Introduction
Background
Kiribati is made up of three distinct island groups - the Gilbert Islands, the Line Islands, and the Phoenix Islands. The first Austronesian voyagers arrived in the Gilbert Islands as early as 3000 B.C., but these islands were not widely settled until about A.D. 200 by Micronesians. Around 1300, Samoans and Tongans invaded the southern Gilbert Islands, bringing Polynesian cultural elements with them. Later arrivals by Fijians brought Melanesian elements to the Gilbert Islands, and extensive intermarriage between the Micronesian, Polynesian, and Melanesian people led to the creation of what would become Gilbertese cultural traditions by the time Europeans spotted the islands in the 1600s. The Phoenix Islands and Line Islands were both visited by various Melanesian and Polynesian peoples, but their isolation and lack of natural resources meant that long-term settlements were not possible and both island groups were uninhabited by the time of European contact.
Kiribati experienced sustained European contact by the 1760s; all three island groups were named and charted by 1826. American whaling ships frequently passed through the islands, and the UK declared a protectorate over the Gilbert and nearby Ellice Islands in 1892 to block growing US influence. Phosphate-rich Banaba Island was annexed to the protectorate in 1900. In 1916, the protectorate became a colony, and some Line Islands were added in 1916 and 1919, with the final ones added in 1972. The Phoenix Islands were added to the colony in 1937, and the UK agreed to share jurisdiction of some of them with the US because of their strategic location for aviation. Japan occupied the northern Gilbert Islands in 1941; the islands of Makin and Tarawa were the sites of major US amphibious victories over entrenched Japanese garrisons in 1943. The UK continued to rule the colony after World War II. The Ellice Islands became its own colony in 1974. The Gilbert Islands became fully self-governing in 1977 and independent in 1979 as Kiribati, the Gilbertese spelling of Gilberts. The US relinquished all claims to the sparsely inhabited Phoenix and Line Islands in a 1979 treaty of friendship.
In 1994, Kiribati adjusted the international date line to the east of the Line Islands, bringing all islands in the country to the same day and giving Kiribati the earliest time zone in the world. Kiribati is a leading climate change and marine protection advocate. The Phoenix Islands Protected Area was established in 2008; in 2010, it became the world's largest (and deepest) UNESCO World Heritage site. In 2012, Kiribati purchased a 22 sq km (8.5 sq mi) plot of land in Fiji for potential eventual resettlement of its population because of climate change.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
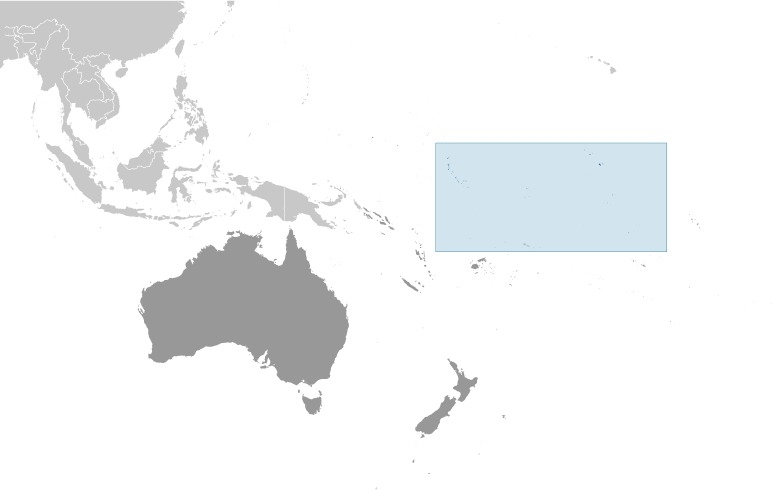
Location
Oceania, group of 32 coral atolls and one raised coral island in the Pacific Ocean, straddling the Equator; the capital Tarawa is about halfway between Hawaii and Australia
Geographic coordinates
1 25 N, 173 00 E
Map references
Oceania
Area
total: 811 sq km
land: 811 sq km
water: 0 sq km
note: includes three island groups - Gilbert Islands, Line Islands, and Phoenix Islands - dispersed over about 3.5 million sq km (1.35 million sq mi)
Area - comparative
four times the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
1,143 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; marine, hot and humid, moderated by trade winds
Terrain
mostly low-lying coral atolls surrounded by extensive reefs
Elevation
highest point: unnamed elevation on Banaba 81 m m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 2 m
Natural resources
phosphate (production discontinued in 1979), coconuts (copra), fish
Land use
agricultural land: 42% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.5% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 39.5% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0% (2018 est.)
