Ethiopia
Introduction
Background
Unique among African countries, the ancient Ethiopian monarchy maintained its freedom from colonial rule with the exception of a short-lived Italian occupation from 1936-41. In 1974, a military junta, the Derg, deposed Emperor Haile SELASSIE (who had ruled since 1930) and established a socialist state. Torn by bloody coups, uprisings, wide-scale drought, and massive refugee problems, the regime was finally toppled in 1991 by a coalition of rebel forces, the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF). A constitution was adopted in 1994, and Ethiopia's first multiparty elections were held in 1995.
A border war with Eritrea in the late 1990s ended with a peace treaty in December 2000. In November 2007, the Eritrea-Ethiopia Border Commission (EEBC) issued specific coordinates as virtually demarcating the border and pronounced its work finished. Alleging that the EEBC acted beyond its mandate in issuing the coordinates, Ethiopia did not accept them and maintained troops in previously contested areas pronounced by the EEBC as belonging to Eritrea. This intransigence resulted in years of heightened tension between the two countries. In August 2012, longtime leader Prime Minister MELES Zenawi died in office and was replaced by his Deputy Prime Minister HAILEMARIAM Desalegn, marking the first peaceful transition of power in decades. Following a wave of popular dissent and anti-government protest that began in 2015, HAILEMARIAM resigned in February 2018 and ABIY Ahmed Ali took office in April 2018 as Ethiopia's first ethnic Oromo prime minister. In June 2018, ABIY announced Ethiopia would accept the border ruling of 2000, prompting rapprochement between Ethiopia and Eritrea that was marked with a peace agreement in July 2018 and a reopening of the border in September 2018. In November 2019, Ethiopia's nearly 30-year ethnic-based ruling coalition - the EPRDF - merged into a single unity party called the Prosperity Party, however, one of the four constituent parties (the Tigray Peoples Liberation Front or TPLF) refused to join.In November 2020, a military conflict erupted between forces aligned with the Tigrayan People’s Liberation Front (TPLF) and Ethiopia’s national military, the Ethiopian National Defense Force; the conflict, which has continued throughout 2021, has exacerbated ethnic violence and has largely centered in Tigray, Amhara, and Afar regional states.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
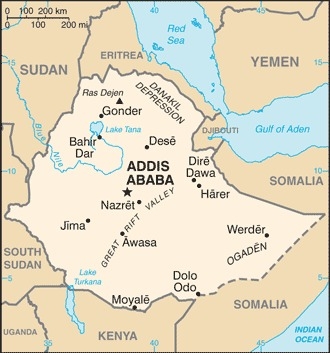
Location
Eastern Africa, west of Somalia
Geographic coordinates
8 00 N, 38 00 E
Map references
Africa
Area
total: 1,104,300 sq km
land: 1,096,570 sq km
water: 7,730 sq km
note: area numbers are approximate since a large portion of the Ethiopia-Somalia border is undefined
Land boundaries
total: 5,925 km
border countries (6): Djibouti 342 km, Eritrea 1033 km, Kenya 867 km, Somalia 1640 km, South Sudan 1299 km, Sudan 744 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
tropical monsoon with wide topographic-induced variation
Terrain
high plateau with central mountain range divided by Great Rift Valley
Elevation
highest point: Ras Dejen 4,550 m
lowest point: Danakil Depression -125 m
mean elevation: 1,330 m
Natural resources
small reserves of gold, platinum, copper, potash, natural gas, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land: 36.3% (2018 est.)
arable land: 15.2% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.1% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 20% (2018 est.)
forest: 12.2% (2018 est.)
