Introduction
Background
Most Cambodians consider themselves to be Khmers, descendants of the Angkor Empire that extended over much of Southeast Asia and reached its zenith between the 10th and 13th centuries. Attacks by the Thai and Cham (from present-day Vietnam) weakened the empire, ushering in a long period of decline. The king placed the country under French protection in 1863, and it became part of French Indochina in 1887. Following Japanese occupation in World War II, Cambodia gained full independence from France in 1953. In April 1975, after a seven-year struggle, communist Khmer Rouge forces captured Phnom Penh and evacuated all cities and towns. At least 1.5 million Cambodians died from execution, forced hardships, or starvation during the Khmer Rouge regime under POL POT. A December 1978 Vietnamese invasion drove the Khmer Rouge into the countryside, began a 10-year Vietnamese occupation, and touched off 20 years of civil war.
The 1991 Paris Peace Accords mandated democratic elections and a cease-fire, which was not fully respected by the Khmer Rouge. UN-sponsored elections in 1993 helped restore some semblance of normalcy under a coalition government. Factional fighting in 1997 ended the first coalition government, but a second round of national elections in 1998 led to the formation of another coalition government and renewed political stability. The remaining elements of the Khmer Rouge surrendered in early 1999. Some of the surviving Khmer Rouge leaders were tried for crimes against humanity by a hybrid UN-Cambodian tribunal supported by international assistance. In 2018, the tribunal heard its final cases, but it remains in operation to hear appeals. Elections in July 2003 were relatively peaceful, but it took one year of negotiations between contending political parties before a coalition government was formed. In October 2004, King Norodom SIHANOUK abdicated the throne and his son, Prince Norodom SIHAMONI, was selected to succeed him. Local (Commune Council) elections were held in Cambodia in 2012, with little of the violence that preceded prior elections. National elections in July 2013 were disputed, with the opposition - the Cambodia National Rescue Party (CNRP) - boycotting the National Assembly. The political impasse was ended nearly a year later, with the CNRP agreeing to enter parliament in exchange for commitments by the ruling Cambodian People’s Party (CPP) to undertake electoral and legislative reforms. The CNRP made further gains in local commune elections in June 2017, accelerating sitting Prime Minister HUN SEN’s efforts to marginalize the CNRP before national elections in 2018. HUN SEN arrested CNRP President KEM SOKHA in September 2017. The Supreme Court dissolved the CNRP in November 2017 and banned its leaders from participating in politics for at least five years. The CNRP’s seats in the National Assembly were redistributed to smaller, less influential opposition parties, while all of the CNRP’s 5,007 seats in the commune councils throughout the country were reallocated to the CPP. With the CNRP banned, the CPP swept the 2018 national elections, winning all 125 National Assembly seats and effectively turning the country into a one-party state.Cambodia has strong and growing economic and political ties with its large neighbor to the north, China. More than 40% of foreign investment in the country in 2019 came from China, and Beijing has provided over $15 billion in financial assistance since the 1990s. The CPP also partly sees Chinese support as a counterbalance to Thailand and Vietnam and to international criticism of the CPP’s human rights and antidemocratic record.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
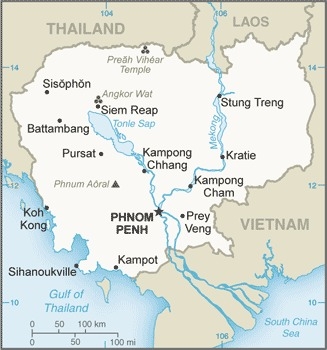
Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Thailand, between Thailand, Vietnam, and Laos
Geographic coordinates
13 00 N, 105 00 E
Map references
Southeast Asia
Land boundaries
total: 2,530 km
border countries (3): Laos 555 km, Thailand 817 km, Vietnam 1158 km
Coastline
443 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; rainy, monsoon season (May to November); dry season (December to April); little seasonal temperature variation
Terrain
mostly low, flat plains; mountains in southwest and north
Elevation
highest point: Phnum Aoral 1,810 m
lowest point: Gulf of Thailand 0 m
mean elevation: 126 m
Natural resources
oil and gas, timber, gemstones, iron ore, manganese, phosphates, hydropower potential, arable land
Land use
agricultural land: 32.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 22.7% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.9% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 8.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 56.5% (2018 est.)
