Gambia, The
Introduction
Background
In the 10th century, Muslim merchants established some of The Gambia’s earliest large settlements as trans-Saharan trade hubs. These settlements eventually grew into major export centers sending slaves, gold, and ivory across the Sahara. Between the 16th and 17th centuries, European colonial powers began establishing trade with The Gambia. In 1664, the United Kingdom established a colony in The Gambia focused on exporting enslaved people across the Atlantic. During the roughly 300 years of the trans-Atlantic slave trade, the UK and other European powers may have exported as many as 3 million people from The Gambia.
In 1965, The Gambia gained its independence from the UK. Geographically surrounded by Senegal, it formed the short-lived confederation of Senegambia between 1982 and 1989. In 1994, Yahya JAMMEH led a military coup overthrowing the president and banning political activity. JAMMEH won every presidential election until 2016. In December 2016, after 22 years of authoritarian rule, President JAMMEH lost to Adama BARROW during free and fair elections. Due to The Gambia’s poor human rights record under JAMMEH, international development partners had substantially reduced aid to the country. These channels have now reopened under the administration of President BARROW. Since the 2016 election, The Gambia and the US have enjoyed improved relations. US assistance to the country has supported military education and training programs, capacity building, and democracy-strengthening activities.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and Senegal
Geographic coordinates
13 28 N, 16 34 W
Map references
Africa
Area - comparative
slightly less than twice the size of Delaware
Land boundaries
total: 749 km
border countries (1): Senegal 749 km
Coastline
80 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 18 nm
continental shelf: extent not specified
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; hot, rainy season (June to November); cooler, dry season (November to May)
Terrain
flood plain of the Gambia River flanked by some low hills
Elevation
highest point: unnamed elevation 53 m
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 34 m
Natural resources
fish, clay, silica sand, titanium (rutile and ilmenite), tin, zircon
Land use
agricultural land: 56.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 41% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.5% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 14.6% (2018 est.)
forest: 43.9% (2018 est.)
other: 0% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
50 sq km (2012)
Major aquifers
Senegalo-Mauritanian Basin
Major rivers (by length in km)
Gambia river mouth (shared with Senegal and Guinea [s]) - 1,094 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Population distribution
settlements are found scattered along the Gambia River; the largest communities, including the capital of Banjul, and the country's largest city, Serekunda, are found at the mouth of the Gambia River along the Atlantic coast as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards
droughts
Geography - note
almost an enclave of Senegal; smallest country on the African mainland
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Gambian(s)
adjective: Gambian
Ethnic groups
Mandinka/Jahanka 33.3%, Fulani/Tukulur/Lorobo 18.2%, Wolof 12.9%, Jola/Karoninka 11%, Serahuleh 7.2%, Serer 3.5%, other 4%, non-Gambian 9.9% (2019-20 est.)
Languages
English (official), Mandinka, Wolof, Fula, other indigenous vernaculars
Religions
Muslim 96.4%, Christian 3.5%, other or none 0.1% (2019-20 est.)
Demographic profile
The Gambia’s youthful age structure – almost 60% of the population is under the age of 25 – is likely to persist because the country’s total fertility rate remains strong at nearly 4 children per woman. The overall literacy rate is around 55%, and is significantly lower for women than for men. At least 70% of the populace are farmers who are reliant on rain-fed agriculture and cannot afford improved seeds and fertilizers. Crop failures caused by droughts between 2011 and 2013 have increased poverty, food shortages, and malnutrition.
The Gambia is a source country for migrants and a transit and destination country for migrants and refugees. Since the 1980s, economic deterioration, drought, and high unemployment, especially among youths, have driven both domestic migration (largely urban) and migration abroad (legal and illegal). Emigrants are largely skilled workers, including doctors and nurses, and provide a significant amount of remittances. The top receiving countries for Gambian emigrants are Spain, the US, Nigeria, Senegal, and the UK. While the Gambia and Spain do not share historic, cultural, or trade ties, rural Gambians have migrated to Spain in large numbers because of its proximity and the availability of jobs in its underground economy (this flow slowed following the onset of Spain’s late 2007 economic crisis).
