Introduction
Background
The peoples of Mongolia have a long history under a number of nomadic empires dating back to the period of the Xiongnu in the 4th century B.C. The name Mongol goes back to at least the 11th century A.D. The most famous Mongol, TEMÜÜJIN (aka Genghis Khan) emerged as the ruler of all Mongols in the early 1200s. By the time of his death in 1227, he had created through conquest a Mongol Empire that extended across much of Eurasia. His descendants, including ÖGÖDEI and KHUBILAI (aka Kublai Khan), continued military campaigns of conquest, taking control of Eastern Europe, the Middle East, and the rest of China where KHUBILAI established the Yuan Dynasty in the 1270s. The Mongols attempted to invade Japan and Java before their empire broke apart in the 14th century. In the 17th century, Mongolia fell under the rule of the Manchus of the Chinese Qing Dynasty. Following the collapse of the Manchus in 1911, Mongolia declared its independence, achieving it with help from the Soviet Union in 1921. Mongolia became a socialist state (the Mongolian People’s Republic) in 1924. Following independence and until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1989, the country was a Soviet satellite state, and heavily reliant on economic, military, and political assistance from Moscow. The period also was marked by periods of purges, political repression, economic stagnation, and tensions with China.
Mongolia peacefully transitioned to an independent democracy in 1990. In 1992, it adopted a new constitution and established a free market economy. Since the country's transition, it has conducted eight presidential and nine legislative elections as of 2021. Throughout the period, the ex-communist Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party (MPRP) - which took the name Mongolian People’s Party (MPP) in 2010 - has competed for political power with the Democratic Party (DP) and several other smaller parties, including a new party formed by former President ENKHBAYAR, which confusingly adopted for itself the MPRP name until it merged with MPP in 2021. In the 2016 parliamentary elections, the MPP won overwhelming control of the Parliament over the DP, which had overseen a sharp decline in Mongolia’s economy during its control of the Parliament in the preceding years. Mongolians elected a DP member, Khaltmaa BATTULGA, as president in 2017. The June 2020 parliamentary elections left the MPP with continued dominant control of the parliament. Mongolians elected former prime minister and MPP member Ukhnaa KHURELSUKH as president in 2021. Mongolia maintains close cultural, political, and military ties with Russia while China is its largest economic partner. Mongolia’s foreign relations are focused on preserving its autonomy by balancing relations with China and Russia, as well as its other major partners, Japan, South Korea, and the US.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
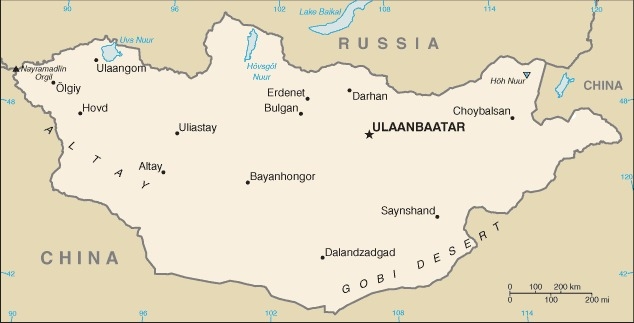
Northern Asia, between China and Russia
Geographic coordinates
46 00 N, 105 00 E
Map references
Asia
Area
total: 1,564,116 sq km
land: 1,553,556 sq km
water: 10,560 sq km
Land boundaries
total: 8,082 km
border countries (2): China 4630 km, Russia 3452 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
desert; continental (large daily and seasonal temperature ranges)
Terrain
vast semidesert and desert plains, grassy steppe, mountains in west and southwest; Gobi Desert in south-central
Elevation
highest point: Nayramadlin Orgil (Khuiten Peak) 4,374 m
lowest point: Hoh Nuur 560 m
mean elevation: 1,528 m
Natural resources
oil, coal, copper, molybdenum, tungsten, phosphates, tin, nickel, zinc, fluorspar, gold, silver, iron
Land use
agricultural land: 73% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 72.6% (2018 est.)