other: 11.4% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
3,540 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Pacific Ocean drainage: Mekong (805,604 sq km)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Tonle Sap - 2,700-16,000 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Mekong (shared with China [s], Burma, Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam [m]) - 4,350 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Population distribution
population concentrated in the southeast, particularly in and around the capital of Phnom Penh; further distribution is linked closely to the Tonle Sap and Mekong Rivers
Natural hazards
monsoonal rains (June to November); flooding; occasional droughts
Geography - note
a land of paddies and forests dominated by the Mekong River and Tonle Sap (Southeast Asia's largest freshwater lake)
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Cambodian(s)
adjective: Cambodian
Ethnic groups
Khmer 95.4%, Cham 2.4%, Chinese 1.5%, other 0.7% (2019-20 est.)
Languages
Khmer (official) 95.8%, minority languages 2.9%, Chinese 0.6%, Vietnamese 0.5%, other 0.2% (2019 est.)
major-language sample(s):
សៀវភៅហេតុការណនៅលើពិភពលោក។ ទីតាំងពត៏មានមូលដានគ្រឹះយាងសំខាន់។. (Khmer)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Buddhist (official) 97.1%, Muslim 2%, Christian 0.3%, other 0.5% (2019 est.)
Demographic profile
Cambodia is a predominantly rural country with among the most ethnically and religiously homogenous populations in Southeast Asia: more than 95% of its inhabitants are Khmer and more than 95% are Buddhist. The population’s size and age structure shrank and then rebounded during the 20th century as a result of conflict and mass death. During the Khmer Rouge regime between 1975 and 1979 as many as 1.5 to 2 million people are estimated to have been killed or died as a result of starvation, disease, or overwork – a loss of about 25% of the population. At the same time, emigration was high, and the fertility rate sharply declined. In the 1980s, after the overthrow of the Khmer Rouge, fertility nearly doubled and reached pre-Khmer Rouge levels of close to 7 children per woman, reflecting in part higher infant survival rates. The baby boom was followed by a sustained fertility decline starting in the early 1990s, eventually decreasing from 3.8 in 2000 to 2.9 in 2010, although the rate varied by income, education, and rural versus urban location. Despite continuing fertility reduction, Cambodia still has a youthful population that is likely to maintain population growth through population momentum. Improvements have also been made in mortality, life expectancy, and contraceptive prevalence, although reducing malnutrition among children remains stalled. Differences in health indicators are pronounced between urban and rural areas, which experience greater poverty.
Cambodia is predominantly a country of migration, driven by the search for work, education, or marriage. Internal migration is more prevalent than international migration, with rural to urban migration being the most common, followed by rural to rural migration. Urban migration focuses on the pursuit of unskilled or semi-skilled jobs in Phnom Penh, with men working mainly in the construction industry and women working in garment factories. Most Cambodians who migrate abroad do so illegally using brokers because it is cheaper and faster than through formal channels, but doing so puts them at risk of being trafficked for forced labor or sexual exploitation. Young Cambodian men and women migrate short distances across the Thai border using temporary passes to work in agriculture, while others migrate long distances primarily into Thailand and Malaysia for work in agriculture, fishing, construction, manufacturing, and domestic service. Cambodia was a refugee sending country in the 1970s and 1980s as a result of the brutality of the Khmer Rouge regime, its ousting by the Vietnamese invasion, and the resultant civil war. Tens of thousands of Cambodians fled to Thailand; more than 100,000 were resettled in the US in the 1980s. Cambodia signed a multi-million dollar agreement with Australia in 2014 to voluntarily resettle refugees seeking shelter in Australia. However, the deal has proven to be a failure because of poor conditions and a lack of support services for the few refugees willing to accept the offer.
