Costa Rica
Introduction
Background
Although explored by the Spanish early in the 16th century, initial attempts at colonizing Costa Rica proved unsuccessful due to a combination of factors, including disease from mosquito-infested swamps, brutal heat, resistance by natives, and pirate raids. It was not until 1563 that a permanent settlement of Cartago was established in the cooler, fertile central highlands. The area remained a colony for some two and a half centuries. In 1821, Costa Rica became one of several Central American provinces that jointly declared their independence from Spain. Two years later it joined the United Provinces of Central America, but this federation disintegrated in 1838, at which time Costa Rica proclaimed its sovereignty and independence. Since the late 19th century, only two brief periods of violence have marred the country's democratic development. On 1 December 1948, Costa Rica dissolved its armed forces. Although it still maintains a large agricultural sector, Costa Rica has expanded its economy to include strong technology and tourism industries. The standard of living is relatively high. Land ownership is widespread.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Nicaragua and Panama
Geographic coordinates
10 00 N, 84 00 W
Map references
Central America and the Caribbean
Area
total: 51,100 sq km
land: 51,060 sq km
water: 40 sq km
note: includes Isla del Coco
Land boundaries
total: 661 km
border countries (2): Nicaragua 313 km, Panama 348 km
Coastline
1,290 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm
Climate
tropical and subtropical; dry season (December to April); rainy season (May to November); cooler in highlands
Terrain
coastal plains separated by rugged mountains including over 100 volcanic cones, of which several are major active volcanoes
Elevation
highest point: Cerro Chirripo 3,819 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 746 m
Natural resources
hydropower
Land use
agricultural land: 37.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 4.9% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 6.7% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 25.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 51.5% (2018 est.)
other: 11.4% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
1,015 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
roughly half of the nation's population resides in urban areas; the capital of San Jose is the largest city and home to approximately one-fifth of the population
Natural hazards
occasional earthquakes, hurricanes along Atlantic coast; frequent flooding of lowlands at onset of rainy season and landslides; active volcanoes
volcanism: Arenal (1,670 m), which erupted in 2010, is the most active volcano in Costa Rica; a 1968 eruption destroyed the town of Tabacon; Irazu (3,432 m), situated just east of San Jose, has the potential to spew ash over the capital city as it did between 1963 and 1965; other historically active volcanoes include Miravalles, Poas, Rincon de la Vieja, and Turrialba
Geography - note
four volcanoes, two of them active, rise near the capital of San Jose in the center of the country; one of the volcanoes, Irazu, erupted destructively in 1963-65
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Costa Rican(s)
adjective: Costa Rican
Ethnic groups
White or Mestizo 83.6%, Mulatto 6.7%, Indigenous 2.4%, Black or African descent 1.1%, other 1.1%, none 2.9%, unspecified 2.2% (2011 est.)
Languages
Spanish (official), English
major-language sample(s):
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Roman Catholic 71.8%, Evangelical and Pentecostal 12.3%, other Protestant 2.6%, Jehovah's Witness 0.5%, other 2.4%, none 10.4% (2016 est.)
Demographic profile
Costa Rica's political stability, high standard of living, and well-developed social benefits system set it apart from its Central American neighbors. Through the government's sustained social spending - almost 20% of GDP annually - Costa Rica has made tremendous progress toward achieving its goal of providing universal access to education, healthcare, clean water, sanitation, and electricity. Since the 1970s, expansion of these services has led to a rapid decline in infant mortality, an increase in life expectancy at birth, and a sharp decrease in the birth rate. The average number of children born per women has fallen from about 7 in the 1960s to 3.5 in the early 1980s to below replacement level today. Costa Rica's poverty rate is lower than in most Latin American countries, but it has stalled at around 20% for almost two decades.
Costa Rica is a popular regional immigration destination because of its job opportunities and social programs. Almost 9% of the population is foreign-born, with Nicaraguans comprising nearly three-quarters of the foreign population. Many Nicaraguans who perform unskilled seasonal labor enter Costa Rica illegally or overstay their visas, which continues to be a source of tension. Less than 3% of Costa Rica's population lives abroad. The overwhelming majority of expatriates have settled in the United States after completing a university degree or in order to work in a highly skilled field.