forest: 7% (2018 est.)
other: 20% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
840 sq km (2012)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Hovsgol Nuur - 2,620 sq km; Har Us Nuur - 1,760 sq km;
Salt water lake(s): Uvs Nuur - 3,350 sq km; Hyargas Nuur - 1,360 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Amur (shared with China [s] and Russia [m]) - 4,444 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Population distribution
sparsely distributed population throughout the country; the capital of Ulaanbaatar and the northern city of Darhan support the highest population densities
Natural hazards
dust storms; grassland and forest fires; drought; "zud," which is harsh winter conditions
Geography - note
landlocked; strategic location between China and Russia
People and Society
Population
3,198,913 (July 2021 est.)
note: Mongolia is one of the least densely populated countries in the world (2 people per sq km); twice as many ethnic Mongols (some 6 million) live in Inner Mongolia (Nei Mongol) in neighboring China
Nationality
noun: Mongolian(s)
adjective: Mongolian
Ethnic groups
Khalkh 83.8%, Kazak 3.8%, Durvud 2.6%, Bayad 2%, Buriad 1.4%, Zakhchin 1.2%, Dariganga 1.1%, other 4.1% (2020 est.)
Languages
Mongolian 90% (official) (Khalkha dialect is predominant), Turkic, Russian (1999)
major-language sample(s):
Дэлхийн баримтат ном, үндсэн мэдээллийн зайлшгүй эх сурвалж. (Mongolian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Buddhist 51.7%, Muslim 3.2%, Shamanist 2.5%, Christian 1.3%, other 0.7%, none 40.6% (2020 est.)
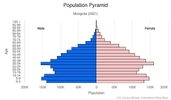
Age structure
0-14 years: 26.96% (male 435,596/female 418,524)
15-24 years: 14.93% (male 239,495/female 233,459)
25-54 years: 45.29% (male 694,481/female 740,334)
55-64 years: 8.04% (male 115,560/female 139,129)
65 years and over: 4.78% (male 60,966/female 90,482) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 54.8
youth dependency ratio: 48.1
elderly dependency ratio: 6.7
potential support ratio: 15 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 29.8 years
male: 28.8 years
female: 30.7 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
sparsely distributed population throughout the country; the capital of Ulaanbaatar and the northern city of Darhan support the highest population densities
Urbanization
urban population: 68.8% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.4% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.615 million ULAANBAATAR (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.94 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.83 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.67 male(s)/female
total population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
20.5 years (2008 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 20-24
Maternal mortality ratio
45 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97Infant mortality rate
total: 20.6 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 23.73 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 17.32 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 71.08 years
male: 66.88 years
female: 75.49 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
48.1% (2018)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 97.6% of population
rural: 59.2% of population
total: 85.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 2.4% of population
rural: 40.8% of population
total: 14.6% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
3.8% (2018)
Physicians density
2.86 physicians/1,000 population (2016)
Hospital bed density
8 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 96.4% of population
rural: 65.1% of population
total: 86.5% of population
unimproved: urban: 3.6% of population
rural: 34.9% of population
total: 13.5% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
<.1% (2020 est.)
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS
<1,000 (2020 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<100 (2020 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.2%
male: 99.1%
female: 99.2% (2020)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 15 years
male: 14 years
female: 16 years (2019)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 17.9%
male: 16.9%
female: 19.5% (2020 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
limited natural freshwater resources in some areas; the burning of soft coal in power plants and the lack of enforcement of environmental laws leads to air pollution in Ulaanbaatar; deforestation and overgrazing increase soil erosion from wind and rain; water pollution; desertification and mining activities have a deleterious effect on the environment
Environment - international agreements
party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 40.42 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 25.37 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 13.72 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
desert; continental (large daily and seasonal temperature ranges)
Land use
agricultural land: 73% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 72.6% (2018 est.)
forest: 7% (2018 est.)
