Mauritania
Introduction
Background
The Berber and Bafour people were among the first to settle in what is now Mauritania. Originally a nomadic people, they were among the first in recorded history to convert from a nomadic to agricultural lifestyle. These groups account for roughly one third of Mauritania’s ethnic makeup. The remainder of Mauritania’s ethnic groups derive from former enslaved peoples and sub-Saharan ethnic groups originating mainly from the Senegal River Valley. These three groups constitute a strict caste system with deep ethnic divides that still exists today.
Mauritania achieved independence from France in 1960. Mauritania initially began as a single-party authoritarian regime and saw 49 years of dictatorships, flawed elections, failed attempts at democracy, and military coups. Following the last coup in 2008, led by Ould Abdel AZIZ, AZIZ was elected president in 2009 and reelected in 2014. International observers recognized the elections as free and fair. Following his two terms, AZIZ became the first Mauritanian president to step down and observe a democratic transfer of power. This solidified Mauritania’s status as an emerging democracy. After winning 52% of the vote, Mohamed Ould Cheikh GHAZOUANI was inaugurated in 2019.
The country is working to address the vestiges of slavery, which was officially abolished in 1981 but not criminalized until 2007. Between 2005 and 2011, Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM) launched a series of attacks killing American and foreign tourists and aid workers, attacking diplomatic and government facilities, and ambushing Mauritanian soldiers and gendarmes. Although Mauritania has not seen an attack since 2011, AQIM and similar groups remain active in the Sahel region.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
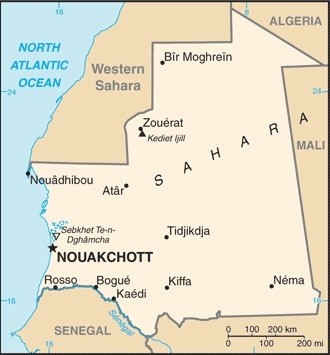
Location
Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Senegal and Western Sahara
Geographic coordinates
20 00 N, 12 00 W
Map references
Africa
Area - comparative
slightly larger than three times the size of New Mexico; about six times the size of Florida
Land boundaries
total: 5,002 km
border countries (4): Algeria 460 km, Mali 2236 km, Morocco 1564 km, Senegal 742 km
Coastline
754 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
Climate
desert; constantly hot, dry, dusty
Terrain
mostly barren, flat plains of the Sahara; some central hills
Elevation
highest point: Kediet Ijill 915 m
lowest point: Sebkhet Te-n-Dghamcha -5 m
mean elevation: 276 m
Natural resources
iron ore, gypsum, copper, phosphate, diamonds, gold, oil, fish
Land use
agricultural land: 38.5% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 38.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 0.2% (2018 est.)
other: 61.3% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
450 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Niger (2,261,741 sq km), Senegal (456,397 sq km)
Major aquifers
Senegalo-Mauritanian Basin, Taodeni-Tanzerouft Basin
Major rivers (by length in km)
Senegal river mouth (shared with Guinea [s], Senegal and Mali) - 1,641 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Population distribution
with most of the country being a desert, vast areas of the country, particularly in the central, northern, and eastern areas, are without sizeable population clusters; half the population lives in or around the coastal capital of Nouakchott; smaller clusters are found near the southern border with Mali and Senegal as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards
hot, dry, dust/sand-laden sirocco wind primarily in March and April; periodic droughts
Geography - note
Mauritania is considered both a part of North Africa's Maghreb region and West Africa's Sahel region; most of the population is concentrated in the cities of Nouakchott and Nouadhibou and along the Senegal River in the southern part of the country
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Mauritanian(s)
adjective: Mauritanian
Ethnic groups
Black Moors (Haratines - Arab-speaking descendants of African origin who are or were enslaved by white Moors) 40%, White Moors (of Arab-Berber descent, known as Beydane) 30%, Sub-Saharan Mauritanians (non-Arabic speaking, largely resident in or originating from the Senegal River Valley, including Halpulaar, Fulani, Soninke, Wolof, and Bambara ethnic groups) 30%
Languages
Arabic (official and national), Pular, Soninke, Wolof (all national languages), French; note - the spoken Arabic in Mauritania differs considerably from the modern standard Arabic used for official written purposes or in the media; the Mauritanian dialect, which incorporates many Berber words, is referred to as Hassaniya
major-language sample(s):
كتاب حقائق العالم، المصدر الذي لا يمكن الاستغناء عنه للمعلومات الأساسية (Arabic)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Muslim (official) 100%
Demographic profile
With a sustained total fertility rate of about 4 children per woman and almost 60% of the population under the age of 25, Mauritania's population is likely to continue growing for the foreseeable future. Mauritania's large youth cohort is vital to its development prospects, but available schooling does not adequately prepare students for the workplace. Girls continue to be underrepresented in the classroom, educational quality remains poor, and the dropout rate is high. The literacy rate is only about 50%, even though access to primary education has improved since the mid-2000s. Women's restricted access to education and discriminatory laws maintain gender inequality - worsened by early and forced marriages and female genital cutting.
