French Polynesia
Introduction
Background
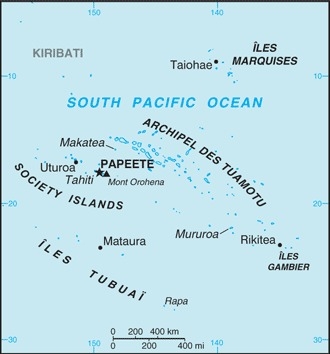
French Polynesia consists of five archipelagos - the Austral Islands, the Gambier Islands, the Marquesas Islands, the Society Islands, and the Tuamotu Archipelago. The Marquesas were first settled around 200 B.C. and the Society Islands around A.D. 300. Raiatea in the Society Islands became a center for religion and culture. Exploration of the other islands emanated from Raiatea and by 1000, there were small permanent settlements in all the island groups. Ferdinand MAGELLAN was the first European to see the islands of French Polynesia in 1520, and successive European voyagers traveled through them over the next two centuries. In 1767, British explorer Samuel WALLIS was the first European to visit Tahiti, followed by French navigator Louis Antoine de BOUGAINVILLE in 1768, and British explorer James COOK in 1769. King POMARE I united Tahiti and surrounding islands into the Kingdom of Tahiti in 1788. Protestant missionaries arrived in 1797 and Pomare I’s successor converted in the 1810s, along with most Tahitians. In the 1830s, Queen POMARE IV refused to allow French Catholic missionaries to operate, leading France to declare a protectorate over Tahiti and fight the French-Tahitian War of the 1840s in an attempt to annex the islands. POMARE IV requested British assistance to fight France, and while the UK did not provide material support, it did diplomatically pressure France to simply maintain its protectorate status.
In 1880, King POMARE V ceded Tahiti and its possessions to France, changing its status into a colony. France then claimed the Gambier Islands and Tuamotu Archipelago and by 1901 had incorporated all five island groups into its establishments in Oceania. A Tahitian nationalist movement formed in 1940, leading France to grant French citizenship to the islanders in 1946 and change it to an overseas territory. In 1957, the islands’ name was changed to French Polynesia and the following year, 64% of voters chose to stay part of France when they approved a new constitution. Uninhabited Mururoa Atoll was established as a French nuclear test site in 1962 and tests were conducted between 1966 and 1992 (underground beginning in 1975). France also conducted tests at Fangataufa Atoll, including its last nuclear test in 1996.
France granted French Polynesia partial internal autonomy in 1977 and expanded autonomy in 1984. French Polynesia was converted into an overseas collectivity in 2003 and renamed an overseas country inside the Republic in 2004. Proindependence politicians won a surprise majority in local elections that same year but in subsequent elections have been relegated to a vocal minority. In 2013, French Polynesia was relisted on the UN List of Non-Self Governing Territories.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Oceania, five archipelagoes (Archipel des Tuamotu, Iles Gambier, Iles Marquises, Iles Tubuai, Society Islands) in the South Pacific Ocean about halfway between South America and Australia
Geographic coordinates
15 00 S, 140 00 W
Map references
Oceania
Area
total: 4,167 sq km (118 islands and atolls; 67 are inhabited)
land: 3,827 sq km
water: 340 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly less than one-third the size of Connecticut
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
2,525 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical, but moderate
Terrain
mixture of rugged high islands and low islands with reefs
Elevation
highest point: Mont Orohena 2,241 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
Natural resources
timber, fish, cobalt, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land: 12.5% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0.7% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 6.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 5.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 43.7% (2018 est.)
other: 43.8% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
10 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
the majority of the population lives in the Society Islands, one of five archipelagos that includes the most populous island - Tahiti - with approximately 70% of the nation's population
Natural hazards
occasional cyclonic storms in January
Geography - note
includes five archipelagoes: four volcanic (Iles Gambier, Iles Marquises, Iles Tubuai, Society Islands) and one coral (Archipel des Tuamotu); the Tuamotu Archipelago forms the largest group of atolls in the world - 78 in total, 48 inhabited; Makatea in the Tuamotu Archipelago is one of the three great phosphate rock islands in the Pacific Ocean - the others are Banaba (Ocean Island) in Kiribati and Nauru
People and Society
Nationality
noun: French Polynesian(s)
adjective: French Polynesian
Ethnic groups
Polynesian 78%, Chinese 12%, local French 6%, metropolitan French 4%
Languages
French (official) 73.5%, Tahitian 20.1%, Marquesan 2.6%, Austral languages 1.2%, Paumotu 1%, other 1.6% (2017 est.)
