Cameroon
Introduction
Background
Much of the area of present-day Cameroon was ruled by powerful chiefdoms before becoming a German colony in 1884 known as Kamerun. After World War I, the territory was divided between France and the UK as League of Nations mandates. French Cameroon became independent in 1960 as the Republic of Cameroon. The following year the southern portion of neighboring British Cameroon voted to merge with the new country to form the Federal Republic of Cameroon. In 1972, a new constitution replaced the federation with a unitary state, the United Republic of Cameroon. The country has generally enjoyed stability, which has enabled the development of agriculture, roads, and railways, as well as a petroleum industry. Despite slow movement toward democratic reform, political power remains firmly in the hands of President Paul BIYA.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
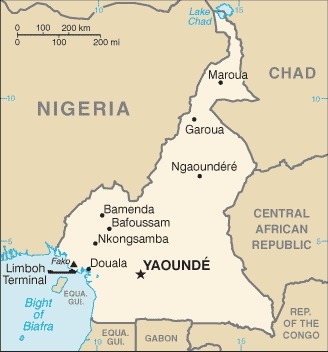
Central Africa, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Equatorial Guinea and Nigeria
Geographic coordinates
6 00 N, 12 00 E
Map references
Africa
Land boundaries
total: 5,018 km
border countries (6): Central African Republic 901 km, Chad 1116 km, Republic of the Congo 494 km, Equatorial Guinea 183 km, Gabon 349 km, Nigeria 1975 km
Coastline
402 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
Climate
varies with terrain, from tropical along coast to semiarid and hot in north
Terrain
diverse, with coastal plain in southwest, dissected plateau in center, mountains in west, plains in north
Elevation
highest point: Fako on Mont Cameroun 4,045 m
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 667 m
Natural resources
petroleum, bauxite, iron ore, timber, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land: 20.6% (2018 est.)
arable land: 13.1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 3.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 4.2% (2018 est.)
forest: 41.7% (2018 est.)
other: 37.7% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
290 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Congo (3,730,881 sq km), Niger (2,261,741 sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Lake Chad (2,497,738 sq km)
Major aquifers
Lake Chad Basin
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Chad (endorheic lake shared with Niger, Nigeria, and Chad) - 10,360-25,900 sq km
note - area varies by season and year to year
Population distribution
population concentrated in the west and north, with the interior of the country sparsely populated as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards
volcanic activity with periodic releases of poisonous gases from Lake Nyos and Lake Monoun volcanoes
volcanism: Mt. Cameroon (4,095 m), which last erupted in 2000, is the most frequently active volcano in West Africa; lakes in Oku volcanic field have released fatal levels of gas on occasion, killing some 1,700 people in 1986
Geography - note
sometimes referred to as the hinge of Africa because of its central location on the continent and its position at the west-south juncture of the Gulf of Guinea; throughout the country there are areas of thermal springs and indications of current or prior volcanic activity; Mount Cameroon, the highest mountain in Sub-Saharan west Africa, is an active volcano
People and Society
Population
28,524,175 (July 2021 est.)
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
Nationality
noun: Cameroonian(s)
adjective: Cameroonian
Ethnic groups
Bamileke-Bamu 24.3%, Beti/Bassa, Mbam 21.6%, Biu-Mandara 14.6%, Arab-Choa/Hausa/Kanuri 11%, Adamawa-Ubangi, 9.8%, Grassfields 7.7%, Kako, Meka/Pygmy 3.3%, Cotier/Ngoe/Oroko 2.7%, Southwestern Bantu 0.7%, foreign/other ethnic group 4.5% (2018 est.)
Languages
24 major African language groups, English (official), French (official)
major-language sample(s):
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information. (English)
The World Factbook, une source indispensable d'informations de base. (French)
Religions
Roman Catholic 38.3%, Protestant 25.5%, other Christian 6.9%, Muslim 24.4%, animist 2.2%, other 0.5%, none 2.2% (2018 est.)
Demographic profile
Cameroon has a large youth population, with more than 60% of the populace under the age of 25. Fertility is falling but remains at a high level, especially among poor, rural, and uneducated women, in part because of inadequate access to contraception. Life expectancy remains low at about 55 years due to the prevalence of HIV and AIDs and an elevated maternal mortality rate, which has remained high since 1990. Cameroon, particularly the northern region, is vulnerable to food insecurity largely because of government mismanagement, corruption, high production costs, inadequate infrastructure, and natural disasters. Despite economic growth in some regions, poverty is on the rise, and is most prevalent in rural areas, which are especially affected by a shortage of jobs, declining incomes, poor school and health care infrastructure, and a lack of clean water and sanitation. Underinvestment in social safety nets and ineffective public financial management also contribute to Cameroon’s high rate of poverty. The activities of Boko Haram, other armed groups, and counterinsurgency operations have worsened food insecurity in the Far North region.