other: 51.5% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
2,900 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Mediterranean Sea) Nile (3,254,853 sq km)
Major aquifers
Ogaden-Juba Basin, Sudd Basin (Umm Ruwaba Aquifer)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Tana - 3,600 sq km; Abaya Hayk - 1,160 sq km; Ch'amo Hayk - 550 sq km
Salt water lake(s): Lake Turkana (shared with Kenya) - 6,400 sq km; Abhe Bid Hayk/Abhe Bad (shared with Djibouti) - 780 sq km;
Major rivers (by length in km)
Blue Nile river source (shared with Sudan [m]) - 1,600 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Population distribution
highest density is found in the highlands of the north and middle areas of the country, particularly around the centrally located capital city of Addis Ababa; the far east and southeast are sparsely populated as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards
geologically active Great Rift Valley susceptible to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions; frequent droughts
volcanism: volcanic activity in the Great Rift Valley; Erta Ale (613 m), which has caused frequent lava flows in recent years, is the country's most active volcano; Dabbahu became active in 2005, forcing evacuations; other historically active volcanoes include Alayta, Dalaffilla, Dallol, Dama Ali, Fentale, Kone, Manda Hararo, and Manda-Inakir
Geography - note
note 1: landlocked - entire coastline along the Red Sea was lost with the de jure independence of Eritrea on 24 May 1993; Ethiopia is, therefore, the most populous landlocked country in the world; the Blue Nile, the chief headstream of the Nile by water volume, rises in T'ana Hayk (Lake Tana) in northwest Ethiopia
note 2: three major crops are believed to have originated in Ethiopia: coffee, grain sorghum, and castor bean
People and Society
Population
110,871,031 (July 2021 est.)
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
Nationality
noun: Ethiopian(s)
adjective: Ethiopian
Ethnic groups
Oromo 34.9%, Amhara (Amara) 27.9%, Tigray (Tigrinya) 7.3%, Sidama 4.1%, Welaita 3%, Gurage 2.8%, Somali (Somalie) 2.7%, Hadiya 2.2%, Afar (Affar) 0.6%, other 12.6% (2016 est.)
Languages
Oromo (official working language in the State of Oromiya) 33.8%, Amharic (official national language) 29.3%, Somali (official working language of the State of Sumale) 6.2%, Tigrigna (Tigrinya) (official working language of the State of Tigray) 5.9%, Sidamo 4%, Wolaytta 2.2%, Gurage 2%, Afar (official working language of the State of Afar) 1.7%, Hadiyya 1.7%, Gamo 1.5%, Gedeo 1.3%, Opuuo 1.2%, Kafa 1.1%, other 8.1%, English (major foreign language taught in schools), Arabic (2007 est.)
major-language sample(s):
Kitaaba Addunyaa Waan Qabataamaatiif - Kan Madda Odeeffannoo bu’uraawaatiif baay’ee barbaachisaa ta’e. (Oromo)
የአለም እውነታ መጽሐፍ፣ ለመሠረታዊ መረጃ እጅግ አስፈላጊ የሆነ ምንጭ። (Amharic)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Ethiopian Orthodox 43.8%, Muslim 31.3%, Protestant 22.8%, Catholic 0.7%, traditional 0.6%, other 0.8% (2016 est.)
Demographic profile
Ethiopia is a predominantly agricultural country – more than 80% of the population lives in rural areas – that is in the early stages of demographic transition. Infant, child, and maternal mortality have fallen sharply over the past decade, but the total fertility rate has declined more slowly and the population continues to grow. The rising age of marriage and the increasing proportion of women remaining single have contributed to fertility reduction. While the use of modern contraceptive methods among married women has increased significantly from 6 percent in 2000 to 27 percent in 2012, the overall rate is still quite low.
Ethiopia’s rapid population growth is putting increasing pressure on land resources, expanding environmental degradation, and raising vulnerability to food shortages. With more than 40 percent of the population below the age of 15 and a fertility rate of over 5 children per woman (and even higher in rural areas), Ethiopia will have to make further progress in meeting its family planning needs if it is to achieve the age structure necessary for reaping a demographic dividend in the coming decades.
