Saudi Arabia
Introduction
Background
Saudi Arabia is the birthplace of Islam and home to Islam's two holiest shrines in Mecca and Medina. The king's official title is the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques. The modern Saudi state was founded in 1932 by ABD AL-AZIZ bin Abd al-Rahman Al SAUD (Ibn Saud) after a 30-year campaign to unify most of the Arabian Peninsula. One of his male descendants rules the country today, as required by the country's 1992 Basic Law. Following Iraq's invasion of Kuwait in 1990, Saudi Arabia accepted the Kuwaiti royal family and 400,000 refugees while allowing Western and Arab troops to deploy on its soil for the liberation of Kuwait the following year. The continuing presence of foreign troops on Saudi soil after the liberation of Kuwait became a source of tension between the royal family and the public until all operational US troops left the country in 2003. Major terrorist attacks in May and November 2003 spurred a strong ongoing campaign against domestic terrorism and extremism. US troops returned to the Kingdom in October 2019 after attacks on Saudi oil infrastructure.
From 2005 to 2015, King ABDALLAH bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud incrementally modernized the Kingdom. Driven by personal ideology and political pragmatism, he introduced a series of social and economic initiatives, including expanding employment and social opportunities for women, attracting foreign investment, increasing the role of the private sector in the economy, and discouraging businesses from hiring foreign workers. These reforms have accelerated under King SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz, who ascended to the throne in 2015, and has since lifted the Kingdom's ban on women driving and allowed cinemas to operate for the first time in decades. Saudi Arabia saw some protests during the 2011 Arab Spring but not the level of bloodshed seen in protests elsewhere in the region. Shia Muslims in the Eastern Province protested primarily against the detention of political prisoners, endemic discrimination, and Bahraini and Saudi Government actions in Bahrain. Riyadh took a cautious but firm approach by arresting some protesters but releasing most of them quickly and by using its state-sponsored clerics to counter political and Islamist activism.
The government held its first-ever elections in 2005 and 2011, when Saudis went to the polls to elect municipal councilors. In December 2015, women were allowed to vote and stand as candidates for the first time in municipal council elections, with 19 women winning seats. After King SALMAN ascended to the throne in 2015, he placed the first next-generation prince, MUHAMMAD BIN NAYIF bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud, in the line of succession as Crown Prince. He designated his son, MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud, as the Deputy Crown Prince. In March 2015, Saudi Arabia led a coalition of 10 countries in a military campaign to restore the legitimate government of Yemen, which had been ousted by Huthi forces allied with former president ALI ABDULLAH al-Salih. The war in Yemen has drawn international criticism for civilian casualties and its effect on the country’s dire humanitarian situation. In December 2015, then Deputy Crown Prince MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN announced Saudi Arabia would lead a 34-nation Islamic Coalition to fight terrorism (it has since grown to 41 nations). In May 2017, Saudi Arabia inaugurated the Global Center for Combatting Extremist Ideology (also known as "Etidal") as part of its ongoing efforts to counter violent extremism. In June 2017, King SALMAN elevated MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN to Crown Prince.
The country remains a leading producer of oil and natural gas and holds about 16% of the world's proven oil reserves as of 2015. The government continues to pursue economic reform and diversification, particularly since Saudi Arabia's accession to the WTO in 2005, and promotes foreign investment in the Kingdom. In April 2016, the Saudi Government announced a broad set of socio-economic reforms, known as Vision 2030. Low global oil prices throughout 2015 and 2016 significantly lowered Saudi Arabia’s governmental revenue. In response, the government cut subsidies on water, electricity, and gasoline; reduced government employee compensation packages; and announced limited new land taxes. In coordination with OPEC and some key non-OPEC countries, Saudi Arabia agreed cut oil output in early 2017 to regulate supply and help elevate global prices.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea, north of Yemen
Geographic coordinates
25 00 N, 45 00 E
Map references
Middle East
Land boundaries
total: 4,272 km
border countries (7): Iraq 811 km, Jordan 731 km, Kuwait 221 km, Oman 658 km, Qatar 87 km, UAE 457 km, Yemen 1307 km
Coastline
2,640 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 18 nm
continental shelf: not specified
Climate
harsh, dry desert with great temperature extremes
Terrain
mostly sandy desert
Elevation
highest point: As Sarawat range, 3,000 m
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
mean elevation: 665 m
Natural resources
petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, gold, copper
Land use
agricultural land: 80.7% (2018 est.)
