Ireland
Introduction
Background
Celtic tribes arrived on the island between 600 and 150 B.C. Invasions by Norsemen that began in the late 8th century were finally ended when King Brian BORU defeated the Danes in 1014. Norman invasions began in the 12th century and set off more than seven centuries of Anglo-Irish struggle marked by fierce rebellions and harsh repressions. The Irish famine of the mid-19th century was responsible for a drop in the island's population by more than one quarter through starvation, disease, and emigration. For more than a century afterward, the population of the island continued to fall only to begin growing again in the 1960s. Over the last 50 years, Ireland's high birthrate has made it demographically one of the youngest populations in the EU.
The modern Irish state traces its origins to the failed 1916 Easter Monday Uprising that galvanized nationalist sentiment and fostered a guerrilla war resulting in independence from the UK in 1921 with the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the creation of the Irish Free State. The treaty was deeply controversial in Ireland in part because it helped solidify the partition of Ireland, with six of the island's 32 counties remaining in the UK as Northern Ireland. The split between pro-Treaty and anti-Treaty partisans led to the Irish Civil War (1922-23). The traditionally dominant political parties in Ireland, Fine Gael and Fianna Fail, are de facto descendants of the opposing sides of the treaty debate. Ireland formally left the British Dominion in 1949 when Ireland declared itself a republic.
Deep sectarian divides between the Catholic and Protestant populations and systemic discrimination in Northern Ireland erupted into years of violence known as the "Troubles" that began in the 1960s. In 1998, the governments of Ireland and the UK, along with most political parties in Northern Ireland, reached the Belfast/Good Friday Agreement with the support of the US. This agreement helped end the Troubles and initiated a new phase of cooperation between the Irish and British Governments.
Ireland was neutral in World War II and continues its policy of military neutrality. Ireland joined the European Community in 1973 and the euro-zone currency union in 1999. The economic boom years of the Celtic Tiger (1995-2007) saw rapid economic growth, which came to an abrupt end in 2008 with the meltdown of the Irish banking system. As a small, open economy, Ireland has excelled at courting foreign direct investment, especially from US multi-nationals, which helped the economy recover from the financial crisis and insolated it from the economic shocks of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
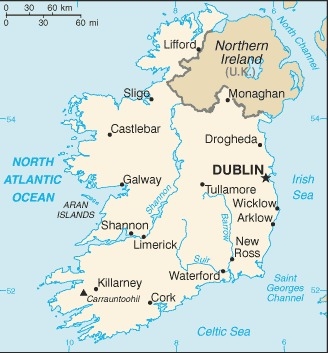
Location
Western Europe, occupying five-sixths of the island of Ireland in the North Atlantic Ocean, west of Great Britain
Geographic coordinates
53 00 N, 8 00 W
Map references
Europe
Land boundaries
total: 490 km
border countries (1): UK 490 km
Coastline
1,448 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm
Climate
temperate maritime; modified by North Atlantic Current; mild winters, cool summers; consistently humid; overcast about half the time
Terrain
mostly flat to rolling interior plain surrounded by rugged hills and low mountains; sea cliffs on west coast
Elevation
highest point: Carrauntoohil 1,041 m
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 118 m
Natural resources
natural gas, peat, copper, lead, zinc, silver, barite, gypsum, limestone, dolomite
Land use
agricultural land: 66.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 15.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 50.7% (2018 est.)
forest: 10.9% (2018 est.)
other: 23% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
0 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
population distribution is weighted to the eastern side of the island, with the largest concentration being in and around Dublin; populations in the west are small due to mountainous land, poorer soil, lack of good transport routes, and fewer job opportunities
Natural hazards
rare extreme weather events
Geography - note
strategic location on major air and sea routes between North America and northern Europe; over 40% of the population resides within 100 km of Dublin
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Irishman(men), Irishwoman(women), Irish (collective plural)
adjective: Irish
Ethnic groups
Irish 82.2%, Irish travelers 0.7%, other White 9.5%, Asian 2.1%, Black 1.4%, other 1.5%, unspecified 2.6% (2016 est.)
