Introduction
Background
Paraguay achieved its independence from Spain in 1811. In the disastrous War of the Triple Alliance (1865-70) - between Paraguay and Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay - Paraguay lost two-thirds of its adult males and much of its territory. The country stagnated economically for the next half century. Following the Chaco War of 1932-35 with Bolivia, Paraguay gained a large part of the Chaco lowland region. The 35-year military dictatorship of Alfredo STROESSNER ended in 1989, and Paraguay has held relatively free and regular presidential elections since the country's return to democracy.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
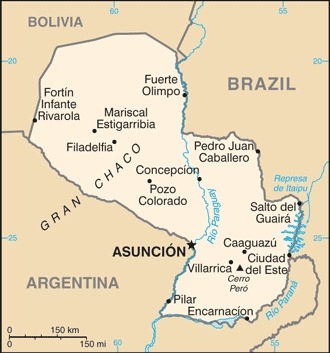
Location
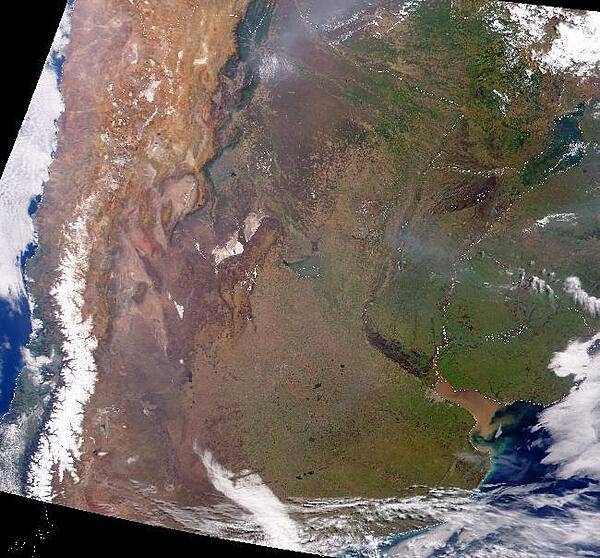
Central South America, northeast of Argentina, southwest of Brazil
Geographic coordinates
23 00 S, 58 00 W
Map references
South America
Land boundaries
total: 4,655 km
border countries (3): Argentina 2531 km, Bolivia 753 km, Brazil 1371 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
subtropical to temperate; substantial rainfall in the eastern portions, becoming semiarid in the far west
Terrain
grassy plains and wooded hills east of Rio Paraguay; Gran Chaco region west of Rio Paraguay mostly low, marshy plain near the river, and dry forest and thorny scrub elsewhere
Elevation
highest point: Cerro Pero 842 m
lowest point: junction of Rio Paraguay and Rio Parana 46 m
mean elevation: 178 m
Natural resources
hydropower, timber, iron ore, manganese, limestone
Land use
agricultural land: 53.8% (2018 est.)
arable land: 10.8% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.2% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 42.8% (2018 est.)
forest: 43.8% (2018 est.)
other: 2.4% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
1,362 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Paraná (2,582,704 sq km)
Major aquifers
Guarani Aquifer System
Major rivers (by length in km)
Rio de la Plata/Parana (shared with Brazil [s], Argentina, and Uruguay [m]) - 4,880 km; Paraguay river mouth (shared with Brazil [s] and Argentina) - 2,549 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Population distribution
most of the population resides in the eastern half of the country; to the west lies the Gran Chaco (a semi-arid lowland plain), which accounts for 60% of the land territory, but only 2% of the overall population
Natural hazards
local flooding in southeast (early September to June); poorly drained plains may become boggy (early October to June)
Geography - note
note 1: landlocked; lies between Argentina, Bolivia, and Brazil; population concentrated in eastern and southern part of country
note 2: pineapples are probably indigenous to the southern Brazil-Paraguay region
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Paraguayan(s)
adjective: Paraguayan
Ethnic groups
Mestizo (mixed Spanish and Amerindian ancestry) 95%, other 5%
Languages
Spanish (official) and Guarani (official) 46.3%, only Guarani 34%, only Spanish 15.2%, other (includes Portuguese, German, other Indigenous languages) 4.1% , no response 0.4%; note - data represent predominant household language (2012 est.)
major-language sample(s):
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Roman Catholic 89.6%, Protestant 6.2%, other Christian 1.1%, other or unspecified 1.9%, none 1.1% (2002 est.)