Poverty, drought, political repression, and forced government resettlement have driven Ethiopia’s internal and external migration since the 1960s. Before the 1974 revolution, only small numbers of the Ethiopian elite went abroad to study and then returned home, but under the brutal Derg regime thousands fled the country, primarily as refugees. Between 1982 and 1991 there was a new wave of migration to the West for family reunification. Since the defeat of the Derg in 1991, Ethiopians have migrated to escape violence among some of the country’s myriad ethnic groups or to pursue economic opportunities. Internal and international trafficking of women and children for domestic work and prostitution is a growing problem.
Age structure
0-14 years: 39.81% (male 21,657,152/female 21,381,628)
15-24 years: 19.47% (male 10,506,144/female 10,542,128)
25-54 years: 32.92% (male 17,720,540/female 17,867,298)
55-64 years: 4.42% (male 2,350,606/female 2,433,319)
65 years and over: 3.38% (male 1,676,478/female 1,977,857) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 76.8
youth dependency ratio: 70.6
elderly dependency ratio: 6.3
potential support ratio: 16 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 19.8 years
male: 19.6 years
female: 20.1 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
highest density is found in the highlands of the north and middle areas of the country, particularly around the centrally located capital city of Addis Ababa; the far east and southeast are sparsely populated as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization
urban population: 22.2% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 4.4% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
5.006 million ADDIS ABABA (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
19.3 years (2019 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 20-49
Maternal mortality ratio
401 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26Infant mortality rate
total: 34.62 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 39.56 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 29.53 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 67.9 years
male: 65.79 years
female: 70.06 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
37% (2019)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 97% of population
rural: 61.7% of population
total: 68.9% of population
unimproved: urban: 3% of population
rural: 38.3% of population
total: 31.1% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
3.3% (2018)
Physicians density
0.08 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
Hospital bed density
0.3 beds/1,000 population (2016)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 49.7% of population
rural: 5.7% of population
total: 14.7% of population
unimproved: urban: 50.3% of population
rural: 94.3% of population
total: 85.3% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 51.8%
male: 57.2%
female: 44.4% (2017)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 9 years
male: 8 years
female: 8 years (2012)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 3.5%
male: 2.7%
female: 4.5% (2013 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification; loss of biodiversity; water shortages in some areas from water-intensive farming and poor management; industrial pollution and pesticides contribute to air, water, and soil pollution
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 34.36 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 14.87 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 114.21 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical monsoon with wide topographic-induced variation
Land use
agricultural land: 36.3% (2018 est.)
arable land: 15.2% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.1% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 20% (2018 est.)
forest: 12.2% (2018 est.)
other: 51.5% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 22.2% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 4.4% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 5.81% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
Food insecurity
widespread lack of access: due to civil conflict - more than 16 million people were estimated to be severely food insecure in the May−June 2021 period; particular concerns exist for the Tigray Region and neighboring zones of Amhara and Afar regions, where 5.5 million people (about 60 percent of the population) are estimated to face severe food insecurity due to the conflict which started in November 2020 (2021)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 6,532,787 tons (2015 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Tana - 3,600 sq km; Abaya Hayk - 1,160 sq km; Ch'amo Hayk - 550 sq km
Salt water lake(s): Lake Turkana (shared with Kenya) - 6,400 sq km; Abhe Bid Hayk/Abhe Bad (shared with Djibouti) - 780 sq km;
Major rivers (by length in km)
Blue Nile river source (shared with Sudan [m]) - 1,600 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Mediterranean Sea) Nile (3,254,853 sq km)
Major aquifers
Ogaden-Juba Basin, Sudd Basin (Umm Ruwaba Aquifer)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 810 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 51.1 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 9.687 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
122 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
conventional short form: Ethiopia
local long form: Ityop'iya Federalawi Demokrasiyawi Ripeblik
local short form: Ityop'iya
former: Abyssinia, Italian East Africa
abbreviation: FDRE
etymology: the country name derives from the Greek word "Aethiopia," which in classical times referred to lands south of Egypt in the Upper Nile region
Government type
federal parliamentary republic
Capital
name: Addis Ababa
geographic coordinates: 9 02 N, 38 42 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name in Amharic means "new flower" and was bestowed on the city in 1889, three years after its founding
Administrative divisions
10 ethnically based regional states (kililoch, singular - kilil) and 2 self-governing administrations* (astedaderoch, singular - astedader); Adis Abeba* (Addis Ababa), Afar, Amara (Amhara), Binshangul Gumuz, Dire Dawa*, Gambela Hizboch (Gambela Peoples), Hareri Hizb (Harari People), Oromiya (Oromia), Sidama, Sumale (Somali), Tigray, Ye Debub Biheroch Bihereseboch na Hizboch (Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples)
Independence
oldest independent country in Africa and one of the oldest in the world - at least 2,000 years (may be traced to the Aksumite Kingdom, which coalesced in the first century B.C.)