The Gambia’s role as a host country to refugees is a result of wars in several of its neighboring West African countries. Since 2006, refugees from the Casamance conflict in Senegal have replaced their pattern of flight and return with permanent settlement in The Gambia, often moving in with relatives along the Senegal-Gambia border. The strain of providing for about 7,400 Casamance refugees has increased poverty among Gambian villagers.
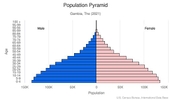
Age structure
0-14 years: 35.15% (male 391,993/female 388,816)
15-24 years: 20.12% (male 221,519/female 225,414)
25-54 years: 36.39% (male 396,261/female 412,122)
55-64 years: 4.53% (male 48,032/female 52,538)
65 years and over: 3.81% (male 38,805/female 45,801) (2021 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 86.9
youth dependency ratio: 82.1
elderly dependency ratio: 4.7
potential support ratio: 21.1 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 21.8 years
male: 21.5 years
female: 22.2 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
settlements are found scattered along the Gambia River; the largest communities, including the capital of Banjul, and the country's largest city, Serekunda, are found at the mouth of the Gambia River along the Atlantic coast as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization
urban population: 63.2% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.75% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
459,000 BANJUL (capital) (2021)
note: includes the local government areas of Banjul and Kanifing
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.91 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
20.7 years (2019/20 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-49
Maternal mortality ratio
597 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13Infant mortality rate
total: 65.04 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 70.93 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 58.98 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 66.15 years
male: 63.8 years
female: 68.57 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
16.8% (2018)
note: percent of women aged 15-49
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 91.4% of population
rural: 80.4% of population
total: 87.1% of population
unimproved: urban: 8.6% of population
rural: 19.6% of population
total: 12.9% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
3.1% (2018)
Physicians density
0.1 physicians/1,000 population (2015)
Hospital bed density
1.1 beds/1,000 population (2011)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 80.4% of population
rural: 44.5% of population
total: 66.3% of population
unimproved: urban: 19.6% of population
rural: 55.5% of population
total: 33.7% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 50.8%
male: 61.8%
female: 41.6% (2015)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 9 years
male: 9 years
female: 9 years (2010)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 25.8%
male: 21%
female: 32.3% (2018 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation due to slash-and-burn agriculture; desertification; water pollution; water-borne diseases
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 32.2 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 0.53 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 1.96 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; hot, rainy season (June to November); cooler, dry season (November to May)
Land use
agricultural land: 56.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 41% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.5% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 14.6% (2018 est.)
forest: 43.9% (2018 est.)
other: 0% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 63.2% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.75% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 2.47% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 193,441 tons (2002 est.)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Gambia river mouth (shared with Senegal and Guinea [s]) - 1,094 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major aquifers
Senegalo-Mauritanian Basin
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 41.2 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 21.2 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 39.2 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
8 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of The Gambia
conventional short form: The Gambia
etymology: named for the Gambia River that flows through the heart of the country
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Banjul
geographic coordinates: 13 27 N, 16 34 W
time difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: Banjul is located on Saint Mary's Island at the mouth of the Gambia River; the Mandinka used to gather fibrous plants on the island for the manufacture of ropes; "bang julo" is Mandinka for "rope fiber"; mispronunciation over time caused the term became the word Banjul
Administrative divisions
5 regions, 1 city*, and 1 municipality**; Banjul*, Central River, Kanifing**, Lower River, North Bank, Upper River, West Coast
Independence
18 February 1965 (from the UK)
National holiday
Independence Day, 18 February (1965)
Constitution