Age structure
0-14 years: 30.18% (male 2,582,427/female 2,525,619)
15-24 years: 17.28% (male 1,452,784/female 1,472,769)
25-54 years: 41.51% (male 3,442,051/female 3,584,592)
55-64 years: 6.44% (male 476,561/female 612,706)
65 years and over: 4.59% (male 287,021/female 490,454) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 55.7
youth dependency ratio: 48.2
elderly dependency ratio: 7.6
potential support ratio: 13.2 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 26.4 years
male: 25.6 years
female: 27.2 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
population concentrated in the southeast, particularly in and around the capital of Phnom Penh; further distribution is linked closely to the Tonle Sap and Mekong Rivers
Urbanization
urban population: 24.7% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.06% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
2.144 million PHNOM PENH (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.78 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.59 male(s)/female
total population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
22.4 years (2014 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-49
Maternal mortality ratio
160 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55Infant mortality rate
total: 45.62 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 52.46 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 38.47 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 66.27 years
male: 63.7 years
female: 68.95 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
56.3% (2014)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 98.4% of population
rural: 77.8% of population
total: 80.3% of population
unimproved: urban: 1.6% of population
rural: 22.2% of population
total: 19.7% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
6% (2018)
Physicians density
0.19 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
Hospital bed density
1.9 beds/1,000 population (2016)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 55.5% of population
total: 65.7% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 44.5% of population
total: 34.3% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, Japanese encephalitis, and malaria
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 80.5%
male: 86.5%
female: 75% (2015)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 11 years
male: 11 years
female: 10 years
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 2.5%
male: 2.7%
female: 2.3% (2019 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
illegal logging activities throughout the country and strip mining for gems in the western region along the border with Thailand have resulted in habitat loss and declining biodiversity (in particular, destruction of mangrove swamps threatens natural fisheries); soil erosion; in rural areas, most of the population does not have access to potable water; declining fish stocks because of illegal fishing and overfishing; coastal ecosystems choked by sediment washed loose from deforested areas inland
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 23.98 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 9.92 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 14.88 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; rainy, monsoon season (May to November); dry season (December to April); little seasonal temperature variation
Land use
agricultural land: 32.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 22.7% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0.9% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 8.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 56.5% (2018 est.)
other: 11.4% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 24.7% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 3.06% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.84% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, Japanese encephalitis, and malaria
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1.089 million tons (2014 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Tonle Sap - 2,700-16,000 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Mekong (shared with China [s], Burma, Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam [m]) - 4,350 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Pacific Ocean drainage: Mekong (805,604 sq km)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 98 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 33 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 2.053 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
476.1 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Kingdom of Cambodia
conventional short form: Cambodia
local long form: Preahreacheanachakr Kampuchea (phonetic transliteration)
local short form: Kampuchea
former: Khmer Republic, Democratic Kampuchea, People's Republic of Kampuchea, State of Cambodia
etymology: the English name Cambodia is an anglicization of the French Cambodge, which is the French transliteration of the native name Kampuchea
Government type
parliamentary constitutional monarchy
Capital
name: Phnom Penh
geographic coordinates: 11 33 N, 104 55 E
time difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: Phnom Penh translates as "Penh's Hill" in Khmer; the city takes its name from the present Wat Phnom (Hill Temple), the tallest religious structure in the city, whose establishment, according to legend, was inspired in the 14th century by a pious nun, Daun PENH
Administrative divisions
24 provinces (khett, singular and plural) and 1 municipality (krong, singular and plural)
provinces: Banteay Meanchey, Battambang, Kampong Cham, Kampong Chhnang, Kampong Speu, Kampong Thom, Kampot, Kandal, Kep, Koh Kong, Kratie, Mondolkiri, Oddar Meanchey, Pailin, Preah Sihanouk, Preah Vihear, Prey Veng, Pursat, Ratanakiri, Siem Reap, Stung Treng, Svay Rieng, Takeo, Tbong Khmum
municipalities: Phnom Penh (Phnum Penh)
Independence
9 November 1953 (from France)
National holiday
Independence Day, 9 November (1953)
Constitution
history: previous 1947; latest promulgated 21 September 1993