National holiday
Derg Downfall Day (defeat of MENGISTU regime), 28 May (1991)
Constitution
history: several previous; latest drafted June 1994, adopted 8 December 1994, entered into force 21 August 1995
amendments: proposals submitted for discussion require two-thirds majority approval in either house of Parliament or majority approval of one-third of the State Councils; passage of amendments other than constitutional articles on fundamental rights and freedoms and the initiation and amendment of the constitution requires two-thirds majority vote in a joint session of Parliament and majority vote by two thirds of the State Councils; passage of amendments affecting rights and freedoms and amendment procedures requires two-thirds majority vote in each house of Parliament and majority vote by all the State Councils
Legal system
civil law system
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Ethiopia
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 4 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President SAHLE-WORK Zewde (since 25 October 2018) (2018)
head of government: Prime Minister ABIY Ahmed Ali (since April 2018, began a new five year term on 4 October 2021); Deputy Prime Minister DEMEKE Mekonnen Hassen (since 29 November 2012) (2021)
cabinet: Council of Ministers selected by the prime minister and approved by the House of People's Representatives
elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by both chambers of Parliament for a 6-year term (eligible for a second term); election held on 21 June 2021 and 30 September 2021 (the scheduled 29 August 2020 election was postponed by Prime Minister ABIY due to the COVID-19 pandemic); prime minister designated by the majority party following legislative elections
election results: SAHLE-WORK Zewde elected president during joint session of Parliament, vote - 659 (unanimous); ABIY Ahmed confirmed Prime Minister by House of Peoples' Representatives (4 October 2021)
note: SAHLE-WORK Zewde is the first female elected head of state in Ethiopia; she is currently the only female president in Africa. Former President Dr. Mulatu TESHOME resigned on 25 October 2018, one year ahead of finishing his six-year term.
