Nicaragua
Introduction
Background
The Pacific coast of Nicaragua was settled as a Spanish colony from Panama in the early 16th century. Independence from Spain was declared in 1821 and the country became an independent republic in 1838. Britain occupied the Caribbean Coast in the first half of the 19th century, but gradually ceded control of the region in subsequent decades. Violent opposition to governmental manipulation and corruption spread to all classes by 1978 and resulted in a short-lived civil war that brought a civic-military coalition, spearheaded by the Marxist Sandinista guerrillas led by Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra to power in 1979. Nicaraguan aid to leftist rebels in El Salvador prompted the US to sponsor anti-Sandinista contra guerrillas through much of the 1980s. After losing free and fair elections in 1990, 1996, and 2001, former Sandinista President Daniel ORTEGA was elected president in 2006, 2011, 2016, and most recently in 2021. Municipal, regional, and national-level elections since 2008 have been marred by widespread irregularities. Democratic institutions have weakened under the ORTEGA administration as the president has garnered full control over all branches of government, especially after cracking down on a nationwide anti-government protest movement in 2018. In the lead-up to the 2021 presidential election, most of the prominent opposition candidates were either arrested or forced into exile leaving only five lesser-known candidates of mostly small parties allied to ORTEGA's Sandinistas to run against him.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
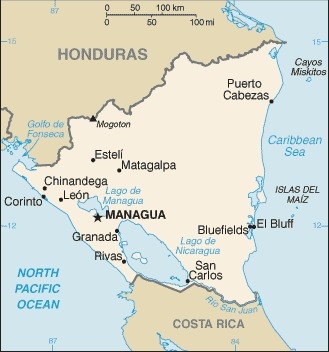
Geography
Location
Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Costa Rica and Honduras
Geographic coordinates
13 00 N, 85 00 W
Map references
Central America and the Caribbean
Land boundaries
total: 1,253 km
border countries (2): Costa Rica 313 km, Honduras 940 km
Coastline
910 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
continental shelf: natural prolongation
Climate
tropical in lowlands, cooler in highlands
Terrain
extensive Atlantic coastal plains rising to central interior mountains; narrow Pacific coastal plain interrupted by volcanoes
Elevation
highest point: Mogoton 2,085 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 298 m
Natural resources
gold, silver, copper, tungsten, lead, zinc, timber, fish
Land use
agricultural land: 42.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 12.5% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 2.5% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 27.2% (2018 est.)
forest: 25.3% (2018 est.)
other: 32.5% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
1,990 sq km (2012)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lago de Nicaragua - 8,150 sq km; Lago de Managua - 1,040 sq km
Population distribution
the overwhelming majority of the population resides in the western half of the country, with much of the urban growth centered in the capital city of Managua; coastal areas also show large population clusters
Natural hazards
destructive earthquakes; volcanoes; landslides; extremely susceptible to hurricanes
volcanism: significant volcanic activity; Cerro Negro (728 m), which last erupted in 1999, is one of Nicaragua's most active volcanoes; its lava flows and ash have been known to cause significant damage to farmland and buildings; other historically active volcanoes include Concepcion, Cosiguina, Las Pilas, Masaya, Momotombo, San Cristobal, and Telica
Geography - note
largest country in Central America; contains the largest freshwater body in Central America, Lago de Nicaragua
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Nicaraguan(s)
adjective: Nicaraguan
Ethnic groups
Mestizo (mixed Amerindian and White) 69%, White 17%, Black 9%, Amerindian 5%
Languages
Spanish (official) 95.3%, Miskito 2.2%, Mestizo of the Caribbean coast 2%, other 0.5%; note - English and indigenous languages found on the Caribbean coast (2005 est.)
major-language sample(s):
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Roman Catholic 50%, Evangelical 33.2%, other 2.9%, none 0.7%, unspecified 13.2% (2017 est.)
Demographic profile
Despite being one of the poorest countries in Latin America, Nicaragua has improved its access to potable water and sanitation and has ameliorated its life expectancy, infant and child mortality, and immunization rates. However, income distribution is very uneven, and the poor, agriculturalists, and indigenous people continue to have less access to healthcare services. Nicaragua's total fertility rate has fallen from around 6 children per woman in 1980 to below replacement level today, but the high birth rate among adolescents perpetuates a cycle of poverty and low educational attainment.