other: 20% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 68.8% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.4% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.14% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 2.9 million tons (2016 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Hovsgol Nuur - 2,620 sq km; Har Us Nuur - 1,760 sq km;
Salt water lake(s): Uvs Nuur - 3,350 sq km; Hyargas Nuur - 1,360 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Amur (shared with China [s] and Russia [m]) - 4,444 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 45.3 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 166.2 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 250.9 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
34.8 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Mongolia
local long form: none
local short form: Mongol Uls
former: Outer Mongolia, Mongolian People's Republic
etymology: the name means "Land of the Mongols" in Latin; the Mongolian name Mongol Uls translates as "Mongol State"
Government type
semi-presidential republic
Capital
name: Ulaanbaatar
geographic coordinates: 47 55 N, 106 55 E
time difference: UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Saturday in March; ends last Saturday in September
time zone note: Mongolia has two time zones - Ulaanbaatar Time (8 hours in advance of UTC) and Hovd Time (7 hours in advance of UTC)
etymology: the name means "red hero" in Mongolian and honors national hero Damdin Sukhbaatar, leader of the partisan army that with Soviet Red Army help, liberated Mongolia from Chinese occupation in the early 1920s
Administrative divisions
21 provinces (aymguud, singular - aymag) and 1 municipality* (singular - hot); Arhangay, Bayanhongor, Bayan-Olgiy, Bulgan, Darhan-Uul, Dornod, Dornogovi, Dundgovi, Dzavhan (Zavkhan), Govi-Altay, Govisumber, Hentiy, Hovd, Hovsgol, Omnogovi, Orhon, Ovorhangay, Selenge, Suhbaatar, Tov, Ulaanbaatar*, Uvs
Independence
29 December 1911 (independence declared from China; in actuality, autonomy attained); 11 July 1921 (from China)
National holiday
Naadam (games) holiday (commemorates independence from China in the 1921 Revolution), 11-15 July; Constitution Day (marks the date that the Mongolian People's Republic was created under a new constitution), 26 November (1924)
Constitution
history: several previous; latest adopted 13 January 1992, effective 12 February 1992
amendments: proposed by the State Great Hural, by the president of the republic, by the government, or by petition submitted to the State Great Hural by the Constitutional Court; conducting referenda on proposed amendments requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the State Great Hural; passage of amendments by the State Great Hural requires at least three-quarters majority vote; passage by referendum requires majority participation of qualified voters and a majority of votes; amended 1999, 2000, 2019
Legal system
civil law system influenced by Soviet and Romano-Germanic legal systems; constitution ambiguous on judicial review of legislative acts
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: both parents must be citizens of Mongolia; one parent if born within Mongolia
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Ukhnaa KHURELSUKH (since 25 June 2021)
head of government: Prime Minister Luvsannamsrai OYUN-ERDENE (since 27 January 2021); Deputy Prime Minister Ulziisaikhan ENKHTUVSHIN (since 18 October 2017)
cabinet: directly appointed by the prime minister following a constitutional amendment ratified in November 2019; prior to the amendment, the cabinet was nominated by the prime minister in consultation with the president and confirmed by the State Great Hural (parliament)
elections/appointments: presidential candidates nominated by political parties represented in the State Great Hural and directly elected by simple majority popular vote for one 6-year term; election last held on 9 June 2021; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition is usually elected prime minister by the State Great Hural
election results: Ukhnaa KHURELSUKH elected president in first round; percent of vote - Ukhnaa KHURELSUKH (Mongolian People's Party) 67.7%, Dangaasuren ENKHBAT (HUN Coalition) 20.31%, Sodnomzundui ERDENE (Democratic Party) 5.99%
Legislative branch