arable land: 1.5% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.1% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 79.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 0.5% (2018 est.)
other: 18.8% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
16,200 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Indian Ocean drainage: (Persian Gulf) Tigris and Euphrates (918,044 sq km)
Major aquifers
Arabian Aquifer System
Population distribution
historically a population that was mostly nomadic or semi-nomadic, the Saudi population has become more settled since petroleum was discovered in the 1930s; most of the economic activities - and with it the country's population - is concentrated in a wide area across the middle of the peninsula, from Ad Dammam in the east, through Riyadh in the interior, to Mecca-Medina in the west near the Red Sea
Natural hazards
frequent sand and dust storms
volcanism: despite many volcanic formations, there has been little activity in the past few centuries; volcanoes include Harrat Rahat, Harrat Khaybar, Harrat Lunayyir, and Jabal Yar
Geography - note
Saudi Arabia is the largest country in the world without a river; extensive coastlines on the Persian Gulf and Red Sea allow for considerable shipping (especially of crude oil) through the Persian Gulf and Suez Canal
People and Society
Population
34,783,757 (July 2021 est.)
note: immigrants make up 38.3% of the total population, according to UN data (2019)
Nationality
noun: Saudi(s)
adjective: Saudi or Saudi Arabian
Ethnic groups
Arab 90%, Afro-Asian 10%
Languages
Arabic (official)
major-language sample(s):
كتاب حقائق العالم، المصدر الذي لا يمكن الاستغناء عنه للمعلومات الأساسية (Arabic)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Muslim (official; citizens are 85-90% Sunni and 10-15% Shia), other (includes Eastern Orthodox, Protestant, Roman Catholic, Jewish, Hindu, Buddhist, and Sikh) (2012 est.)
note: despite having a large expatriate community of various faiths (more than 30% of the population), most forms of public religious expression inconsistent with the government-sanctioned interpretation of Sunni Islam are restricted; non-Muslims are not allowed to have Saudi citizenship and non-Muslim places of worship are not permitted (2013)
Age structure
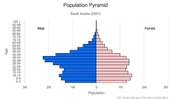
0-14 years: 24.84% (male 4,327,830/female 4,159,242)
15-24 years: 15.38% (male 2,741,371/female 2,515,188)
25-54 years: 50.2% (male 10,350,028/female 6,804,479)
55-64 years: 5.95% (male 1,254,921/female 778,467)
65 years and over: 3.63% (male 657,395/female 584,577) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 39.3
youth dependency ratio: 34.4
elderly dependency ratio: 4.9
potential support ratio: 20.5 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 30.8 years
male: 33 years
female: 27.9 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
historically a population that was mostly nomadic or semi-nomadic, the Saudi population has become more settled since petroleum was discovered in the 1930s; most of the economic activities - and with it the country's population - is concentrated in a wide area across the middle of the peninsula, from Ad Dammam in the east, through Riyadh in the interior, to Mecca-Medina in the west near the Red Sea
Urbanization
urban population: 84.5% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.69% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
7.388 million RIYADH (capital), 4.697 million Jeddah, 2.079 million Mecca, 1.518 million Medina, 1.279 million Ad Dammam, 1.279 million Hufuf-Mubarraz (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.09 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.52 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.61 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 1.12 male(s)/female
total population: 1.3 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
17 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131Infant mortality rate
total: 12.58 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 13.86 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 11.24 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 76.4 years
male: 74.81 years
female: 78.07 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
24.6% (2016)
Drinking water source
improved: total: 100% of population
unimproved: total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
6.4% (2018)
Physicians density
2.61 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
Hospital bed density
2.2 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: total: 100% of population
unimproved: total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
<.1% (2020 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<200 (2020 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 97.6%
male: 98.6%
female: 96% (2020)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 16 years
male: 16 years
female: 16 years (2020)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 27.2%
male: 21.5%
female: 43.8% (2020 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
desertification; depletion of underground water resources; the lack of perennial rivers or permanent water bodies has prompted the development of extensive seawater desalination facilities; coastal pollution from oil spills; air pollution; waste management
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 78.38 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 563.45 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 45.47 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
harsh, dry desert with great temperature extremes
Land use
agricultural land: 80.7% (2018 est.)