The denial of education to black Moors also helps to perpetuate slavery. Although Mauritania abolished slavery in 1981 (the last country in the world to do so) and made it a criminal offense in 2007, the millenniums-old practice persists largely because anti-slavery laws are rarely enforced and the custom is so ingrained. According to a 2018 nongovernmental organization's report, a little more than 2% of Mauritania's population is enslaved, which includes individuals sujbected to forced labor and forced marriage, although many thousands of individuals who are legally free contend with discrimination, poor education, and a lack of identity papers and, therefore, live in de facto slavery. The UN and international press outlets have claimed that up to 20% of Mauritania's population is enslaved, which would be the highest rate worldwide.
Drought, poverty, and unemployment have driven outmigration from Mauritania since the 1970s. Early flows were directed toward other West African countries, including Senegal, Mali, Cote d'Ivoire, and Gambia. The 1989 Mauritania-Senegal conflict forced thousands of black Mauritanians to take refuge in Senegal and pushed labor migrants toward the Gulf, Libya, and Europe in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Mauritania has accepted migrants from neighboring countries to fill labor shortages since its independence in 1960 and more recently has received refugees escaping civil wars, including tens of thousands of Tuaregs who fled Mali in 2012.
Mauritania was an important transit point for Sub-Saharan migrants moving illegally to North Africa and Europe. In the mid-2000s, as border patrols increased in the Strait of Gibraltar, security increased around Spain's North African enclaves (Ceuta and Melilla), and Moroccan border controls intensified, illegal migration flows shifted from the Western Mediterranean to Spain's Canary Islands. In 2006, departure points moved southward along the West African coast from Morocco and then Western Sahara to Mauritania's two key ports (Nouadhibou and the capital Nouakchott), and illegal migration to the Canaries peaked at almost 32,000. The numbers fell dramatically in the following years because of joint patrolling off the West African coast by Frontex (the EU's border protection agency), Spain, Mauritania, and Senegal; the expansion of Spain's border surveillance system; and the 2008 European economic downturn.
Age structure
0-14 years: 37.56% (male 755,788/female 748,671)
15-24 years: 19.71% (male 387,140/female 402,462)
25-54 years: 33.91% (male 630,693/female 727,518)
55-64 years: 4.9% (male 88,888/female 107,201)
65 years and over: 3.92% (male 66,407/female 90,707) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 75
youth dependency ratio: 69.5
elderly dependency ratio: 5.6
potential support ratio: 18 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 21 years
male: 20.1 years
female: 22 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
with most of the country being a desert, vast areas of the country, particularly in the central, northern, and eastern areas, are without sizeable population clusters; half the population lives in or around the coastal capital of Nouakchott; smaller clusters are found near the southern border with Mali and Senegal as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization
urban population: 56.1% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.84% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.372 million NOUAKCHOTT (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.87 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.83 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.73 male(s)/female
total population: 0.93 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
766 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7Infant mortality rate
total: 52.05 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 57.96 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 45.96 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 64.86 years
male: 62.43 years
female: 67.37 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
17.8% (2015)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 98.7% of population
rural: 68.4% of population
total: 84.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 1.3% of population
rural: 31.6% of population
total: 15.6% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
4.6% (2018)
Physicians density
0.19 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 83.5% of population
rural: 25.2% of population
total: 56% of population
unimproved: urban: 16.5% of population
rural: 74.8% of population
total: 44% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<500 (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 53.5%
male: 63.7%
female: 43.4% (2017)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 9 years
male: 9 years
female: 10 years (2019)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 21.1%
male: 18.8%
female: 24.9% (2017 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
overgrazing, deforestation, and soil erosion aggravated by drought are contributing to desertification; limited natural freshwater resources away from the Senegal, which is the only perennial river; locust infestation
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 40.82 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 2.74 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 6.16 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
desert; constantly hot, dry, dusty
Land use
agricultural land: 38.5% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 38.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 0.2% (2018 est.)