amendments: proposed by the monarch, by the prime minister, or by the president of the National Assembly if supported by one fourth of the Assembly membership; passage requires two-thirds majority of the Assembly membership; constitutional articles on the multiparty democratic form of government and the monarchy cannot be amended; amended 1999, 2008, 2014, 2018
Legal system
civil law system (influenced by the UN Transitional Authority in Cambodia) customary law, Communist legal theory, and common law
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Cambodia
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: King Norodom SIHAMONI (since 29 October 2004)
head of government: Prime Minister HUN SEN (since 14 January 1985)
cabinet: Council of Ministers named by the prime minister and appointed by the monarch
elections/appointments: monarch chosen by the 9-member Royal Council of the Throne from among all eligible males of royal descent; following legislative elections, a member of the majority party or majority coalition named prime minister by the Chairman of the National Assembly and appointed by the monarch
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliament of Cambodia consists of:
Senate (62 seats; 58 indirectly elected by parliamentarians and commune councils, 2 indirectly elected by the National Assembly, and 2 appointed by the monarch; members serve 6-year terms)
National Assembly (125 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote; members serve 5-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last held on 25 February 2018 (next to be held in 2024); National Assembly - last held on 29 July 2018 (next to be held in 2023)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - CPP 96%, FUNCINPEC 2.4%, KNUP 1.6%; seats by party - CPP 58; composition - men 53, women 9, percent of women 14.5%
National Assembly - percent of vote by party - CPP 76.9%, FUNCINPEC 5.9%, LDP 4.9%, Khmer Will Party 3.4%, other 8.9%; seats by party - CPP 125; composition - men 100, women 25, percent of women 20%; note - total Parliament of Cambodia percent of women 18.2%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Council (organized into 5- and 9-judge panels and includes a court chief and deputy chief); Constitutional Court (consists of 9 members); note - in 1997, the Cambodian Government requested UN assistance in establishing trials to prosecute former Khmer Rouge senior leaders for crimes against humanity committed during the 1975-1979 Khmer Rouge regime; the Extraordinary Chambers of the Courts of Cambodia (also called the Khmer Rouge Tribunal) was established in 2006 and began hearings for the first case in 2009; court proceedings remain ongoing in 2019
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court and Constitutional Council judge candidates recommended by the Supreme Council of Magistracy, a 17-member body chaired by the monarch and includes other high-level judicial officers; judges of both courts appointed by the monarch; Supreme Court judges appointed for life; Constitutional Council judges appointed for 9-year terms with one-third of the court renewed every 3 years
subordinate courts: Appellate Court; provincial and municipal courts; Military Court
Political parties and leaders
Cambodian People's Party or CPP [HUN SEN]
National United Front for Independent, Neutral, Peaceful, and Cooperative Cambodia or FUNCINPEC [Prince NORODOM CHAKRAVUTH]
League for Democracy Party or LDP [KHEM Veasna]
Khmer Will Party [KONG MONIKA]
Khmer National Unity Party or KNUP [NHEK BUN CHHAY]
Cambodia National Rescue Party or CNRP [KHEM SOKHA] (dissolved by the Cambodian Supreme Court in November 2017; formed from a 2012 merger of the Sam Rangsi Party or SRP and the former Human Rights Party or HRP [KHEM SOKHA, also spelled KEM SOKHA])
(Dec 2021)
International organization participation
ADB, ARF, ASEAN, CICA, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, MINUSMA, MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador CHUM SOUNRY (since 17 September 2018)
chancery: 4530 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20011
telephone: [1] (202) 726-7742
FAX: [1] (202) 726-8381
email address and website:
camemb.usa@mfaic.gov
https://www.embassyofcambodiadc.org/
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador W. Patrick MURPHY (since 23 October 2019)
embassy: #1, Street 96, Sangkat Wat Phnom, Khan Daun Penh, Phnom Penh
mailing address: 4540 Phnom Penh Place, Washington DC 20521-4540
telephone: [855] (23) 728-000
FAX: [855] (23) 728-700
email address and website:
ACSPhnomPenh@state.gov
https://kh.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
three horizontal bands of blue (top), red (double width), and blue with a white, three-towered temple, representing Angkor Wat, outlined in black in the center of the red band; red and blue are traditional Cambodian colors
note: only national flag to prominently incorporate an actual identifiable building into its design (a few other national flags - those of Afghanistan, San Marino, Portugal, and Spain - show small generic buildings as part of their coats of arms on the flag)
National symbol(s)
Angkor Wat temple, kouprey (wild ox); national colors: red, blue
National anthem
name: "Nokoreach" (Royal Kingdom)
lyrics/music: CHUON NAT/F. PERRUCHOT and J. JEKYLL
note: adopted 1941, restored 1993; the anthem, based on a Cambodian folk tune, was restored after the defeat of the Communist regime
Economy
Economic overview
Cambodia has experienced strong economic growth over the last decade; GDP grew at an average annual rate of over 8% between 2000 and 2010 and about 7% since 2011. The tourism, garment, construction and real estate, and agriculture sectors accounted for the bulk of growth. Around 700,000 people, the majority of whom are women, are employed in the garment and footwear sector. An additional 500,000 Cambodians are employed in the tourism sector, and a further 200,000 people in construction. Tourism has continued to grow rapidly with foreign arrivals exceeding 2 million per year in 2007 and reaching 5.6 million visitors in 2017. Mining also is attracting some investor interest and the government has touted opportunities for mining bauxite, gold, iron and gems.
