Somalia
Introduction
Background
Humans with ancestral links to ethnic Somalis inhabited the northern Somalia Peninsula beginning as early as 5000 BCE and gradually expanded from the coast to occupy all of present day Somalia, Djibouti, the Ogaden region of Ethiopia, and parts of northern Kenya. By 2480 BCE, these humans were engaged in trade with Egypt, and between 800 AD and 1100 AD, immigrant Muslim Arabs and Persians set up coastal trading posts along the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean, solidifying Somalia’s close trading relationship with the Arab Peninsula. In the late 19th century, Britain and Italy established colonies in the Somali Peninsula, where they remained until 1960, when British Somaliland gained independence and joined with Somalia Italiana to form the Republic of Somalia. The country functioned as a parliamentary democracy until 1969, when General Mohamed SIAD Barre took control in a coup, beginning a 22-year authoritarian socialist dictatorship. In an effort to centralize power, SIAD called for the eradication of the clan, the key cultural and social organizing principle in Somali society. Resistance to SIAD’s socialist leadership, which was causing a rapid deterioration of the country, prompted allied clan militias to overthrow SIAD in early 1991, resulting in state collapse. Subsequent fighting between rival clans for resources and territory overwhelmed the country, resulting in a manmade famine and prompting international intervention. Beginning in 1993, the United Nations spearheaded a humanitarian mission supported by international forces, but the international community largely withdrew by 1995 following Black Hawk Down - an incident in which two American Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk helicopters were shot down in Mogadishu, killing 21 international forces and wounding 82.
International peace conferences in the 2000s resulted in a number of transitional governments that operated outside of Somalia. Left largely to themselves, Somalis in the country established alternative governance structures; some areas formed their own administrations, such as Somaliland and Puntland, while others developed localized institutions. Many local populations turned to using sharia courts, an Islamic judicial system that implements religious law. Several of these courts came together in 2006 to form the Islamic Courts Union (ICU). The ICU established order in many areas of central and southern Somalia, including Mogadishu, but was forced out when Ethiopia intervened militarily in December 2006 on behalf of the Somali Transitional Federal Government (TFG). While the TFG settled in the capital, the ICU fled to rural areas or from Somalia altogether, reemerging less than a year later as the Islamic insurgent and terrorist movement al-Shabaab, which is still active today. In January 2007, the African Union (AU) established the AU Mission in Somalia (AMISOM) peacekeeping force, which allowed Ethiopia to withdraw its forces, took over security responsibility for the country, and gave the TFG space to develop Somalia’s new government. By 2012, Somali powerbrokers agreed on a provisional constitution with a loose federal structure and established the central government in Mogadishu. Since then, four interim regional administrations have been established and there have been two presidential elections. However, significant and fundamental governance and security problems remain.
.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Eastern Africa, bordering the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean, east of Ethiopia
Geographic coordinates
10 00 N, 49 00 E
Map references
Africa
Land boundaries
total: 2,385 km
border countries (3): Djibouti 61 km, Ethiopia 1640 km, Kenya 684 km
Coastline
3,025 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 200 nm; note: the US does not recognize this claim
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
principally desert; northeast monsoon (December to February), moderate temperatures in north and hot in south; southwest monsoon (May to October), torrid in the north and hot in the south, irregular rainfall, hot and humid periods (tangambili) between monsoons
Terrain
mostly flat to undulating plateau rising to hills in north
Elevation
highest point: Mount Shimbiris 2,460 m
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 410 m
Natural resources
uranium and largely unexploited reserves of iron ore, tin, gypsum, bauxite, copper, salt, natural gas, likely oil reserves
Land use
agricultural land: 70.3% (2018 est.)
arable land: 1.8% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 68.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 10.6% (2018 est.)