Demographic profile
Paraguay falls below the Latin American average in several socioeconomic categories, including immunization rates, potable water, sanitation, and secondary school enrollment, and has greater rates of income inequality and child and maternal mortality. Paraguay's poverty rate has declined in recent years but remains high, especially in rural areas, with more than a third of the population below the poverty line. However, the well-being of the poor in many regions has improved in terms of housing quality and access to clean water, telephone service, and electricity. The fertility rate continues to drop, declining sharply from an average 4.3 births per woman in the late 1990s to about 2 in 2013, as a result of the greater educational attainment of women, increased use of contraception, and a desire for smaller families among young women.
Paraguay is a country of emigration; it has not attracted large numbers of immigrants because of political instability, civil wars, years of dictatorship, and the greater appeal of neighboring countries. Paraguay first tried to encourage immigration in 1870 in order to rebound from the heavy death toll it suffered during the War of the Triple Alliance, but it received few European and Middle Eastern immigrants. In the 20th century, limited numbers of immigrants arrived from Lebanon, Japan, South Korea, and China, as well as Mennonites from Canada, Russia, and Mexico. Large flows of Brazilian immigrants have been arriving since the 1960s, mainly to work in agriculture. Paraguayans continue to emigrate to Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay, the United States, Italy, Spain, and France.
Age structure
0-14 years: 23.41% (male 857,303/female 826,470)
15-24 years: 17.71% (male 640,400/female 633,525)
25-54 years: 42.63% (male 1,532,692/female 1,532,851)
55-64 years: 8.37% (male 306,100/female 295,890)
65 years and over: 7.88% (male 267,351/female 299,103) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 55.5
youth dependency ratio: 49.9
elderly dependency ratio: 10.6
potential support ratio: 9.4 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 29.7 years
male: 29.5 years
female: 29.9 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
most of the population resides in the eastern half of the country; to the west lies the Gran Chaco (a semi-arid lowland plain), which accounts for 60% of the land territory, but only 2% of the overall population
Urbanization
urban population: 62.5% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.64% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
3.394 million ASUNCION (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.89 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
22.9 years (2008 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality ratio
84 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77Infant mortality rate
total: 23.83 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 28.23 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 19.21 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 78.13 years
male: 75.46 years
female: 80.93 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
68.4% (2016)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
6.7% (2018)
Physicians density
1.35 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
Hospital bed density
0.8 beds/1,000 population (2016)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 98.4% of population
rural: 84.8% of population
total: 93.1% of population
unimproved: urban: 1.6% of population
rural: 15.2% of population
total: 6.8% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<500 (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: intermediate (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 94.5%
male: 94.9%
female: 94.2% (2020)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 12 years
male: 12 years
female: 13 years (2010)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 17.1%
male: 13.1%
female: 23.3% (2020 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation; water pollution; rivers suffer from toxic dumping; tanneries release mercury and chromium into rivers and streams; loss of wetlands; inadequate means for waste disposal pose health risks for many urban residents
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Nuclear Test Ban, Tropical Timber 2006
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 11.16 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 7.41 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 27.65 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
subtropical to temperate; substantial rainfall in the eastern portions, becoming semiarid in the far west
Land use
agricultural land: 53.8% (2018 est.)
arable land: 10.8% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.2% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 42.8% (2018 est.)
forest: 43.8% (2018 est.)
other: 2.4% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 62.5% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.64% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 1.21% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: intermediate (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1,818,501 tons (2015 est.)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Rio de la Plata/Parana (shared with Brazil [s], Argentina, and Uruguay [m]) - 4,880 km; Paraguay river mouth (shared with Brazil [s] and Argentina) - 2,549 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Paraná (2,582,704 sq km)
Major aquifers
Guarani Aquifer System
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 362 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 154 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 1.897 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
387.77 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Paraguay
conventional short form: Paraguay