forest: 15% (2018 est.)
other: 43% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
0 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
consists of three achipelagos spread out over an area roughly the size of India; the eastern Line Islands and central Phoenix Islands are sparsely populated, but the western Gilbert Islands are some of the most densely settled places on earth, with the main island of South Tarawa boasting a population density similar to Tokyo or Hong Kong
Natural hazards
typhoons can occur any time, but usually November to March; occasional tornadoes; low level of some of the islands make them sensitive to changes in sea level
Geography - note
21 of the 33 islands are inhabited; Banaba (Ocean Island) in Kiribati is one of the three great phosphate rock islands in the Pacific Ocean - the others are Makatea in French Polynesia, and Nauru; Kiribati is the only country in the world to fall into all four hemispheres (northern, southern, eastern, and western)
People and Society
Nationality
noun: I-Kiribati (singular and plural)
adjective: I-Kiribati
Ethnic groups
I-Kiribati 96.2%, I-Kiribati/mixed 1.8%, Tuvaluan 0.2%, other 1.8% (2015 est.)
Languages
I-Kiribati, English (official)
Religions
Roman Catholic 57.3%, Kiribati Uniting Church 31.3%, Christ of Jesus Christ 5.3%, Baha'i 2.1%, Seventh Day Adventist 1.9%, other 2.1% (2015 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 28.47% (male 16,223/female 15,604)
15-24 years: 20.24% (male 11,171/female 11,459)
25-54 years: 40.05% (male 21,530/female 23,249)
55-64 years: 6.65% (male 3,350/female 4,084)
65 years and over: 4.59% (male 2,004/female 3,122) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 67
youth dependency ratio: 60
elderly dependency ratio: 7
potential support ratio: 14.2 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 25.7 years
male: 24.8 years
female: 26.6 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
consists of three achipelagos spread out over an area roughly the size of India; the eastern Line Islands and central Phoenix Islands are sparsely populated, but the western Gilbert Islands are some of the most densely settled places on earth, with the main island of South Tarawa boasting a population density similar to Tokyo or Hong Kong
Urbanization
urban population: 56.3% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 2.77% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
64,000 TARAWA (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.93 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.82 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.64 male(s)/female
total population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
23.1 years (2009 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality ratio
92 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73Infant mortality rate
total: 33.66 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 35.61 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 31.62 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 67.59 years
male: 65 years
female: 70.3 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
33.5% (2018/19)
Drinking water source
improved: total: 71.6% of population
unimproved: total: 28.4% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
12.1% (2018)
Physicians density
0.2 physicians/1,000 population (2013)
Hospital bed density
1.9 beds/1,000 population (2016)
Sanitation facility access
improved: total: 61.1% of population
unimproved: total: 38.9% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: malaria
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 12 years
male: 11 years
female: 12 years (2008)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 22.5%
male: 21.2%
female: 24.6% (2019 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
heavy pollution in lagoon of south Tarawa atoll due to overcrowding mixed with traditional practices such as lagoon latrines and open-pit dumping; ground water at risk; potential for water shortages, disease; coastal erosion
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 10.45 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 0.07 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 0.02 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; marine, hot and humid, moderated by trade winds
Land use
agricultural land: 42% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.5% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 39.5% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0% (2018 est.)
forest: 15% (2018 est.)
other: 43% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 56.3% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 2.77% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.04% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: malaria
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 35,724 tons (2016 est.)
