Introduction
Background
Guam was settled by Austronesian people around 1500 B.C. These people became the indigenous Chamorro and were influenced by later migrations, including the Micronesians in the first millennium A.D., and island Southeast Asians around 900. Society was stratified with higher classes living along the coast and lower classes living inland. Spanish explorer Ferdinand MAGELLAN was the first European to see Guam in 1521 and Spain claimed the island in 1565 as it served as a refueling stop for ships between Mexico and the Philippines. Spain formally colonized Guam in 1668. Spain’s brutal repression of Chamorro, along with new diseases and intermittent warfare, reduced the indigenous population from more than 100,000 to less than 5,000 by the 1700s. Spain tried to repopulate the island by forcing people from nearby islands to settle on Guam and preventing them from escaping.
Guam became a hub for whalers and traders in the western Pacific in the early 1800s. During the 1898 Spanish-American War, the US Navy occupied Guam and set up a military administration. The US Navy opposed local control of government despite repeated petitions by Chamorro. Japan invaded Guam in 1941 and instituted a repressive regime. During the US recapture of Guam in 1944, the island’s two largest villages were destroyed. After World War II, political pressure from local Chamorro leaders led to Guam being established as an unincorporated organized territory in 1950 with US citizenship granted to all Chamorro. In a referendum in 1982, more than 75% of voters chose closer relations with the US over independence, although no change in status was made because of disagreements on the future right of Chamorro self-determination. The US military holds about 29% of Guam’s land and stations several thousand troops on the island. The installations are some of the most strategically important US bases in the Pacific; they also constitute the island’s most important source of income and economic stability.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
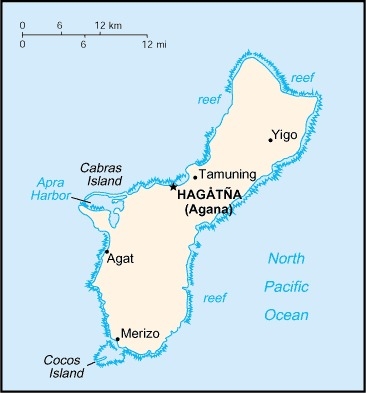
Geography
Location
Oceania, island in the North Pacific Ocean, about three-quarters of the way from Hawaii to the Philippines
Geographic coordinates
13 28 N, 144 47 E
Map references
Oceania
Area - comparative
three times the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
125.5 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical marine; generally warm and humid, moderated by northeast trade winds; dry season (January to June), rainy season (July to December); little seasonal temperature variation
Terrain
volcanic origin, surrounded by coral reefs; relatively flat coralline limestone plateau (source of most fresh water), with steep coastal cliffs and narrow coastal plains in north, low hills in center, mountains in south
Elevation
highest point: Mount Lamlam 406 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
Natural resources
aquatic wildlife (supporting tourism), fishing (largely undeveloped)
Land use
agricultural land: 33.4% (2018 est.)
arable land: 1.9% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 16.7% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 14.8% (2018 est.)
forest: 47.9% (2018 est.)
other: 18.7% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
2 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
no large cities exist on the island, though large villages (municipalities) attract much of the population; the largest of these is Dededo
Natural hazards
frequent squalls during rainy season; relatively rare but potentially destructive typhoons (June to December)
Geography - note
largest and southernmost island in the Mariana Islands archipelago and the largest island in Micronesia; strategic location in western North Pacific Ocean
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Guamanian(s) (US citizens)
adjective: Guamanian
Ethnic groups
Chamorro 37.3%, Filipino 26.3%, White 7.1%, Chuukese 7%, Korean 2.2%, other Pacific Islander 2%, other Asian 2%, Chinese 1.6%, Palauan 1.6%, Japanese 1.5%, Pohnpeian 1.4%, mixed 9.4%, other 0.6% (2010 est.)
Languages
English 43.6%, Filipino 21.2%, Chamorro 17.8%, other Pacific island languages 10%, Asian languages 6.3%, other 1.1% (2010 est.)
Religions
Christian (predominantly Roman Catholic) 94.2%, folk religions 1.5%, Buddhist 1.1%, other 1.6%, unaffiliated 1.7% (2020 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 27.22% (male 23,748/female 22,122)
15-24 years: 16.08% (male 14,522/female 12,572)
25-54 years: 36.65% (male 31,880/female 29,871)
55-64 years: 10.5% (male 9,079/female 8,610)
65 years and over: 9.54% (male 7,504/female 8,577) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 52.4
youth dependency ratio: 36.4
elderly dependency ratio: 16.1
potential support ratio: 6.2 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 29.4 years
male: 28.7 years
female: 30.2 years (2020 est.)