International migration has been driven by unemployment (including fewer government jobs), poverty, the search for educational opportunities, and corruption. The US and Europe are preferred destinations, but, with tighter immigration restrictions in these countries, young Cameroonians are increasingly turning to neighboring states, such as Gabon and Nigeria, South Africa, other parts of Africa, and the Near and Far East. Cameroon’s limited resources make it dependent on UN support to host more than 420,000 refugees and asylum seekers as of September 2020. These refugees and asylum seekers are primarily from the Central African Republic and Nigeria. Internal and external displacement have grown dramatically in recent years. Boko Haram's attacks and counterattacks by government forces in the Far North since 2014 have increased the number of internally displaced people. Armed conflict between separatists and Cameroon's military in the the Northwest and Southwest since 2016 have displaced hundreds of thousands of the country's Anglophone minority.
Age structure
0-14 years: 42.34% (male 5,927,640/female 5,820,226)
15-24 years: 20.04% (male 2,782,376/female 2,776,873)
25-54 years: 30.64% (male 4,191,151/female 4,309,483)
55-64 years: 3.87% (male 520,771/female 552,801)
65 years and over: 3.11% (male 403,420/female 460,248) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 81.1
youth dependency ratio: 76.2
elderly dependency ratio: 4.9
potential support ratio: 20.3 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 18.5 years
male: 18.2 years
female: 18.8 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
population concentrated in the west and north, with the interior of the country sparsely populated as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization
urban population: 58.1% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.43% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
4.164 million YAOUNDE (capital), 3.793 million Douala (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.94 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.88 male(s)/female
total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
20.1 years (2018 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-49
Maternal mortality ratio
529 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18Infant mortality rate
total: 50.09 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 55.01 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 45.02 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 62.79 years
male: 61.07 years
female: 64.57 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
19.3% (2018)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 94% of population
rural: 54.6% of population
total: 76.5% of population
unimproved: urban: 6% of population
rural: 45.3% of population
total: 23.5% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
3.5% (2018)
Physicians density
0.09 physicians/1,000 population (2011)
Hospital bed density
1.3 beds/1,000 population
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 83.3% of population
rural: 25.6% of population
total: 57.7% of population
unimproved: urban: 16.7% of population
rural: 74.4% of population
total: 42.3% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 77.1%
male: 82.6%
female: 71.6% (2018)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 12 years
male: 13 years
female: 11 years (2016)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 6.3%
male: 5.8%
female: 6.8% (2014 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
waterborne diseases are prevalent; deforestation and overgrazing result in erosion, desertification, and reduced quality of pastureland; poaching; overfishing; overhunting
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Nuclear Test Ban
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 65.26 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 8.29 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 30.71 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
varies with terrain, from tropical along coast to semiarid and hot in north
Land use
agricultural land: 20.6% (2018 est.)
arable land: 13.1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 3.3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 4.2% (2018 est.)
forest: 41.7% (2018 est.)