Nicaraguans emigrate primarily to Costa Rica and to a lesser extent the United States. Nicaraguan men have been migrating seasonally to Costa Rica to harvest bananas and coffee since the early 20th century. Political turmoil, civil war, and natural disasters from the 1970s through the 1990s dramatically increased the flow of refugees and permanent migrants seeking jobs, higher wages, and better social and healthcare benefits. Since 2000, Nicaraguan emigration to Costa Rica has slowed and stabilized. Today roughly 300,000 Nicaraguans are permanent residents of Costa Rica - about 75% of the foreign population - and thousands more migrate seasonally for work, many illegally.
Age structure
0-14 years: 25.63% (male 811,731/female 777,984)
15-24 years: 19.51% (male 609,962/female 600,567)
25-54 years: 42.41% (male 1,254,683/female 1,376,052)
55-64 years: 6.63% (male 188,591/female 222,766)
65 years and over: 5.82% (male 159,140/female 201,965) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 54.3
youth dependency ratio: 45.5
elderly dependency ratio: 8.8
potential support ratio: 11.4 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 27.3 years
male: 26.4 years
female: 28.2 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
the overwhelming majority of the population resides in the western half of the country, with much of the urban growth centered in the capital city of Managua; coastal areas also show large population clusters
Urbanization
urban population: 59.3% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.45% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.073 million MANAGUA (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.91 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.85 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.79 male(s)/female
total population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
19.2 years (2011/12 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality ratio
198 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47Infant mortality rate
total: 19.57 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 22.83 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 16.16 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 74.51 years
male: 72.28 years
female: 76.86 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
80.4% (2011/12)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 97.6% of population
rural: 62.6% of population
total: 83.1% of population
unimproved: urban: 2.4% of population
rural: 37.4% of population
total: 16.9% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
8.6% (2018)
Physicians density
0.98 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
Hospital bed density
0.9 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 89.8% of population
rural: 66.5% of population
total: 80.1% of population
unimproved: urban: 10.2% of population
rural: 33.5% of population
total: 19.9% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<500 (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 82.6%
male: 82.4%
female: 82.8% (2015)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 8.5%
male: 6.4%
female: 12.9% (2014 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation; soil erosion; water pollution; drought
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 16.87 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 5.59 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 6.46 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical in lowlands, cooler in highlands
Land use
agricultural land: 42.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 12.5% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 2.5% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 27.2% (2018 est.)
forest: 25.3% (2018 est.)
other: 32.5% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 59.3% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.45% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 1.26% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1,528,816 tons (2010 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lago de Nicaragua - 8,150 sq km; Lago de Managua - 1,040 sq km
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 286 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 73.6 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 1.185 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
164.52 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Nicaragua
conventional short form: Nicaragua
local long form: Republica de Nicaragua
local short form: Nicaragua
etymology: Nicarao was the name of the largest indigenous settlement at the time of Spanish arrival; conquistador Gil GONZALEZ Davila, who explored the area (1622-23), combined the name of the community with the Spanish word "agua" (water), referring to the two large lakes in the west of the country (Lake Managua and Lake Nicaragua)
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Managua
geographic coordinates: 12 08 N, 86 15 W
time difference: UTC-6 (1 hour behind Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: may derive from the indigenous Nahuatl term "mana-ahuac," which translates as "adjacent to the water" or a site "surrounded by water"; the city is situated on the southwestern shore of Lake Managua
Administrative divisions
15 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento) and 2 autonomous regions* (regiones autonomistas, singular - region autonoma); Boaco, Carazo, Chinandega, Chontales, Costa Caribe Norte*, Costa Caribe Sur*, Esteli, Granada, Jinotega, Leon, Madriz, Managua, Masaya, Matagalpa, Nueva Segovia, Rio San Juan, Rivas
Independence
15 September 1821 (from Spain)
National holiday
Independence Day, 15 September (1821)
Constitution
history: several previous; latest adopted 19 November 1986, effective 9 January 1987
