Introduction
Background
Trade centers such as Mombasa have existed along the Kenyan and Tanzanian coastlines, known as the Land of Zanj, since at least the 2nd century. These centers traded with the outside world, including China, India, Indonesia, the Middle East, North Africa, and Persia. By around the 9th century, the mix of Africans, Arabs, and Persians who lived and traded there became known as Swahili (“people of the coast”) with a distinct language (KiSwahili) and culture. The Portuguese arrived in the 1490s and, using Mombasa as a base, sought to monopolize trade in the Indian Ocean. The Portuguese were pushed out in the late 1600s by the combined forces of Oman and Pate, an island off the coast. In 1890, Germany and the UK divided up the region, with the UK taking the north and the Germans the south, including present-day Tanzania, Burundi, and Rwanda. The British established the East Africa Protectorate in 1895, which in 1920 was converted into a colony and named Kenya after its highest mountain. Numerous political disputes between the colony and the UK subsequently led to the violent Mau Mau Uprising, which began in 1952, and the eventual declaration of independence in 1963.
Jomo KENYATTA, the founding president and an icon of the liberation struggle,led Kenya from independence in 1963 until his death in 1978, when Vice President Daniel Arap MOI took power in a constitutional succession. The country was a de facto one-party state from 1969 until 1982, after which time the ruling Kenya African National Union (KANU) changed the constitution to make itself the sole legal political party in Kenya. MOI acceded to internal and external pressure for political liberalization in late 1991. The ethnically fractured opposition failed to dislodge KANU from power in elections in 1992 and 1997, which were marred by violence and fraud. President MOI stepped down in December 2002 following fair and peaceful elections. Mwai KIBAKI, running as the candidate of the multiethnic, united opposition group, the National Rainbow Coalition (NARC), defeated KANU candidate Uhuru KENYATTA, the son of founding president Jomo KENYATTA, and assumed the presidency following a campaign centered on an anticorruption platform.KIBAKI's reelection in 2007 resulted in two months of post-election ethnic violence that caused the death of more than 1,100 people and the dislocation of hundreds of thousands. Opposition candidate Raila ODINGA, accused the government of widespread vote rigging. African Union-sponsored mediation led by former UN Secretary General Kofi ANNAN resulted in a power-sharing accord that brought ODINGA into the government in the restored position of prime minister. The power sharing accord included a broad reform agenda, the centerpiece of which was constitutional reform. In 2010, Kenyans overwhelmingly adopted a new constitution in a national referendum. The new constitution introduced additional checks and balances to executive power and devolved power and resources to 47 newly created counties. It also eliminated the position of prime minister. Uhuru KENYATTA won the first presidential election under the new constitution in March 2013. KENYATTA won a second and final term in office in November 2017 following a contentious, repeat election.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
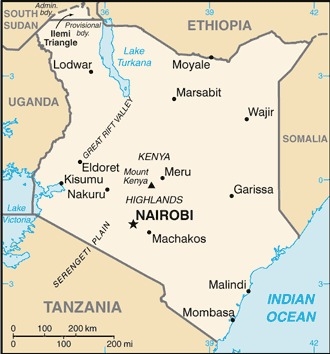
Eastern Africa, bordering the Indian Ocean, between Somalia and Tanzania
Geographic coordinates
1 00 N, 38 00 E
Map references
Africa
Land boundaries
total: 3,457 km
border countries (5): Ethiopia 867 km, Somalia 684 km, South Sudan 317 km, Tanzania 775 km, Uganda 814 km
Coastline
536 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Climate
varies from tropical along coast to arid in interior
Terrain
low plains rise to central highlands bisected by Great Rift Valley; fertile plateau in west
Elevation
highest point: Mount Kenya 5,199 m
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 762 m
Natural resources
limestone, soda ash, salt, gemstones, fluorspar, zinc, diatomite, gypsum, wildlife, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land: 48.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 9.8% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.9% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 37.4% (2018 est.)
forest: 6.1% (2018 est.)