other: 37.7% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 58.1% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.43% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 2.5% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
Food insecurity
severe localized food insecurity: due to civil insecurity and population displacements - according to a March 2021 analysis, about 1.9 million people (7 percent of the total population) were projected to be severely food insecure in the June‑August 2021 period; this mainly results from the effects of Boko Haram incursions in the Far North Region, the socio‑political unrest in the Northwest and Southwest regions and COVID‑19 related economic shocks, which disrupted trade flows and agricultural practices, deteriorated livelihoods and displaced people (2021)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 3,270,617 tons (2013 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 13,082 tons (2009 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 0.4% (2009 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Chad (endorheic lake shared with Niger, Nigeria, and Chad) - 10,360-25,900 sq km
note - area varies by season and year to year
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Congo (3,730,881 sq km), Niger (2,261,741 sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Lake Chad (2,497,738 sq km)
Major aquifers
Lake Chad Basin
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 246.8 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 104.6 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 737 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
283.15 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Cameroon
conventional short form: Cameroon
local long form: Republique du Cameroun/Republic of Cameroon
local short form: Cameroun/Cameroon
former: Kamerun, French Cameroon, British Cameroon, Federal Republic of Cameroon, United Republic of Cameroon
etymology: in the 15th century, Portuguese explorers named the area near the mouth of the Wouri River the Rio dos Camaroes (River of Prawns) after the abundant shrimp in the water; over time the designation became Cameroon in English; this is the only instance where a country is named after a crustacean
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Yaounde
geographic coordinates: 3 52 N, 11 31 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: founded as a German colonial settlement of Jaunde in 1888 and named after the local Yaunde (Ewondo) people
Administrative divisions
10 regions (regions, singular - region); Adamaoua, Centre, East (Est), Far North (Extreme-Nord), Littoral, North (Nord), North-West (Nord-Ouest), West (Ouest), South (Sud), South-West (Sud-Ouest)
Independence
1 January 1960 (from French-administered UN trusteeship)
National holiday
State Unification Day (National Day), 20 May (1972)
Constitution
history: several previous; latest effective 18 January 1996
amendments: proposed by the president of the republic or by Parliament; amendment drafts require approval of at least one third of the membership in either house of Parliament; passage requires absolute majority vote of the Parliament membership; passage of drafts requested by the president for a second reading in Parliament requires two-thirds majority vote of its membership; the president can opt to submit drafts to a referendum, in which case passage requires a simple majority; constitutional articles on Cameroon’s unity and territorial integrity and its democratic principles cannot be amended; amended 2008
Legal system
mixed legal system of English common law, French civil law, and customary law
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Cameroon
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
20 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Paul BIYA (since 6 November 1982)
head of government: Prime Minister Joseph Dion NGUTE (since 4 January 2019); Deputy Prime Minister Amadou ALI (since 2014)
cabinet: Cabinet proposed by the prime minister, appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 7-year term (no term limits); election last held on 7 October 2018 (next to be held in October 2025); prime minister appointed by the president
election results: Paul BIYA reelected president; percent of vote - Paul BIYA (CPDM) 71.3%, Maurice KAMTO (MRC) 14.2%, Cabral LIBII (Univers) 6.3%, other 8.2%
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliament or Parlement consists of:
Senate or Senat (100 seats; 70 members indirectly elected by regional councils and 30 appointed by the president; members serve 5-year terms)
National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (180 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 5-year terms)
elections: Senate - last held on 25 March 2018 (next to be held in 2023)
National Assembly - last held on 9 February 2020 (current term extended by President); note - the constitutional court has ordered a partial rerun of elections in the English speaking areas; date to be determined
election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - CDPM 81.1%, SDF 8.6%, UNDP 5.8%, UDC 1.16%, other 2.8%; seats by party - CPDM 63, SDF 7
National Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - CPDM 139, UNDP 7, SDF 5, PCRN 5, UDC 4, FSNC 3, MDR 2, Union of Socialist Movements 2; 13 vacant; composition - NA
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court of Cameroon (consists of 9 titular and 6 surrogate judges and organized into judicial, administrative, and audit chambers); Constitutional Council (consists of 11 members)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president with the advice of the Higher Judicial Council of Cameroon, a body chaired by the president and includes the minister of justice, selected magistrates, and representatives of the National Assembly; judge term NA; Constitutional Council members appointed by the president for single 9-year terms
subordinate courts: Parliamentary Court of Justice (jurisdiction limited to cases involving the president and prime minister); appellate and first instance courts; circuit and magistrates' courts
Political parties and leaders
Alliance for Democracy and Development