amendments: proposed by the president of the republic or assent of at least half of the National Assembly membership; passage requires approval by 60% of the membership of the next elected Assembly and promulgation by the president of the republic; amended several times, last in 2021
Legal system
civil law system; Supreme Court may review administrative acts
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: no, except in cases where bilateral agreements exist
residency requirement for naturalization: 4 years
Suffrage
16 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Jose Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra (since 10 January 2007); Vice President Rosario MURILLO Zambrana (since 10 January 2017); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Jose Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra (since 10 January 2007); Vice President Rosario MURILLO Zambrana (since 10 January 2017)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by qualified plurality vote for a 5-year term (no term limits as of 2014); election last held on 7 November 2021 (next to be held on 1 November 2026)
election results:
2021: Jose Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra reelected president for a fourth consecutive term; percent of vote - Jose Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra (FSLN) 75.9%, Walter ESPINOZA (PLC) 14.3%, Guillermo OSORNO (CCN) 3.3%, Marcelo MONTIEL (ALN) 3.1%, other 3.4%
2016: Jose Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra reelected president for a third consecutive term; percent of vote - Jose Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra (FSLN) 72.4%, Maximino RODRIGUEZ (PLC) 15%, Jose del Carmen ALVARADO (PLI) 4.5%, Saturnino CERRATO Hodgson (ALN) 4.3%, other 3.7%
Legislative branch
description: unicameral National Assembly or Asamblea Nacional (92 seats; 70 members in multi-seat constituencies, representing the country's 15 departments and 2 autonomous regions, and 20 members in a single nationwide constituency directly elected by party-list proportional representation vote; 2 seats reserved for the previous president and the runner-up candidate in the previous presidential election; members serve 5-year terms)
elections: last held on 7 November 2021 (next to be held on 1 November 2026)
election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - FSLN 75, PLC 9, ALN 2, APRE 1, CCN 1, PLI 1, YATAMA 1; composition - men 46, women 45, percent of women 49.4%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court or Corte Suprema de Justicia (consists of 16 judges organized into administrative, civil, criminal, and constitutional chambers)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges elected by the National Assembly to serve 5-year staggered terms
subordinate courts: Appeals Court; first instance civil, criminal, and labor courts; military courts are independent of the Supreme Court
Political parties and leaders
Alliance for the Republic or APRE [Carlos CANALES]
Conservative Party or PC [Alfredo CESAR]
Independent Liberal Party or PLI [Jose del Carmen ALVARADO]
Liberal Constitutionalist Party or PLC [Maria Haydee OSUNA]
Nicaraguan Liberal Alliance or ALN [Alejandro MEJIA Ferreti]
Nicaraguan Party of the Christian Path or CCN [Guillermo OSORNO]
Sandinista National Liberation Front or FSLN [Jose Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra]
Sandinista Renovation Movement or MRS [Suyen BARAHONA]
Sons of Mother Earth or YATAMA [Brooklyn RIVERA]
International organization participation
BCIE, CACM, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA (observer), MIGA, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, SICA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Francisco Obadiah CAMPBELL Hooker (since 28 June 2010)
chancery: 1627 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone: [1] (202) 939-6570; [1] (202) 939-6573
FAX: [1] (202) 939-6545
consulate(s) general: Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, San Francisco
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Kevin K. SULLIVAN (since 14 November 2018)
embassy: Kilometer 5.5 Carretera Sur, Managua
mailing address: 3240 Managua Place, Washington DC 20521-3240
telephone: [505] 2252-7100,
FAX: [505] 2252-7250
email address and website:
ACS.Managua@state.gov
https://ni.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of blue (top), white, and blue with the national coat of arms centered in the white band; the coat of arms features a triangle encircled by the words REPUBLICA DE NICARAGUA on the top and AMERICA CENTRAL on the bottom; the banner is based on the former blue-white-blue flag of the Federal Republic of Central America; the blue bands symbolize the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, while the white band represents the land between the two bodies of water
note: similar to the flag of El Salvador, which features a round emblem encircled by the words REPUBLICA DE EL SALVADOR EN LA AMERICA CENTRAL centered in the white band; also similar to the flag of Honduras, which has five blue stars arranged in an X pattern centered in the white band
National symbol(s)
turquoise-browed motmot (bird); national colors: blue, white
National anthem
name: "Salve a ti, Nicaragua" (Hail to Thee, Nicaragua)
lyrics/music: Salomon Ibarra MAYORGA/traditional, arranged by Luis Abraham DELGADILLO
note: although only officially adopted in 1971, the music was approved in 1918 and the lyrics in 1939; the tune, originally from Spain, was used as an anthem for Nicaragua from the 1830s until 1876
Economy
Economic overview
Nicaragua, the poorest country in Central America and the second poorest in the Western Hemisphere, has widespread underemployment and poverty. GDP growth of 4.5% in 2017 was insufficient to make a significant difference. Textiles and agriculture combined account for nearly 50% of Nicaragua's exports. Beef, coffee, and gold are Nicaragua’s top three export commodities.