local long form: Republica del Paraguay
local short form: Paraguay
etymology: the precise meaning of the name Paraguay is unclear, but it seems to derive from the river of the same name; one explanation has the name meaning "water of the Payagua" (an indigenous tribe that lived along the river)
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Asuncion
geographic coordinates: 25 16 S, 57 40 W
time difference: UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins first Sunday in October; ends last Sunday in March
etymology: the name means "assumption" and derives from the original name given to the city at its founding in 1537, Nuestra Senora Santa Maria de la Asuncion (Our Lady Saint Mary of the Assumption)
Administrative divisions
17 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento) and 1 capital city*; Alto Paraguay, Alto Parana, Amambay, Asuncion*, Boqueron, Caaguazu, Caazapa, Canindeyu, Central, Concepcion, Cordillera, Guaira, Itapua, Misiones, Neembucu, Paraguari, Presidente Hayes, San Pedro
Independence
14-15 May 1811 (from Spain); note - the uprising against Spanish authorities took place during the night of 14-15 May 1811 and both days are celebrated in Paraguay
National holiday
Independence Day, 14-15 May (1811) (observed 15 May); 14 May is celebrated as Flag Day
Constitution
history: several previous; latest approved and promulgated 20 June 1992
amendments: proposed at the initiative of at least one quarter of either chamber of the National Congress, by the president of the republic, or by petition of at least 30,000 voters; passage requires absolute majority vote by both chambers and approval in a referendum; amended 2011
Legal system
civil law system with influences from Argentine, Spanish, Roman, and French civil law models; judicial review of legislative acts in Supreme Court of Justice
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a native-born citizen of Paraguay
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 3 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal and compulsory until the age of 75
Executive branch
chief of state: President Mario Abdo BENITEZ (since 15 August 2018); Vice President Hugo Adalberto VELAZQUEZ Moreno (since 15 August 2018); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Mario Abdo BENITEZ (since 15 August 2018); Vice President Hugo Adalberto VELAZQUEZ Moreno (since 15 August 2018)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by simple majority popular vote for a single 5-year term; election last held on 22 April 2018 (next to be held in April 2023)
election results:
2018: Mario Abdo BENITEZ elected president; percent of vote - Mario Abdo BENITEZ (ANR) 46.4%, Efrain ALEGRE (PLRA) 42.7%, Juan Bautista YBANEZ 3.3%, other 7.6%
2013: Horacio CARTES elected president; percent of vote - Horacio CARTES (ANR) 48.5%, Efrain ALEGRE (PLRA) 39%, Mario FERREIRO (AP) 6.2%, Anibal CARRILLO (FG) 3.5%, other 2.8%
Legislative branch
description: bicameral National Congress or Congreso Nacional consists of:
Chamber of Senators or Camara de Senadores (45 seats; members directly elected in a single nationwide constituency by closed-list proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)
Chamber of Deputies or Camara de Diputados (80 seats; members directly elected in 18 multi-seat constituencies - corresponding to the country's 17 departments and capital city - by closed-list proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)
elections:
Chamber of Senators - last held on 22 April 2018 (next to be held in April 2023)
Chamber of Deputies - last held on 22 April 2018 (next to be held in April 2023)
election results:
Chamber of Senators - percent of vote by party/coalition - ANR 32.52%, PLRA 24.18%, FG 11.83%, PPQ 6.77%, MH 4.47%, PDP 3.66%, MCN 2.48%, UNACE 2.12%, other 11.97%; seats by party/coalition - ANR 17, PLRA 13, FG 6, PPQ 3, MH 2, PDP 2, MCN 1, UNACE 1; composition - men 36, women 9, percent of women 20%
Chamber of Deputies - percent of vote by party/coalition - ANR 39.1%, PLRA 17.74%, Ganar Alliance 12.08%, PPQ 4.46%, MH 3.19%; other 23.43%; seats by party/coalition - ANR 42, PLRA 17, Ganar Alliance 13, PPQ 3, MH 2, other 3; composition - men 66, women 14, percent of women 17.5%; note - total National Congress percent of women 18.4%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court of Justice or Corte Suprema de Justicia (consists of 9 justices divided 3 each into the Constitutional Court, Civil and Commercial Chamber, and Criminal Division)
judge selection and term of office: justices proposed by the Council of Magistrates or Consejo de la Magistratura, a 6-member independent body, and appointed by the Chamber of Senators with presidential concurrence; judges can serve until mandatory retirement at age 75
subordinate courts: appellate courts; first instance courts; minor courts, including justices of the peace
Political parties and leaders
Asociacion Nacional Republicana - Colorado Party or ANR [Pedro ALLIANA]
Avanza Pais coalition or AP [Adolfo FERREIRO]
Broad Front coalition (Frente Guasu) or FG [Esperanza MARTINEZ]
Ganar Alliance (alliance between PLRA and Guasu Front)
Movimiento Cruzada Nacional or MCN
Movimiento Hagamos or MH [Antonio "Tony" APURIL]
Movimiento Union Nacional de Ciudadanos Eticos or UNACE [Jorge OVIEDO MATTO]
Partido del Movimiento al Socialismo or P-MAS [Camilo Ernesto SOARES Machado]
Partido Democratica Progresista or PDP [Rafael FILIZZOLA]
Partido Encuentro Nacional or PEN [Hermann RATZLAFFIN Klippemstein]
Partido Liberal Radical Autentico or PLRA [Efrain ALEGRE]
Partido Pais Solidario or PPS [Carlos Alberto FILIZZOLA Pallares]
Partido Popular Tekojoja or PPT [Sixto PEREIRA Galeano]
Patria Querida (Beloved Fatherland Party) or PPQ [Miguel CARRIZOSA]
International organization participation