Cameroon People's Democratic Movement or CPDM [Paul BIYA]
Cameroon People's Party or CPP [Edith Kah WALLA]
Cameroon Renaissance Movement or MRC [Maurice KAMTO]
Cameroonian Democratic Union or UDC [Adamou Ndam NJOYA]
Cameroonian Party for National Reconciliation or PCRN [Cabral LIBII]
Front for the National Salvation of Cameroon or FSNC [Issa Tchiroma BAKARY]
Movement for the Defense of the Republic or MDR [Dakole DAISSALA]
Movement for the Liberation and Development of Cameroon or MLDC [Marcel YONDO]
National Union for Democracy and Progress or UNDP [Maigari BELLO BOUBA]
Progressive Movement or MP [Jean-Jacques EKINDI]
Social Democratic Front or SDF [John FRU NDI]
Union of Peoples of Cameroon or UPC [Provisionary Management Bureau]
Union of Socialist Movements
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, BDEAC, C, CEMAC, EITI (compliant country), FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Henri ETOUNDI ESSOMBA (since 27 June 2016)
chancery: 2349 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 265-8790
FAX: [1] (202) 387-3826
email address and website:
cs@cameroonembassyusa.org
https://www.cameroonembassyusa.org/mainFolder/index.html
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Deputy Chief of Mission (currently serving as Charge d'Affaires) Mary E. DASCHBACH
embassy: Avenue Rosa Parks, Yaoundé
mailing address: 2520 Yaounde Place, Washington, DC 20521-2520
telephone: [237] 22251-4000/[237] 22220-1500
FAX: [237] 22220-1500, Ext. 4531
email address and website:
YaoundeACS@state.gov
https://cm.usembassy.gov/
branch office(s): Douala
Flag description
three equal vertical bands of green (hoist side), red, and yellow, with a yellow five-pointed star centered in the red band; the vertical tricolor recalls the flag of France; red symbolizes unity, yellow the sun, happiness, and the savannahs in the north, and green hope and the forests in the south; the star is referred to as the "star of unity"
note: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia
National symbol(s)
lion; national colors: green, red, yellow
National anthem
name: "O Cameroun, Berceau de nos Ancetres" (O Cameroon, Cradle of Our Forefathers)
lyrics/music: Rene Djam AFAME, Samuel Minkio BAMBA, Moise Nyatte NKO'O [French], Benard Nsokika FONLON [English]/Rene Djam AFAME
note: adopted 1957; Cameroon's anthem, also known as "Chant de Ralliement" (The Rallying Song), has been used unofficially since 1948 and officially adopted in 1957; the anthem has French and English versions whose lyrics differ
Economy
Economic overview
Cameroon’s market-based, diversified economy features oil and gas, timber, aluminum, agriculture, mining and the service sector. Oil remains Cameroon’s main export commodity, and despite falling global oil prices, still accounts for nearly 40% of exports. Cameroon’s economy suffers from factors that often impact underdeveloped countries, such as stagnant per capita income, a relatively inequitable distribution of income, a top-heavy civil service, endemic corruption, continuing inefficiencies of a large parastatal system in key sectors, and a generally unfavorable climate for business enterprise.
Since 1990, the government has embarked on various IMF and World Bank programs designed to spur business investment, increase efficiency in agriculture, improve trade, and recapitalize the nation's banks. The IMF continues to press for economic reforms, including increased budget transparency, privatization, and poverty reduction programs. The Government of Cameroon provides subsidies for electricity, food, and fuel that have strained the federal budget and diverted funds from education, healthcare, and infrastructure projects, as low oil prices have led to lower revenues.
Cameroon devotes significant resources to several large infrastructure projects currently under construction, including a deep seaport in Kribi and the Lom Pangar Hydropower Project. Cameroon’s energy sector continues to diversify, recently opening a natural gas-powered electricity generating plant. Cameroon continues to seek foreign investment to improve its inadequate infrastructure, create jobs, and improve its economic footprint, but its unfavorable business environment remains a significant deterrent to foreign investment.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$94.94 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$94.25 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$90.87 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
3.5% (2017 est.)
4.6% (2016 est.)
5.7% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$3,600 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$3,600 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$3,600 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$34.99 billion (2017 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.4% (2019 est.)
1% (2018 est.)
0.6% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: B (2006)
Moody's rating: B2 (2016)
Standard & Poors rating: B- (2020)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 16.7% (2017 est.)
industry: 26.5% (2017 est.)
services: 56.8% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 66.3% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 11.8% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 21.6% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: -0.3% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 21.6% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -20.9% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
cassava, plantains, maize, oil palm fruit, taro, sugar cane, sorghum, tomatoes, bananas, vegetables
Industries
petroleum production and refining, aluminum production, food processing, light consumer goods, textiles, lumber, ship repair
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 70%
industry: 13%
services: 17% (2001 est.)
Population below poverty line
37.5% (2014 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
46.5 (2014 est.)
46.6 (2014 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 37.5%
highest 10%: 35.4% (2001)
Budget
revenues: 5.363 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 6.556 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
1 July - 30 June
Current account balance
-$932 million (2017 est.)