other: 45.8% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
1,030 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Mediterranean Sea) Nile (3,254,853 sq km)
Major aquifers
Ogaden-Juba Basin
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Victoria (shared with Tanzania and Uganda) - 62,940 sq km
Salt water lake(s): Lake Turkana (shared with Ethiopia) - 6,400 sq km
Population distribution
population heavily concentrated in the west along the shore of Lake Victoria; other areas of high density include the capital of Nairobi, and in the southeast along the Indian Ocean coast as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards
recurring drought; flooding during rainy seasons
volcanism: limited volcanic activity; the Barrier (1,032 m) last erupted in 1921; South Island is the only other historically active volcano
Geography - note
the Kenyan Highlands comprise one of the most successful agricultural production regions in Africa; glaciers are found on Mount Kenya, Africa's second highest peak; unique physiography supports abundant and varied wildlife of scientific and economic value; Lake Victoria, the world's largest tropical lake and the second largest fresh water lake, is shared among three countries: Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda
People and Society
Population
54,685,051 (July 2021 est.)
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
Nationality
noun: Kenyan(s)
adjective: Kenyan
Ethnic groups
Kikuyu 17.1%, Luhya 14.3%, Kalenjin 13.4%, Luo 10.7%, Kamba 9.8%, Somali 5.8%, Kisii 5.7%, Mijikenda 5.2%, Meru 4.2%, Maasai 2.5%, Turkana 2.1%, non-Kenyan 1%, other 8.2% (2019 est.)
Languages
English (official), Kiswahili (official), numerous indigenous languages
major-language sample(s):
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information. (English)
The World Factbook, Chanzo cha Lazima Kuhusu Habari ya Msingi. (Kiswahili)
Religions
Christian 85.5% (Protestant 33.4%, Catholic 20.6%, Evangelical 20.4%, African Instituted Churches 7%, other Christian 4.1%), Muslim 10.9%, other 1.8%, none 1.6%, don't know/no answer 0.2% (2019 est.)
Demographic profile
Kenya has experienced dramatic population growth since the mid-20th century as a result of its high birth rate and its declining mortality rate. More than 40% of Kenyans are under the age of 15 because of sustained high fertility, early marriage and childbearing, and an unmet need for family planning. Kenya’s persistent rapid population growth strains the labor market, social services, arable land, and natural resources. Although Kenya in 1967 was the first Sub-Saharan country to launch a nationwide family planning program, progress in reducing the birth rate has largely stalled since the late 1990s, when the government decreased its support for family planning to focus on the HIV epidemic. Government commitment and international technical support spurred Kenyan contraceptive use, decreasing the fertility rate (children per woman) from about 8 in the late 1970s to less than 5 children twenty years later, but it has plateaued at just over 3 children today.
Kenya is a source of emigrants and a host country for refugees. In the 1960s and 1970s, Kenyans pursued higher education in the UK because of colonial ties, but as British immigration rules tightened, the US, the then Soviet Union, and Canada became attractive study destinations. Kenya’s stagnant economy and political problems during the 1980s and 1990s led to an outpouring of Kenyan students and professionals seeking permanent opportunities in the West and southern Africa. Nevertheless, Kenya’s relative stability since its independence in 1963 has attracted hundreds of thousands of refugees escaping violent conflicts in neighboring countries; Kenya shelters more than 300,000 Somali refugees as of April 2017.