other: 19.1% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
2,000 sq km (2012)
Major aquifers
Ogaden-Juba Basin
Population distribution
distribution varies greatly throughout the country; least densely populated areas are in the northeast and central regions, as well as areas along the Kenyan border; most populated areas are in and around the cities of Mogadishu, Marka, Boorama, Hargeysa, and Baidoa as shown on this population distribution map
Natural hazards
recurring droughts; frequent dust storms over eastern plains in summer; floods during rainy season
Geography - note
strategic location on Horn of Africa along southern approaches to Bab el Mandeb and route through Red Sea and Suez Canal
People and Society
Population
12,094,640 (July 2021 est.)
note: this estimate was derived from an official census taken in 1975 by the Somali Government; population counting in Somalia is complicated by the large number of nomads and by refugee movements in response to famine and clan warfare
Nationality
noun: Somali(s)
adjective: Somali
Ethnic groups
Somali 85%, Bantu and other non-Somali 15% (including 30,000 Arabs)
Languages
Somali (official, according to the 2012 Transitional Federal Charter), Arabic (official, according to the 2012 Transitional Federal Charter), Italian, English
major-language sample(s):
Buugga Xaqiiqda Aduunka, waa laga maarmaanka macluumaadka assasiga. (Somali)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Sunni Muslim (Islam) (official, according to the 2012 Transitional Federal Charter)
Demographic profile
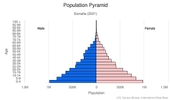
Somalia scores very low for most humanitarian indicators, suffering from poor governance, protracted internal conflict, underdevelopment, economic decline, poverty, social and gender inequality, and environmental degradation. Despite civil war and famine raising its mortality rate, Somalia’s high fertility rate and large proportion of people of reproductive age maintain rapid population growth, with each generation being larger than the prior one. More than 60% of Somalia’s population is younger than 25, and the fertility rate is among the world’s highest at almost 6 children per woman – a rate that has decreased little since the 1970s.
A lack of educational and job opportunities is a major source of tension for Somalia’s large youth cohort, making them vulnerable to recruitment by extremist and pirate groups. Somalia has one of the world’s lowest primary school enrollment rates – just over 40% of children are in school – and one of world’s highest youth unemployment rates. Life expectancy is low as a result of high infant and maternal mortality rates, the spread of preventable diseases, poor sanitation, chronic malnutrition, and inadequate health services.
During the two decades of conflict that followed the fall of the SIAD regime in 1991, hundreds of thousands of Somalis fled their homes. Today Somalia is the world’s third highest source country for refugees, after Syria and Afghanistan. Insecurity, drought, floods, food shortages, and a lack of economic opportunities are the driving factors.
As of 2016, more than 1.1 million Somali refugees were hosted in the region, mainly in Kenya, Yemen, Egypt, Ethiopia, Djibouti, and Uganda, while more than 1.1 million Somalis were internally displaced. Since the implementation of a tripartite voluntary repatriation agreement among Kenya, Somalia, and the UNHCR in 2013, nearly 40,000 Somali refugees have returned home from Kenya’s Dadaab refugee camp – still houses to approximately 260,000 Somalis. The flow sped up rapidly after the Kenyan Government in May 2016 announced its intention to close the camp, worsening security and humanitarian conditions in receiving communities in south-central Somalia. Despite the conflict in Yemen, thousands of Somalis and other refugees and asylum seekers from the Horn of Africa risk their lives crossing the Gulf of Aden to reach Yemen and beyond (often Saudi Arabia). Bossaso in Puntland overtook Obock, Djibouti, as the primary departure point in mid-2014.