-$1.034 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$7.73 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$7.3 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
China 17%, Netherlands 14%, Italy 9%, United Arab Emirates 8%, India 7%, United States 6%, Belgium 6%, Spain 5%, France 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
crude petroleum, cocoa beans, lumber, gold, natural gas, bananas (2019)
Imports
$9.09 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$8.42 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
China 28%, Nigeria 15%, France 9%, Belgium 6% (2019)
Imports - commodities
crude petroleum, scrap vessels, rice, special purpose ships, packaged medicines (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$3.235 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$2.26 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$9.375 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$7.364 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Cooperation Financiere en Afrique Centrale francs (XAF) per US dollar -
605.3 (2017 est.)
593.01 (2016 est.)
593.01 (2015 est.)
591.45 (2014 est.)
494.42 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 6.3%
male: 5.8%
female: 6.8% (2014 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 70% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 98% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 32% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
1.558 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122Electricity - from fossil fuels
52% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
47% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44Electricity - from other renewable sources
1% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149Refined petroleum products - production
39,080 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82Refined petroleum products - consumption
45,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109Natural gas - proved reserves
135.1 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 883,015 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3.33 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 25,245,134 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 95.1 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Cameroon’s 3G and LTE services are improving through growing competition and a government program to improve national connectivity and support digital economy; saturated use of transactions through m-commerce; developing broadband sector; improved submarine and terrestrial cable connectivity strengthened international bandwidth and lowered prices; pushing start of fiber link to Congo; fiber rollout continues with new government funding; operators opened new data center in 2020 and developed contracts for satellite broadband; government awarded contract to provide connectivity to universities (2020)
domestic: only about 4 per 100 persons for fixed-line subscriptions; mobile-cellular usage has increased sharply, reaching a subscribership base of over 82 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 237; landing points for the SAT-3/WASC, SAIL, ACE, NCSCS, Ceiba-2, and WACS fiber-optic submarine cable that provides connectivity to Europe, South America, and West Africa; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
government maintains tight control over broadcast media; state-owned Cameroon Radio Television (CRTV), broadcasting on both a TV and radio network, was the only officially recognized and fully licensed broadcaster until August 2007, when the government finally issued licenses to 2 private TV broadcasters and 1 private radio broadcaster; about 70 privately owned, unlicensed radio stations operating but are subject to closure at any time; foreign news services required to partner with state-owned national station (2019)
Internet users
total: 9.15 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 23.2% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 713,845 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2.69 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 3
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 265,136 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 70,000 mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 11
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 22
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 10
under 914 m: 8 (2013)
Pipelines
53 km gas, 5 km liquid petroleum gas, 1107 km oil, 35 km water (2013)
Railways
total: 987 km (2014)
narrow gauge: 987 km 1.000-m gauge (2014)
note: railway connections generally efficient but limited; rail lines connect major cities of Douala, Yaounde, Ngaoundere, and Garoua; passenger and freight service provided by CAMRAIL
Roadways
total: 77,589 km (2016)
paved: 5,133 km (2016)
unpaved: 72,456 km (2016)
Waterways
(major rivers in the south, such as the Wouri and the Sanaga, are largely non-navigable; in the north, the Benue, which connects through Nigeria to the Niger River, is navigable in the rainy season only to the port of Garoua) (2010)
Merchant marine
total: 94
by type: bulk carrier 3, container ship 1,general cargo 35, oil tanker 24, other 31 (2021)
Ports and terminals
oil terminal(s): Limboh Terminal
river port(s): Douala (Wouri)
Garoua (Benoue)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Cameroon Armed Forces (Forces Armees Camerounaises, FAC): Army (L'Armee de Terre), Navy (Marine Nationale Republique, MNR, includes naval infantry), Air Force (Armee de l'Air du Cameroun, AAC), Rapid Intervention Battalion (Bataillons d’Intervention Rapide, BIR), Gendarmerie, Presidential Guard (2021)
note(s) - the National Police (under the General Delegation of National Security) and the Gendarmerie are responsible for internal security; the Rapid Intervention Battalion (RIB) is a large brigade-sized force comprised of approximately 9 battalions, detachments, or groups (5 infantry, 1 airborne, 1 amphibious, 1 armored reconnaissance, and 1 counter-terrorism); the RIB maintains its own command and control structure and reports directly to the president, rather than the defense minister