Languages
English (official, the language generally used), Irish (Gaelic or Gaeilge) (official, spoken by approximately 39.8% of the population as of 2016; mainly spoken in areas along Ireland's western coast known as gaeltachtai, which are officially recognized regions where Irish is the predominant language)
Religions
Roman Catholic 78.3%, Church of Ireland 2.7%, other Christian 1.6%, Orthodox 1.3%, Muslim 1.3%, other 2.4%, none 9.8%, unspecified 2.6% (2016 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 21.15% (male 560,338/female 534,570)
15-24 years: 12.08% (male 316,239/female 308,872)
25-54 years: 42.19% (male 1,098,058/female 1,085,794)
55-64 years: 10.77% (male 278,836/female 278,498)
65 years and over: 13.82% (male 331,772/female 383,592) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 54.8
youth dependency ratio: 32.3
elderly dependency ratio: 22.6
potential support ratio: 4.4 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 37.8 years
male: 37.4 years
female: 38.2 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
population distribution is weighted to the eastern side of the island, with the largest concentration being in and around Dublin; populations in the west are small due to mountainous land, poorer soil, lack of good transport routes, and fewer job opportunities
Urbanization
urban population: 63.9% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.15% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.242 million DUBLIN (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
30.7 years (2019 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
5 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165Infant mortality rate
total: 3.52 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 3.97 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 3.06 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 81.45 years
male: 79.12 years
female: 83.9 years (2021 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 97% of population
rural: 98.1% of population
total: 97.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 3% of population
rural: 1.9% of population
total: 2.6% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
6.9% (2018)
Physicians density
3.31 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
Hospital bed density
3 beds/1,000 population (2018)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 97.7% of population
rural: 99% of population
total: 98.2% of population
unimproved: urban: 2.3% of population
rural: 1% of population
total: 1.8% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS
7,800 (2020 est.)
note: estimate does not include children
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<100 (2020 est.)
note: estimate does not include children
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 19 years
male: 19 years
female: 19 years (2019)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 15.3%
male: 15.3%
female: 15.3% (2020 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
water pollution, especially of lakes, from agricultural runoff; acid rain kills plants, destroys soil fertility, and contributes to deforestation
Environment - international agreements
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Heavy Metals, Air Pollution-Multi-effect Protocol, Marine Life Conservation
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 8.26 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 37.71 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 13.67 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
temperate maritime; modified by North Atlantic Current; mild winters, cool summers; consistently humid; overcast about half the time
Land use
agricultural land: 66.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 15.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 50.7% (2018 est.)
forest: 10.9% (2018 est.)
other: 23% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 63.9% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.15% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.01% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 2,692,537 tons (2012 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 888,537 tons (2012 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 33% (2012 est.)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 631 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 51 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 179 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
52 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Ireland
local long form: none
local short form: Eire
etymology: the modern Irish name "Eire" evolved from the Gaelic "Eriu," the name of the matron goddess of Ireland (goddess of the land); the names "Ireland" in English and "Eire" in Irish are direct translations of each other
Government type
parliamentary republic
Capital
name: Dublin
geographic coordinates: 53 19 N, 6 14 W
time difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: derived from Irish "dubh" and "lind" meaning respectively "black, dark" and "pool" and which referred to the dark tidal pool where the River Poddle entered the River Liffey; today the area is the site of the castle gardens behind Dublin Castle
Administrative divisions