CAN (associate), CD, CELAC, FAO, G-11, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, Mercosur, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM (observer), OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, Pacific Alliance (observer), PCA, UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Luis Jose GONZALEZ FERNANDEZ, Minister (since 12 April 2021)
chancery: 2400 Massachusetts Avenue, NW, Washington DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 483-6960
FAX: [1] (202) 234-4508
email address and website:
eeuuembaparsc@mre.gov.py; secretaria@embaparusa.gov.py
consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, Miami, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Joseph SALAZAR (since 20 January 2021 )
embassy: 1776 Mariscal Lopez Avenue, Asuncion
mailing address: 3020 Asuncion Place, Washington DC 20521-3020
telephone: [595] (21) 248-3000
FAX: [595] (21) 213-728
email address and website:
ParaguayACS@state.gov
https://py.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal, horizontal bands of red (top), white, and blue with an emblem centered in the white band; unusual flag in that the emblem is different on each side; the obverse (hoist side at the left) bears the national coat of arms (a yellow five-pointed star within a green wreath capped by the words REPUBLICA DEL PARAGUAY, all within two circles); the reverse (hoist side at the right) bears a circular seal of the treasury (a yellow lion below a red Cap of Liberty and the words PAZ Y JUSTICIA (Peace and Justice)); red symbolizes bravery and patriotism, white represents integrity and peace, and blue denotes liberty and generosity
note: the three color bands resemble those on the flag of the Netherlands; one of only three national flags that differ on their obverse and reverse sides - the others are Moldova and Saudi Arabia
National symbol(s)
lion; national colors: red, white, blue
National anthem
name: "Paraguayos, Republica o muerte!" (Paraguayans, The Republic or Death!)
lyrics/music: Francisco Esteban ACUNA de Figueroa/disputed
note: adopted 1934, in use since 1846; officially adopted following its re-arrangement in 1934
Economy
Economic overview
Landlocked Paraguay has a market economy distinguished by a large informal sector, featuring re-export of imported consumer goods to neighboring countries, as well as the activities of thousands of microenterprises and urban street vendors. A large percentage of the population, especially in rural areas, derives its living from agricultural activity, often on a subsistence basis. Because of the importance of the informal sector, accurate economic measures are difficult to obtain.
On a per capita basis, real income has grown steadily over the past five years as strong world demand for commodities, combined with high prices and favorable weather, supported Paraguay's commodity-based export expansion. Paraguay is the fifth largest soy producer in the world. Drought hit in 2008, reducing agricultural exports and slowing the economy even before the onset of the global recession. The economy fell 3.8% in 2009, as lower world demand and commodity prices caused exports to contract. Severe drought and outbreaks of hoof-and-mouth disease in 2012 led to a brief drop in beef and other agricultural exports. Since 2014, however, Paraguay’s economy has grown at a 4% average annual rate due to strong production and high global prices, at a time when other countries in the region have contracted.
The Paraguayan Government recognizes the need to diversify its economy and has taken steps in recent years to do so. In addition to looking for new commodity markets in the Middle East and Europe, Paraguayan officials have promoted the country’s low labor costs, cheap energy from its massive Itaipu Hydroelectric Dam, and single-digit tax rate on foreign firms. As a result, the number of factories operating in the country – mostly transplants from Brazil - has tripled since 2014.
Corruption, limited progress on structural reform, and deficient infrastructure are the main obstacles to long-term growth. Judicial corruption is endemic and is seen as the greatest barrier to attracting more foreign investment. Paraguay has been adverse to public debt throughout its history, but has recently sought to finance infrastructure improvements to attract foreign investment.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$87.98 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$88.87 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$89.23 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
4.8% (2017 est.)
4.3% (2016 est.)
3.1% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$12,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$12,600 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$12,800 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$38.94 billion (2017 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
3.6% (2017 est.)
4.1% (2016 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: BB+ (2018)
Moody's rating: Ba1 (2015)
Standard & Poors rating: BB (2014)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 17.9% (2017 est.)
industry: 27.7% (2017 est.)
services: 54.5% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 66.7% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 11.3% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 17.3% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.3% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 46.6% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -42.2% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
soybeans, sugar cane, maize, cassava, wheat, rice, beef, milk, oranges, oil palm fruit
Industries
sugar processing, cement, textiles, beverages, wood products, steel, base metals, electric power
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 26.5%
industry: 18.5%
services: 55% (2008)
Population below poverty line
23.5% (2019 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
46.2 (2018 est.)