major-language sample(s):
The World Factbook, une source indispensable d'informations de base. (French)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Protestant 54%, Roman Catholic 30%, other 10%, no religion 6%
Age structure
0-14 years: 21.69% (male 32,920/female 31,100)
15-24 years: 14.72% (male 22,640/female 20,793)
25-54 years: 44.24% (male 66,921/female 63,636)
55-64 years: 10.31% (male 15,610/female 14,823)
65 years and over: 9.04% (male 12,854/female 13,824) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 45.5
youth dependency ratio: 32.3
elderly dependency ratio: 13.2
potential support ratio: 7.6 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 33.3 years
male: 33 years
female: 33.5 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
the majority of the population lives in the Society Islands, one of five archipelagos that includes the most populous island - Tahiti - with approximately 70% of the nation's population
Urbanization
urban population: 62.1% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 0.65% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
136,000 PAPEETE (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.09 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.93 male(s)/female
total population: 1.05 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Infant mortality rate
total: 4.46 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 5.37 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 3.51 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 78.19 years
male: 75.86 years
female: 80.63 years (2021 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: total: 100% of population
unimproved: total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
Physicians density
2.13 physicians/1,000 population (2009)
Sanitation facility access
improved: total: 96.9% of population
unimproved: total: 3.1% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: malaria
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 56.7%
male: 54.5%
female: 59.7% (2012 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
sea level rise; extreme weather events (cyclones, storms, and tsunamis producing floods, landslides, erosion, and reef damage); droughts; fresh water scarcity
Air pollutants
carbon dioxide emissions: 0.77 megatons (2016 est.)
Climate
tropical, but moderate
Land use
agricultural land: 12.5% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0.7% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 6.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 5.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 43.7% (2018 est.)
other: 43.8% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 62.1% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 0.65% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: malaria
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 147,000 tons (2013 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 57,330 tons (2013 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 39% (2013 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Overseas Lands of French Polynesia
conventional short form: French Polynesia
local long form: Pays d'outre-mer de la Polynesie Francaise
local short form: Polynesie Francaise
former: Establishments in Oceania, French Establishments in Oceania
etymology: the term "Polynesia" is an 18th-century construct composed of two Greek words, "poly" (many) and "nesoi" (islands), and refers to the more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean
Government type
parliamentary democracy (Assembly of French Polynesia); an overseas collectivity of France
Dependency status
overseas country of France; note - overseas territory of France from 1946-2003; overseas collectivity of France since 2003, though it is often referred to as an overseas country due to its degree of autonomy
Capital
name: Papeete (located on Tahiti)
geographic coordinates: 17 32 S, 149 34 W
time difference: UTC-10 (5 hours behind Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name means "water basket" and refers to the fact that the islanders originally used calabashes enclosed in baskets to fetch water at a spring in the area
Administrative divisions
5 administrative subdivisions (subdivisions administratives, singular - subdivision administrative): Iles Australes (Austral Islands), Iles du Vent (Windward Islands), Iles Marquises (Marquesas Islands), Iles Sous-le-Vent (Leeward Islands), Iles Tuamotu-Gambier; note - the Leeward Islands and the Windward Islands together make up the Society Islands (Iles de la Societe)
Independence
none (overseas lands of France)
National holiday
Fete de la Federation, 14 July (1790); note - the local holiday is Internal Autonomy Day, 29 June (1880)
Constitution
history: 4 October 1958 (French Constitution)
amendments: French constitution amendment procedures apply
Legal system
the laws of France, where applicable, apply
Citizenship
see France
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Emmanuel MACRON (since 14 May 2017), represented by High Commissioner of the Republic Dominique SORAIN (since 10 July 2019)
head of government: President of French Polynesia Edouard FRITCH (since 12 September 2014)
cabinet: Council of Ministers approved by the Assembly from a list of its members submitted by the president