28 counties and 3 cities*; Carlow, Cavan, Clare, Cork, Cork*, Donegal, Dublin*, Dun Laoghaire-Rathdown, Fingal, Galway, Galway*, Kerry, Kildare, Kilkenny, Laois, Leitrim, Limerick, Longford, Louth, Mayo, Meath, Monaghan, Offaly, Roscommon, Sligo, South Dublin, Tipperary, Waterford, Westmeath, Wexford, Wicklow
Independence
6 December 1921 (from the UK by the Anglo-Irish Treaty, which ended British rule); 6 December 1922 (Irish Free State established); 18 April 1949 (Republic of Ireland Act enabled)
National holiday
Saint Patrick's Day, 17 March; note - marks the traditional death date of Saint Patrick, patron saint of Ireland, during the latter half of the fifth century A.D. (most commonly cited years are c. 461 and c. 493); although Saint Patrick's feast day was celebrated in Ireland as early as the ninth century, it only became an official public holiday in Ireland in 1903
Constitution
history: previous 1922; latest drafted 14 June 1937, adopted by plebiscite 1 July 1937, effective 29 December 1937
amendments: proposed as bills by Parliament; passage requires majority vote by both the Senate and House of Representatives, majority vote in a referendum, and presidential signature; amended many times, last in 2019
Legal system
common law system based on the English model but substantially modified by customary law; judicial review of legislative acts by Supreme Court
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no, unless a parent of a child born in Ireland has been legally resident in Ireland for at least three of the four years prior to the birth of the child
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 4 of the previous 8 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Michael D. HIGGINS (since 11 November 2011)
head of government: Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Micheál MARTIN (since 27 June 2020); note - MARTIN will serve through December 2022 and will then be succeeded by Leo VARADKAR
cabinet: Cabinet nominated by the prime minister, appointed by the president, approved by the Dali Eireann (lower house of Parliament)
elections/appointments: president directly elected by majority popular vote for a 7-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 26 October 2018 (next to be held no later than November 2025); taoiseach (prime minister) nominated by the House of Representatives (Dail Eireann), appointed by the president
election results: Michael D. HIGGINS reelected president; percent of vote - Michael D. HIGGINS (independent) 55.8%, Peter CASEY (independent) 23.3%, Sean GALLAGHER (independent) 6.4%, Liadh NI RIADA (Sinn Fein) 6.4%, Joan FREEMAN (independent) 6%, Gavin DUFFY (independent) 2.2%
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliament or Oireachtas consists of:
Senate or Seanad Eireann (60 seats; 49 members indirectly elected from 5 vocational panels of nominees by an electoral college, 11 appointed by the prime minister
House of Representatives or Dail Eireann (160 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote; all Parliament members serve 5-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last held early on 30-21 May 2020 (next to be held in March 2025)
House of Representatives - last held on 8 February 2020 (next to be held no later than 2025)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Fianna Fail 16, Fine Gael 12, Labor Party 5, Sinn Fein 5, Green Party 2, independent 9; composition - men 36, women 24, percent of women 40%
House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - Sinn Fein 23%, Fianna Fail 23%, Fine Gael 22%, Green Party 8%, Labor Party 4%, Social Democrats 4%, AAA-PBD 3%, Aontu 0.6%, Independents for Change 0.6%, Ceann Comhairle 0.6%, independent 12%; seats by party - Sinn Fein 37, Fianna Fail 37, Fine Gael 35, Green Party 12, Labor Party 6, Social Democrats 6, AAA-PBD 5, Aontu l, Independents for Change 1, Ceann Comhairle 1, Independents 19; composition as of September 2021 - men 124, women 36, percent of women 22.2%; note - total Parliament percent of women 27.3%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court of Ireland (consists of the chief justice, 9 judges, 2 ex-officio members - the presidents of the High Court and Court of Appeal - and organized in 3-, 5-, or 7-judge panels, depending on the importance or complexity of an issue of law)
judge selection and term of office: judges nominated by the prime minister and Cabinet and appointed by the president; chief justice serves in the position for 7 years; judges can serve until age 70
subordinate courts: High Court, Court of Appeal; circuit and district courts; criminal courts
Political parties and leaders
Solidarity-People Before Profit or AAAS-PBP [collective leadership]
Fianna Fail [Micheal MARTIN]
Fine Gael [Leo VARADKAR]
Green Party [Eamon RYAN]
Labor (Labour) Party [Alan KELLY]
Renua Ireland (vacant)
Sinn Fein [Mary Lou MCDONALD]
Social Democrats [Catherine MURPHY, Roisin SHORTALL]
Socialist Party [collective leadership]
The Workers' Party [Michael DONNELLY]
International organization participation
ADB (nonregional member), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNOCI, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Daniel Gerard MULHALL (since 8 September 2017)
chancery: 2234 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 462-3939
FAX: [1] (202) 232-5993
email address and website:
https://www.dfa.ie/irish-embassy/usa/