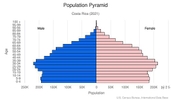
Age structure
0-14 years: 22.08% (male 575,731/female 549,802)
15-24 years: 15.19% (male 395,202/female 379,277)
25-54 years: 43.98% (male 1,130,387/female 1,111,791)
55-64 years: 9.99% (male 247,267/female 261,847)
65 years and over: 8.76% (male 205,463/female 241,221) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 45.1
youth dependency ratio: 30.2
elderly dependency ratio: 14.9
potential support ratio: 6.7 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 32.6 years
male: 32.1 years
female: 33.1 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
roughly half of the nation's population resides in urban areas; the capital of San Jose is the largest city and home to approximately one-fifth of the population
Urbanization
urban population: 81.4% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.5% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.421 million SAN JOSE (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.94 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
27 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116Infant mortality rate
total: 8.59 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 9.66 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 7.46 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 79.41 years
male: 76.75 years
female: 82.22 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
70.9% (2018)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
7.6% (2018)
Physicians density
2.89 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
Hospital bed density
1.1 beds/1,000 population (2019)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 98.4% of population
rural: 95.8% of population
total: 97.8% of population
unimproved: urban: 1.6% of population
rural: 4.2% of population
total: 2.2% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<500 (2020 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: intermediate (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 97.9%
male: 97.8%
female: 97.9% (2018)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 17 years
male: 16 years
female: 17 years (2019)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 40.7%
male: 34%
female: 50.9% (2020 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation and land use change, largely a result of the clearing of land for cattle ranching and agriculture; soil erosion; coastal marine pollution; fisheries protection; solid waste management; air pollution
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Marine Life Conservation
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 15.85 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 8.02 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 5.61 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical and subtropical; dry season (December to April); rainy season (May to November); cooler in highlands
Land use
agricultural land: 37.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 4.9% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 6.7% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 25.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 51.5% (2018 est.)
other: 11.4% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 81.4% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.5% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.82% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: intermediate (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1.46 million tons (2014 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 18,396 tons (2014 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 1.3% (2014 est.)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 652 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 240 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 2.302 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
113 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Costa Rica
conventional short form: Costa Rica
local long form: Republica de Costa Rica
local short form: Costa Rica
etymology: the name means "rich coast" in Spanish and was first applied in the early colonial period of the 16th century
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: San Jose
geographic coordinates: 9 56 N, 84 05 W
time difference: UTC-6 (1 hour behind Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: named in honor of Saint Joseph
Administrative divisions
7 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia); Alajuela, Cartago, Guanacaste, Heredia, Limon, Puntarenas, San Jose
Independence
15 September 1821 (from Spain)
National holiday
Independence Day, 15 September (1821)
Constitution
history: many previous; latest effective 8 November 1949
amendments: proposals require the signatures of at least 10 Legislative Assembly members or petition of at least 5% of qualified voters; consideration of proposals requires two-thirds majority approval in each of three readings by the Assembly, followed by preparation of the proposal as a legislative bill and its approval by simple majority of the Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly membership; a referendum is required only if approved by at least two thirds of the Assembly; amended many times, last in 2020
Legal system
civil law system based on Spanish civil code; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
Executive branch
chief of state: President Carlos ALVARADO Quesada (since 8 May 2018); First Vice President Epsy CAMPBELL Barr (since 8 May 2018); Second Vice President Marvin RODRIGUEZ Cordero (since 8 May 2018); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Carlos ALVARADO Quesada (since 8 May 2018); First Vice President Epsy CAMPBELL Barr (since 8 May 2018); Second Vice President Marvin RODRIGUEZ Cordero (since 8 May 2018)