Age structure
0-14 years: 42.38% (male 2,488,604/female 2,493,527)
15-24 years: 19.81% (male 1,167,807/female 1,161,040)
25-54 years: 30.93% (male 1,881,094/female 1,755,166)
55-64 years: 4.61% (male 278,132/female 264,325)
65 years and over: 2.27% (male 106,187/female 161,242) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 96.3
youth dependency ratio: 90.6
elderly dependency ratio: 5.7
potential support ratio: 17.6 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 18.5 years
male: 18.7 years
female: 18.3 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
distribution varies greatly throughout the country; least densely populated areas are in the northeast and central regions, as well as areas along the Kenyan border; most populated areas are in and around the cities of Mogadishu, Marka, Boorama, Hargeysa, and Baidoa as shown on this population distribution map
Urbanization
urban population: 46.7% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 4.2% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
2.388 million MOGADISHU (capital), 1.033 million Hargeysa (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.66 male(s)/female
total population: 1.02 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
829 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6Infant mortality rate
total: 88.03 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 97.71 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 78.05 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 55.32 years
male: 53.02 years
female: 57.7 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
6.9% (2018/19)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 98.1% of population
rural: 72.5% of population
total: 83.8% of population
unimproved: urban: 1.9% of population
rural: 27.5% of population
total: 16.2% of population (2017 est.)
Physicians density
0.02 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
Hospital bed density
0.9 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 86.2% of population
rural: 27.1% of population
total: 53.3% of population
unimproved: urban: 13.8% of population
rural: 72.9% of population
total: 46.7% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
<.1% (2020 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<500 (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, malaria, and Rift Valley fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
Environment
Environment - current issues
water scarcity; contaminated water contributes to human health problems; improper waste disposal; deforestation; land degradation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified: Nuclear Test Ban
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 29.51 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 0.65 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 20.13 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
principally desert; northeast monsoon (December to February), moderate temperatures in north and hot in south; southwest monsoon (May to October), torrid in the north and hot in the south, irregular rainfall, hot and humid periods (tangambili) between monsoons
Land use
agricultural land: 70.3% (2018 est.)
arable land: 1.8% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 68.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 10.6% (2018 est.)
other: 19.1% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 46.7% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 4.2% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, malaria, and Rift Valley fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
Food insecurity
exceptional shortfall in aggregate food production/supplies: due to poor seasonal rains - about 2.8 million people are estimated to be severely food insecure in the April−September 2021 period, mainly as a result of the cumulative impact of poor October−December 2020 “Deyr” rains and April−June “Gu” rains, which severely affected crop and livestock production; below‑average cereal output gathered in 2020; production of 2021 main season cereals forecast at 20‑40 percent below average due to unfavorable seasonal rains; severe pasture and water shortages in pastoral areas are affecting livestock conditions (2021)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 2,326,099 tons (2016 est.)
Major aquifers
Ogaden-Juba Basin
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 15 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 2 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 3.281 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
14.7 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Federal Republic of Somalia
conventional short form: Somalia
local long form: Jamhuuriyadda Federaalkaa Soomaaliya
local short form: Soomaaliya
former: Somali Republic, Somali Democratic Republic
etymology: "Land of the Somali" (ethnic group)
Government type
federal parliamentary republic
Capital
name: Mogadishu
geographic coordinates: 2 04 N, 45 20 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: several theories attempt to explain the city's name; one of the more plausible is that it derives from "maq'ad-i-shah" meaning "the seat of the shah," reflecting the city's links with Persia
