Introduction
Background
Humans arrived in the Palauan archipelago around 1000 B.C. from Southeast Asia and developed a complex, highly organized matrilineal society where high-ranking women picked the chiefs. The islands were the westernmost part of the widely scattered Pacific islands north of New Guinea that Spanish explorers named the Caroline Islands in the 17th century. There were several failed attempts by Spanish Jesuit missionaries to visit the islands in the early 1700s. Spain gained some influence in the islands and administered it from the Philippines but sold Palau to Germany in 1899 after it lost the Philippines in the Spanish-American War.
Japan seized Palau in 1914, was granted a League of Nations mandate to administer the islands in 1920, and made Koror the capital of its South Seas Mandate in 1922. By the outbreak of World War II, there were four times as many Japanese living in Koror as Palauans. In 1944, the Battle of Peleliu between US and Japanese forces resulted in more than 15,000 deaths. Following the war, Palau became part of the US-administered Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands.
Palau voted against joining the Federated States of Micronesia in 1978 and adopted its own constitution in 1981, which stated that Palau was a nuclear-free country. In 1982, Palau signed a Compact of Free Association (COFA) with the US, which granted Palau financial assistance and access to many US domestic programs in exchange for exclusive US military access and defense responsibilities. However, many Palauans saw the COFA as incompatible with the Palauan Constitution because of the US military’s nuclear arsenal, and seven referenda failed to achieve ratification. Following a constitutional amendment and eighth referendum in 1993, the COFA was ratified and entered into force in 1994 when the islands gained their independence. Its funding was renewed in 2010.
Palau has been on the frontlines of combatting climate change and protecting marine resources. In 2011, Palau banned commercial shark fishing and created the world’s first shark sanctuary. In 2017, Palau began stamping the Palau Pledge into passports, reminding visitors to act in ecologically and culturally responsible ways. In 2020, Palau banned coral reef-toxic sunscreens and expanded its fishing prohibition to include 80% of its exclusive economic zone.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
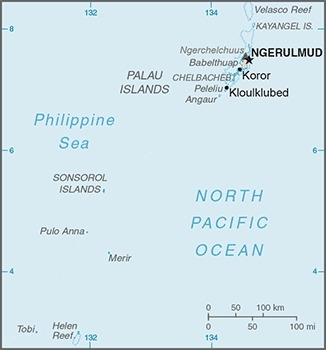
Location
Oceania, group of islands in the North Pacific Ocean, southeast of the Philippines
Geographic coordinates
7 30 N, 134 30 E
Map references
Oceania
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
1,519 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; hot and humid; wet season May to November
Terrain
varying topography from the high, mountainous main island of Babelthuap to low, coral islands usually fringed by large barrier reefs
Elevation
highest point: Mount Ngerchelchuus 242 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
Natural resources
forests, minerals (especially gold), marine products, deep-seabed minerals
Land use
agricultural land: 10.8% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.2% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 4.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 4.3% (2018 est.)
forest: 87.6% (2018 est.)
other: 1.6% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
0 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
most of the population is located on the southern end of the main island of Babelthuap
Natural hazards
typhoons (June to December)
Geography - note
westernmost archipelago in the Caroline chain, consists of six island groups totaling more than 300 islands; includes World War II battleground of Beliliou (Peleliu) and world-famous Rock Islands
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Palauan(s)
adjective: Palauan
Ethnic groups
Palauan (Micronesian with Malayan and Melanesian admixtures) 73%, Carolinian 2%, Asian 21.7%, Caucasian 1.2%, other 2.1% (2015 est.)
Languages
Palauan (official on most islands) 65.2%, other Micronesian 1.9%, English (official) 19.1%, Filipino 9.9%, Chinese 1.2%, other 2.8% (2015 est.)
note: Sonsoralese is official in Sonsoral; Tobian is official in Tobi; Angaur and Japanese are official in Angaur
Religions
Roman Catholic 45.3%, Protestant 34.9% (includes Evangelical 26.4%, Seventh Day Adventist 6.9%, Assembly of God .9%, Baptist .7%), Modekngei 5.7% (indigenous to Palau), Muslim 3%, Church of Jesus Christ 1.5%, other 9.7% (2015 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 18.68% (male 2,090/female 1,961)
15-24 years: 15.86% (male 1,723/female 1,716)
25-54 years: 45.33% (male 6,026/female 3,804)
55-64 years: 10.68% (male 853/female 1,463)
65 years and over: 9.45% (male 501/female 1,548) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: NA
youth dependency ratio: NA
elderly dependency ratio: NA
potential support ratio: NA
Median age
total: 33.9 years
male: 32.9 years
female: 35.9 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
most of the population is located on the southern end of the main island of Babelthuap
Urbanization
urban population: 81.5% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.59% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
277 NGERULMUD (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.58 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.58 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.32 male(s)/female
total population: 1.07 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Infant mortality rate
total: 11.52 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 13.53 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 9.39 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 74.38 years
male: 71.19 years
female: 77.75 years (2021 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
10.9% (2018)
Physicians density
1.42 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
Hospital bed density
4.8 beds/1,000 population (2010)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: malaria
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 96.6%
male: 96.8%
female: 96.3% (2015)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 17 years
male: 16 years
female: 17 years (2013)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 5.6%
Environment
Environment - current issues
inadequate facilities for disposal of solid waste; threats to the marine ecosystem from sand and coral dredging, illegal and destructive fishing practices, and overfishing; climate change contributes to rising sea level and coral bleaching; drought
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 12.18 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 0.22 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 0.06 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; hot and humid; wet season May to November
Land use
agricultural land: 10.8% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.2% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 4.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 4.3% (2018 est.)