arable land: 1.5% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.1% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 79.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 0.5% (2018 est.)
other: 18.8% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 84.5% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.69% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 16,125,701 tons (2015 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 2,418,855 tons (2015 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 15% (2015 est.)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Indian Ocean drainage: (Persian Gulf) Tigris and Euphrates (918,044 sq km)
Major aquifers
Arabian Aquifer System
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 3.15 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 1 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 19.2 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
2.4 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
conventional short form: Saudi Arabia
local long form: Al Mamlakah al Arabiyah as Suudiyah
local short form: Al Arabiyah as Suudiyah
etymology: named after the ruling dynasty of the country, the House of Saud; the name "Arabia" can be traced back many centuries B.C., the ancient Egyptians referred to the region as "Ar Rabi"
Government type
absolute monarchy
Capital
name: Riyadh
geographic coordinates: 24 39 N, 46 42 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name derives from the Arabic word "riyadh," meaning "gardens," and refers to various oasis towns in the area that merged to form the city
Administrative divisions
13 regions (manatiq, singular - mintaqah); Al Bahah, Al Hudud ash Shamaliyah (Northern Border), Al Jawf, Al Madinah al Munawwarah (Medina), Al Qasim, Ar Riyad (Riyadh), Ash Sharqiyah (Eastern), 'Asir, Ha'il, Jazan, Makkah al Mukarramah (Mecca), Najran, Tabuk
Independence
23 September 1932 (unification of the kingdom)
National holiday
Saudi National Day (Unification of the Kingdom), 23 September (1932)
Constitution
history: 1 March 1992 - Basic Law of Government, issued by royal decree, serves as the constitutional framework and is based on the Qur'an and the life and traditions of the Prophet Muhammad
amendments: proposed by the king directly or proposed to the king by the Consultative Assembly or by the Council of Ministers; passage by the king through royal decree; Basic Law amended many times, last in 2017
Legal system
Islamic (sharia) legal system with some elements of Egyptian, French, and customary law; note - several secular codes have been introduced; commercial disputes handled by special committees
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Saudi Arabia; a child born out of wedlock in Saudi Arabia to a Saudi mother and unknown father
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; restricted to males; universal for municipal elections
Executive branch
chief of state: King and Prime Minister SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (since 23 January 2015); Crown Prince MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (born 31 August 1985); note - the monarch is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: King and Prime Minister SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (since 23 January 2015); Crown Prince MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (born 31 August 1985)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the monarch every 4 years and includes many royal family members
elections/appointments: none; the monarchy is hereditary; an Allegiance Council created by royal decree in October 2006 established a committee of Saudi princes for a voice in selecting future Saudi kings
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Consultative Council or Majlis al-Shura (150 seats; members appointed by the monarch to serve 4-year terms); note - in early 2013, the monarch granted women 30 seats on the Council
note: composition as of 2013 - men 121, women 30, percent of women 19.9%
Judicial branch
highest courts: High Court (consists of the court chief and organized into circuits with 3-judge panels, except for the criminal circuit, which has a 5-judge panel for cases involving major punishments)
judge selection and term of office: High Court chief and chiefs of the High Court Circuits appointed by royal decree upon the recommendation of the Supreme Judiciary Council, a 10-member body of high-level judges and other judicial heads; new judges and assistant judges serve 1- and 2-year probations, respectively, before permanent assignment
subordinate courts: Court of Appeals; Specialized Criminal Court, first-degree courts composed of general, criminal, personal status, and commercial courts; Labor Court; a hierarchy of administrative courts
International organization participation
ABEDA, AfDB (nonregional member), AFESD, AMF, BIS, CAEU, CP, FAO, G-20, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OAS (observer), OIC, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Princess REEMA bint Bandar Al Saud (since 8 July 2019)
chancery: 601 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20037
telephone: [1] (202) 342-3800
FAX: [1] (202) 295-3625
email address and website:
info@saudiembassy.net
https://www.saudiembassy.net/
consulate(s) general: Houston, Los Angeles, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Martina STRONG (since February 2021)
embassy: Riyadh 11564
mailing address: 6300 Riyadh Place, Washington DC 20521-6300
telephone: [966] (11) 835-4000
FAX: [966] (11) 488-7360
email address and website:
RiyadhACS@state.gov
https://sa.usembassy.gov/
consulate(s) general: Dhahran, Jeddah
Flag description
green, a traditional color in Islamic flags, with the Shahada or Muslim creed in large white Arabic script (translated as "There is no god but God; Muhammad is the Messenger of God") above a white horizontal saber (the tip points to the hoist side); design dates to the early twentieth century and is closely associated with the Al Saud family, which established the kingdom in 1932; the flag is manufactured with differing obverse and reverse sides so that the Shahada reads - and the sword points - correctly from right to left on both sides