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliament consists of:
House of Federation or Yefedereshein Mikir Bete (153 seats; members indirectly elected by state assemblies to serve 5-year terms)
House of People's Representatives or Yehizb Tewokayoch Mekir Bete (547 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote; 22 seats reserved for minorities; all members serve 5-year terms)
elections: House of Federation - last held 24 May 2015 (next originally scheduled on 29 August 2020 but postponed a year due to the COVID-19 pandemic)
House of People's Representatives - last held on 24 May 2015 (next election to be held June 2021)
election results: House of Federation - percent of vote by coalition/party - NA; seats by coalition/party - NA; composition - men 104, women 49, percent of women 32%
House of Representatives - percent of vote by coalition/party - NA; seats by coalition/party - EPRDF 501, SPDP 24, BGPDUP 9, ANDP 8, GPUDM 3, APDO 1, HNL 1; composition - men 335, women 212, percent of women 38.8%; note - total Parliament percent of women 37.3%
note: House of Federation is responsible for interpreting the constitution and federal-regional issues and the House of People's Representatives is responsible for passing legislation
Judicial branch
highest courts: Federal Supreme Court (consists of 11 judges); note - the House of Federation has jurisdiction for all constitutional issues
judge selection and term of office: president and vice president of Federal Supreme Court recommended by the prime minister and appointed by the House of People's Representatives; other Supreme Court judges nominated by the Federal Judicial Administrative Council (a 10-member body chaired by the president of the Federal Supreme Court) and appointed by the House of People's Representatives; judges serve until retirement at age 60
subordinate courts: federal high courts and federal courts of first instance; state court systems (mirror structure of federal system); sharia courts and customary and traditional courts
Political parties and leaders
Afar National Democratic Party or ANDP [Taha AHMED]
Argoba People Democratic Organization or APDO
Benishangul Gumuz People's Democratic Unity Party or BGPDUP
Ethiopian Federal Democratic Unity Forum or MEDREK or FORUM [Beyene PETROS] (includes ESD-SCUP, OFC, SLM, and UTDS)
Ethiopia Citizens for Social Justice or ECSJ Party (formed in May 2019 from 7 other parties, including Patriotic Genbot 7, Ethiopian Democratic Party (EDP), All Ethiopian Democratic Party (AEDP), Semayawi Party, New Generation Party, Gambella Regional Movement (GRM), Unity for Democracy and Justice (UDJ) Party [Berhanu Negu])
Prosperity Party or PP [ABIY Ahmed] (created in November 2019 from member parties of the former Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front or EPRDF, which included the Amhara National Democratic Movement (ANDM), Oromo People's Democratic Organization (OPDO), Southern Ethiopian People's Democratic Movement (SEPDM), plus other ERPRF allies
Ethiopian Social Democracy-Southern Coalition Unity Party or ESD-SCUP
Gambella Peoples Unity Democratic Movement or GPUDM
Harari National League or HNL [Murad ABDULHADI]
Oromo Fderalist Congress or OFC
Sidama Liberaton Movement or SLM
Somali People's Democratic Party or SPDP
Union of Tigraians for Democracy & Sovergnty or UTDS
Tigray People's Liberation Front or TPLF [DEBRETSION Gebremichael] (note: de-registered by Ethiopian electoral board in Jan 2021)
Tigray Independence Party [Girmay BERHE] (2020)
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, COMESA, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador FITSUM Arega Gebrekidan (since 9 April 2019)
chancery: 3506 International Drive NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 364-1200
FAX: [1] (202) 587-0195
email address and website:
ethiopia@ethiopianembassy.org
https://ethiopianembassy.org/
consulate(s) general: Los Angeles
consulate(s): New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Geeta PASI
embassy: Entoto Street, P.O. Box 1014, Addis Ababa
mailing address: 2030 Addis Ababa Place, Washington DC 20521-2030
telephone: [251] 111-30-60-00
FAX: [251] 111-24-24-01
email address and website:
AddisACS@state.gov
https://et.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of green (top), yellow, and red, with a yellow pentagram and single yellow rays emanating from the angles between the points on a light blue disk centered on the three bands; green represents hope and the fertility of the land, yellow symbolizes justice and harmony, while red stands for sacrifice and heroism in the defense of the land; the blue of the disk symbolizes peace and the pentagram represents the unity and equality of the nationalities and peoples of Ethiopia
note: Ethiopia is the oldest independent country in Africa, and the three main colors of her flag (adopted ca. 1895) were so often appropriated by other African countries upon independence that they became known as the Pan-African colors; the emblem in the center of the current flag was added in 1996
National symbol(s)
Abyssinian lion (traditional), yellow pentagram with five rays of light on a blue field (promoted by current government); national colors: green, yellow, red
National anthem
name: "Whedefit Gesgeshi Woud Enat Ethiopia" (March Forward, Dear Mother Ethiopia)
lyrics/music: DEREJE Melaku Mengesha/SOLOMON Lulu
note: adopted 1992
Economy
Economic overview
Ethiopia - the second most populous country in Africa - is a one-party state with a planned economy. For more than a decade before 2016, GDP grew at a rate between 8% and 11% annually – one of the fastest growing states among the 188 IMF member countries. This growth was driven by government investment in infrastructure, as well as sustained progress in the agricultural and service sectors. More than 70% of Ethiopia’s population is still employed in the agricultural sector, but services have surpassed agriculture as the principal source of GDP.