Administrative divisions
18 regions (plural - NA, singular - gobolka); Awdal, Bakool, Banaadir, Bari, Bay, Galguduud, Gedo, Hiiraan, Jubbada Dhexe (Middle Jubba), Jubbada Hoose (Lower Jubba), Mudug, Nugaal, Sanaag, Shabeellaha Dhexe (Middle Shabeelle), Shabeellaha Hoose (Lower Shabeelle), Sool, Togdheer, Woqooyi Galbeed
Independence
1 July 1960 (from a merger of British Somaliland, which became independent from the UK on 26 June 1960, and Italian Somaliland, which became independent from the Italian-administered UN trusteeship on 1 July 1960 to form the Somali Republic)
National holiday
Foundation of the Somali Republic, 1 July (1960); note - 26 June (1960) in Somaliland
Constitution
history: previous 1961, 1979; latest drafted 12 June 2012, adopted 1 August 2012 (provisional)
amendments: proposed by the federal government, by members of the state governments, the Federal Parliament, or by public petition; proposals require review by a joint committee of Parliament with inclusion of public comments and state legislatures’ comments; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote in both houses of Parliament and approval by a majority of votes cast in a referendum; constitutional clauses on Islamic principles, the federal system, human rights and freedoms, powers and authorities of the government branches, and inclusion of women in national institutions cannot be amended; note - in late December 2020, the president signed a decree blocking the approval of amendments (2021)
Legal system
mixed legal system of civil law, Islamic (sharia) law, and customary law (referred to as Xeer)
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Somalia
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Mohamed ABDULLAHI Mohamed "Farmaajo" (since 8 February 2017)
head of government: Prime Minister Mohamed Hussein ROBLE (since 27 September 2020)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the prime minister, approved by the House of the People
elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by the Federal Parliament by two-thirds majority vote in 2 rounds if needed for a single 4-year term; election last held on 8 February 2017; prime minister appointed by the president, approved by the House of the People; note - elections were scheduled for 10 October 2021 but did not take place; clan elders are scheduled to pick members of a lower house of parliament in November 2021; the parliament will then select a new president at an undetermined future date
election results: Mohamed ABDULLAHI Mohamed "Farmaajo" elected president in second round; Federal Parliament second round vote - Mohamed ABDULLAHI Mohamed "Farmaajo" (TPP) 184, HASSAN SHEIKH Mohamud (PDP) 97, Sheikh SHARIF Sheikh Ahmed (ARS) 46
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Federal Parliament to consist of:
Upper House (54 seats; senators indirectly elected by state assemblies to serve 4-year terms)
House of the People (275 seats; members indirectly elected by electoral colleges, each consisting of 51 delegates selected by the 136 Traditional Elders in consultation with sub-clan elders; members serve 4-year terms)
elections:
Upper House - first held on 10 October 2016 (next to be held in November 2020)
House of the People - first held 23 October - 10 November 2016 (next to be held in November 2020)
election results:
Upper House - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; composition - men 41, women 13, percent of women 24.1%
House of the People - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; composition - men 208, women 67, percent of women 24.4%; note - total Parliament percent of women 24.3%
note: the inaugural House of the People was appointed in September 2012 by clan elders; in 2016 and 2017, the Federal Parliament became bicameral with elections scheduled for 10 October 2016 for the Upper House and 23 October to 10 November 2016 for the House of the People; while the elections were delayed, they were eventually held in most regions despite voting irregularities; on 27 December 2016, 41 Upper House senators and 242 House of the People members were sworn in
Judicial branch
highest courts: the provisional constitution stipulates the establishment of the Constitutional Court (consists of 5 judges, including the chief judge and deputy chief judge); note - under the terms of the 2004 Transitional National Charter, a Supreme Court based in Mogadishu and the Appeal Court were established; yet most regions have reverted to local forms of conflict resolution, either secular, traditional Somali customary law, or Islamic law
judge selection and term of office: judges appointed by the president upon proposal of the Judicial Service Commission, a 9-member judicial and administrative body; judge tenure NA
subordinate courts: federal courts; federal member state-level courts; military courts; sharia courts
Political parties and leaders
Cosmopolitan Democratic Party [Yarow Sharef ADEN]
Daljir Party or DP [Hassan MOALIM]