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Austin (TX), Boston, Chicago, New York, San Francisco
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Alexandra MCKNIGHT (since 19 January 2021)
embassy: 42 Elgin Road, Ballsbridge, Dublin 4
mailing address: 5290 Dublin Place, Washington DC 20521-5290
telephone: [353] (1) 668-8777
FAX: [353] (1) 688-8056
email address and website:
ACSDublin@state.gov
https://ie.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal vertical bands of green (hoist side), white, and orange; officially the flag colors have no meaning, but a common interpretation is that the green represents the Irish nationalist (Gaelic) tradition of Ireland; orange represents the Orange tradition (minority supporters of William of Orange); white symbolizes peace (or a lasting truce) between the green and the orange
note: similar to the flag of Cote d'Ivoire, which is shorter and has the colors reversed - orange (hoist side), white, and green; also similar to the flag of Italy, which is shorter and has colors of green (hoist side), white, and red
National symbol(s)
harp, shamrock (trefoil); national colors: blue, green
National anthem
name: "Amhran na bhFiann" (The Soldier's Song)
lyrics/music: Peadar KEARNEY [English], Liam O RINN [Irish]/Patrick HEENEY and Peadar KEARNEY
note: adopted 1926; instead of "Amhran na bhFiann," the song "Ireland's Call" is often used at athletic events where citizens of Ireland and Northern Ireland compete as a unified team
Economy
Economic overview
Ireland is a small, modern, trade-dependent economy. It was among the initial group of 12 EU nations that began circulating the euro on 1 January 2002. GDP growth averaged 6% in 1995-2007, but economic activity dropped sharply during the world financial crisis and the subsequent collapse of its domestic property market and construction industry during 2008-11. Faced with sharply reduced revenues and a burgeoning budget deficit from efforts to stabilize its fragile banking sector, the Irish Government introduced the first in a series of draconian budgets in 2009. These measures were not sufficient to stabilize Ireland’s public finances. In 2010, the budget deficit reached 32.4% of GDP - the world's largest deficit, as a percentage of GDP. In late 2010, the former COWEN government agreed to a $92 billion loan package from the EU and IMF to help Dublin recapitalize Ireland’s banking sector and avoid defaulting on its sovereign debt. In March 2011, the KENNY government intensified austerity measures to meet the deficit targets under Ireland's EU-IMF bailout program.
In late 2013, Ireland formally exited its EU-IMF bailout program, benefiting from its strict adherence to deficit-reduction targets and success in refinancing a large amount of banking-related debt. In 2014, the economy rapidly picked up. In late 2014, the government introduced a fiscally neutral budget, marking the end of the austerity program. Continued growth of tax receipts has allowed the government to lower some taxes and increase public spending while keeping to its deficit-reduction targets. In 2015, GDP growth exceeded 26%. The magnitude of the increase reflected one-off statistical revisions, multinational corporate restructurings in intellectual property, and the aircraft leasing sector, rather than real gains in the domestic economy, which was still growing. Growth moderated to around 4.1% in 2017, but the recovering economy assisted lowering the deficit to 0.6% of GDP.
In the wake of the collapse of the construction sector and the downturn in consumer spending and business investment during the 2008-11 economic crisis, the export sector, dominated by foreign multinationals, has become an even more important component of Ireland's economy. Ireland’s low corporation tax of 12.5% and a talented pool of high-tech laborers have been some of the key factors in encouraging business investment. Loose tax residency requirements made Ireland a common destination for international firms seeking to pay less tax or, in the case of U.S. multinationals, defer taxation owed to the United States. In 2014, amid growing international pressure, the Irish government announced it would phase in more stringent tax laws, effectively closing a commonly used loophole. The Irish economy continued to grow in 2017 and is forecast to do so through 2019, supported by a strong export sector, robust job growth, and low inflation, to the point that the Government must now address concerns about overheating and potential loss of competitiveness. The greatest risks to the economy are the UK’s scheduled departure from the European Union ("Brexit") in March 2019, possible changes to international taxation policies that could affect Ireland’s revenues, and global trade pressures.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$447.97 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$433.17 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$410.33 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
5.86% (2019 est.)
9.42% (2018 est.)
9.49% (2017 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$89,700 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$87,800 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$84,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$398.476 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
0.9% (2019 est.)