Age structure
0-14 years: 38.71% (male 10,412,321/female 10,310,908)
15-24 years: 20.45% (male 5,486,641/female 5,460,372)
25-54 years: 33.75% (male 9,046,946/female 9,021,207)
55-64 years: 4.01% (male 1,053,202/female 1,093,305)
65 years and over: 3.07% (male 750,988/female 892,046) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 69.8
youth dependency ratio: 65.5
elderly dependency ratio: 4.3
potential support ratio: 23.5 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 20 years
male: 19.9 years
female: 20.1 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
population heavily concentrated in the west along the shore of Lake Victoria; other areas of high density include the capital of Nairobi, and in the southeast along the Indian Ocean coast as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization
urban population: 28.5% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 4.09% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
4.922 million NAIROBI (capital), 1.341 million Mombassa (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.02 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.84 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
20.3 years (2014 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-49
Maternal mortality ratio
342 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32Infant mortality rate
total: 28.81 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 31.93 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 25.63 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 69.32 years
male: 67.65 years
female: 71.03 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
59.7% (2019)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 89% of population
rural: 60.4% of population
total: 68% of population
unimproved: urban: 11% of population
rural: 39.6% of population
total: 32% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
5.2% (2018)
Physicians density
0.16 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
Hospital bed density
1.4 beds/1,000 population (2010)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 78.8% of population
rural: 41.2% of population
total: 51.2% of population
unimproved: urban: 21.2% of population
rural: 58.8% of population
total: 48.8% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and Rift Valley fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 81.5%
male: 85%
female: 78.2% (2018)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 11 years
male: 11 years
female: 11 years (2009)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 12.9%
male: 12%
female: 13.8% (2019)
Environment
Environment - current issues
water pollution from urban and industrial wastes; water shortage and degraded water quality from increased use of pesticides and fertilizers; flooding; water hyacinth infestation in Lake Victoria; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; poaching
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 25.85 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 17.91 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 37.65 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
varies from tropical along coast to arid in interior
Land use
agricultural land: 48.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 9.8% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.9% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 37.4% (2018 est.)
forest: 6.1% (2018 est.)
other: 45.8% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 28.5% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 4.09% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 1.3% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and Rift Valley fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
Food insecurity
exceptional shortfall in aggregate food production/supplies: due to poor seasonal rains, and desert locusts - about 2 million people were estimated to be severely food insecure in the March−May 2021 period, reflecting the poor performance of both the October−December 2020 “short-rains” and the March−May 2021 “long-rains” that affected crop and livestock production in northern and eastern pastoral, agro-pastoral and marginal agriculture areas; other limiting factors include the measures implemented to curb the spread of the COVID‑19 pandemic which affected off‑farm income earning opportunities, including petty trade, charcoal and firewood sales, and to localized but significant locust‑induced pasture losses (2021)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 5,595,099 tons (2010 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 447,608 tons (2009 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 8% (2009 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Victoria (shared with Tanzania and Uganda) - 62,940 sq km
Salt water lake(s): Lake Turkana (shared with Ethiopia) - 6,400 sq km
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Mediterranean Sea) Nile (3,254,853 sq km)
Major aquifers
Ogaden-Juba Basin
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 495 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 303 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 3.234 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
30.7 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Kenya
conventional short form: Kenya
local long form: Republic of Kenya/Jamhuri ya Kenya
local short form: Kenya
former: British East Africa
etymology: named for Mount Kenya; the meaning of the name is unclear but may derive from the Kikuyu, Embu, and Kamba words "kirinyaga," "kirenyaa," and "kiinyaa" - all of which mean "God's resting place"
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Nairobi