forest: 87.6% (2018 est.)
other: 1.6% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 81.5% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.59% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: malaria
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 9,427 tons (2016 est.)
Total renewable water resources
0 cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Palau
conventional short form: Palau
local long form: Beluu er a Belau
local short form: Belau
former: Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, Palau District
etymology: from the Palauan name for the islands, Belau, which likely derives from the Palauan word "beluu" meaning "village"
Government type
presidential republic in free association with the US
Capital
name: Ngerulmud
geographic coordinates: 7 30 N, 134 37 E
time difference: UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the Palauan meaning is "place of fermented 'mud'" ('mud' being the native name for the keyhole angelfish); the site of the new capitol (established in 2006) had been a large hill overlooking the ocean, Ngerulmud, on which women would communally gather to offer fermented angelfish to the gods
note: Ngerulmud, on Babeldaob Island, is the smallest national capital on earth by population, with only a few hundred people; the name is pronounced en-jer-al-mud; Koror, on Koror Island, with over 11,000 residents is by far the largest settlement in Palau; it served as the country's capital from independence in 1994 to 2006
Administrative divisions
16 states; Aimeliik, Airai, Angaur, Hatohobei, Kayangel, Koror, Melekeok, Ngaraard, Ngarchelong, Ngardmau, Ngatpang, Ngchesar, Ngeremlengui, Ngiwal, Peleliu, Sonsorol
Independence
1 October 1994 (from the US-administered UN trusteeship)
National holiday
Constitution Day, 9 July (1981), day of a national referendum to pass the new constitution; Independence Day, 1 October (1994)
Constitution
history: ratified 9 July 1980, effective 1 January 1981
amendments: proposed by a constitutional convention (held at least once every 15 years with voter approval), by public petition of at least 25% of eligible voters, or by a resolution adopted by at least three fourths of National Congress members; passage requires approval by a majority of votes in at least three fourths of the states in the next regular general election; amended several times, last in 2020
Legal system
mixed legal system of civil, common, and customary law
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Palau
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: note - no procedure for naturalization
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Surangel WHIPPS Jr. (since 21 January 2021); Vice President Jerrlyn Uduch Sengebau SENIOR (since 21 January 2021); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Surangel WHIPPS Jr. (since 21 January 2021); Vice President Jerrlyn Uduch Sengebau SENIOR (since 21 January 2021)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the Senate; also includes the vice president; the Council of Chiefs consists of chiefs from each of the states who advise the president on issues concerning traditional laws, customs, and their relationship to the constitution and laws of Palau
elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on separate ballots by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 3 November 2020 (next to be held in November 2024)
election results: Surangel WHIPPS, Jr. elected president (in second round); percent of vote - Surangel WHIPPS, Jr. (independent) 56.7%, Raynold OILUCH (independent) 43.3%
Legislative branch
description: bicameral National Congress or Olbiil Era Kelulau consists of:
Senate (13 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by majority vote to serve 4-year terms)
House of Delegates (16 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 4-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last held on 3 November 2020 (next to be held in November 2024)
House of Delegates - last held on 3 November 2020 (next to be held in November 2024)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote - NA; seats - independent 13; composition - men 12, women 1; percent of women 7.7%
House of Delegates - percent of vote - NA; seats - independent 16; composition - men 15, women 1; percent of women 6.3%; note - overall percent of women in National Congress 6.9%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and 3 associate justices organized into appellate trial divisions; the Supreme Court organization also includes the Common Pleas and Land Courts)
judge selection and term of office: justices nominated by a 7-member independent body consisting of judges, presidential appointees, and lawyers and appointed by the president; judges can serve until mandatory retirement at age 65
subordinate courts: National Court and other 'inferior' courts
International organization participation
ACP, ADB, AOSIS, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IPU, MIGA, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, WHO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Hersey KYOTA (since 12 November 1997)
chancery: 1701 Pennsylvania Avenue NW, Suite 200, Washington, DC 20006
telephone: [1] (202) 349-8598
FAX: [1] (202) 452-6281
email address and website:
info@palauembassy.org
https://www.palauembassy.org/
consulate(s): Tamuning (Guam)
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador John HENNESSEY-NILAND (since 6 March 2020)
embassy: Omsangel/Beklelachieb, Airai 96940
mailing address: 4260 Koror Place, Washington, DC 20521-4260
telephone: [680] 587-2920
FAX: [680] 587-2911
email address and website:
ConsularKoror@state.gov
https://pw.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
light blue with a large yellow disk shifted slightly to the hoist side; the blue color represents the ocean, the disk represents the moon; Palauans consider the full moon to be the optimum time for human activity; it is also considered a symbol of peace, love, and tranquility
National symbol(s)
bai (native meeting house); national colors: blue, yellow
National anthem
name: "Belau rekid" (Our Palau)
lyrics/music: multiple/Ymesei O. EZEKIEL
note: adopted 1980
Economy
Economic overview
The economy is dominated by tourism, fishing, and subsistence agriculture. Government is a major employer of the work force relying on financial assistance from the US under the Compact of Free Association (Compact) with the US that took effect after the end of the UN trusteeship on 1 October 1994. The US provided Palau with roughly $700 million in aid for the first 15 years following commencement of the Compact in 1994 in return for unrestricted access to its land and waterways for strategic purposes. The population enjoys a per capita income roughly double that of the Philippines and much of Micronesia.