note: the only national flag to display an inscription as its principal design; one of only three national flags that differ on their obverse and reverse sides - the others are Moldova and Paraguay
National symbol(s)
palm tree surmounting two crossed swords; national colors: green, white
National anthem
name: "Aash Al Maleek" (Long Live Our Beloved King)
lyrics/music: Ibrahim KHAFAJI/Abdul Rahman al-KHATEEB
note: music adopted 1947, lyrics adopted 1984
Economy
Economic overview
Saudi Arabia has an oil-based economy with strong government controls over major economic activities. It possesses about 16% of the world's proven petroleum reserves, ranks as the largest exporter of petroleum, and plays a leading role in OPEC. The petroleum sector accounts for roughly 87% of budget revenues, 42% of GDP, and 90% of export earnings.
Saudi Arabia is encouraging the growth of the private sector in order to diversify its economy and to employ more Saudi nationals. Approximately 6 million foreign workers play an important role in the Saudi economy, particularly in the oil and service sectors; at the same time, however, Riyadh is struggling to reduce unemployment among its own nationals. Saudi officials are particularly focused on employing its large youth population.
In 2017, the Kingdom incurred a budget deficit estimated at 8.3% of GDP, which was financed by bond sales and drawing down reserves. Although the Kingdom can finance high deficits for several years by drawing down its considerable foreign assets or by borrowing, it has cut capital spending and reduced subsidies on electricity, water, and petroleum products and recently introduced a value-added tax of 5%. In January 2016, Crown Prince and Deputy Prime Minister MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN announced that Saudi Arabia intends to list shares of its state-owned petroleum company, ARAMCO - another move to increase revenue and outside investment. The government has also looked at privatization and diversification of the economy more closely in the wake of a diminished oil market. Historically, Saudi Arabia has focused diversification efforts on power generation, telecommunications, natural gas exploration, and petrochemical sectors. More recently, the government has approached investors about expanding the role of the private sector in the health care, education and tourism industries. While Saudi Arabia has emphasized their goals of diversification for some time, current low oil prices may force the government to make more drastic changes ahead of their long-run timeline.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$1,543,240,000,000 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$1,609,320,000,000 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$1,604,010,000,000 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
-0.9% (2017 est.)
1.7% (2016 est.)
4.1% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$44,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$47,000 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$47,600 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$792.849 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
-2% (2019 est.)
-4.5% (2018 est.)
-0.8% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: A (2019)
Moody's rating: A1 (2016)
Standard & Poors rating: A- (2016)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 2.6% (2017 est.)
industry: 44.2% (2017 est.)
services: 53.2% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 41.3% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 24.5% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 23.2% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 4.7% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 34.8% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -28.6% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
milk, dates, poultry, fruit, watermelons, barley, wheat, potatoes, eggs, tomatoes
Industries
crude oil production, petroleum refining, basic petrochemicals, ammonia, industrial gases, sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), cement, fertilizer, plastics, metals, commercial ship repair, commercial aircraft repair, construction
Labor force
13.8 million (2017 est.)
note: comprised of 3.1 million Saudis and 10.7 million non-Saudis
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 6.7%
industry: 21.4%
services: 71.9% (2005 est.)
Unemployment rate
6% (2017 est.)
5.6% (2016 est.)
note: data are for total population; unemployment among Saudi nationals is more than double
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
45.9 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 181 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 241.8 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
$15.23 billion (2017 est.)
-$23.87 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$184.11 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$285.86 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$314.92 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
China 20%, India 11%, Japan 11%, South Korea 9%, United States 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
crude petroleum, refined petroleum, polymers, industrial alcohols, natural gas (2019)
Imports
$179.8 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$218.94 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$209.59 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
China 18%, United Arab Emirates 12%, United States 9%, Germany 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
cars, broadcasting equipment, refined petroleum, packaged medicines, telephones (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$496.4 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$535.8 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$205.1 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$189.3 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Saudi riyals (SAR) per US dollar -
3.7514 (2020 est.)