geographic coordinates: 1 17 S, 36 49 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name derives from the Maasai expression meaning "cool waters" and refers to a cold water stream that flowed through the area in the late 19th century
Administrative divisions
47 counties; Baringo, Bomet, Bungoma, Busia, Elgeyo/Marakwet, Embu, Garissa, Homa Bay, Isiolo, Kajiado, Kakamega, Kericho, Kiambu, Kilifi, Kirinyaga, Kisii, Kisumu, Kitui, Kwale, Laikipia, Lamu, Machakos, Makueni, Mandera, Marsabit, Meru, Migori, Mombasa, Murang'a, Nairobi City, Nakuru, Nandi, Narok, Nyamira, Nyandarua, Nyeri, Samburu, Siaya, Taita/Taveta, Tana River, Tharaka-Nithi, Trans Nzoia, Turkana, Uasin Gishu, Vihiga, Wajir, West Pokot
Independence
12 December 1963 (from the UK)
National holiday
Jamhuri Day (Independence Day), 12 December (1963); note - Madaraka Day, 1 June (1963) marks the day Kenya attained internal self-rule
Constitution
history: previous 1963, 1969; latest drafted 6 May 2010, passed by referendum 4 August 2010, promulgated 27 August 2010
amendments: proposed by either house of Parliament or by petition of at least one million eligible voters; passage of amendments by Parliament requires approval by at least two-thirds majority vote of both houses in each of two readings, approval in a referendum by majority of votes cast by at least 20% of eligible voters in at least one half of Kenya’s counties, and approval by the president; passage of amendments introduced by petition requires approval by a majority of county assemblies, approval by majority vote of both houses, and approval by the president
Legal system
mixed legal system of English common law, Islamic law, and customary law; judicial review in the new Supreme Court established by the new constitution
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Kenya
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 4 out of the previous 7 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Uhuru KENYATTA (since 9 April 2013); Deputy President William RUTO (since 9 April 2013); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Uhuru KENYATTA (since 9 April 2013); Deputy President William RUTO (since 9 April 2013); note - position of the prime minister was abolished after the March 2013 elections
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president, subject to confirmation by the National Assembly
elections/appointments: president and deputy president directly elected on the same ballot by qualified majority popular vote for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); in addition to receiving an absolute majority popular vote, the presidential candidate must also win at least 25% of the votes cast in at least 24 of the 47 counties to avoid a runoff; election last held on 26 October 2017 (next to be held in 2022)
election results: Uhuru KENYATTA reelected president; percent of vote - Uhuru KENYATTA (Jubilee Party) 98.3%, Raila ODINGA (ODM) 1%, other 0.7%; note - Kenya held a previous presidential election on 8 August 2017, but Kenya's Supreme Court on 1 September 2017 nullified the results, citing irregularities; the political opposition boycotted the October vote
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliament consists of:
Senate (67 seats; 47 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 20 directly elected by proportional representation vote - 16 women, 2 representing youth, and 2 representing the disabled; members serve 5-year terms)
National Assembly (349 seats; 290 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote, 47 women in single-seat constituencies elected by simple majority vote, and 12 members nominated by the National Assembly - 6 representing youth and 6 representing the disabled; members serve 5-year terms)
elections: Senate - last held on 8 August 2017 (next to be held in August 2022)
National Assembly - last held on 8 August 2017 (next to be held in August 2022)
election results: Senate - percent of vote by party/coalition - NA; seats by party/coalition - Jubilee Party 24; National Super Alliance 28, other 14, independent 1; composition - men 46, women 41, percent of women is 31.3%
National Assembly - percent of vote by party/coalition - NA; seats by party/coalition - Jubilee Party 165, National Super Alliance 119, other 51, independent 13; composition - men 273, women 76, percent of women 21.8%; note - total Parliament percent of women is 23%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of chief and deputy chief justices and 5 judges)
judge selection and term of office: chief and deputy chief justices nominated by Judicial Service Commission (JSC) and appointed by the president with approval of the National Assembly; other judges nominated by the JSC and appointed by president; chief justice serves a nonrenewable 10-year term or until age 70, whichever comes first; other judges serve until age 70
subordinate courts: High Court; Court of Appeal; military courts; magistrates' courts; religious courts
Political parties and leaders
Alliance Party of Kenya or APK [Kiraitu MURUNGI]
Amani National Congress or ANC [Musalia MUDAVADI]
Federal Party of Kenya or FPK [Cyrus JIRONGA]
Forum for the Restoration of Democracy-Kenya or FORD-K [Moses WETANGULA]
Forum for the Restoration of Democracy-People or FORD-P [Henry OBWOCHA]
Jubilee Party [Uhuru KENYATTA]
Kenya African National Union or KANU [Gideon MOI]
National Rainbow Coalition or NARC [Charity NGILU]
Orange Democratic Movement Party of Kenya or ODM [Raila ODINGA]
Wiper Democratic Movement-K or WDM-K (formerly Orange Democratic Movement-Kenya or ODM-K) [Kalonzo MUSYOKA]