Democratic Green Party of Somalia or DGPS [Abdullahi Y. MAHAMOUD]
Democratic Party of Somalia or DPS [Maslah Mohamed SIAD]
Green Leaf for Democracy or GLED
Hiil Qaran
Justice and Communist Party [Mohamed NUR]
Justice and Development of Democracy and Self-Respectfulness Party or CAHDI [Abdirahman Abdigani IBRAHIM Bile]
Justice Party [SAKARIYE Haji]
Liberal Party of Somalia
National Democratic Party [Abdirashid ALI]
National Unity Party (Xisbiga MIdnimo-Quaran) [Abdurahman BAADIYOW]
Peace and Development Party or PDP
Somali Green Party (local chapter of Federation of Green Parties of Africa)
Somali National Party or SNP [Mohammed Ameen Saeed AHMED]
Somali People's Party [Salad JEELE]
Somali Society Unity Party [Yasin MAALIM]
Tayo or TPP [Mohamed Abdullahi MOHAMED]
Tiir Party [Fadhil Sheik MOHAMUD]
Union for Peace and Development or UPD [HASSAN SHEIKH Mohamud]
United and Democratic Party [FAUZIA Haji]
United Somali Parliamentarians
United Somali Republican Party [Ali TIMA-JLIC]
inactive: Alliance for the Reliberation of Somalia; reportedly inactive since 2009
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AU, CAEU (candidate), FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, LAS, NAM, OIC, OPCW, OPCW (signatory), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UPU, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Ali Sharif AHMED (since 16 September 2019)
chancery: 1609 22nd Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 853-9164
email address and website:
info@somaliembassydc.net
https://somaliembassydc.net/
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Colleen CRENWELGE (since July 2021)
embassy: Mogadishu, (reopened October 2019 on the grounds of the Mogadishu Airport)
mailing address: P.O. Box 606 Village Market
00621 Nairobi, Kenya
telephone: [254] 20 363-6451
email address and website:
Kenya_ACS@state.gov
https://so.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
light blue with a large white five-pointed star in the center; the blue field was originally influenced by the flag of the UN but today is said to denote the sky and the neighboring Indian Ocean; the five points of the star represent the five regions in the horn of Africa that are inhabited by Somali people: the former British Somaliland and Italian Somaliland (which together make up Somalia), Djibouti, Ogaden (Ethiopia), and the North East Province (Kenya)
National symbol(s)
leopard; national colors: blue, white
National anthem
name: "Qolobaa Calankeed" (Every Nation Has its own Flag)
lyrics/music: lyrics/music: Abdullahi QARSHE
note: adopted 2012; written in 1959
Government - note
regional and local governing bodies continue to exist and control various areas of the country, including the self-declared Republic of Somaliland in northwestern Somalia
Economy
Economic overview
Despite the lack of effective national governance, Somalia maintains an informal economy largely based on livestock, remittance/money transfer companies, and telecommunications. Somalia's government lacks the ability to collect domestic revenue and external debt – mostly in arrears – was estimated at about 77% of GDP in 2017.
Agriculture is the most important sector, with livestock normally accounting for about 40% of GDP and more than 50% of export earnings. Nomads and semi-pastoralists, who are dependent upon livestock for their livelihood, make up a large portion of the population. Economic activity is estimated to have increased by 2.4% in 2017 because of growth in the agriculture, construction and telecommunications sector. Somalia's small industrial sector, based on the processing of agricultural products, has largely been looted and the machinery sold as scrap metal.
In recent years, Somalia's capital city, Mogadishu, has witnessed the development of the city's first gas stations, supermarkets, and airline flights to Turkey since the collapse of central authority in 1991. Mogadishu's main market offers a variety of goods from food to electronic gadgets. Hotels continue to operate and are supported with private-security militias. Formalized economic growth has yet to expand outside of Mogadishu and a few regional capitals, and within the city, security concerns dominate business. Telecommunication firms provide wireless services in most major cities and offer the lowest international call rates on the continent. In the absence of a formal banking sector, money transfer/remittance services have sprouted throughout the country, handling up to $1.6 billion in remittances annually, although international concerns over the money transfers into Somalia continues to threaten these services’ ability to operate in Western nations. In 2017, Somalia elected a new president and collected a record amount of foreign aid and investment, a positive sign for economic recovery.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$13.19 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$13.39 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$13.01 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2016 US dollars
Real GDP growth rate
2.3% (2017 est.)
4.4% (2016 est.)