Ethiopia has the lowest level of income-inequality in Africa and one of the lowest in the world, with a Gini coefficient comparable to that of the Scandinavian countries. Yet despite progress toward eliminating extreme poverty, Ethiopia remains one of the poorest countries in the world, due both to rapid population growth and a low starting base. Changes in rainfall associated with world-wide weather patterns resulted in the worst drought in 30 years in 2015-16, creating food insecurity for millions of Ethiopians.
The state is heavily engaged in the economy. Ongoing infrastructure projects include power production and distribution, roads, rails, airports and industrial parks. Key sectors are state-owned, including telecommunications, banking and insurance, and power distribution. Under Ethiopia's constitution, the state owns all land and provides long-term leases to tenants. Title rights in urban areas, particularly Addis Ababa, are poorly regulated, and subject to corruption.
Ethiopia’s foreign exchange earnings are led by the services sector - primarily the state-run Ethiopian Airlines - followed by exports of several commodities. While coffee remains the largest foreign exchange earner, Ethiopia is diversifying exports, and commodities such as gold, sesame, khat, livestock and horticulture products are becoming increasingly important. Manufacturing represented less than 8% of total exports in 2016, but manufacturing exports should increase in future years due to a growing international presence.
The banking, insurance, telecommunications, and micro-credit industries are restricted to domestic investors, but Ethiopia has attracted roughly $8.5 billion in foreign direct investment (FDI), mostly from China, Turkey, India and the EU; US FDI is $567 million. Investment has been primarily in infrastructure, construction, agriculture/horticulture, agricultural processing, textiles, leather and leather products.
To support industrialization in sectors where Ethiopia has a comparative advantage, such as textiles and garments, leather goods, and processed agricultural products, Ethiopia plans to increase installed power generation capacity by 8,320 MW, up from a capacity of 2,000 MW, by building three more major dams and expanding to other sources of renewable energy. In 2017, the government devalued the birr by 15% to increase exports and alleviate a chronic foreign currency shortage in the country.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$264.05 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$248.97 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$229.76 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
10.9% (2017 est.)
8% (2016 est.)
10.4% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$2,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$2,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$2,100 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$92.154 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
15.7% (2019 est.)
13.9% (2018 est.)
10.8% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: B (2014)
Moody's rating: B2 (2020)
Standard & Poors rating: B (2014)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 34.8% (2017 est.)
industry: 21.6% (2017 est.)
services: 43.6% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 69.6% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 10% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 43.5% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: -0.1% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 8.1% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -31.2% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
maize, cereals, wheat, sorghum, milk, barley, sweet potatoes, roots/tubers nes, sugar cane, millet
Industries
food processing, beverages, textiles, leather, garments, chemicals, metals processing, cement
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 72.7%
industry: 7.4%
services: 19.9% (2013 est.)
Population below poverty line
23.5% (2015 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
35 (2015 est.)
30 (2000)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 4.1%
highest 10%: 25.6% (2005)
Budget
revenues: 11.24 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 13.79 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
8 July - 7 July
Current account balance
-$6.551 billion (2017 est.)
-$6.574 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$7.62 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$2.814 billion (2016 est.)
Exports - partners
China 17%, United States 16%, United Arab Emirates 8%, Saudi Arabia 6%, South Korea 5%, Germany 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
coffee, sesame seeds, gold, cut flowers, zinc (2019)
Imports
$19.93 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$14.69 billion (2016 est.)