0.4% (2018 est.)
0.3% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: A+ (2017)
Moody's rating: A2 (2017)
Standard & Poors rating: AA- (2019)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 1.2% (2017 est.)
industry: 38.6% (2017 est.)
services: 60.2% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 34% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 10.1% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 23.4% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 1.2% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 119.9% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -89.7% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
milk, barley, beef, wheat, potatoes, pork, oats, poultry, mushrooms/truffles, mutton
Industries
pharmaceuticals, chemicals, computer hardware and software, food products, beverages and brewing; medical devices
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 5%
industry: 11%
services: 84% (2015 est.)
Population below poverty line
13.1% (2018 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
32.8 (2016 est.)
35.9 (1987 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2.9%
highest 10%: 27.2% (2000)
Budget
revenues: 86.04 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 87.19 billion (2017 est.)
Public debt
68.6% of GDP (2017 est.)
73.6% of GDP (2016 est.)
note: data cover general government debt and include debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intragovernmental debt; intragovernmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$44.954 billion (2019 est.)
$24.154 billion (2018 est.)
Exports
$502.31 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$471.6 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$440.693 billion (2017 est.)
Exports - partners
United States 28%, Belgium 10%, Germany 10%, UK 9%, China 5%, Netherlands 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
medical cultures/vaccines, nitrogen compounds, packaged medicines, integrated circuits, scented mixtures (2019)
Imports
$452.98 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$361.12 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$359.725 billion (2017 est.)
Imports - partners
United Kingdom 31%, United States 16%, Germany 10%, Netherlands 5%, France 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
aircraft, computers, packaged medicines, refined petroleum, medical cultures/vaccines (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$4.412 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$2.203 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
Debt - external
$2,829,303,000,000 (2019 est.)
$2,758,949,000,000 (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
euros (EUR) per US dollar -
0.82771 (2020 est.)
0.90338 (2019 est.)
0.87789 (2018 est.)
0.885 (2014 est.)
0.7634 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 15.3%
male: 15.3%
female: 15.3% (2020 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
9.945 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61Electricity - from fossil fuels
65% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
2% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138Electricity - from other renewable sources
33% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11Refined petroleum products - production
64,970 bbl/day (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76Refined petroleum products - consumption
153,700 bbl/day (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66Natural gas - proved reserves
9.911 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 1,678,651 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 34 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 5,234,027 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 106 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: infrastructure projects are underway, including the national plan to deliver fiber-based service of at least 150Mb/s nationally by the end of 2022; operators invested in fiber-based networks to deliver a 1Gb/s service to most premises, and on 5G to cover more than half of population; operator test of satellite broadband; Dublin is a smart city (2020)
domestic: increasing levels of broadband access particularly in urban areas; fixed-line 36 per 100 and mobile-cellular 105 per 100 subscriptions; digital system using cable and microwave radio relay (2019)
international: country code - 353; landing point for the AEConnect -1, Celtic-Norse, Havfrue/AEC-2, GTT Express, Celtic, ESAT-1, IFC-1, Solas, Pan European Crossing, ESAT-2, CeltixConnect -1 & 2, GTT Atlantic, Sirius South, Emerald Bridge Fibres and Geo Eirgrid submarine cable with links to the US, Canada, Norway, Isle of Man and UK; satellite earth stations - 81 (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
publicly owned broadcaster Radio Telefis Eireann (RTE) operates 4 TV stations; commercial TV stations are available; about 75% of households utilize multi-channel satellite and TV services that provide access to a wide range of stations; RTE operates 4 national radio stations and has launched digital audio broadcasts on several stations; a number of commercial broadcast stations operate at the national, regional, and local levels (2019)
Internet users
total: 4.51 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 92% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 1,516,252 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 30.71 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 9 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 450