cabinet: Cabinet selected by the president
elections/appointments: president and vice presidents directly elected on the same ballot by modified majority popular vote (40% threshold) for a 4-year term (eligible for non-consecutive terms); election last held on 4 February 2018 with a runoff on 1 April 2018 (next to be held on 6 February 2022)
election results:
2018: Carlos ALVARADO Quesada elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Fabricio ALVARADO Munoz (PRN) 25%; Carlos ALVARADO Quesada (PAC) 21.6%; Antonio ALVAREZ (PLN) 18.6%; Rodolfo PIZA (PUSC) 16%; Juan Diego CASTRO (PIN) 9.5%; Rodolfo HERNANDEZ (PRS) 4.9%, other 4.4%; percent of vote in second round - Carlos ALVARADO Quesada (PAC) 60.7%; Fabricio ALVARADO Munoz (PRN) 39.3%
2014: Luis Guillermo SOLIS Rivera elected president; percent of vote - Luis Guillermo SOLIS Rivera (PAC) 77.8%; Johnny ARAYA (PLN) 22.2%
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Legislative Assembly or Asamblea Legislativa (57 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies - corresponding to the country's 7 provinces - by closed party-list proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 4 February 2018 (next to be held on 6 February 2022)
election results: percent of vote by party - PLN 19.5%, PRN 18.2%, PAC 16.3%, PUSC 14.6%, PIN 7.7%, PRS 4.2%, PFA 4%, ADC 2.5%, ML 2.3%, PASE 2.3%, PNG 2.2%, other 6.2%; seats by party - PLN 17, PRN 14, PAC 10, PUSC 9, PIN 4, PRS 2, PFA 1; composition - men 31, women 26, percent of women 45.6%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court of Justice (consists of 22 judges organized into 3 cassation chambers each with 5 judges and the Constitutional Chamber with 7 judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court of Justice judges elected by the National Assembly for 8-year terms with renewal decided by the National Assembly
subordinate courts: appellate courts; trial courts; first instance and justice of the peace courts; Superior Electoral Tribunal
Political parties and leaders
Accessibility Without Exclusion or PASE [Oscar Andres LOPEZ Arias]
Broad Front (Frente Amplio) or PFA [Ana Patricia MORA Castellanos]
Christian Democratic Alliance or ADC [Mario REDONDO Poveda]
Citizen Action Party or PAC [Marta Eugenia SOLANO Arias]
Costa Rican Renewal Party or PRC [Justo OROZCO Alvarez]
Libertarian Movement Party or ML [Victor Danilo CUBERO Corrales]
National Integration Party or PIN [Walter MUNOZ Cespedes]
National Liberation Party or PLN [Jorge Julio PATTONI Saenz]
National Restoration Party or PRN [Carlos Luis AVENDANO Calvo]
New Generation or PNG [Sergio MENA]
Patriotic Alliance [Jorge ARAYA Westover]
Social Christian Republican Party or PRS [Dragos DOLANESCU Valenciano]
Social Christian Unity Party or PUSC [Pedro MUNOZ Fonseca]
International organization participation
BCIE, CACM, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA (observer), MIGA, NAM (observer), OAS, OIF (observer), OPANAL, OPCW, Pacific Alliance (observer), PCA, SICA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Fernando LLORCA Castro (since 17 September 2018)
chancery: 2114 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 499-2984
FAX: [1] (202) 265-4795
email address and website:
embcr-us@rree.go.cr
http://www.costarica-embassy.org/index.php?q=node/21
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, Washington DC
honorary consulate(s): San Juan (Puerto Rico), Saint Paul (MN), Tucson (AZ)
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Gloria BERBENA (since January 2021)
embassy: Calle 98 Via 104, Pavas, San Jose
mailing address: 3180 St. George's Place, Washington DC 20521-3180
telephone: [506] 2519-2000
FAX: [506] 2519-2305
email address and website:
acssanjose@state.gov
https://cr.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
five horizontal bands of blue (top), white, red (double width), white, and blue, with the coat of arms in a white elliptical disk placed toward the hoist side of the red band; Costa Rica retained the earlier blue-white-blue flag of Central America until 1848 when, in response to revolutionary activity in Europe, it was decided to incorporate the French colors into the national flag and a central red stripe was added; today the blue color is said to stand for the sky, opportunity, and perseverance, white denotes peace, happiness, and wisdom, while red represents the blood shed for freedom, as well as the generosity and vibrancy of the people
note: somewhat resembles the flag of North Korea; similar to the flag of Thailand but with the blue and red colors reversed
National symbol(s)
yiguirro (clay-colored robin); national colors: blue, white, red
National anthem
name: "Himno Nacional de Costa Rica" (National Anthem of Costa Rica)
lyrics/music: Jose Maria ZELEDON Brenes/Manuel Maria GUTIERREZ
note: adopted 1949; the anthem's music was originally written for an 1853 welcome ceremony for diplomatic missions from the US and UK; the lyrics were added in 1903
Economy
Economic overview
Since 2010, Costa Rica has enjoyed strong and stable economic growth - 3.8% in 2017. Exports of bananas, coffee, sugar, and beef are the backbone of its commodity exports. Various industrial and processed agricultural products have broadened exports in recent years, as have high value-added goods, including medical devices. Costa Rica's impressive biodiversity also makes it a key destination for ecotourism.
