: 4,304 km (2003)
paved: 1,119 km (2003)
unpaved: 3,185 km (2003)
Waterways
1,200 km (most navigable by ships with drafts up to 7 m) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 59Merchant marine
total: 10
by type: general cargo 5, oil tanker 3, other 2 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Paramaribo, Wageningen
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Suriname Army (National Leger, NL): Army, Navy, Air Force, Military Police (2021)
Military expenditures
1.1% of GDP (2017 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2016 est.)
1.4% of GDP (2015 est.)
1.3% of GDP (2014 est.)
1.3% of GDP (2013 est.)
no figures available after 2017
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Suriname Army is comprised of approximately 1,800 active personnel (ground, air, naval, and military police) (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Suriname Army has a limited inventory comprised of a mix of older, foreign-supplied equipment; since 2010, Suriname has received small quantities of military hardware from several countries, including the US (2021)
Military service age and obligation
18 is the legal minimum age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2021)
Military - note
as of 2021, a key mission of the National Leger was assisting the Suriname police as part of the government’s overall efforts to secure the country’s borders and combat crime, particularly narco-trafficking, including joint military and police patrols, as well as joint special security teams
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
area claimed by French Guiana between Riviere Litani and Riviere Marouini (both headwaters of the Lawa); Suriname claims a triangle of land between the New and Kutari/Koetari rivers in a historic dispute over the headwaters of the Courantyne; Guyana seeks UN Convention on the Law of the Sea arbitration to resolve the longstanding dispute with Suriname over the axis of the territorial sea boundary in potentially oil-rich waters
Illicit drugs
a transit country for South American cocaine en route to Europe, the United States and Africa; marijuana is the primary drug consumed locally