history: previous 1965 (Independence Act), 1970; latest adopted 8 April 1996, approved by referendum 8 August 1996, effective 16 January 1997; note - in early 2018, the "Constitutional Review Commission," was established to draft and assist in instituting a new constitution; a second draft completed in March 2020 was rejected by the National Assembly in September
amendments: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires at least three-fourths majority vote by the Assembly membership in each of several readings and approval by the president of the republic; a referendum is required for amendments affecting national sovereignty, fundamental rights and freedoms, government structures and authorities, taxation, and public funding; passage by referendum requires participation of at least 50% of eligible voters and approval by at least 75% of votes cast; amended 2001, 2004, 2018
Legal system
mixed legal system of English common law, Islamic law, and customary law
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Adama BARROW (since 19 January 2017); Vice President Isatou TOURAY (since 15 March 2019); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Adama BARROW (since 19 January 2017); Vice President Isatou TOURAY (since 15 March 2019)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 5-year term (no term limits); election last held on 4 December 2021 (next to be held in 2026); vice president appointed by the president
election results: Adama BARROW reelected president; percent of vote - Adama BARROW (National People's Party) 53.2%, Ousainou DARBOE (United Democratic Party) 27.7%, Mamma KANDEH (GDC)12.3%, Halifa SALLAH (PDOIS) 3.8%, Essa M. FAAL (Independent) 2%, Abdoulie Ebrima JAMMEH (NUP) 0.96%
Legislative branch
description: unicameral National Assembly (58 seats; 53 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 5 appointed by the president; members serve 5-year terms)
elections: last held on 6 April 2017 (next to be held in 2022)
election results: percent of vote by party - UDP 37.5%, GDC 17.4%, APRC 16%, PDOIS 9%, NRP 6.3%, PPP 2.5%, other 1.7%, independent 9.6%; seats by party - UDP 31, APRC 5, GDC 5, NRP 5, PDOIS 4, PPP 2, independent 1; composition - men 52, women 6, percent of women 10.3%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court of The Gambia (consists of the chief justice and 6 justices; court sessions held with 5 justices)
judge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the president after consultation with the Judicial Service Commission, a 6-member independent body of high-level judicial officials, a presidential appointee, and a National Assembly appointee; justices appointed for life or until mandatory retirement at age 75
subordinate courts: Court of Appeal; High Court; Special Criminal Court; Khadis or Muslim courts; district tribunals; magistrates courts; cadi courts
Political parties and leaders
Alliance for Patriotic Reorientation and Construction or APRC [Fabakary JATTA]
Coalition 2016 [collective leadership] (electoral coalition includes UDP, PDOIS, NRP, GMC, GDC, PPP, and GPDP)
Gambia Democratic Congress or GDC [Mama KANDEH]
Gambia Moral Congress or GMC [Mai FATTY]
Gambia Party for Democracy and Progress or GPDP [Sarja JARJOU]
National Convention Party or NCP [Yaya SANYANG and Majanko SAMUSA (both claiming leadership)]
National Democratic Action Movement or NDAM [Lamin Yaa JUARA]
National People's Party or NPP [Adama BARROW]
National Reconciliation Party or NRP [Hamat BAH]
People's Democratic Organization for Independence and Socialism or PDOIS [Sidia JATTA]
People's Progressive Party or PPP [Yaya CEESAY)]
United Democratic Party or UDP [Ousainou DARBOE]
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, ECOWAS, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSMA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Dawda D. FADERA (since 24 January 2018)
chancery: 5630 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20011
telephone: [1] (202) 785-1399; [1] (202) 785-1428
FAX: [1] (202) 785-1430
email address and website:
info@gambiaembassy.us
https://www.gambiaembassydc.us/home
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Richard Carlton "Carl" PASCHALL (since 9 April 2019)
embassy: Kairaba Avenue, Fajara, P.M.B. 19, Banjul
mailing address: 2070 Banjul Place, Washington DC 20521-2070
telephone: [220] 439-2856
FAX: [220] 439-2475
email address and website:
ConsularBanjul@state.gov
https://gm.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), blue with white edges, and green; red stands for the sun and the savannah, blue represents the Gambia River, and green symbolizes forests and agriculture; the white stripes denote unity and peace
National symbol(s)
lion; national colors: red, blue, green, white
National anthem
name: For The Gambia, Our Homeland
lyrics/music: Virginia Julie HOWE/adapted by Jeremy Frederick HOWE
note: adopted 1965; the music is an adaptation of the traditional Mandinka song "Foday Kaba Dumbuya"
Economy
Economic overview
The government has invested in the agriculture sector because three-quarters of the population depends on the sector for its livelihood and agriculture provides for about one-third of GDP, making The Gambia largely reliant on sufficient rainfall. The agricultural sector has untapped potential - less than half of arable land is cultivated and agricultural productivity is low. Small-scale manufacturing activity features the processing of cashews, groundnuts, fish, and hides. The Gambia's reexport trade accounts for almost 80% of goods exports and China has been its largest trade partner for both exports and imports for several years.