Foreign investors remain attracted by the country's political stability and relatively high education levels, as well as the incentives offered in the free-trade zones; Costa Rica has attracted one of the highest levels of foreign direct investment per capita in Latin America. The US-Central American-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR), which became effective for Costa Rica in 2009, helped increase foreign direct investment in key sectors of the economy, including insurance and telecommunication. However, poor infrastructure, high energy costs, a complex bureaucracy, weak investor protection, and uncertainty of contract enforcement impede greater investment.
Costa Rica’s economy also faces challenges due to a rising fiscal deficit, rising public debt, and relatively low levels of domestic revenue. Poverty has remained around 20-25% for nearly 20 years, and the government’s strong social safety net has eroded due to increased constraints on its expenditures. Costa Rica’s credit rating was downgraded from stable to negative in 2015 and again in 2017, upping pressure on lending rates - which could hurt small business, on the budget deficit - which could hurt infrastructure development, and on the rate of return on investment - which could soften foreign direct investment (FDI). Unlike the rest of Central America, Costa Rica is not highly dependent on remittances - which represented just 1 % of GDP in 2016, but instead relies on FDI - which accounted for 5.1% of GDP.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$100.25 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$105.02 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$102.79 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
3.3% (2017 est.)
4.2% (2016 est.)
3.6% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$19,700 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$20,800 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$20,600 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$61.855 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2% (2019 est.)
2.2% (2018 est.)
1.6% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: B (2020)
Moody's rating: B2 (2020)
Standard & Poors rating: B (2020)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 5.5% (2017 est.)
industry: 20.6% (2017 est.)
services: 73.9% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 64.2% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 17.3% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 17.1% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 1% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 33.3% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -32.9% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
sugar cane, pineapples, bananas, milk, oil palm fruit, fruit, oranges, watermelons, cassava, rice
Industries
medical equipment, food processing, textiles and clothing, construction materials, fertilizer, plastic products
Labor force
1.843 million (2020 est.)
note: official estimate; excludes Nicaraguans living in Costa Rica
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 14%
industry: 22%
services: 64% (2006 est.)
Population below poverty line
21% (2019 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
48 (2018 est.)
49.2 (2013)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 1.5%
highest 10%: 36.9% (2014 est.)
Budget
revenues: 8.357 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 11.92 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$1.692 billion (2017 est.)
-$1.326 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$21.2 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$20.53 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
United States 38%, Netherlands 6%, Belgium 5%, Guatemala 5%, Panama 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
medical instruments, bananas, tropical fruits, orthopedic appliances, food preparations (2019)
Imports
$19.39 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$19.64 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
United States 41%, China 13%, Mexico 7% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, cars, medical instruments, packaged medicines (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$7.15 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$7.574 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$29.589 billion (2019 est.)
$28.553 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
Costa Rican colones (CRC) per US dollar -
573.5 (2017 est.)
544.74 (2016 est.)
544.74 (2015 est.)
534.57 (2014 est.)