Imports - partners
China 27%, India 9%, United Arab Emirates 9%, France 9%, United Kingdom 7% (2019)
Imports - commodities
aircraft, gas turbines, packaged medicines, electric filament, cars (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$3.013 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$3.022 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$27.27 billion (2019 est.)
$26.269 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
birr (ETB) per US dollar -
25 (2017 est.)
21.732 (2016 est.)
21.732 (2015 est.)
21.55 (2014 est.)
19.8 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 3.5%
male: 2.7%
female: 4.5% (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 47% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 96% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 34% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
2.784 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99Electricity - from fossil fuels
3% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 207Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
86% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11Electricity - from other renewable sources
11% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75Refined petroleum products - consumption
74,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89Natural gas - proved reserves
24.92 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 1.14 million (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1.04 (2018 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 39.54 million (2018)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 37.22 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: telecom market challenged by political factionalism and reorganization of ruling party; despite some gains in access, Ethiopia remains one of the least-connected countries in the world; state-owned telecom held a monopoly over services until 2019 when government approved legislation and opened the market to competition and foreign investment; new expansion of LTE services; government reduced tariffs leading to increases in data and voice traffic; government launched mobile app as part of e-government initiative to build smart city; Huawei provides infrastructure to government operator and built data center in Addis Ababa; government disrupted service during political crises; importer of broadcasting equipment from China (2020)
domestic: fixed-line subscriptions at 1 per 100 while mobile-cellular stands at 36 per 100; the number of mobile telephones is increasing steadily (2019)
international: country code - 251; open-wire to Sudan and Djibouti; microwave radio relay to Kenya and Djibouti; 2 domestic satellites provide the national trunk service; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Pacific Ocean) (2016)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
6 public TV stations broadcasting nationally and 10 public radio broadcasters; 7 private radio stations and 19 community radio stations (2017)
Internet users
total: 23.96 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 18.62% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 62,950 (2017 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2017 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 75
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 11,501,244 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 2,089,280,000 mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 17
over 3,047 m: 3
2,438 to 3,047 m: 8
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
under 914 m: 2 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 40
2,438 to 3,047 m: 3
1,524 to 2,437 m: 9
914 to 1,523 m: 20
under 914 m: 8 (2013)
Railways
total: 659 km (Ethiopian segment of the 756 km Addis Ababa-Djibouti railroad) (2017)
standard gauge: 659 km 1.435-m gauge (2017)
note: electric railway with redundant power supplies; under joint control of Djibouti and Ethiopia and managed by a Chinese contractor
Merchant marine
total: 11
by type: general cargo 9, oil tanker 2 (2020)
Ports and terminals
Ethiopia is landlocked and uses the ports of Djibouti in Djibouti and Berbera in Somalia
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Ethiopian National Defense Force (ENDF): Ground Forces, Ethiopian Air Force (Ye Ityopya Ayer Hayl, ETAF) (2021)
note(s) - in January 2020 the Ethiopian Government announced it had re-established a navy, which was disbanded in 1996; in March 2019 Ethiopia signed a defense cooperation agreement with France which stipulated that France would support the establishment of an Ethiopian navy, which will reportedly be based out of Djibouti
in 2018, Ethiopia established a Republican Guard for protecting senior officials; the Republican Guard is a military unit accountable to the Prime Minister
Military expenditures