3.75 (2019 est.)
3.7518 (2018 est.)
3.75 (2014 est.)
3.75 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 27.2%
male: 21.5%
female: 43.8% (2020 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
82.94 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14Electricity - from fossil fuels
100% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 198Electricity - from other renewable sources
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205Crude oil - proved reserves
266.2 billion bbl (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2Refined petroleum products - production
2.476 million bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8Refined petroleum products - consumption
3.287 million bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6Refined petroleum products - exports
1.784 million bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5Natural gas - proved reserves
8.619 trillion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 5,749,058 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 16.51 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 43,215,439 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 124.1 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: one of the most progressive telecom markets in the Middle East; mobile penetration high, with a saturated market; mobile operators competitive and meeting the demand for workers, students and citizens working from home; Huawei partners with operator to provide 5G to dozens of cities; broadband is available with DSL, fiber, and wireless; mobile penetration is high; restrictive monarchy places limits on information and services available online; authorities operate extensive censorship and surveillance systems; major importer of broadcasting equipment from UAE and China (2020)
domestic: fixed-line 16 per 100 and mobile-cellular subscribership has been increasing rapidly to 121 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 966; landing points for the SeaMeWe-3, -4, -5, AAE-1, EIG, FALCON, FEA, IMEWE, MENA/Gulf Bridge International, SEACOM, SAS-1, -2, GBICS/MENA, and the Tata TGN-Gulf submarine cables providing connectivity to Europe, Africa, the Middle East, Asia, Southeast Asia and Australia; microwave radio relay to Bahrain, Jordan, Kuwait, Qatar, UAE, Yemen, and Sudan; coaxial cable to Kuwait and Jordan; satellite earth stations - 5 Intelsat (3 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Indian Ocean), 1 Arabsat, and 1 Inmarsat (Indian Ocean region) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
broadcast media are state-controlled; state-run TV operates 4 networks; Saudi Arabia is a major market for pan-Arab satellite TV broadcasters; state-run radio operates several networks; multiple international broadcasters are available
Internet users
total: 33.58 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 97.86% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 7,890,261 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 22.66 (2020 est.)
Communications - note
the innovative King Abdulaziz Center for World Culture (informally known as Ithra, meaning "enrichment") opened on 1 December 2017 in Dhahran, Eastern Region; its facilities include a grand library, several museums, an archive, an Idea Lab, a theater, a cinema, and an Energy Exhibit, all which are meant to provide visitors an immersive and transformative experience
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 12 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 230
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 39,141,660 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 1,085,470,000 mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 82
over 3,047 m: 33
2,438 to 3,047 m: 16
1,524 to 2,437 m: 27
914 to 1,523 m: 2
under 914 m: 4 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 132
2,438 to 3,047 m: 7
1,524 to 2,437 m: 72
914 to 1,523 m: 37
under 914 m: 16 (2013)
Heliports
10 (2013)
Pipelines
209 km condensate, 2940 km gas, 1183 km liquid petroleum gas, 5117 km oil, 1151 km refined products (2013)
Railways
total: 5,410 km (2016)
standard gauge: 5,410 km 1.435-m gauge (with branch lines and sidings) (2016)
Roadways
total: 221,372 km (2006)
paved: 47,529 km (includes 3,891 km of expressways) (2006)
unpaved: 173,843 km (2006)
Merchant marine
total: 392
by type: bulk carrier 5, container ship 1, general cargo 21, oil tanker 58, other 307 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Ad Dammam, Al Jubayl, Jeddah, King Abdulla, Yanbu'
container port(s) (TEUs): Ad Dammam (1,822,642), Jeddah (4,433,991), King Abdulla (2,020,683) (2019)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Ministry of Defense: Royal Saudi Land Forces, Royal Saudi Naval Forces (includes marines, special forces, naval aviation), Royal Saudi Air Force, Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces, Royal Saudi Strategic Missiles Force; Ministry of the National Guard (SANG); Ministry of Interior: police, Border Guard, Facilities Security Force; State Security Presidency: General Directorate of Investigation (Mabahith), Special Security Forces, Special Emergency Forces (2021)
note - SANG (also known as the White Army) is a land force separate from the Ministry of Defense that is responsible for internal security, protecting the royal family, and external defense
Military expenditures
7.8% of GDP (2020 est.)