53.2 (2009)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 1.5%
highest 10%: 37.6% (2013 est.)
Budget
revenues: 5.524 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 5.968 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$298 million (2017 est.)
$416 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$11.81 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$13.27 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$14.36 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
Brazil 32%, Argentina 22%, Chile 8%, Russia 8% (2019)
Exports - commodities
soybeans and soybean products, electricity, beef, corn, insulated wiring (2019)
Imports
$10.62 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$13.15 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$13.88 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
Brazil 24%, United States 22%, China 17%, Argentina 10%, Chile 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
broadcasting equipment, cars, pesticides, refined petroleum, tires (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$7.877 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$6.881 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$16.622 billion (2019 est.)
$16.238 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
guarani (PYG) per US dollar -
7,045 (2020 est.)
6,426 (2019 est.)
5,915.4 (2018 est.)
5,160.4 (2014 est.)
4,462.2 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 17.1%
male: 13.1%
female: 23.3% (2020 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
8.87 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65Electricity - from fossil fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
99% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3Electricity - from other renewable sources
1% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161Refined petroleum products - consumption
43,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 272,656 (2019)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3.87 (2019 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 7,761,848 (2019)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 110.2 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: limited progress on structural reform and deficient infrastructure of the landlocked country are obstacles to telecom platform; monopolized fixed-line service; effective competition in mobile market, serving 96% of population through LTE; deployment of fiber; South Korean investment in education centers; operator enabled 100 free Internet points across the country; Inter-American Development Bank loan supports modernization within regulatory framework; dependent on neighboring countries for access to submarine cables; major importer of broadcasting equipment from the USA (2020)
domestic: deficiencies in provision of fixed-line service have resulted in a rapid expansion of mobile-cellular services fostered by competition among multiple providers; Internet market also open to competition; fixed-line 4 per 100 and mobile-cellular 107 per 100 (2019)
international: country code - 595; Paraguay's landlocked position means they must depend on neighbors for interconnection with submarine cable networks, making it cost more for broadband services; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
6 privately owned TV stations; about 75 commercial and community radio stations; 1 state-owned radio network (2019)
Internet users
total: 4.92 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 74.52% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 377,379 (2019)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 5.36 (2019 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 8
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 560,631 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 1.97 million mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 15
over 3,047 m: 3
1,524 to 2,437 m: 7
914 to 1,523 m: 5 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 784
1,524 to 2,437 m: 23
914 to 1,523 m: 290
under 914 m: 471 (2013)
Railways
total: 30 km (2014)
standard gauge: 30 km 1.435-m gauge (2014)
Roadways
total: 74,676 km (2017)
paved: 6,167 km (2017)
unpaved: 68,509 km (2017)
Waterways
3,100 km (primarily on the Paraguay and Paraná River systems) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 32Merchant marine
total: 110
by type: container ship 3, general cargo 25, oil tanker 5, other 77 (2021)
note: as of 2017, Paraguay registered 2,012 fluvial vessels of which 1,741 were commercial barges
Ports and terminals
river port(s): Asuncion, Villeta, San Antonio, Encarnacion (Parana)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Armed Forces Command (Commando de las Fuerzas Militares): Army (Ejercito), Navy (Armada, includes marines), Air Force (Fuerza Aerea) (2021)
Military expenditures
1% of GDP (2020 est.)
1% of GDP (2019)
0.9% of GDP (2018)
0.9% of GDP (2017)
1% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Armed Forces of Paraguay have approximately 14,000 active personnel (9,000 Army; 3,000 Navy; 2,000 Air Force) (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Paraguayan military forces inventory is comprised of mostly older equipment from a variety of foreign suppliers, particularly Brazil and the US; since 2010, Paraguay has acquired small quantities of mostly second-hand military equipment from several countries, including Argentina, Brazil, Israel, Taiwan, and the US (2021)
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military service; conscript service obligation is 12 months for Army, 24 months for Navy; volunteers for the Air Force must be younger than 22 years of age with a secondary school diploma (2019)
Military - note
as of 2021, the armed forces were principally focused on the Paraguayan People's Army (Ejército del Pueblo Paraguayo, EPP), a Marxist-nationalist insurgent group operating in the rural northern part of the country
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
unruly region at convergence of Argentina-Brazil-Paraguay borders is locus of money laundering, smuggling, arms and illegal narcotics trafficking, and fundraising for violent extremist organizations
Illicit drugs
cannabis cultivation and the trafficking of Andean cocaine in the tri-border area shared with Argentina, and Brazil facilitates money laundering, violence and other criminal activity.