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, CD, COMESA, EAC, EADB, FAO, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, NAM, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Lazarus Ombai AMAYO (since 17 July 2020)
chancery: 1616 P Street NW, Suite 340, Washington, DC 20036
telephone: [1] (202) 387-6101
FAX: [1] (202) 462-3829
email address and website:
information@kenyaembassydc.org
https://kenyaembassydc.org/#
consulate(s) general: Los Angeles
consulate(s): New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Eric W. Kneedler (since 20 January 2021)
embassy: P.O. Box 606 Village Market, 00621 Nairobi
mailing address: 8900 Nairobi Place, Washington, DC 20521-8900
telephone: [254] (20) 363-6000
FAX: [254] (20) 363-6157
email address and website:
kenya_acs@state.gov
https://ke.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of black (top), red, and green; the red band is edged in white; a large Maasai warrior's shield covering crossed spears is superimposed at the center; black symbolizes the majority population, red the blood shed in the struggle for freedom, green stands for natural wealth, and white for peace; the shield and crossed spears symbolize the defense of freedom
National symbol(s)
lion; national colors: black, red, green, white
National anthem
name: "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu" (Oh God of All Creation)
lyrics/music: Graham HYSLOP, Thomas KALUME, Peter KIBUKOSYA, Washington OMONDI, and George W. SENOGA-ZAKE/traditional, adapted by Graham HYSLOP, Thomas KALUME, Peter KIBUKOSYA, Washington OMONDI, and George W. SENOGA-ZAKE
note: adopted 1963; based on a traditional Kenyan folk song
Economy
Economic overview
Kenya is the economic, financial, and transport hub of East Africa. Kenya’s real GDP growth has averaged over 5% for the last decade. Since 2014, Kenya has been ranked as a lower middle income country because its per capita GDP crossed a World Bank threshold. While Kenya has a growing entrepreneurial middle class and steady growth, its economic development has been impaired by weak governance and corruption. Although reliable numbers are hard to find, unemployment and under-employment are extremely high, and could be near 40% of the population. In 2013, the country adopted a devolved system of government with the creation of 47 counties, and is in the process of devolving state revenues and responsibilities to the counties.
Agriculture remains the backbone of the Kenyan economy, contributing one-third of GDP. About 75% of Kenya’s population of roughly 48.5 million work at least part-time in the agricultural sector, including livestock and pastoral activities. Over 75% of agricultural output is from small-scale, rain-fed farming or livestock production. Tourism also holds a significant place in Kenya’s economy. In spite of political turmoil throughout the second half of 2017, tourism was up 20%, showcasing the strength of this sector. Kenya has long been a target of terrorist activity and has struggled with instability along its northeastern borders. Some high visibility terrorist attacks during 2013-2015 (e.g., at Nairobi’s Westgate Mall and Garissa University) affected the tourism industry severely, but the sector rebounded strongly in 2016-2017 and appears poised to continue growing.
Inadequate infrastructure continues to hamper Kenya’s efforts to improve its annual growth so that it can meaningfully address poverty and unemployment. The KENYATTA administration has been successful in courting external investment for infrastructure development. International financial institutions and donors remain important to Kenya's growth and development, but Kenya has also successfully raised capital in the global bond market issuing its first sovereign bond offering in mid-2014, with a second occurring in February 2018. The first phase of a Chinese-financed and constructed standard gauge railway connecting Mombasa and Nairobi opened in May 2017.
In 2016 the government was forced to take over three small and undercapitalized banks when underlying weaknesses were exposed. The government also enacted legislation that limits interest rates banks can charge on loans and set a rate that banks must pay their depositors. This measure led to a sharp shrinkage of credit in the economy. A prolonged election cycle in 2017 hurt the economy, drained government resources, and slowed GDP growth. Drought-like conditions in parts of the country pushed 2017 inflation above 8%, but the rate had fallen to 4.5% in February 2018.
The economy, however, is well placed to resume its decade-long 5%-6% growth rate. While fiscal deficits continue to pose risks in the medium term, other economic indicators, including foreign exchange reserves, interest rates, current account deficits, remittances and FDI are positive. The credit and drought-related impediments were temporary. Now In his second term, President KENYATTA has pledged to make economic growth and development a centerpiece of his second administration, focusing on his "Big Four" initiatives of universal healthcare, food security, affordable housing, and expansion of manufacturing.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$226.94 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$227.64 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$216.05 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
5.39% (2019 est.)
6.32% (2018 est.)
4.79% (2017 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$4,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$4,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$4,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$95.52 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
5.1% (2019 est.)
4.6% (2018 est.)
8% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: B+ (2007)
Moody's rating: B2 (2018)
Standard & Poors rating: B+ (2010)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 34.5% (2017 est.)
industry: 17.8% (2017 est.)
services: 47.5% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 79.5% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 14.3% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 18.9% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: -1% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 13.9% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -25.5% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
sugar cane, milk, maize, potatoes, bananas, camel milk, cassava, sweet potatoes, mangoes/guavas, cabbages
Industries
small-scale consumer goods (plastic, furniture, batteries, textiles, clothing, soap, cigarettes, flour), agricultural products, horticulture, oil refining; aluminum, steel, lead; cement, commercial ship repair, tourism, information technology
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 61.1%
industry: 6.7%
services: 32.2% (2005 est.)
Population below poverty line
36.1% (2015 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
40.8 (2015 est.)
42.5 (2008 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 1.8%
highest 10%: 37.8% (2005)
Budget
revenues: 13.95 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 19.24 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
1 July - 30 June
Current account balance
-$57.594 billion (2019 est.)
-$56.194 billion (2018 est.)
Exports
$11.49 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$11.56 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$9.723 billion (2017 est.)
Exports - partners
Uganda 10%, United States 9%, Netherlands 8%, Pakistan 7%, United Kingdom 6%, United Arab Emirates 6%, Tanzania 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
tea, cut flowers, refined petroleum, coffee, titanium (2019)
Imports
$20.41 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$20.17 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$18.653 billion (2017 est.)
Imports - partners
China 24%, United Arab Emirates 10%, India 10%, Saudi Arabia 7%, Japan 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, cars, packaged medicines, wheat, iron products (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$7.354 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$7.256 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$29.289 billion (2019 est.)
$25.706 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
Kenyan shillings (KES) per US dollar -
111.45 (2020 est.)
101.4 (2019 est.)
102.4 (2018 est.)
98.179 (2014 est.)
87.921 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 12.9%
male: 12%
female: 13.8% (2019)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 85% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 99% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 79% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
2.401 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109Electricity - from fossil fuels
33% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
34% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62Electricity - from other renewable sources
33% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12Refined petroleum products - production
13,960 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96Refined petroleum products - consumption
109,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 66,646 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 61,408,904 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 114.2 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: through increased competition, Kenya’s telecom market has improved international bandwidth and experienced rapid development in mobile sector, including remote regions; four fiber-optic submarine cables reduced costs and increased service to population; government supported LTE and broadband, promising economic support of free WiFi; mobile operators progress with 5G tests; e-commerce interoperability; importer of broadcasting equipment, video displays, and computers from China (2020)
domestic: fixed-line subscriptions stand at less than 1 per 100 persons; multiple providers in the mobile-cellular segment of the market fostering a boom in mobile-cellular telephone usage with teledensity reaching 104 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 254; landing point for the EASSy, TEAMS, LION2, DARE1, PEACE Cable, and SEACOM fiber-optic submarine cable systems covering East, North and South Africa, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia; satellite earth stations - 4 Intelsat; launched first micro satellites in 2018 (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
about a half-dozen large-scale privately owned media companies with TV and radio stations, as well as a state-owned TV broadcaster, provide service nationwide; satellite and cable TV subscription services available; state-owned radio broadcaster operates 2 national radio channels and provides regional and local radio services in multiple languages; many private radio stations broadcast on a national level along with over 100 private and non-profit regional stations broadcasting in local languages; TV transmissions of all major international broadcasters available, mostly via paid subscriptions; direct radio frequency modulation transmissions available for several foreign government-owned broadcasters (2019)
Internet users
total: 21.75 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 22.57% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 674,191 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1.25 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 25 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 188