The Dominican Republic-Central America-United States Free Trade Agreement has been in effect since April 2006 and has expanded export opportunities for many Nicaraguan agricultural and manufactured goods.
In 2013, the government granted a 50-year concession with the option for an additional 50 years to a newly formed Chinese-run company to finance and build an inter-oceanic canal and related projects, at an estimated cost of $50 billion. The canal construction has not started.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$34.98 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$35.68 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$37.05 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
4.9% (2017 est.)
4.7% (2016 est.)
4.8% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$5,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$5,500 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$5,700 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$12.57 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
5.3% (2019 est.)
4.9% (2018 est.)
3.8% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: B- (2018)
Moody's rating: B3 (2020)
Standard & Poors rating: B- (2018)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 15.5% (2017 est.)
industry: 24.4% (2017 est.)
services: 60% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 69.9% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 15.3% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 28.1% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 1.7% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 41.2% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -55.4% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
sugar cane, milk, rice, maize, plantains, groundnuts, cassava, beans, coffee, poultry
Industries
food processing, chemicals, machinery and metal products, knit and woven apparel, petroleum refining and distribution, beverages, footwear, wood, electric wire harness manufacturing, mining
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 31%
industry: 18%
services: 50% (2011 est.)
Unemployment rate
6.4% (2017 est.)
6.2% (2016 est.)
note: underemployment was 46.5% in 2008
Population below poverty line
24.9% (2016 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
46.2 (2014 est.)
45.8 (2009)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 1.8%
highest 10%: 47.1% (2014)
Budget
revenues: 3.871 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 4.15 billion (2017 est.)
Public debt
33.3% of GDP (2017 est.)
31.2% of GDP (2016 est.)
note: official data; data cover general government debt and include debt instruments issued (or owned) by Government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities, as well as intragovernmental debt; intragovernmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as retirement, medical care, and unemployment, debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions; Nicaragua rebased its GDP figures in 2012, which reduced the figures for debt as a percentage of GDP
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$694 million (2017 est.)
-$989 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$5.34 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$5.71 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$5.56 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
United States 60%, El Salvador 5%, Mexico 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
clothing and apparel, gold, insulated wiring, coffee, beef (2019)
Imports
$5.94 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$6.25 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$6.75 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
United States 27%, Mexico 12%, China 11%, Guatemala 9%, Costa Rica 7%, El Salvador 6%, Honduras 6% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, clothing and apparel, crude petroleum, packaged medicines, insulated wiring (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$2.758 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$2.448 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$11.674 billion (2019 est.)
$11.771 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
cordobas (NIO) per US dollar -
30.11 (2017 est.)
28.678 (2016 est.)
28.678 (2015 est.)
27.257 (2014 est.)
26.01 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 8.5%
male: 6.4%
female: 12.9% (2014 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 97% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 99.2% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 92% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
1.551 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123Electricity - from fossil fuels
56% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
9% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120Electricity - from other renewable sources
35% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8Refined petroleum products - production
14,720 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95Refined petroleum products - consumption
37,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 210,981 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3.18 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 5,976,479 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 90.22 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: with authoritarian government, weak public institutions, and impoverished citizenry, Nicaragua’s telecom system is dependent on upgrades through foreign investment, primarily from Russia and China; World Bank funded national fiber broadband network and links to Caribbean submarine cables; Chinese-financed projects, including airport, oil pipeline, and roads in process; nearly all installed telecom capacity now uses financed digital technology; lowest fixed-line tele-density and mobile penetration in Central America; Internet cafes provide access to Internet and email services; rural areas lack access to most basic telecom infrastructure; LTE service in dozens of towns and cities; importer of broadcasting equipment and computers from China (2020)