Total renewable water resources
0 cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Kiribati
conventional short form: Kiribati
local long form: Republic of Kiribati
local short form: Kiribati
former: Gilbert Islands
etymology: the name is the local pronunciation of "Gilberts," the former designation of the islands; originally named after explorer Thomas GILBERT, who mapped many of the islands in 1788
note: pronounced keer-ree-bahss
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Tarawa
geographic coordinates: 1 21 N, 173 02 E
time difference: UTC+12 (17 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
time zone note: Kiribati has three time zones: the Gilbert Islands group at UTC+12, the Phoenix Islands at UTC+13, and the Line Islands at UTC+14
etymology: in Kiribati creation mythology, "tarawa" was what the spider Nareau named the land to distinguish it from "karawa" (the sky) and "marawa" (the ocean)
Administrative divisions
3 geographical units: Gilbert Islands, Line Islands, Phoenix Islands; note - there are no first-order administrative divisions, but there are 6 districts (Banaba, Central Gilberts, Line Islands, Northern Gilberts, Southern Gilberts, Tarawa) and 21 island councils - one for each of the inhabited islands (Abaiang, Abemama, Aranuka, Arorae, Banaba, Beru, Butaritari, Kanton, Kiritimati, Kuria, Maiana, Makin, Marakei, Nikunau, Nonouti, Onotoa, Tabiteuea, Tabuaeran, Tamana, Tarawa, Teraina)
Independence
12 July 1979 (from the UK)
National holiday
Independence Day, 12 July (1979)
Constitution
history: The Gilbert and Ellice Islands Order in Council 1915, The Gilbert Islands Order in Council 1975 (preindependence); latest promulgated 12 July 1979 (at independence)
amendments: proposed by the House of Assembly; passage requires two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly membership; passage of amendments affecting the constitutional section on amendment procedures and parts of the constitutional chapter on citizenship requires deferral of the proposal to the next Assembly meeting where approval is required by at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly membership and support of the nominated or elected Banaban member of the Assembly; amendments affecting the protection of fundamental rights and freedoms also requires approval by at least two-thirds majority in a referendum; amended several times, last in 2018
Legal system
English common law supplemented by customary law
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a native-born citizen of Kiribati
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Taneti MAAMAU (since 11 March 2016); Vice President Teuea TOATU (since 19 June 2019); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Taneti MAAMAU (since 11 March 2016); Vice President Teuea TOATU (since 19 June 2019)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president from among House of Assembly members
elections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote following nomination of candidates from among House of Assembly members; term is 4 years (eligible for 2 additional terms); election last held on 22 June 2020 (next to be held in 2024); vice president appointed by the president
election results: Taneti MAAMAU reelected president; percent of vote - Taneti MAAMAU (TKB) 59.3%, Banuera BERINA (BKM) 40.7%.
Legislative branch
description: unicameral House of Assembly or Maneaba Ni Maungatabu (46 seats; 44 members directly elected in single- and multi-seat constituencies by absolute majority vote in two-rounds if needed; 1 member appointed by the Rabi Council of Leaders - representing Banaba Island, and 1 ex officio member - the attorney general; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: legislative elections originally scheduled to be held in two rounds on 7 and 15 April 2020 but rescheduled for 14 and 21 April (next to be held in 2024)
election results: percent of vote by party (second round) - NA; seats by party (second round) - TKB 22, BKM 22, 1 independent
Judicial branch
highest courts: High Court (consists of a chief justice and other judges as prescribed by the president); note - the High Court has jurisdiction on constitutional issues
judge selection and term of office: chief justice appointed by the president on the advice of the cabinet in consultation with the Public Service Commission (PSC); other judges appointed by the president on the advice of the chief justice along with the PSC
subordinate courts: Court of Appeal; magistrates' courts
Political parties and leaders
Boutokaan Kiribati Moa Party (BKM) [Tessie LAMBOURNE]
Tobwaan Kiribati Party or TKP [Taneti MAAMAU]
International organization participation
ABEDA, ACP, ADB, AOSIS, C, FAO, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IOC, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission:
Ambassador Teburoro TITO (since 24 January 2018)
chancery: 685 Third Avenue, Suite 1109, New York, NY 10017
telephone: [1] (212) 867-3310
FAX: [1] (212) 867-3320
email address and website:
Kimission.newyork@mfa.gov.ki
note - the Kiribati Permanent Mission to the UN serves as the embassy
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: the US does not have an embassy in Kiribati; the US Ambassador to Fiji is accredited to Kiribati
Flag description
the upper half is red with a yellow frigatebird flying over a yellow rising sun, and the lower half is blue with three horizontal wavy white stripes to represent the Pacific ocean; the white stripes represent the three island groups - the Gilbert, Line, and Phoenix Islands; the 17 rays of the sun represent the 16 Gilbert Islands and Banaba (formerly Ocean Island); the frigatebird symbolizes authority and freedom
National symbol(s)
frigatebird; national colors: red, white, blue, yellow
National anthem
name: "Teirake kaini Kiribati" (Stand Up, Kiribati)
lyrics/music: Urium Tamuera IOTEBA
note: adopted 1979
Economy
Economic overview
A remote country of 33 scattered coral atolls, Kiribati has few natural resources and is one of the least developed Pacific Island countries. Commercially viable phosphate deposits were exhausted by the time of independence from the United Kingdom in 1979. Earnings from fishing licenses and seafarer remittances are important sources of income. Although the number of seafarers employed declined due to changes in global shipping demands, remittances are expected to improve with more overseas temporary and seasonal work opportunities for Kiribati nationals.