0.5% of GDP (2020 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2019 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2018 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2017 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2016 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; prior to the 2020-21 Tigray conflict, approximately 150,000 active duty troops, including about 3,000 Air Force personnel (no personnel numbers available for the newly-established Navy) (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the ENDF's inventory is comprised mostly of Soviet-era equipment from the 1970s; since 2010, Russia and Ukraine are the leading suppliers of largely second-hand weapons and equipment to the ENDF; Ethiopia has a modest industrial defense base centered on small arms and production of armored vehicles (2020)
Military deployments
prior to the 2020-21 Tigray conflict, up to 10,000 Somalia (4,500 for AMISOM; the remainder under a bilateral agreement with Somalia); 3,300 Sudan (UNISFA); 1,500 South Sudan (UNMISS) (2021)
note - in August 2021, Sudan asked the UN to remove the Ethiopian troops from the UNISFA mission
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service; no compulsory military service, but the military can conduct callups when necessary and compliance is compulsory (2021)
note - in November 2021, the Ethiopian Government issued a nationwide state of emergency that enabled officials to order military-age citizens to undergo training and accept military duty in support of the Tigray conflict
Military - note
each of the nine states has a regional and/or a "special" paramilitary security forces that report to regional civilian authorities; local militias operate across the country in loose and varying coordination with these regional security and police forces, the Ethiopian Federal Police (EFP), and the Ethiopian military; the EFP reports to the Ministry of Peace, which was created in October of 2018
since November 2020, the Government of Ethiopia has been engaged in a protracted military conflict with the Tigrayan People’s Liberation Front (TPLF), the former governing party of the Tigray Region; the government deemed a TPLF attack on Ethiopia military forces as a domestic terrorism incident and launched a military/law enforcement offensive in response; the TPLF asserted that its actions were self-defense in the face of planned Ethiopian Government action to remove it from the provincial government; the Ethiopian Government sent large elements of the ENDF into Tigray to remove the TPLF and invited militia and paramilitary forces from the states of Afar and Amara, as well as the military forces of Eritrea, to assist; fighting continued through 2021 with heavy civilian and military casualties and widespread human rights abuses reported
the military forces of the Tigray regional government are known as the Tigray Defense Force (TDF); the TDF is comprised of state paramilitary forces, local militia, and troops that defected from the ENDF; it reportedly had up to 250,000 fighters at the start of the conflict; in August 2021, the TPLF struck an alliance with the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA)
as of 2021, the Ethiopian military consisted of approximately 22 Army divisions (approximately 14 light infantry, 6 mechanized, and 1 commando/special operations), while the Air Force had 2 fighter/ground attack and 2 mixed attack/transport helicopter squadrons
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
al-Shabaab; IRGC/Qods Force
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Eritrea and Ethiopia agreed to abide by the 2002 Eritrea-Ethiopia Boundary Commission's (EEBC) delimitation decision, but neither party responded to the revised line detailed in the November 2006 EEBC Demarcation Statement; the undemarcated former British administrative line has little meaning as a political separation to rival clans within Ethiopia's Ogaden and southern Somalia's Oromo region; Ethiopian forces invaded southern Somalia and routed Islamist courts from Mogadishu in January 2007; "Somaliland" secessionists provide port facilities in Berbera and trade ties to landlocked Ethiopia; civil unrest in eastern Sudan has hampered efforts to demarcate the porous boundary with Ethiopia; Ethiopia's construction of a large dam (the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam) on the Blue Nile since 2011 has become a focal point of relations with Egypt and Sudan; as of 2020, four years of three-way talks between the three capitals over operating the dam and filling its reservoir had made little progress; Ethiopia began filling the dam in July 2020
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 383,084 (South Sudan), 218,022 (Somalia), 158,300 (Eritrea), 46,181 (Sudan) (2021)
IDPs: 1,990,168 (includes conflict- and climate-induced IDPs, excluding unverified estimates from the Amhara region; border war with Eritrea from 1998-2000; ethnic clashes; and ongoing fighting between the Ethiopian military and separatist rebel groups in the Somali and Oromia regions; natural disasters; intercommunal violence; most IDPs live in Sumale state) (2021)
Illicit drugs
transit hub for heroin originating in Southwest and Southeast Asia and destined for Europe, as well as cocaine destined for markets in southern Africa; cultivates qat (khat) for local use and regional export, principally to Djibouti and Somalia (legal in all three countries); the lack of a well-developed financial system limits the country's utility as a money laundering center