Military expenditures
1% of GDP (2020 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2019)
1.1% of GDP (2018)
1.3% of GDP (2017)
1.3% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies widely; approximately 40,000 active duty troops; (25,000 ground forces, including the BIR and Presidential Guard; 2,000 Navy; 1,000 Air Force; 12,000 Gendarmerie) (2020)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the FAC inventory includes a mix of mostly older or second-hand Chinese, Russian, and Western equipment, with a limited quantity of more modern weapons; since 2010, China is the leading supplier of armaments to the FAC (2020)
Military deployments
750 Central African Republic (MINUSCA) (Aug 2021)
note: Cameroon has committed approximately 2,000-2,500 troops to the Multinational Joint Task Force (MNJTF) against Boko Haram; national MNJTF troop contingents are deployed within their own country territories, although cross‐border operations occur occasionally
Maritime threats
tthe International Maritime Bureau reports the territorial and offshore waters in the Niger Delta and Gulf of Guinea remain a very high risk for piracy and armed robbery of ships; in 2020, there were 98 reported incidents of piracy and armed robbery at sea in the Gulf of Guinea region; although a 24% decrease from the total number of incidents in 2019, it included all three hijackings and 9 of 11 ships fired upon worldwide; while boarding and attempted boarding to steal valuables from ships and crews are the most common types of incidents, almost a third of all incidents involve a hijacking and/or kidnapping; in 2020, a record 130 crew members were kidnapped in 22 separate incidents in the Gulf of Guinea, representing 95% of kidnappings worldwide; approximately 51% of all incidents of piracy and armed robbery are taking place off Nigeria, which is a decrease from the 71% in 2019 and an indication pirates are traveling further to target vessels; Nigerian pirates are well armed and very aggressive, operating as far as 200 nm offshore; the Maritime Administration of the US Department of Transportation has issued a Maritime Advisory (2021-002 - Gulf of Guinea-Piracy/Armed Robbery/Kidnapping for Ransom) effective 9 January 2021, which states in part, "Piracy, armed robbery, and kidnapping for ransom continue to serve as significant threats to US-flagged vessels transiting or operating in the Gulf of Guinea.”
Military service age and obligation
18-23 years of age for male and female voluntary military service; no conscription; high school graduation required; service obligation 4 years; periodic government calls for volunteers (2019)
Military - note
the FAC is largely focused on the threat from the terror group Boko Haram along its frontiers with Nigeria and Chad (Far North region) and an insurgency from armed Anglophone separatist groups in the North-West and South-West regions (as of Feb 2021, this internal conflict has left an estimated 3,000 civilians dead and over 700,000 people displaced since fighting started in 2016); in addition, the FAC often deploys units to the border region with the Central African Republic to counter intrusions from armed militias and bandits
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Boko Haram; Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham – West Africa
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Joint Border Commission with Nigeria reviewed 2002 ICJ ruling on the entire boundary and bilaterally resolved differences, including June 2006 Greentree Agreement that immediately ceded sovereignty of the Bakassi Peninsula to Cameroon with a full phase-out of Nigerian control and patriation of residents in 2008; Cameroon and Nigeria agreed on maritime delimitation in March 2008; sovereignty dispute between Equatorial Guinea and Cameroon over an island at the mouth of the Ntem River; only Nigeria and Cameroon have heeded the Lake Chad Commission's admonition to ratify the delimitation treaty, which also includes the Chad-Niger and Niger-Nigeria boundaries
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 345,471 (Central African Republic), 119,552 (Nigeria) (2021)
IDPs: 1,052,591 (2021) (includes far north, northwest, and southwest)
Trafficking in persons
current situation: human traffickers exploit domestic and foreign victims in Cameroon and Cameroonians abroad; deteriorating economic and education conditions and diminished police and judicial presence caused by conflict in the Northwest and Southwest has left displaced persons vulnerable to trafficking; parents may be lured by promises of education or a better life for their children in urban areas, and then the children are subject to forced labor and sex trafficking; teenagers and adolescents may be lured to cities with promises of employment and then become victims of forced labor and sex trafficking; children from neighboring countries are forced to work in spare parts shops or cattle grazing by business owners and herders; Cameroonians, often from rural areas, are exploited in forced labor and sex trafficking in the Middle East, Europe, the United States, and African countries
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List — Cameroon does not meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking, but is making significant efforts to do so; authorities investigated at least nine suspected trafficking cases, identified 77 victims, and provided some training on trafficking indicators to officials and teachers; however, officials prosecuted and convicted fewer traffickers; standard operating procedures for the identification and referral of trafficking victims were not implemented, and officials were not trained on the measures; the government did not report referring trafficking victims to government institutions for vulnerable children, but NGO-funded centers provided care for an unknown number of child victims; 2012 anti-trafficking legislation addressing victim and witness protection in conformity with international law was not passed for the eighth consecutive year (2020)