The Gambia has sparse natural resource deposits. It relies heavily on remittances from workers overseas and tourist receipts. Remittance inflows to The Gambia amount to about one-fifth of the country’s GDP. The Gambia's location on the ocean and proximity to Europe has made it one of the most frequented tourist destinations in West Africa, boosted by private sector investments in eco-tourism and facilities. Tourism normally brings in about 20% of GDP, but it suffered in 2014 from tourists’ fears of Ebola virus in neighboring West African countries. Unemployment and underemployment remain high.
Economic progress depends on sustained bilateral and multilateral aid, on responsible government economic management, and on continued technical assistance from multilateral and bilateral donors. International donors and lenders were concerned about the quality of fiscal management under the administration of former President Yahya JAMMEH, who reportedly stole hundreds of millions of dollars of the country’s funds during his 22 years in power, but anticipate significant improvements under the new administration of President Adama BARROW, who assumed power in early 2017. As of April 2017, the IMF, the World Bank, the European Union, and the African Development Bank were all negotiating with the new government of The Gambia to provide financial support in the coming months to ease the country’s financial crisis.
The country faces a limited availability of foreign exchange, weak agricultural output, a border closure with Senegal, a slowdown in tourism, high inflation, a large fiscal deficit, and a high domestic debt burden that has crowded out private sector investment and driven interest rates to new highs. The government has committed to taking steps to reduce the deficit, including through expenditure caps, debt consolidation, and reform of state-owned enterprises.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$5.22 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$5.22 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$4.92 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
4.6% (2017 est.)
0.4% (2016 est.)
5.9% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$2,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$2,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$2,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$1.746 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
7.1% (2019 est.)
6.5% (2018 est.)
8% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 20.4% (2017 est.)
industry: 14.2% (2017 est.)
services: 65.4% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 90.7% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 12% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 19.2% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: -2.7% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 20.8% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -40% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
groundnuts, milk, oil palm fruit, millet, sorghum, rice, maize, vegetables, cassava, fruit
Industries
peanuts, fish, hides, tourism, beverages, agricultural machinery assembly, woodworking, metalworking, clothing
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 75%
industry: 19%
services: 6% (1996 est.)
Population below poverty line
48.6% (2015 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
35.9 (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2%
highest 10%: 36.9% (2003)
Budget
revenues: 300.4 million (2017 est.)
expenditures: 339 million (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$194 million (2017 est.)
-$85 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$350 million note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$448 million (2018 est.)
$435 million (2017 est.)
Exports - partners
China 38%, India 22%, Mali 7%, Chile 5% (2017)
Exports - commodities
lumber, cashews, refined petroleum, fish oil, ground nut oil (2019)
Imports
$620 million note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$851 million (2018 est.)
$754 million (2017 est.)
Imports - partners
China 33%, India 10%, Senegal 5%, Brazil 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
clothing and apparel, refined petroleum, rice, raw sugar, palm oil (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$170 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$87.64 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$586.8 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$571.2 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
dalasis (GMD) per US dollar -
51.75 (2020 est.)
51.4 (2019 est.)
49.515 (2018 est.)
41.89 (2014 est.)