other: 61.3% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 56.1% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.84% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 1.3% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
Food insecurity
severe localized food insecurity: due to poor performance of pastoral cropping season - according to the latest analysis, about 484,000 people are assessed to need humanitarian assistance in the June−August 2021 period as a result of fodder production deficits in Trarza, Brakna, Gorgol, Guidimaka and Assaba districts (2021)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 454,000 tons (2009 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 36,320 tons (2009 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 8% (2009 est.)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Senegal river mouth (shared with Guinea [s], Senegal and Mali) - 1,641 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Niger (2,261,741 sq km), Senegal (456,397 sq km)
Major aquifers
Senegalo-Mauritanian Basin, Taodeni-Tanzerouft Basin
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 95.4 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 31.8 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 1.223 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
11.4 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Islamic Republic of Mauritania
conventional short form: Mauritania
local long form: Al Jumhuriyah al Islamiyah al Muritaniyah
local short form: Muritaniyah
etymology: named for the ancient kingdom of Mauretania (3rd century B.C. to 1st century A.D.) and the subsequent Roman province (1st-7th centuries A.D.), which existed further north in present-day Morocco; the name derives from the Mauri (Moors), the Berber-speaking peoples of northwest Africa
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Nouakchott
geographic coordinates: 18 04 N, 15 58 W
time difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: may derive from the Berber "nawakshut" meaning "place of the winds"
Administrative divisions
15 regions (wilayas, singular - wilaya); Adrar, Assaba, Brakna, Dakhlet Nouadhibou, Gorgol, Guidimaka, Hodh ech Chargui, Hodh El Gharbi, Inchiri, Nouakchott Nord, Nouakchott Ouest, Nouakchott Sud, Tagant, Tiris Zemmour, Trarza
Independence
28 November 1960 (from France)
National holiday
Independence Day, 28 November (1960)
Constitution
history: previous 1964; latest adopted 12 July 1991
amendments: proposed by the president of the republic or by Parliament; consideration of amendments by Parliament requires approval of at least one third of the membership; a referendum is held only if the amendment is approved by two-thirds majority vote; passage by referendum requires simple majority vote by eligible voters; passage of amendments proposed by the president can bypass a referendum if approved by at least three-fifths majority vote by Parliament; amended 2006, 2012, 2017
Legal system
mixed legal system of Islamic and French civil law
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Mauritania
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Mohamed Ould Cheikh el GHAZOUANI (since 1 August 2019) (2019)
head of government: Prime Minister Mohamed Ould BILAL (since 6 August 2020) (2020)
cabinet: Council of Ministers - nominees suggested by the prime minister, appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 22 June 2019 (next scheduled for 22 June 2024); prime minister appointed by the president (2019)
election results: Mohamed Ould Cheikh El GHAZOUANI elected president in first round; percent of vote - Mahamed Ould Cheikh El GHAZOUANI (UPR) 52%, Biram Dah Ould ABEID (independent) 18.6%, Sidi Mohamed Ould BOUBACAR (independent) 17.9%, other 11.55%
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Parliament or Barlamane consists of the National Assembly or Al Jamiya Al Wataniya (157 seats; 113 members in single- and multi-seat constituencies directly elected by a combination of plurality and proportional representation voting systems, 40 members in a single, nationwide constituency directly elected by proportional representation vote, and 4 members directly elected by the diaspora; all members serve 5-year terms)
elections: first held as the unicameral National Assembly in 2 rounds on 1 and 15 September 2018 (next to be held in 2023)
election results: National Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; composition - NA
note: a referendum held in August 2017 approved a constitutional amendment to change the Parliament structure from bicameral to unicameral by abolishing the Senate and creating Regional Councils for local development