elections/appointments: French president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); high commissioner appointed by the French president on the advice of the French Ministry of Interior; French Polynesia president indirectly elected by Assembly of French Polynesia for a 5-year term (no term limits)
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Assembly of French Polynesia or Assemblée de la Polynésie française (57 seats; elections held in 2 rounds; in the second round, 38 members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by a closed-list proportional representation vote; the party receiving the most votes gets an additional 19 seats; members serve 5-year terms; French Polynesia indirectly elects 2 senators to the French Senate via an electoral college by absolute majority vote for 6-year terms with one-half the membership renewed every 3 years and directly elects 3 deputies to the French National Assembly by absolute majority vote in 2 rounds if needed for 5-year terms
French Polynesia indirectly elects 2 senators to the French Senate via an electoral college by absolute majority vote for 6-year terms with one-half the membership renewed every 3 years and directly elects 3 deputies to the French National Assembly by absolute majority vote in 2 rounds if needed for 5-year terms
elections: Assembly of French Polynesia - last held on 22 April 2018 and 6 May 2018 (next to be held in 2023)
French Senate - last held on 28 September 2020 (next to be held on 30 September 2023)
French National Assembly - last held in 2 rounds on 3 and 17 June 2017 (next to be held in 2022)
election results: Assembly of French Polynesia - percent of vote by party - Tapura Huiraatira 45.1%, Popular Rally 29.3%, Tavini Huiraatira 25.6%; seats by party - Tapura Huiraatira 38, Popular Rally 11, Tavini Huiraatira 8; composition - men 27, women 30, percent of women 52.6%
French Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Popular Rally 1, People's Servant Party 1; composition - NA
French National Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Tapura Huiractura 2, Tavini Huiraatura 1; composition - NA
Judicial branch
highest courts: Court of Appeal or Cour d'Appel (composition NA); note - appeals beyond the French Polynesia Court of Appeal are heard by the Court of Cassation (in Paris)
judge selection and term of office: judges assigned from France normally for 3 years
subordinate courts: Court of the First Instance or Tribunal de Premiere Instance; Court of Administrative Law or Tribunal Administratif
Political parties and leaders
A Tia Porinetia [Teva ROHFRITSCH]
Alliance for a New Democracy or ADN (includes The New Star [Philip SCHYLE], This Country is Yours [Nicole BOUTEAU])
New Fatherland Party (Ai'a Api) [Emile VERNAUDON]
Our Home alliance
People's Servant Party (Tavini Huiraatira) [Oscar TEMARU]
Popular Rally (Tahoeraa Huiraatira) [Gaston FLOSSE]
Tapura Huiraatira [Edouard FRITICH]
Tavini Huiraatira [James CHANCELOR]
Union for Democracy alliance or UPD [Oscar TEMARU]
International organization participation
ITUC (NGOs), PIF (associate member), SPC, UPU, WMO
Diplomatic representation in the US
none (overseas lands of France)
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: none (overseas lands of France)
Flag description
two red horizontal bands encase a wide white band in a 1:2:1 ratio; centered on the white band is a disk with a blue and white wave pattern depicting the sea on the lower half and a gold and white ray pattern depicting the sun on the upper half; a Polynesian canoe rides on the wave pattern; the canoe has a crew of five represented by five stars that symbolize the five island groups; red and white are traditional Polynesian colors
note: identical to the red-white-red flag of Tahiti, the largest and most populous of the islands in French Polynesia, but which has no emblem in the white band; the flag of France is used for official occasions
National symbol(s)
outrigger canoe, Tahitian gardenia (Gardenia taitensis) flower; national colors: red, white
National anthem
name: "Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui" (Long Live Tahiti Nui)
lyrics/music: Maeva BOUGES, Irmine TEHEI, Angele TEROROTUA, Johanna NOUVEAU, Patrick AMARU, Louis MAMATUI, and Jean-Pierre CELESTIN (the compositional group created both the lyrics and music)
note: adopted 1993; serves as a local anthem; as a territory of France, "La Marseillaise" is official (see France)
Government - note
under certain acts of France, French Polynesia has acquired autonomy in all areas except those relating to police, monetary policy, tertiary education, immigration, and defense and foreign affairs; the duties of its president are fashioned after those of the French prime minister
Economy
Economic overview
Since 1962, when France stationed military personnel in the region, French Polynesia has changed from a subsistence agricultural economy to one in which a high proportion of the work force is either employed by the military or supports the tourist industry. With the halt of French nuclear testing in 1996, the military contribution to the economy fell sharply.
After growing at an average yearly rate of 4.2% from 1997-2007, the economic and financial crisis in 2008 marked French Polynesia’s entry into recession. However, since 2014, French Polynesia has shown signs of recovery. Business turnover reached 1.8% year-on-year in September 2016, tourism increased 1.8% in 2015, and GDP grew 2.0% in 2015.