Net migration rate
-10.98 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2021 est.)
country comparison to the world: 222Population distribution
no large cities exist on the island, though large villages (municipalities) attract much of the population; the largest of these is Dededo
Urbanization
urban population: 95% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 0.84% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
147,000 HAGATNA (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.16 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.87 male(s)/female
total population: 1.06 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Infant mortality rate
total: 11.73 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 11.75 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 11.72 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 77.25 years
male: 74.81 years
female: 79.85 years (2021 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: total: 100% of population
unimproved: total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 89.8% of population (2015 est.)
rural: 89.8% of population (2015 est.)
total: 89.8% of population (2015 est.)
unimproved: urban: 10.2% of population (2015 est.)
rural: 10.2% of population (2015 est.)
total: 10.2% of population (2015 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 29.4%
male: 29.7%
female: 28.9% (2011 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
fresh water scarcity; reef damage; inadequate sewage treatment; extermination of native bird populations by the rapid proliferation of the brown tree snake, an exotic, invasive species
Climate
tropical marine; generally warm and humid, moderated by northeast trade winds; dry season (January to June), rainy season (July to December); little seasonal temperature variation
Land use
agricultural land: 33.4% (2018 est.)
arable land: 1.9% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 16.7% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 14.8% (2018 est.)
forest: 47.9% (2018 est.)
other: 18.7% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 95% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 0.84% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 141,500 tons (2012 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 25,258 tons (2011 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 17.9% (2011 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Guam
local long form: none
local short form: Guahan
abbreviation: GU
etymology: the native Chamorro name for the island "Guahan" (meaning "we have" or "ours") was changed to Guam in the 1898 Treaty of Paris, whereby Spain relinquished Guam, Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines to the US
Government type
unincorporated organized territory of the US with local self-government; republican form of territorial government with separate executive, legislative, and judicial branches
Dependency status
unincorporated organized territory of the US with policy relations between Guam and the federal government under the jurisdiction of the Office of Insular Affairs, US Department of the Interior
Capital
name: Hagatna (Agana)
geographic coordinates: 13 28 N, 144 44 E
time difference: UTC+10 (15 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name is derived from the Chamoru word "haga," meaning "blood", and may refer to the bloodlines of the various families that established the original settlement
Administrative divisions
none (territory of the US)
Independence
none (territory of the US)
National holiday
Discovery Day (or Magellan Day), first Monday in March (1521)
Constitution
history: effective 1 July 1950 (Guam Act of 1950 serves as a constitution)
amendments: amended many times, last in 2015
Legal system
common law modeled on US system; US federal laws apply
Citizenship
see United States
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal; note - Guamanians are US citizens but do not vote in US presidential elections
Executive branch
chief of state:
President Joseph R. BIDEN Jr. (since 20 January 2021); Vice President Kamala D. HARRIS (since 20 January 2021)
head of government: Governor Lourdes LEON GUERRERO (since 7 January 2019); Lieutenant Governor Josh TENORIO (since 7 January 2019)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the governor with the consent of the Legislature
elections/appointments: president and vice president indirectly elected on the same ballot by an Electoral College of 'electors' chosen from each state to serve a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); under the US Constitution, residents of unincorporated territories, such as Guam, do not vote in elections for US president and vice president; however, they may vote in Democratic and Republican presidential primary elections; governor and lieutenant governor elected on the same ballot by absolute majority vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 4-year term (eligible for 2 consecutive terms); election last held on 6 November 2018 (next to be held in November 2022)
election results: Lourdes LEON GUERRERO elected governor; percent of vote - Lourdes LEON GUERRERO (Democratic Party) 50.7%, Ray TENORIO (Republican Party) 26.4%; Josh TENORIO (Democratic Party) elected lieutenant governor
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Legislature of Guam or Liheslaturan Guahan (15 seats; members elected in a single countrywide constituency by simple majority vote to serve 2-year terms)
Guam directly elects 1 member by simple majority vote to serve a 2-year term as the delegate to the US House of Representatives; note - the delegate can vote when serving on a committee and when the House meets as the Committee of the Whole House, but not when legislation is submitted for a “full floor” House vote
elections: Guam Legislature - last held on 3 November 2020 (next to be held on 5 November 2022)
delegate to the US House of Representatives - last held on 3 November 2020 with runoff on 17 November (next to be held on 5 November 2022)
election results: Guam Legislature - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Democratic Party 10, Republican Party 5; composition - men 5, women 10, percent of women 66.7%
Guam delegate to the US House of Representatives - Democratic Party 1 (man)
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court of Guam (consists of 3 justices); note - appeals beyond the Supreme Court of Guam are referred to the US Supreme Court