domestic: since privatization, access to fixed-line and mobile-cellular services has improved; fixed-line teledensity roughly 4 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular telephone subscribership has increased to 88 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 505; landing point for the ARCOS fiber-optic submarine cable which provides connectivity to South and Central America, parts of the Caribbean, and the US; satellite earth stations - 1 Intersputnik (Atlantic Ocean region) and 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
multiple terrestrial TV stations, supplemented by cable TV in most urban areas; nearly all are government-owned or affiliated; more than 300 radio stations, both government-affiliated and privately owned (2019)
Internet users
total: 2.78 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 27.86% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 290,351 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4.38 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 7
Airports - with paved runways
total: 12
2,438 to 3,047 m: 3
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 3
under 914 m: 4 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 135
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 15
under 914 m: 119 (2013)
Pipelines
54 km oil (2013)
Roadways
total: 23,897 km (2014)
paved: 3,346 km (2014)
unpaved: 20,551 km (2014)
Waterways
2,220 km (navigable waterways as well as the use of the large Lake Managua and Lake Nicaragua; rivers serve only the sparsely populated eastern part of the country) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 39Merchant marine
total: 5
by type: general cargo 1, oil tanker 1, other 3 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Bluefields, Corinto
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Army of Nicaragua (Ejercito de Nicaragua, EN): Land Forces (Fuerza Terrestre); Naval Forces (Fuerza Naval); Air Forces (Fuerza Aérea); Special Operations Command (Comando de Operaciones Especiales); Nicaraguan National Police (2021)
note - both the military and the police report directly to the president
Military expenditures
0.7% of GDP (2020 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2019)
0.6% of GDP (2018)
0.6% of GDP (2017)
0.5% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 12,000 active personnel (10,000 Army; 800 Navy; 1,200 Air Force) (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Nicaraguan military's inventory includes mostly second-hand Russian/Soviet-era equipment; since 2010, Russia is the leading arms supplier to Nicaragua (2021)
Military service age and obligation
18-30 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; tour of duty 18-36 months; requires Nicaraguan nationality and 6th-grade education (2021)
Military - note
the modern Army of Nicaragua was created in 1979 as the Sandinista Popular Army (1979-1984); prior to 1979, the military was known as the National Guard, which was organized and trained by the US in the 1920s and 1930s; the first commander of the National Guard, Anastasio SOMOZA García, seized power in 1937 and ran the country as a military dictator until his assassination in 1956; his sons ran the country either directly or through figureheads until the Sandinistas came to power in 1979; the defeated National Guard was disbanded by the Sandinistas
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
the 1992 ICJ ruling for El Salvador and Honduras advised a tripartite resolution to establish a maritime boundary in the Gulf of Fonseca, which considers Honduran access to the Pacific; Nicaragua and Costa Rica regularly file border dispute cases over the delimitations of the San Juan River and the northern tip of Calero Island to the ICJ; there is an ongoing case in the ICJ to determine Pacific and Atlantic ocean maritime borders as well as land borders; in 2009, the ICJ ruled that Costa Rican vessels carrying out police activities could not use the river, but official Costa Rican vessels providing essential services to riverside inhabitants and Costa Rican tourists could travel freely on the river; in 2011, the ICJ provisionally ruled that both countries must remove personnel from the disputed area; in 2013, the ICJ rejected Nicaragua's 2012 suit to halt Costa Rica's construction of a highway paralleling the river on the grounds of irreparable environmental damage; in 2013, the ICJ, regarding the disputed territory, ordered that Nicaragua should refrain from dredging or canal construction and refill and repair damage caused by trenches connecting the river to the Caribbean and upheld its 2010 ruling that Nicaragua must remove all personnel; in early 2014, Costa Rica brought Nicaragua to the ICJ over offshore oil concessions in the disputed region; Nicaragua filed a case against Colombia in 2013 over the delimitation of the Continental shelf beyond the 200 nautical miles from the Nicaraguan coast, as well as over the alleged violation by Colombia of Nicaraguan maritime space in the Caribbean Sea
Trafficking in persons
current situation: human traffickers exploit domestic and foreign victims in Nicaragua and Nicaraguans abroad; women, children, and migrants are most at risk; women and children are subject to sex trafficking within the country and its two Caribbean autonomous regions, as well as in other Central American countries, Mexico, Spain, and the United States; traffickers used social media to recruit victims with promises of high-paying jobs in restaurants, hotels, construction, and security outside of Nicaragua where they are subjected to sex or labor trafficking; traffickers exploit children through forced participation in illegal drug production and trafficking; children and persons with disabilities are subjected to forced begging; Nicaragua is also a destination for child sex tourists from the United States, Canada, and Western Europe
tier rating: Tier 3 — Nicaragua does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so and was downgraded to Tier 3; the government identified slightly more victims than in the previous reporting period and prosecuted a trafficker; however, no traffickers were convicted and victim identification remained inadequate; authorities did not investigate, prosecute, or convict government employees complicit in trafficking; the government provided no victim services; prosecution, protection, and prevention efforts in the two Caribbean autonomous regions of Nicaragua continued to be much weaker than in the rest of the country (2020)
Illicit drugs
a transit route for drug traffickers smuggling cocaine from South America through Mexico into the United States via maritime and air routes