41.733 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 25.8%
male: 21%
female: 32.3% (2018 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 49% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 69% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 16% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
117,000 kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178Electricity - from fossil fuels
97% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172Electricity - from other renewable sources
3% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124Refined petroleum products - consumption
3,800 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 185Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 44,000 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1.93 (2018 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 2,677,954 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 110.8 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: state-owned telecom partially privatized but retains a monopoly with fixed-line service; multiple mobile networks provide 2G to almost all citizens and above the African average; high poverty rates continue to limit access to the Internet, especially via fixed-line services in rural areas; weak political support for development of communications infrastructure, including National Broadband Network program; government depends on donors and loans from China and Islamic Development banks; two submarine cables provide international connectivity within African continent and Europe (2020)
domestic: fixed-line stands at 2 per 100 subscriptions with one dominant company and mobile-cellular teledensity, aided by multiple mobile-cellular providers, is over 140 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 220; landing point for the ACE submarine cable to West Africa and Europe; microwave radio relay links to Senegal and Guinea-Bissau; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
1 state-run TV-channel; one privately-owned TV-station; 1 Online TV-station; three state-owned radio station and 31 privately owned radio stations; eight community radio stations; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are available, some via shortwave radio; cable and satellite TV subscription services are obtainable in some parts of the country
(2019)Internet users
total: 580,200 (2021 est.)
percent of population: 19.84% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 4,433 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2018 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 6
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 53,735 (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 1
over 3,047 m: 1 (2019)
Roadways
total: 2,977 km (2011)
paved: 518 km (2011)
unpaved: 2,459 km (2011)
Waterways
390 km (on River Gambia; small oceangoing vessels can reach 190 km) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 88Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Banjul
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Gambia Armed Forces: the Gambian National Army (GNA; includes a small air wing), Navy, Republican National Guard (responsible for VIP protection, riot control, and presidential security) (2021)
Military expenditures
0.8% of GDP (2020 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2019)
0.7% of GDP (2018)
1% of GDP (2015)
1.2% of GDP (2014)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; approximately 2,000 total active troops (2020)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the GNA has a limited equipment inventory; since 2000, it has received only a few secondhand items (2021)
Military service age and obligation
18-25 years of age for male and female voluntary military service (18-22 for officers); no conscription; service obligation 6 months (2020)
Military - note
in 2017, several members of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) sent security forces to The Gambia to conduct stability operations and provide assistance and training following the 2016 election; as of 2021, the ECOWAS Mission in the Gambia (ECOMIG) was comprised of about 1,000 military and gendarmerie personnel from Ghana, Nigeria, and Senegal; ECOMIG is slated to become a police mission by the end of 2021
the Gambian Armed Forces (GAF) traces its origins to the Gambia Regiment of the British Army; established in 1901, the Gambia Regiment was part of the West African Frontier Force (WAFF, later Royal West African Frontier Force or RWAFF) and served in both World Wars, including the British 1944-45 military campaign in Burma; the Gambia Regiment was disbanded in 1958 and replaced by the Field Force, a police paramilitary unit; the Field Force was responsible for The Gambia’s security until the establishment of the Gambian Armed Forces in 1985; in addition, a defense agreement signed in 1965 between The Gambia and Senegal provided mutual assistance in the face of an external threat; from 1981-1989, The Gambia and Senegal formed a Confederal Army that was made up of two-thirds Senegalese and one-third Gambian soldiers
the military in Gambia, including the Field Force, has a history of heavy involvement in the country’s politics, including multiple coups or coup attempts and mutinies
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
attempts to stem refugees, cross-border raids, arms smuggling, and other illegal activities by separatists from southern Senegal's Casamance region, as well as from conflicts in other west African states
Trafficking in persons
current situation: The Gambia is a source, transit, and destination country for women and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; Gambian women, children, and, to a lesser extent, boys are exploited for prostitution and domestic servitude; women, girls, and boys from West African countries are trafficked to the Gambia for sexual exploitation, particularly catering to European tourists seeking sex with children; some Gambian trafficking victims have been identified in neighboring West African countries and the UK; boys in some Koranic schools are forced into street vending or begging
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List — The Gambia does not meet the minimum standards for eliminating trafficking, but it is making significant efforts to do so; the government has increased investigations, identified more trafficking victims, improved security at a Department of Social Welfare shelter, increased training for officials, and raised public awareness of the problem of trafficking; the government was upgraded to Tier 2 Watch List during this rating period; despite these efforts, the government did not convict a trafficker for the third consecutive year; victim services remained inadequate, and some law enforcement officers reportedly requested bribes to register trafficking complaints (2020)