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court or Cour Supreme (subdivided into 7 chambers: 2 civil, 2 labor, 1 commercial, 1 administrative, and 1 criminal, each with a chamber president and 2 councilors ); Constitutional Council (consists of 6 members)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court president appointed by the president of the republic to serve a 5-year renewable term; Constitutional Council members appointed - 3 by the president of the republic, 2 by the president of the National Assembly, and 1 by the president of the Senate; members serve single, 9-year terms with one-third of membership renewed every 3 years
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; courts of first instance or wilya courts are established in the regions' headquarters and include commercial and labor courts, criminal courts, Moughataa (district) Courts, and informal/customary courts
Political parties and leaders
Alliance for Justice and Democracy/Movement for Renewal or AJD/MR [Ibrahima Moctar SARR]
Burst of Youth for the Nation [Lalla Mint CHERIF]
Coalition of Majority Parties or CPM (includes UPR, UDP)
El Karama Party [Cheikhna Ould Mohamed Ould HAJBOU]
El Vadila Party [Ethmane Ould Ahmed ABOULMAALY]
National Forum for Democracy and Unity or FNDU [Mohamed Ould MAOLOUD] (coalition of hard-line opposition parties, includes RNRD-TAWASSOUL)
National Rally for Reform and Development or RNRD-TAWASSOUL [Mohamed Mahmoud Ould SEYIDI]
Party of Unity and Development or PUD [Mohamed BARO]
Popular Progressive Alliance or APP [Messaoud Ould BOULKHEIR]
Rally of Democratic Forces or RFD [Ahmed Ould DADDAH]
Ravah Party [ Mohamed Ould VALL]
Republican Party for Democracy and Renewal or PRDR [Mintata Mint HEDEID]
Union for Democracy and Progress or UDP [Naha Mint MOUKNASS]
Union of Progress Forces [Mohamed Ould MAOULOUD]
Union for the Republic or UPR [Seyidna Ali Ould MOHAMED KHOUNA]
International organization participation
ABEDA, ACP, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AMU, AU, CAEU (candidate), EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO (pending member), ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAS, MIGA, MIUSMA, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Jiddou JIDDOU, First Secretary (since 24 June 2021)
chancery: 2129 Leroy Place NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 232-5700
FAX: [1] (202) 319-2623
email address and website:
office@mauritaniaembassyus.com
http://mauritaniaembassyus.com/
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Cynthia KIERSCHT (since 27 January 2021)
embassy: Nouadhibou Road, Avenue Al Quds, NOT PRTZ, Nouakchott
mailing address: 2430 Nouakchott Place, Washington DC 20521-2430
telephone: [222] 4525-2660
FAX: [222] 4525-1592
email address and website:
consularnkc@state.gov
https://mr.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
green with a yellow, five-pointed star between the horns of a yellow, upward-pointing crescent moon; red stripes along the top and bottom edges; the crescent, star, and color green are traditional symbols of Islam; green also represents hope for a bright future; the yellow color stands for the sands of the Sahara; red symbolizes the blood shed in the struggle for independence
National symbol(s)
five-pointed star between the horns of a horizontal crescent moon; national colors: green, yellow
National anthem
name: "Hymne National de la Republique Islamique de Mauritanie" (National Anthem of the Islamic Republic of Mauritania)
lyrics/music: Baba Ould CHEIKH/traditional, arranged by Tolia NIKIPROWETZKY
note: adopted 1960; the unique rhythm of the Mauritanian anthem makes it particularly challenging to sing; Mauritania in November 2017 adopted a new national anthem, "Bilada-l ubati-l hudati-l kiram" (The Country of Fatherhood is the Honorable Gift) composed by Rageh Daoud (sound file of the new anthem is forthcoming)
Economy
Economic overview
Mauritania's economy is dominated by extractive industries (oil and mines), fisheries, livestock, agriculture, and services. Half the population still depends on farming and raising livestock, even though many nomads and subsistence farmers were forced into the cities by recurrent droughts in the 1970s, 1980s, 2000s, and 2017. Recently, GDP growth has been driven largely by foreign investment in the mining and oil sectors.
Mauritania's extensive mineral resources include iron ore, gold, copper, gypsum, and phosphate rock, and exploration is ongoing for tantalum, uranium, crude oil, and natural gas. Extractive commodities make up about three-quarters of Mauritania's total exports, subjecting the economy to price swings in world commodity markets. Mining is also a growing source of government revenue, rising from 13% to 30% of total revenue from 2006 to 2014. The nation's coastal waters are among the richest fishing areas in the world, and fishing accounts for about 15% of budget revenues, 45% of foreign currency earnings. Mauritania processes a total of 1,800,000 tons of fish per year, but overexploitation by foreign and national fleets threaten the sustainability of this key source of revenue.