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 5,935,831 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 294.97 million mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 16
over 3,047 m: 5
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 6
under 914 m: 1 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 181
1,524 to 2,437 m: 14
914 to 1,523 m: 107
under 914 m: 60 (2013)
Pipelines
4 km oil, 1,432 km refined products (2018)
Railways
total: 3,819 km (2018)
standard gauge: 485 km 1.435-m gauge (2018)
narrow gauge: 3,334 km 1.000-m gauge (2018)
Roadways
total: 177,800 km (2018)
paved: 14,420 km (8,500 km highways, 1,872 urban roads, and 4,048 rural roads) (2017)
unpaved: 147,032 km (2017)
Waterways
none specifically; the only significant inland waterway is the part of Lake Victoria within the boundaries of Kenya; Kisumu is the main port and has ferry connections to Uganda and Tanzania (2011)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Kisumu, Mombasa
LNG terminal(s) (import): Mombasa
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Kenya Defense Forces: Kenya Army, Kenya Navy, Kenya Air Force (2021)
note - the National Police Service maintains internal security and reports to the Ministry of Interior and Coordination of National Government; it includes a paramilitary General Service Unit; the Kenya Coast Guard Service (established 2018) is under the Ministry of Interior, but led by a military officer and comprised of personnel from the military, as well as the National Police Service, intelligence services, and other government agencies
Military expenditures
1.2% of GDP (2020)
1.3% of GDP (2019)
1.2% of GDP (2018)
1.3% of GDP (2017)
1.3% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Kenyan Defense Forces (KDF) are comprised of approximately 24,000 personnel (20,000 Army; 1,500 Navy; 2,500 Air Force) (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the KDF's inventory traditionally carried mostly older or second-hand Western weapons systems, particularly from France, the UK, and the US; however, since the 2000s it has sought to modernize and diversify its imports; suppliers since 2010 include China, France, Italy, Jordan, Serbia, South Africa, Spain, and the US (2021)
Military deployments
3,650 Somalia (AMISOM) (2021)
Maritime threats
the International Maritime Bureau reports that shipping in territorial and offshore waters in the Indian Ocean remain at risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships
Military service age and obligation
no conscription; 18-26 years of age for male and female voluntary service (under 18 with parental consent; upper limit 30 years of age for specialists, tradesmen, or women with a diploma; 39 years of age for chaplains/imams), with a 9-year obligation (7 years for Kenyan Navy) and subsequent 3-year re-enlistments; applicants must be Kenyan citizens (2021)
Military - note
Kenyan military forces intervened in Somalia in October 2011 to combat the al Qaida-affiliated al-Shabaab terrorist group, which had conducted numerous cross-border attacks into Kenya; in November 2011, the UN and the African Union invited Kenya to incorporate the force into the African Union Mission in Somalia (AMISOM); Kenyan forces were formally integrated into AMISOM in February 2012; as of mid-2021, they consisted of approximately 3,600 troops and were responsible for AMISOM’s Sector 2 comprising Lower and Middle Jubba (see Appendix-T for additional details on al-Shabaab)
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
al-Shabaab; Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps/Qods Force
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Kenya served as an important mediator in brokering Sudan's north-south separation in February 2005; as of March 2019, Kenya provides shelter to nearly 475,000 refugees and asylum seekers, including Ugandans who flee across the border periodically to seek protection from Lord's Resistance Army rebels; Kenya works hard to prevent the clan and militia fighting in Somalia from spreading across the border, which has long been open to nomadic pastoralists; the boundary that separates Kenya's and Sudan's sovereignty is unclear in the "Ilemi Triangle," which Kenya has administered since colonial times; in 2018, Kenya signed an MoU with Uganda and South Sudan to help demarcate their borders
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 281,812 (Somalia), 134,473 (South Sudan), 30,534 (Democratic Republic of the Congo), 20,655 (Ethiopia), 7,233 (Burundi) (2021)
IDPs: 190,000 (election-related violence, intercommunal violence, resource conflicts, al-Shabaab attacks in 2017 and 2018) (2020)
stateless persons: 16,820 (2020); note - the stateless population consists of Nubians, Kenyan Somalis, and coastal Arabs; the Nubians are descendants of Sudanese soldiers recruited by the British to fight for them in East Africa more than a century ago; Nubians did not receive Kenyan citizenship when the country became independent in 1963; only recently have Nubians become a formally recognized tribe and had less trouble obtaining national IDs; Galjeel and other Somalis who have lived in Kenya for decades are included with more recent Somali refugees and denied ID cards
Illicit drugs
a transit country for a variety of illicit drugs, including heroin and cocaine; transit location for precursor chemicals used to produce methamphetamine and other drugs; heroin from Southwest Asia enters Kenya destined for international markets, mainly Europe; cocaine transits through Kenya shipped through Ethiopia from South America; cultivates cannabis and miraa (khat) for both local use and export