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 167,598,633 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 168.71 million mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 16
over 3,047 m: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 5
under 914 m: 5 (2019)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 24
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 2
under 914 m: 21 (2013)
Pipelines
2,427 km gas (2017)
Railways
total: 4,301 km (2018)
narrow gauge: 1,930 km 0.914-m gauge (operated by the Irish Peat Board to transport peat to power stations and briquetting plants) (2018)
broad gauge: 2,371 km 1.600-m gauge (53 km electrified) (2018)
Roadways
total: 99,830 km (2018)
paved: 99,830 km (includes 2,717 km of expressways) (2018)
Merchant marine
total: 96
by type: bulk carrier 12, general cargo 36, oil tanker 1, other 47 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Dublin, Shannon Foynes
cruise port(s): Cork (250,000), Dublin (359,966) (2020)
container port(s) (TEUs): Dublin (529,563) (2016)
river port(s): Cork (Lee), Waterford (Suir)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Irish Defense Forces (Oglaigh na h-Eireannn): Army, Air Corps, Naval Service, Reserve Defense Forces (2021)
Military expenditures
0.27% of GDP (2020)
0.29% of GDP (2019)
0.29% of GDP (2018)
0.31% of GDP (2017)
0.33% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Irish Defense Forces have approximately 8,700 active duty personnel (7,000 Army; 1,000 Navy; 700 Air Force) (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Irish Defense Forces have a small inventory of imported weapons systems from a variety of mostly European countries; the UK is the leading supplier of military hardware to Ireland since 2010 (2020)
Military deployments
135 Golan Heights (UNDOF); 330 Lebanon (UNIFIL) (Oct 2021)
Military service age and obligation
18-25 years of age for male and female voluntary military service recruits to the Defence Forces (18-27 years of age for the Naval Service); 18-26 for cadetship (officer) applicants; 12-year service (5 active, 7 reserves); Irish citizen, European Economic Area citizenship, or refugee status (2021)
Military - note
the Irish Defense Forces trace their origins back to the Irish Volunteers, which was established in 1913; the Irish Volunteers took part in the 1916 Easter Rising and the Irish War of Independence, 1919-1921
Ireland has a long-standing policy of military neutrality; however, it participates in international peacekeeping and humanitarian operations, as well as crisis management; Ireland is a signatory of the EU’s Common Security and Defense Policy and has committed a battalion of troops to the EU’s Rapid Reaction Force; Ireland is not a member of NATO, but has a relationship going back to 1997 when it deployed personnel in support of the NATO-led peacekeeping operations in Bosnia and Herzegovina; Ireland joined NATO’s Partnership for Peace program in 1999; Ireland has been an active participate in UN peacekeeping operations since the 1950s
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Continuity Irish Republican Army; New Irish Republican Army; Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (ISIS) (2019)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Ireland, Iceland, and the UK dispute Denmark's claim that the Faroe Islands' continental shelf extends beyond 200 nm
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 106 (2020)
Trafficking in persons
current situation: human traffickers exploit domestic and foreign victims in Ireland and Irish victims abroad; traffickers subject Irish children and foreign trafficking victims from Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and South America to sex trafficking; victims are exploited in forced domestic work, the restaurant industry, waste management, fishing, seasonal agriculture, and car washing services; Vietnamese and Chinese nationals convicted for cannabis cultivation often report indicators of forced labor, such as document retention, restriction of movement, and non-payment of wages; undocumented workers in the fishing industry and domestic workers, particularly au pairs, are vulnerable to trafficking; women from Eastern Europe forced into marriage in Ireland are at risk for sex trafficking and forced labor; the problem of forced labor in the country is growing
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List — Ireland does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking but is making significant efforts to do so; efforts included increasing prosecutions and funding to NGOs for victim assistance, increasing the number of police and immigration officers receiving anti-trafficking training, and reorganizing its anti-trafficking coordination unit; however, the government did not demonstrate overall increasing efforts; no traffickers have been convicted since the anti-trafficking law was amended in 2013; weakened deterrence meant impunity for traffickers and undermined efforts to support victims testifying against traffickers; systematic deficiencies in victim identification, a lack of specialized services for victims continued, and the amended working scheme for sea fishers increased their vulnerability to trafficking (2020)
Illicit drugs
transshipment point for and consumer of hashish from North Africa to the UK and Netherlands and of European-produced synthetic drugs; increasing consumption of South American cocaine; minor transshipment point for heroin and cocaine destined for Western Europe; despite recent legislation, narcotics-related money laundering - using bureaux de change, trusts, and shell companies involving the offshore financial community - remains a concern