3.9% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$800 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$900 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$900 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$7.052 billion (2017 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
1.5% (2017 est.)
-71.1% (2016 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 60.2% (2013 est.)
industry: 7.4% (2013 est.)
services: 32.5% (2013 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 72.6% (2015 est.)
government consumption: 8.7% (2015 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 20% (2015 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.8% (2016 est.)
exports of goods and services: 0.3% (2015 est.)
imports of goods and services: -1.6% (2015 est.)
Agricultural products
camel milk, milk, sheep milk, goat milk, sugar cane, fruit, sorghum, cassava, vegetables, maize
Industries
light industries, including sugar refining, textiles, wireless communication
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 71%
industry: 29%
industry and services: 29% (1975)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 145.3 million (2014 est.)
expenditures: 151.1 million (2014 est.)
Current account balance
-$464 million (2017 est.)
-$427 million (2016 est.)
Exports - partners
United Arab Emirates 47%, Saudi Arabia 19%, India 5%, Japan 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
gold, sheep, goats, sesame seeds, insect resins, cattle (2019)
Imports - partners
United Arab Emirates 32%, China 20%, India 17%, Turkey 7% (2019)
Imports - commodities
cigarettes, raw sugar, rice, broadcasting equipment, textiles (2019)
Exchange rates
Somali shillings (SOS) per US dollar -
23,960 (2016 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 18% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 34% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 4% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
85,000 kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182Electricity - from fossil fuels
93% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 185Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202Electricity - from other renewable sources
7% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96Refined petroleum products - consumption
5,600 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174Natural gas - proved reserves
5.663 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 74,800 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 0 (2018 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 7,653,040 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 50.99 (2018 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: the public telecom system was almost completely destroyed during years of civil war; private companies offer limited local fixed-line and wireless service in most major cities; early 2020 landing of DARE 1 submarine cables in Mogadishu and Bossaso eased dependence on expensive satellite dependency for Internet access; in 2019, Al Shabaab Islamic militant group forced closure of Internet services in some parts of the country; new telecom regulatory sector in place (2020)
domestic: seven networks compete for customers in the mobile sector; some of these mobile-service providers offer fixed-lines and Internet services; fixed-line less than 1 per 100 and mobile-cellular 49 per 100 (2019)
international: country code - 252; landing points for the G2A, DARE1, PEACE, and EASSy fiber-optic submarine cable system linking East Africa, Indian Ocean Islands, the Middle East, North Africa and Europe (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
2 private TV stations rebroadcast Al-Jazeera and CNN; Somaliland has 1 government-operated TV station and Puntland has 1 private TV station; the transitional government operates Radio Mogadishu; 1 SW and roughly 10 private FM radio stations broadcast in Mogadishu; several radio stations operate in central and southern regions; Somaliland has 1 government-operated radio station; Puntland has roughly a half-dozen private radio stations; transmissions of at least 2 international broadcasters are available (2019)
Internet users
total: 1.95 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 2% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 98,000 (2017 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2019 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 6 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 7
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 4,486 (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 8
over 3,047 m: 5
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2 (2020)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 44
2,438 to 3,047 m: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m: 16
914 to 1,523 m: 22
under 914 m: 1 (2020)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Berbera, Kismaayo
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Ministry of Defense: Somali National Army (SNA); Ministry of Internal Security: Somali National Police (SNP, includes a maritime unit and a Turkish-trained commando unit known as Harmacad, or Cheetah) (2021)
note - Somalia has numerous militia and regional forces operating throughout the country; these forces include ones that are clan- and warlord-based, semi-official paramilitary and special police forces (aka darwish), and externally-sponsored militias; the SNA is attempting to incorporate some of these militia units
Military expenditures
1.3% of GDP (2017 est.)
1.3% of GDP (2016 est.)