French Polynesia’s tourism-dominated service sector accounted for 85% of total value added for the economy in 2012. Tourism employs 17% of the workforce. Pearl farming is the second biggest industry, accounting for 54% of exports in 2015; however, the output has decreased to 12.5 tons – the lowest level since 2008. A small manufacturing sector predominantly processes commodities from French Polynesia’s primary sector - 8% of total economy in 2012 - including agriculture and fishing.
France has agreed to finance infrastructure, marine businesses, and cultural and ecological sites at roughly $80 million per year between 2015 and 2020. Japan, the US, and China are French Polynesia’s three largest trade partners.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$5.49 billion (2017 est.)
$5.383 billion (2016 est.)
$6.963 billion (2015 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
2% (2015 est.)
-2.7% (2014 est.)
-2.5% (2010 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$17,000 (2015 est.)
$20,100 (2014 est.)
$22,700 (2010)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$4.795 billion (2015 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 2.5% (2009)
industry: 13% (2009)
services: 84.5% (2009)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 66.9% (2014 est.)
government consumption: 33.6% (2014 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 19.4% (2014 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.1% (2014 est.)
exports of goods and services: 17.5% (2014 est.)
imports of goods and services: -37.5% (2014 est.)
Agricultural products
coconuts, fruit, roots/tubers nes, pineapples, cassava, sugar cane, eggs, tropical fruit, tomatoes
Industries
tourism, pearls, agricultural processing, handicrafts, phosphates
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 13%
industry: 19%
services: 68% (2013 est.)
Population below poverty line
19.7% (2009 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 1.891 billion (2012)
expenditures: 1.833 billion (2011)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
$207.7 million (2014 est.)
$158.8 million (2013 est.)
Exports - partners
Japan 23.1%, Hong Kong 21.5%, Kyrgyzstan 15.9%, US 15.9%, France 12.4% (2017)
Exports - commodities
cultured pearls, coconut products, mother-of-pearl, vanilla, shark meat
Imports - partners
France 27.9%, South Korea 12.1%, US 10.1%, China 7.3%, NZ 6.7%, Singapore 4.2% (2017)
Imports - commodities
fuels, foodstuffs, machinery and equipment
Exchange rates
Comptoirs Francais du Pacifique francs (XPF) per US dollar -
110.2 (2017 est.)
107.84 (2016 est.)
107.84 (2015 est.)
89.85 (2014 est.)
90.56 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 56.7%
male: 54.5%
female: 59.7% (2012 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
253,000 kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163Electricity - from fossil fuels
70% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
19% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89Electricity - from other renewable sources
11% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76Refined petroleum products - consumption
6,600 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 60,123 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 32.51 (2018 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 302,673 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 104.3 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: French Polynesia has one of the most advanced telecom infrastructures in the Pacific islands; high penetration of mobile broadband coverage; almost half of mobile connections on 3G, growing subscribership to 4G LTE; universal mobile penetration; host of uplink systems for the Galileo satellite network, creating hub for communications in the region and vastly improving international connectivity; submarine cable connections increase international bandwidth; additional domestic submarine cable will connect remote islands (2020)
domestic: fixed-line subscriptions 22 per 100 persons and mobile-cellular density is roughly 104 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 689; landing points for the NATITUA, Manatua, and Honotua submarine cables to other French Polynesian Islands, Cook Islands, Niue, Samoa and US; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
French public overseas broadcaster Reseau Outre-Mer provides 2 TV channels and 1 radio station; 1 government-owned TV station; a small number of privately owned radio stations (2019)
Internet users
total: 204,800 (2021 est.)
percent of population: 72.7% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 59,790 (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 21.53 (2018 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 2 (registered in France) (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 19 (registered in France)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 45
over 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 5
914 to 1,523 m: 33
under 914 m: 5 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 9
914 to 1,523 m: 4
under 914 m: 5 (2013)
Heliports
1 (2013)
Roadways
total: 2,590 km (1999)
paved: 1,735 km (1999)
unpaved: 855 km (1999)
Merchant marine
total: 24
by type: general cargo 14, other 10 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Papeete
Military and Security
Military and security forces
no regular military forces
Military - note
defense is the responsibility of France; France maintains forces in French Polynesia