Business and leisure tourist arrivals reached a record 167,966 in 2015, a 14.4% increase over the previous year, but fell to 138,408 in 2016. Long-run prospects for tourism have been bolstered by the expansion of air travel in the Pacific, the rising prosperity of industrial East Asia, and the willingness of foreigners to finance infrastructure development. Proximity to Guam, the region's major destination for tourists from East Asia, and a regionally competitive tourist infrastructure enhance Palau's advantage as a destination.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$320 million note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$330 million note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
$317 million (2017 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
-3.7% (2017 est.)
0% (2016 est.)
10.1% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$17,600 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$18,400 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
$17,841 (2017 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$292 million (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 3% (2016 est.)
industry: 19% (2016 est.)
services: 78% (2016 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 60.5% (2016 est.)
government consumption: 27.2% (2016 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 22.7% (2016 est.)
investment in inventories: 1.9% (2016 est.)
exports of goods and services: 55.2% (2016 est.)
imports of goods and services: -67.6% (2016 est.)
Agricultural products
coconuts, cassava (manioc, tapioca), sweet potatoes; fish, pigs, chickens, eggs, bananas, papaya, breadfruit, calamansi, soursop, Polynesian chestnuts, Polynesian almonds, mangoes, taro, guava, beans, cucumbers, squash/pumpkins (various), eggplant, green onions, kangkong (watercress), cabbages (various), radishes, betel nuts, melons, peppers, noni, okra
Industries
tourism, fishing, subsistence agriculture
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 1.2%
industry: 12.4%
services: 86.4% (2016)
Population below poverty line
24.9% NA (2006)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 193 million (2012 est.)
expenditures: 167.3 million (2012 est.)
Fiscal year
1 October - 30 September
Current account balance
-$53 million (2017 est.)
-$36 million (2016 est.)
Exports - partners
Japan 70%, South Korea 15%, United States 7% (2019)
Exports - commodities
fish, computers, broadcasting equipment, office machinery/parts, scrap vessels (2019)
Imports - partners
South Korea 19%, China 18%, Taiwan 17%, United States 17%, Japan 16% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, fish, cars, broadcasting equipment, modeling instruments (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$0 (31 December 2017 est.)
$580.9 million (31 December 2015 est.)
Debt - external
$18.38 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$16.47 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
Exchange rates
the US dollar is used
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2018)
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 7,204 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 40.78 (2018 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 23,743 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 134.4 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: well-developed mobile sector, recently boosted by satellite network capacity upgrades; 3G services available with satellite; lack of telecom regulations; newest and most powerful commercial satellite, Kacific-1 satellite, launched in 2019 to improve telecommunications in the Asia Pacific region (2020)
domestic: fixed-line 41 per 100 and mobile-cellular services 134 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 680; landing point for the SEA-US submarine cable linking Palau, Philippines, Micronesia, Indonesia, Hawaii (US), Guam (US) and California (US); satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
no broadcast TV stations; a cable TV network covers the major islands and provides access to 4 local cable stations, rebroadcasts (on a delayed basis) of a number of US stations, as well as access to a number of real-time satellite TV channels; about a half dozen radio stations (1 government-owned) (2019)
Internet users
total: 6,752 (2021 est.)
percent of population: 26.97% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 1,224 (2016)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 6.93 (2018)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 1
Airports - with paved runways
total: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2019)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2 (2013)
Roadways
total: 125 km (2018)
paved: 89 km (2018)
unpaved: 36 km (2018)
Merchant marine
total: 264
by type: bulk carrier 16, container ship 7, general cargo 107, oil tanker 40, other 94 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Koror
Military and Security
Military and security forces
no regular military forces; the Ministry of Justice includes divisions/bureaus for public security, police functions, and maritime law enforcement
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
since 2018, Australia and Japan have provided patrol boats to the Palau's Division of Marine Law Enforcement (2020)
Military - note
under a 1994 Compact of Free Association between Palau and the US, the US until 2044 is responsible for the defense of Palaus and the US military is granted access to the islands, but it has not stationed any military forces there
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
maritime delineation negotiations continue with Philippines, Indonesia