Economic development is constrained by a shortage of skilled workers, weak infrastructure, and remoteness from international markets. The public sector dominates economic activity, with ongoing capital projects in infrastructure including road rehabilitation, water and sanitation projects, and renovations to the international airport, spurring some growth. Public debt increased from 23% of GDP at the end of 2015 to 25.8% in 2016.
Kiribati is dependent on foreign aid, which was estimated to have contributed over 32.7% in 2016 to the government’s finances. The country’s sovereign fund, the Revenue Equalization Reserve Fund (RERF), which is held offshore, had an estimated balance of $855.5 million in late July 2016. The RERF seeks to avoid exchange rate risk by holding investments in more than 20 currencies, including the Australian dollar, US dollar, the Japanese yen, and the Euro. Drawdowns from the RERF helped finance the government’s annual budget.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$270 million note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$270 million note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$260 million note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
3.1% (2017 est.)
1.1% (2016 est.)
10.3% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$2,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$2,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$2,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$197 million (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 23% (2016 est.)
industry: 7% (2016 est.)
services: 70% (2016 est.)
Agricultural products
coconuts, roots/tubers nes, bananas, vegetables, taro, tropical fruit, poultry, pork, nuts, eggs
Industries
fishing, handicrafts
Labor force
39,000 (2010 est.)
note: economically active, not including subsistence farmers
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 15%
industry: 10%
services: 75% (2010)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 151.2 million (2017 est.)
expenditures: 277.5 million (2017 est.)
Current account balance
$18 million (2017 est.)
$35 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$30 million note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$20 million note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
Thailand 53%, Philippines 17%, South Korea 10%, Japan 9% (2019)
Exports - commodities
fish and fish produces, ships, coconut oil, copra (2019)
Imports
$180 million note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$170 million note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
China 20%, Fiji 19%, Australia 12%, Taiwan 11%, South Korea 11%, New Zealand 7%, Japan 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, netting, raw sugar, rice, poultry meats (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$0 (31 December 2017 est.)
$8.37 million (31 December 2010 est.)
Debt - external
$40.9 million (2016 est.)
$32.3 million (2015 est.)
Exchange rates
Australian dollars (AUD) per US dollar -
1.31 (2017 est.)
1.34 (2016 est.)
1.34 (2015 est.)
1.33 (2014 est.)
1.11 (2013 est.)
note: the Australian dollar circulates as legal tender
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 22.5%
male: 21.2%
female: 24.6% (2019 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
11,000 kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208Electricity - from fossil fuels
73% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181Electricity - from other renewable sources
27% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 33 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 54,661 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 45.76 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: generally good national and international service; wireline service available on Tarawa and Kiritimati (Christmas Island); connections to outer islands by HF/VHF radiotelephone; recently formed (mobile network operator) MNO is implementing the first phase of improvements with 3G and 4G upgrades on some islands; islands are connected to each other and the rest of the world via satellite; launch of Kacific-1 in December 2019 will improve telecommunication for Kiribati (2020)
domestic: fixed-line 1 per 100 and mobile-cellular 46 per 100 subscriptions (2019)
international: country code - 686; landing point for the Southern Cross NEXT submarine cable system from Australia, 7 Pacific Ocean island countries to the US; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
multi-channel TV packages provide access to Australian and US stations; 1 government-operated radio station broadcasts on AM, FM, and shortwave (2017)
Internet users
total: 17,600 (2021 est.)
percent of population: 14.58% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 185 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 less than 1 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 8
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 66,567 (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 4
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 15
914 to 1,523 m: 10
under 914 m: 5 (2013)
Merchant marine
total: 88
by type: bulk carrier 3, general cargo 35, oil tanker 12, other 38 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Betio (Tarawa Atoll), Canton Island, English Harbor
Military and Security
Military and security forces
no regular military forces; Kiribati Police and Prison Service (Ministry of Justice)
Military - note
defense assistance is provided by Australia and NZ