judge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the governor and confirmed by the Guam legislature; justices appointed for life subject to retention election every 10 years
subordinate courts: Superior Court of Guam - includes several divisions; US Federal District Court for the District of Guam (a US territorial court; appeals beyond this court are heard before the US Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit)
Political parties and leaders
Democratic Party [Joaquin "Kin" PEREZ]
Republican Party [Jerry CRISOSTOMO]
International organization participation
AOSIS (observer), IOC, PIF (observer), SPC, UPU
Diplomatic representation in the US
none (territory of the US)
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: none (territory of the US)
Flag description
territorial flag is dark blue with a narrow red border on all four sides; centered is a red-bordered, pointed, vertical ellipse containing a beach scene, a proa or outrigger canoe with sail, and a palm tree with the word GUAM superimposed in bold red letters; the proa is sailing in Agana Bay with the promontory of Punta Dos Amantes, near the capital, in the background; the shape of the central emblem is that of a Chamorro sling stone, used as a weapon for defense or hunting; blue represents the sea and red the blood shed in the struggle against oppression
note: the US flag is the national flag
National symbol(s)
coconut tree; national colors: deep blue, red
National anthem
name: "Fanohge Chamoru" (Stand Ye Guamanians)
lyrics/music: Ramon Manalisay SABLAN [English], Lagrimas UNTALAN [Chamoru]/Ramon Manalisay SABLAN
note: adopted 1919; the local anthem is also known as "Guam Hymn"; as a territory of the United States, "The Star-Spangled Banner," which generally follows the playing of "Stand Ye Guamanians," is official (see United States)
Economy
Economic overview
US national defense spending is the main driver of Guam’s economy, followed closely by tourism and other services. Guam serves as a forward US base for the Western Pacific and is home to thousands of American military personnel. Total federal spending (defense and non-defense) amounted to $1.988 billion in 2016, or 34.2 of Guam’s GDP. Of that total, federal grants and cover-over payments amounted to $3444.1 million in 2016, or 35.8% of Guam’s total revenues for the fiscal year. In 2016, Guam’s economy grew 0.3%. Despite slow growth, Guam’s economy has been stable over the last decade. National defense spending cushions the island’s economy against fluctuations in tourism. Service exports, mainly spending by foreign tourists in Guam, amounted to over $1 billion for the first time in 2016, or 17.8% of GDP.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$5.793 billion (2016 est.)
$5.697 billion (2015 est.)
$5.531 billion (2014 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
0.4% (2016 est.)
0.5% (2015 est.)
1.6% (2014 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$35,600 (2016 est.)
$35,200 (2015 est.)
$34,400 (2014 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$5.793 billion (2016 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: NA
industry: NA
services: 58.4% (2015 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 56.2% (2016 est.)
government consumption: 55% (2016 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 20.6% (2016 est.)
investment in inventories: NA (2016 est.)
exports of goods and services: 19.4% (2016 est.)
imports of goods and services: -51.2% (2016 est.)
Agricultural products
fruits, copra, vegetables; eggs, pork, poultry, beef
Industries
national defense, tourism, construction, transshipment services, concrete products, printing and publishing, food processing, textiles
Labor force
73,210 (2016 est.)
note: includes only the civilian labor force
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 0.3%
industry: 21.6%
services: 78.1% (2013 est.)
Population below poverty line
23% (2001 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 1.24 billion (2016 est.)
expenditures: 1.299 billion (2016 est.)
Fiscal year
1 October - 30 September
Exports - partners
South Korea 31%, Hong Kong 27%, Taiwan 18%, Philippines 7% (2019)
Exports - commodities
scrap iron, electric batteries, gas turbines, scrap copper, beauty products (2019)
Imports - partners
Singapore 33%, Japan 21%, South Korea 18%, Hong Kong 9%, Malaysia 6% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, trunks/cases, cars, insulated wire, broadcasting equipment (2019)
Exchange rates
the US dollar is used
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 29.4%
male: 29.7%
female: 28.9% (2011 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
560,000 kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143Electricity - from fossil fuels
94% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175Electricity - from other renewable sources
6% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97Refined petroleum products - consumption
14,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 68,000 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 42.01 (2018 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 98,000 (2004 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 61.99 (2004 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: integrated with US facilities for direct dialing, including free use of 800 numbers (2020)
domestic: three major companies provide both fixed-line and mobile services, as well as access to the Internet; fixed-line 42 per 100 and 113 per 100 for mobile-cellular (2019)
international: country code - 1-671; major landing points for Atisa, HANTRU1, HK-G, JGA-N, JGA-S, PIPE-1, SEA-US, SxS, Tata TGN-Pacific, AJC, GOKI, AAG, AJC and Mariana-Guam Cable submarine cables between Asia, Australia, and the US (Guam is a transpacific communications hub for major carriers linking the US and Asia); satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
about a dozen TV channels, including digital channels; multi-channel cable TV services are available; roughly 20 radio stations
Internet users
total: 136,500 (2021 est.)
percent of population: 80.51% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 3,000 (2014)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1.86 (2019)
Transportation
Airports - with paved runways
total: 4
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 1
under 914 m: 1 (2013)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Apra Harbor
Military and Security
Military - note
defense is the responsibility of the US