8% of GDP (2019)
9.5% of GDP (2018)
11.1% of GDP (2017)
10.8% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Saudi military forces have about 225,000 active troops; approximately 125,000 under the Ministry of Defense (75,000 Land Forces; 14,000 Naval Forces; 36,000 Air Force/Air Defense/Strategic Missile Forces) and approximately 100,000 in the Saudi Arabia National Guard (SANG) (2021)
note - SANG also has an irregular force (Fowj), primarily Bedouin tribal volunteers, with a total strength of approximately 25,000 men
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the inventory of the Saudi military forces, including the SANG, includes a mix of mostly modern weapons systems from the US and Europe; since 2010, the US is the leading supplier of armaments, followed by France and the UK; Saudi Arabia is the world's largest arms importer (2021)
Military deployments
est. 2,500-5,000 Yemen (varies depending on operations, which continued into 2021) (2021)
Military service age and obligation
17-40 for men; no conscription; as of 2021, women (aged 17-40) were allowed to serve in the Army, Air Defense, Navy, Strategic Missile Force, medical services, and internal security forces up to the rank of non-commissioned officer (2021)
Military - note
in 2015, a Saudi-led coalition of Arab states intervened militarily in Yemen in support of the Republic of Yemen Government against the separatist Huthis; as of 2021, the coalition (consisting largely of Saudi forces) and the Huthis continued to engage in fighting, mostly with air and missile forces, although heavy ground fighting was also reportedly taking place over the key province of Marib; the Saudis have conducted numerous air strikes in northern Yemen, while the Huthis have launched attacks into Saudi territory with ballistic missiles and unmanned aerial vehicles armed with explosives; the Saudi-led coalition controlled the country’s airspace and the port of Hodeida; Saudi Arabia also has raised and equipped paramilitary/militia security forces in Yemen--based largely on tribal or regional affiliation--to deploy along the Saudi-Yemen border, especially the areas bordering the governorates of Saada and Al-Jawf
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (ISIS); al-Qa’ida; al-Qa’ida in the Arabian Peninsula
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Saudi Arabia has reinforced its concrete-filled security barrier along sections of the now fully demarcated border with Yemen to stem illegal cross-border activities; Kuwait and Saudi Arabia continue discussions on a maritime boundary with Iran
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 70,000 (2020); note - thousands of biduns (stateless Arabs) are descendants of nomadic tribes who were not officially registered when national borders were established, while others migrated to Saudi Arabia in search of jobs; some have temporary identification cards that must be renewed every five years, but their rights remain restricted; most Palestinians have only legal resident status; some naturalized Yemenis were made stateless after being stripped of their passports when Yemen backed Iraq in its invasion of Kuwait in 1990; Saudi women cannot pass their citizenship on to their children, so if they marry a non-national, their children risk statelessness
Trafficking in persons
current situation: Saudi Arabia is a destination country for men and women subjected to forced labor and, to a lesser extent, forced prostitution; men and women primarily from South and Southeast Asia and Africa voluntarily travel to Saudi Arabia to work in domestic service, construction, agriculture or other low-skilled jobs, but some subsequently face conditions indicative of involuntary servitude (many are forced to work months or years beyond their contract term because employers withhold passports and required exit visas); women, primarily from Asian and African countries, are reported to be forced into prostitution in Saudi Arabia
tier rating:
Tier 2 Watch List — Saudi Arabia does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking, but is making significant efforts to do so and was upgraded to Tier 2 Watch List;
the government enacted the country’s first-ever national referral mechanism (NRM) and increased the number of prosecutions and convictions under the anti-trafficking law; victims are identified and referred for care; the government convicted and sentenced two Saudi officials complicit in trafficking crimes; however, the government continued to fine, jail, and/or deport migrant workers for prostitution or immigration violations who may have been trafficking victims; authorities regularly misclassified potential trafficking crimes as labor law violations rather than as criminal offenses (2020)Illicit drugs
regularly sentences drug traffickers to the death penalty, although a moratorium on executions for drug offences has been in place since at least 2020; improving anti-money-laundering legislation and enforcement