538.32 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 40.7%
male: 34%
female: 50.9% (2020 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
3.584 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94Electricity - from fossil fuels
18% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
64% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25Electricity - from other renewable sources
18% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47Refined petroleum products - consumption
53,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 559,882 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 10.99 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 7,512,370 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 147.5 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Costa Rica has broad telecom coverage though geographical distribution of digital service is unequal; recent regulator liberalization spurred expansion in all sectors; broadband market is the most advanced and highest penetration in Central America yet lags behind many South American countries; operators investing in NGN technology; number portability and cheaper broadband costs will increase competition; government aims to subsidize tele-health and e-learning (2018)
domestic: 13 per 100 fixed-line, 162 per 100 mobile-cellular; point-to-point and point-to-multi-point microwave, fiber-optic, and coaxial cable link rural areas; Internet service is available (2019)
international: country code - 506; landing points for the ARCOS-1, MAYA-1, and the PAC submarine cables that provide links to South and Central America, parts of the Caribbean, and the US; connected to Central American Microwave System; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
multiple privately owned TV stations and 1 publicly owned TV station; cable network services are widely available; more than 100 privately owned radio stations and a public radio network (2017)
Internet users
total: 4.15 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 80.53% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 992,725 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 19.49 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 39
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 1,948,546 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 11.13 million mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 47
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 27
under 914 m: 16 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 114
914 to 1,523 m: 18
under 914 m: 96 (2013)
Pipelines
662 km refined products (2013)
Railways
total: 278 km (2014)
narrow gauge: 278 km 1.067-m gauge (2014)
note: the entire rail network fell into disrepair and out of use at the end of the 20th century; since 2005, certain sections of rail have been rehabilitated
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Atlantic Ocean (Caribbean) - Puerto Limon
Pacific Ocean - Caldera
Military and Security
Military and security forces
no regular military forces; Ministry of Public Security: the Public Force (Fuerza Pública (National Police)), Air Surveillance Service (Servicio de Vigilancia Aérea), and National Coast Guard Service (Servicio Nacional de Guardacostas) (2021)
note - Costa Rica's armed forces were constitutionally abolished in 1949
Military expenditures
0.7% of GDP (2020)
0.7% of GDP (2019)
0.7% of GDP (2018)
0.7% of GDP (2017)
0.7% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
12,500 Public Force personnel; approximately 400-500 air and 400-500 coast guard personnel (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Public Force is lightly armed with an inventory that includes mostly second-hand US equipment, including light helicopters and second-hand coast guard cutters (2021)
Military - note
Costa Rica relies on specialized paramilitary units within the MPS for internal security missions and countering transnational threats such as narcotics smuggling and organized crime, as well as for participating in regional security operations and exercises; MPS forces have received advisory and training support from both Colombia and the US; since 2012, the US has also provided equipment, including aircraft and patrol boats (2021)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Costa Rica and Nicaragua regularly file border dispute cases over the delimitations of the San Juan River and the northern tip of Calero Island to the International Court of Justice (ICJ); in 2009, the ICJ ruled that Costa Rican vessels carrying out police activities could not use the river, but official Costa Rican vessels providing essential services to riverside inhabitants and Costa Rican tourists could travel freely on the river; in 2011, the ICJ provisionally ruled that both countries must remove personnel from the disputed area; in 2013, the ICJ rejected Nicaragua's 2012 suit to halt Costa Rica's construction of a highway paralleling the river on the grounds of irreparable environmental damage; in 2013, the ICJ, regarding the disputed territory, ordered that Nicaragua should refrain from dredging or canal construction and refill and repair damage caused by trenches connecting the river to the Caribbean and upheld its 2010 ruling that Nicaragua must remove all personnel; in early 2014, Costa Rica brought Nicaragua to the ICJ over offshore oil concessions in the disputed region
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 29,906 (Venezuela) (economic and political crisis; includes Venezuelans who have claimed asylum, are recognized as refugees, or received alternative legal stay) (2021)
stateless persons: 199 (2020)
Illicit drugs
significant transit country for drugs entering the United States; a growing drug consumption problem; drugs warehoused in Costa Rica end up in the local market where criminal organizations use cocaine as payment for services.