The economy is highly sensitive to international food and extractive commodity prices. Other risks to Mauritania's economy include its recurring droughts, dependence on foreign aid and investment, and insecurity in neighboring Mali, as well as significant shortages of infrastructure, institutional capacity, and human capital. In December 2017, Mauritania and the IMF agreed to a three year agreement under the Extended Credit Facility to foster economic growth, maintain macroeconomic stability, and reduce poverty. Investment in agriculture and infrastructure are the largest components of the country’s public expenditures.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$23.17 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$23.52 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$22.2 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
3.5% (2017 est.)
1.8% (2016 est.)
0.4% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$5,000 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$5,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$5,000 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$706 million (2018 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.2% (2019 est.)
3.1% (2018 est.)
2.2% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 27.8% (2017 est.)
industry: 29.3% (2017 est.)
services: 42.9% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 64.9% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 21.8% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 56.1% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: -3.2% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 39% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -78.6% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
rice, milk, goat milk, sheep milk, sorghum, mutton, beef, camel milk, camel meat, dates
Industries
fish processing, oil production, mining (iron ore, gold, copper)
note: gypsum deposits have never been exploited
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 50%
industry: 1.9%
services: 48.1% (2014 est.)
Population below poverty line
31% (2014 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
32.6 (2014 est.)
39 (2006 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2.5%
highest 10%: 29.5% (2000)
Budget
revenues: 1.354 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 1.396 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$711 million (2017 est.)
-$707 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$2.52 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$2.06 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$302 million (2017 est.)
Exports - partners
China 32%, Switzerland 13%, Spain 9%, Japan 9%, Italy 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
iron ore, fish products, gold, mollusks, processed crustaceans (2019)
Imports
$3.68 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$3.28 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$319 million (2017 est.)
Imports - partners
China 26%, France 6%, Spain 6%, Morocco 6%, United Arab Emirates 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
ships, aircraft, wheat, raw sugar, refined petroleum (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$875 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$849.3 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$4.15 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$3.899 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
ouguiyas (MRO) per US dollar -
363.6 (2017 est.)
352.37 (2016 est.)
352.37 (2015 est.)
319.7 (2014 est.)
299.5 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 21.1%
male: 18.8%
female: 24.9% (2017 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 32% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 56% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 4% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
558,000 kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144Electricity - from fossil fuels
65% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
16% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100Electricity - from other renewable sources
20% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38Refined petroleum products - consumption
17,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150Natural gas - proved reserves
28.32 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 62,099 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1.34 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 4,932,571 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 106.1 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Mauritania’s small population and low economic output limit sustained growth; transparency and tax burdens hinder foreign investment; World Bank and European Investment Bank support regulations to promote fixed-line broadband, improvement of the national backbone network, and connectivity to international cables; limited system of cable and open-wire lines, mobile-cellular services expanding though monopolies, and little stimulus for competition; 3G penetration high yet little development in LTE; mobile broadband access speeds are low; importer of broadcasting equipment from UAE (2020)
domestic: fixed-line teledensity 1 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular network coverage extends mainly to urban areas with a teledensity of roughly 104 per 100 persons; mostly cable and open-wire lines; a domestic satellite telecommunications system links Nouakchott with regional capitals (2019)
international: country code - 222; landing point for the ACE submarine cable for connectivity to 19 West African countries and 2 European countries; satellite earth stations - 3 (1 Intelsat - Atlantic Ocean, 2 Arabsat) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