description: unicameral State Great Hural or Ulsyn Ikh Khural (76 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote; each constituency requires at least 50% voter participation for the poll to be valid; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 24 June 2020 (next to be held in 2024)
election results: percent of vote by party - MPP 44.9%, DP 24.5%, Our Coalition 8.1%, independent 8.7%, Right Person Electorate Coalition 5.2%, other 8.5%; seats by party - MPP 62, DP 11, Our Coalition 1, Right Person Electorate Coalition 1; independent 1; composition - 63 men, 13 women; percent of women 17.1%; note - the MPRP, Civil Will-Green Party, and Mongolian Traditionally United Party formed Our Coalition for the 2020 election; the Right Person Electorate Coalition was established in 2020 by the National Labor Party, Mongolian Social Democratic Party, and Justice Party
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of the Chief Justice and 24 judges organized into civil, criminal, and administrative chambers); Constitutional Court or Tsets (consists of the chairman and 8 members)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice and judges appointed by the president upon recommendation by the General Council of Courts - a 14-member body of judges and judicial officials - to the State Great Hural; appointment is for life; chairman of the Constitutional Court elected from among its members; members appointed from nominations by the State Great Hural - 3 each by the president, the State Great Hural, and the Supreme Court; appointment is 6 years; chairmanship limited to a single renewable 3-year term
subordinate courts: aimag (provincial) and capital city appellate courts; soum, inter-soum, and district courts; Administrative Cases Courts
Political parties and leaders
Democratic Party or DP [disputed]
Mongolian National Democratic Party or MNDP [Bayanjargal TSOGTGEREL]
Mongolian People's Party or MPP [Luvsannamsrai OYUN-ERDENE]
Civil Will-Green Party or CWGP [Tserendorj GANKHUYAG]
Mongolian Traditionally United Party or MTUP [Batdelgeriin BATBOLD]
National Labor Party or HUN [Togmid Dorhkhand]
Mongolian Social Democratic Party or MSDP [Adiya GANBAATAR]
Justice Party [Batbayar NASANBILEG]
note: there are 35 total registered parties as of December 2021
International organization participation
ADB, ARF, CD, CICA, CP, EBRD, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NAM, OPCW, OSCE, SCO (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Ulziidelger BATBAYAR (since 8 November 2021)
chancery: 2833 M Street NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone: [1] (202) 333-7117
FAX: [1] (202) 298-9227
email address and website:
washington@mfa.gov.mn
http://mongolianembassy.us/
consulate(s) general: New York, San Francisco
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Michael S. KLECHESKI (since 22 February 2019)
embassy: Denver Street #3, 11th Micro-District, Ulaanbaatar 14190
mailing address: 4410 Ulaanbaatar Place, Washington DC 20521-4410
telephone: [976] 7007-6001
FAX: [976] 7007-6174
email address and website:
UlaanbaatarACS@state.gov
https://mn.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three, equal vertical bands of red (hoist side), blue, and red; centered on the hoist-side red band in yellow is the national emblem ("soyombo" - a columnar arrangement of abstract and geometric representation for fire, sun, moon, earth, water, and the yin-yang symbol); blue represents the sky, red symbolizes progress and prosperity
National symbol(s)
soyombo emblem; national colors: red, blue, yellow
National anthem
name: "Mongol ulsyn toriin duulal" (National Anthem of Mongolia)
lyrics/music: Tsendiin DAMDINSUREN/Bilegiin DAMDINSUREN and Luvsanjamts MURJORJ
note: music adopted 1950, lyrics adopted 2006; lyrics altered on numerous occasions
Economy
Economic overview
Foreign direct investment in Mongolia's extractive industries – which are based on extensive deposits of copper, gold, coal, molybdenum, fluorspar, uranium, tin, and tungsten - has transformed Mongolia's landlocked economy from its traditional dependence on herding and agriculture. Exports now account for more than 40% of GDP. Mongolia depends on China for more than 60% of its external trade - China receives some 90% of Mongolia's exports and supplies Mongolia with more than one-third of its imports. Mongolia also relies on Russia for 90% of its energy supplies, leaving it vulnerable to price increases. Remittances from Mongolians working abroad, particularly in South Korea, are significant.