1.3% of GDP (2015 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2014 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2013 est.)
no figures available after 2017
Military and security service personnel strengths
estimates for the size of the Somali National Army (SNA) vary widely, from a low of about 10,000 to a high of some 25,000 due to inconsistent internal reporting and the ongoing attempts to integrate various militias (2021)
note(s) - in 2017, the Somali Government announced a plan for the SNA to eventually number about 18,000 troops; the same plan called for 32,000 federal and regional police; estimates for the number of militia forces operating in the country run as high as 50,000
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the SNA is lightly armed with an inventory that includes a variety of older, second-hand equipment largely from Italy, Russia, South Africa, and the UK; since 2015, it has received small quantities of second-hand equipment from up to 10 different countries, usually as aid/donations (2021)
Maritime threats
the International Maritime Bureau’s (IMB) Piracy Reporting Center (PRC) received zero incidents of piracy and armed robbery in 2020 for the Horn of Africa; while there were no recorded incidents, the IMB PRC warns that Somalia pirates continue to possess the capacity to carry out attacks in the Somali basin and wider Indian Ocean; in particular, the report warns that, "Masters and crew must remain vigilant and cautious when transiting these waters."; the presence of several naval task forces in the Gulf of Aden and additional anti-piracy measures on the part of ship operators, including the use of on-board armed security teams, contributed to the drop in incidents; the EU naval mission, Operation ATALANTA, continues its operations in the Gulf of Aden and Indian Ocean through 2022; naval units from China, India, Japan, Pakistan, South Korea, the US, and other countries also operate in conjunction with EU forces; China has established a logistical base in Djibouti to support its deployed naval units in the Horn of Africa
Military service age and obligation
18 is the legal minimum age for compulsory and voluntary military service (2021)
Military - note
as of late 2021, a significant portion of the country remained outside government control and under the control of the insurgent Islamist group al-Shabaab; al-Shabaab contested government control in some other areas (see Appendix T)
as of 2021, a significant portion of the SNA was comprised of militia forces that lacked the discipline, structure, weapons, and overall capabilities for effective military operations; of the SNA’s approximately 13 brigades, the most effective were assessed to be the US-trained Danab ("Lightning") Advanced Infantry Brigade and those of the Turkish-trained Gorgor ("Eagle") Special Division; in 2020, the Danab Brigade conducted most of the SNA’s offensive operations in Somalia and nearly all counterterrorism operations against the al-Shabaab terrorist group; as of early 2021, it numbered about 1,000 troops with an eventual projected strength of 3,000, while the Gorgor Division was estimated to have 4,500-5,000 trained troops
UN Assistance Mission in Somalia (UNSOM) is mandated by the Security Council to work with the Federal Government of Somalia to support national reconciliation, provide advice on peace-building and state-building, monitor the human rights situation, and help coordinate the efforts of the international community
the UN Support Office in Somalia (UNSOS) is responsible for providing logistical field support to AMISOM, UNSOM, the Somali National Army, and the Somali Police Force on joint operations with AMISOM
the European Union Training Mission in Somalia (EUTM-S) has operated in the country since 2010; the EUTM provides advice and training to the Somali military; the US and Turkey maintain separate unilateral military training missions in Somalia
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
al-Shabaab; Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham – Somalia
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Ethiopian forces invaded southern Somalia and routed Islamist Courts from Mogadishu in January 2007; "Somaliland" secessionists provide port facilities in Berbera to landlocked Ethiopia and have established commercial ties with other regional states; "Puntland" and "Somaliland" "governments" seek international support in their secessionist aspirations and overlapping border claims; the undemarcated former British administrative line has little meaning as a political separation to rival clans within Ethiopia's Ogaden and southern Somalia's Oromo region; Kenya works hard to prevent the clan and militia fighting in Somalia from spreading south across the border, which has long been open to nomadic pastoralists
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 6,371 (Yemen) (2020)
IDPs: 2.968 million (civil war since 1988, clan-based competition for resources; 2011 famine; insecurity because of fighting between al-Shabaab and the Transitional Federal Government's allied forces) (2020)