10 TV stations: 5 government-owned and 5 private; in October 2017, the government suspended all private TV stations due to non-payment of broadcasting fees; as of April 2018, only one private TV station was broadcasting, Al Mourabitoune, the official TV of the Mauritanian Islamist party, Tewassoul; the other stations are negotiating payment options with the government and hope to be back on the air soon; 18 radio broadcasters: 15 government-owned, 3 (Radio Nouakchott Libre, Radio Tenwir, Radio Kobeni) private; all 3 private radio stations broadcast from Nouakchott; of the 15 government stations, 3 broadcast from Nouakchott (Radio Mauritanie, Radio Jeunesse, Radio Koran) and the other 12 broadcast from each of the 12 regions outside Nouakchott; Radio Jeunesse and Radio Koran are now also being re-broadcast in the regions (2019)
Internet users
total: 1.56 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 20.8% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 19,246 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 6
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 454,435 (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 9
2,438 to 3,047 m: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 21
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 10
914 to 1,523 m: 8
under 914 m: 2 (2013)
Railways
total: 728 km (2014)
standard gauge: 728 km 1.435-m gauge (2014)
Roadways
total: 12,253 km (2018)
paved: 3,988 km (2018)
unpaved: 8,265 km (2018)
Waterways
(some navigation possible on the Senegal River) (2011)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Nouadhibou, Nouakchott
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Mauritanian Armed Forces: Army, Mauritanian Navy (Marine Mauritanienne), Islamic Republic of Mauritania Air Group (Groupement Aerienne Islamique de Mauritanie, GAIM); Gendarmerie (Ministry of Defense); Ministry of Interior and Decentralization: National Guard, General Group for Road Safety (2021)
note(s) - the Gendarmerie is responsible for maintaining civil order around metropolitan areas and providing law enforcement services in rural areas; the National Guard performs a limited police function in keeping with its peacetime role of providing security at government facilities, to include prisons; the General Group for Road Safety maintains security on roads and operates checkpoints throughout the country
Military expenditures
2.5% of GDP (2020 est.)
2.8% of GDP (2019 est.)
3% of GDP (2018)
2.9% of GDP (2017)
2.9% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Mauritanian Armed Forces have approximately 16,000 active personnel (15,000 Army; 700 Navy; 300 Air Force); est. 3,000 Gendarmerie; est. 2,000 National Guard (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Mauritanian Armed Forces' inventory is limited and made up largely of older French and Soviet-era equipment; since 2010, Mauritania has received a limited amount of mostly secondhand military equipment from a variety of suppliers, including Brazil, China, France, and Turkey (2021)
Military deployments
450 Central African Republic (MINUSCA) (Sep 2021)
note - Mauritania is part of a five-nation anti-jihadist task force known as the G5 Sahel Group, set up in 2014 with Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, and Niger
Military service age and obligation
18 is the legal minimum age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2021)
Military - note
since a spate of terrorist attacks in the 2000s, including a 2008 attack on a military base in the country’s north that resulted in the deaths of 12 soldiers, the Mauritanian Government has increased the defense budget and military equipment acquisitions, enhanced military training, heightened security cooperation with its neighbors and the international community, and built up the military’s special operations and civil-military affairs forces
Mauritania is part of a five-nation anti-jihadist task force known as the G5 Sahel Group, set up in 2014 with Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, and Niger; it has committed 550 troops and 100 gendarmes to the force; in early 2020, G5 Sahel military chiefs of staff agreed to allow defense forces from each of the states to pursue terrorist fighters up to 100 km into neighboring countries; the G5 force is backed by the UN, US, and France; G5 troops periodically conduct joint operations with French forces deployed to the Sahel under Operation Barkhane (2021)
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Mauritanian claims to Western Sahara remain dormant
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 26,001 (Sahrawis) (2020); 72,816 (Mali) (2021)
IDPs: 744,944 (conflict in North Mozambique) (2021)
Trafficking in persons
current situation: Mauritania is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to conditions of forced labor and sex trafficking; adults and children from traditional slave castes are subjected to slavery-related practices rooted in ancestral master-slave relationships; Mauritanian boys are trafficked within the country by religious teachers for forced begging; Mauritanian girls, as well as girls from Mali, Senegal, The Gambia, and other West African countries, are forced into domestic servitude; Mauritanian women and girls are forced into prostitution in the country or transported to countries in the Middle East for the same purpose
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List — Mauritania does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking but is making significant efforts to do so and was upgraded to Tier 2 Watch List; the government convicted five hereditary slaveholders, drafted new anti-trafficking legislation and a national action plan, raised awareness on child forced begging in Quranic schools with imams and religious leaders by establishing an inter-ministerial committee, published a child protection guide, and operated a cash transfer program; however, the government rarely imprisoned convicted slaveholders and did not identify any victims; government agencies lacked resources; government officials refuse to investigate or prosecute political offenders (2020)