Soviet assistance, at its height one-third of GDP, disappeared almost overnight in 1990 and 1991 at the time of the dismantlement of the USSR. The following decade saw Mongolia endure both deep recession, because of political inaction, and natural disasters, as well as strong economic growth, because of market reforms and extensive privatization of the formerly state-run economy. The country opened a fledgling stock exchange in 1991. Mongolia joined the WTO in 1997 and seeks to expand its participation in regional economic and trade regimes.
Growth averaged nearly 9% per year in 2004-08 largely because of high copper prices globally and new gold production. By late 2008, Mongolia was hit by the global financial crisis and Mongolia's real economy contracted 1.3% in 2009. In early 2009, the IMF reached a $236 million Stand-by Arrangement with Mongolia and it emerged from the crisis with a stronger banking sector and better fiscal management. In October 2009, Mongolia passed long-awaited legislation on an investment agreement to develop the Oyu Tolgoi (OT) mine, among the world's largest untapped copper-gold deposits. However, a dispute with foreign investors developing OT called into question the attractiveness of Mongolia as a destination for foreign investment. This caused a severe drop in FDI, and a slowing economy, leading to the dismissal of Prime Minister Norovyn ALTANKHUYAG in November 2014. The economy had grown more than 10% per year between 2011 and 2013 - largely on the strength of commodity exports and high government spending - before slowing to 7.8% in 2014, and falling to the 2% level in 2015. Growth rebounded from a brief 1.6% contraction in the third quarter of 2016 to 5.8% during the first three quarters of 2017, largely due to rising commodity prices.
The May 2015 agreement with Rio Tinto to restart the OT mine and the subsequent $4.4 billion finance package signing in December 2015 stemmed the loss of investor confidence. The current government has made restoring investor trust and reviving the economy its top priority, but has failed to invigorate the economy in the face of the large drop-off in foreign direct investment, mounting external debt, and a sizeable budget deficit. Mongolia secured a $5.5 billion financial assistance package from the IMF and a host of international creditors in May 2017, which is expected to improve Mongolia’s long-term fiscal and economic stability as long as Ulaanbaatar can advance the agreement’s difficult contingent reforms, such as consolidating the government’s off-balance sheet liabilities and rehabilitating the Mongolian banking sector.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$37.6 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$39.72 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$37.77 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
5.1% (2017 est.)
1.2% (2016 est.)
2.4% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$11,500 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$12,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$11,900 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$11.14 billion (2017 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
4.6% (2017 est.)
0.5% (2016 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: B (2018)
Moody's rating: B3 (2018)
Standard & Poors rating: B (2018)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 12.1% (2017 est.)
industry: 38.2% (2017 est.)
services: 49.7% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 49.2% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 12.3% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 23.8% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 12.4% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 59.5% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -57.1% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
milk, wheat, goat milk, potatoes, mutton, sheep milk, beef, goat meat, horse meat, carrots/turnips
Industries
construction and construction materials; mining (coal, copper, molybdenum, fluorspar, tin, tungsten, gold); oil; food and beverages; processing of animal products, cashmere and natural fiber manufacturing
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 31.1%
industry: 18.5%
services: 50.5% (2016)
Population below poverty line
28.4% (2018 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
32.7 (2018 est.)
36.5 (2008)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 13.7%
highest 10%: 5.7% (2017)
Budget
revenues: 2.967 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 3.681 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$1.155 billion (2017 est.)
-$700 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$7.65 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$8.42 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$7.71 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
China 81%, Switzerland 9% (2019)
Exports - commodities
coal, copper, gold, iron, crude petroleum (2019)
Imports
$7.34 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$9.25 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$8.48 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
China 31%, Russia 29%, Japan 10%, South Korea 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, cars, delivery trucks, construction vehicles, aircraft (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$3.016 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$1.296 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$29.945 billion (2019 est.)
$28.046 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
togrog/tugriks (MNT) per US dollar -
2,378.1 (2017 est.)
2,140.3 (2016 est.)
2,140.3 (2015 est.)
1,970.3 (2014 est.)
1,817.9 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 17.9%
male: 16.9%
female: 19.5% (2020 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 91% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 99% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 73% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
1.134 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125Electricity - from fossil fuels
87% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
2% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140Electricity - from other renewable sources
11% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78Crude oil - proved reserves
NA bbl (1 January 2017)
Refined petroleum products - consumption
27,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 160,153 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4.89 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 4,363,919 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 133.1 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: liberalized and competitive telecom market; steady growth in mobile broadband, but fixed-line broadband is still an economical option; installation of a fiber-optic network improved broadband and communication services between major urban centers; compared to other Asian countries, Mongolia's growth in telecom is moderate; mobile broadband rate is growing through competition among operators with reasonable tariffs; launch of 4G LTE services by all major operators; South Korean investment in landline and cellular services; partner in China’s economic corridor project; import of broadcasting equipment from China (2020)
domestic: very low fixed-line teledensity 12 per 100; there are four mobile-cellular providers and subscribership is increasing with 137 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 976; satellite earth stations - 7 (2016)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
following a law passed in 2005, Mongolia's state-run radio and TV provider converted to a public service provider; also available are 68 radio and 160 TV stations, including multi-channel satellite and cable TV providers; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are available (2019)
Internet users
total: 2.01 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 62.5% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 307,166 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 9.37 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 4 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 12
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 670,360 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 7.82 million mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 15
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 10
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 29
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 24
under 914 m: 1 (2013)
Heliports
1 (2013)
Railways
total: 1,815 km (2017)
broad gauge: 1,815 km 1.520-m gauge (2017)
note: national operator Ulaanbaatar Railway is jointly owned by the Mongolian Government and by the Russian State Railway
Roadways
total: 113,200 km (2017)
paved: 10,600 km (2017)
unpaved: 102,600 km (2017)
Waterways
580 km (the only waterway in operation is Lake Hovsgol) (135 km); Selenge River (270 km) and Orhon River (175 km) are navigable but carry little traffic; lakes and rivers ice free from May to September) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 81Merchant marine
total: 302
by type: bulk carrier 4, container ship 7, general cargo 131, oil tanker 64, other 96 (2021)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Mongolian Armed Forces (Mongol ulsyn zevsegt huchin): General Purpose Troops (Mongolian Army), Air/Air Defense Force, Cyber Security, Special Forces, Civil Engineering, Civil Defense Forces; Border Troops; Internal Security Troops
Ministry of Justice and Home Affairs: National Police Agency, General Authority for Border Protection
(2021)
Military expenditures
0.8% of GDP (2020 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2019 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2018 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2017 est.)
0.9% of GDP (2016 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
estimates vary; approximately 9,000 active duty troops (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the MAF are armed with Soviet-era equipment supplemented by deliveries of second-hand Russian weapons (2021)
Military deployments
870 South Sudan (UNMISS) (Oct 2021)
note - from 2003 to July 2021, some 3,300 Mongolian troops served in Afghanistan, including about 1,300 since 2015 under the NATO-led mission Resolute Support Mission
Military service age and obligation
18-27 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military service; 1-year conscript service obligation in army or air forces or police for males only (can be exchanged for a 24‐month stint in the civil service or a tax voucher); after conscription, soldiers can contract into military service for 2 or 4 years; citizens can also voluntarily join the armed forces (2021)
Military - note
Mongolia has been engaged in dialogue and cooperation with NATO since 2005 and is considered by NATO to be a global partner; Mongolia supported the NATO-led Kosovo Force from 2005-2007 and contributed troops to the NATO-led International Security Assistance Force in Afghanistan from 2009-2014, as well as to the follow-on Resolute Support Mission that provided training, advice, and other assistance to the Afghan security forces (2015-2021)
Transnational Issues
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 17 (2019)