Still, Cambodia remains one of the poorest countries in Asia, and long-term economic development remains a daunting challenge, inhibited by corruption, limited human resources, high income inequality, and poor job prospects. According to the Asian Development Bank (ADB), the percentage of the population living in poverty decreased to 13.5% in 2016. More than 50% of the population is less than 25 years old. The population lacks education and productive skills, particularly in the impoverished countryside, which also lacks basic infrastructure.
The World Bank in 2016 formally reclassified Cambodia as a lower middle-income country as a result of continued rapid economic growth over the past several years. Cambodia’s graduation from a low-income country will reduce its eligibility for foreign assistance and will challenge the government to seek new sources of financing. The Cambodian Government has been working with bilateral and multilateral donors, including the Asian Development Bank, the World Bank and IMF, to address the country's many pressing needs; more than 20% of the government budget will come from donor assistance in 2018. A major economic challenge for Cambodia over the next decade will be fashioning an economic environment in which the private sector can create enough jobs to handle Cambodia's demographic imbalance.
Textile exports, which accounted for 68% of total exports in 2017, have driven much of Cambodia’s growth over the past several years. The textile sector relies on exports to the United States and European Union, and Cambodia’s dependence on its comparative advantage in textile production is a key vulnerability for the economy, especially because Cambodia has continued to run a current account deficit above 9% of GDP since 2014.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$70.08 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$72.36 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$67.59 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP per capita
$4,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$4,400 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$4,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$22.09 billion (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Moody's rating: B2 (2007)
Standard & Poors rating: N/A (2014)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 25.3% (2017 est.)
industry: 32.8% (2017 est.)
services: 41.9% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 76% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 5.4% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 21.8% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 1.2% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 68.6% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -73% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
cassava, rice, maize, vegetables, sugar cane, soybeans, rubber, oil palm fruit, bananas, pork
Industries
tourism, garments, construction, rice milling, fishing, wood and wood products, rubber, cement, gem mining, textiles
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 48.7%
industry: 19.9%
services: 31.5% (2013 est.)
Unemployment rate
0.3% (2017 est.)
0.2% (2016 est.)
note: high underemployment, according to official statistics
Population below poverty line
16.5% (2016 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
37.9 (2008 est.)
41.9 (2004 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2%
highest 10%: 28% (2013 est.)
Budget
revenues: 3.947 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 4.354 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$1.871 billion (2017 est.)
-$1.731 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$19.4 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$21.07 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$18.41 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
United States 21%, Singapore 8%, Thailand 8%, Germany 7%, Japan 6%, China 5%, Canada 5%, United Kingdom 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
clothing, precious metal scraps, trunks/cases, gold, leather footwear (2019)
Imports
$23.12 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$25.52 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$21.86 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
China 27%, Thailand 25%, Vietnam 15%, Singapore 8% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, clothing, gold, cars, flavored water (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$12.2 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$9.122 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$11.87 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$10.3 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
riels (KHR) per US dollar -
4,055 (2017 est.)
4,058.7 (2016 est.)
4,058.7 (2015 est.)
4,067.8 (2014 est.)
4,037.5 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 2.5%
male: 2.7%
female: 2.3% (2019 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 75% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 100% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 67% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
1.697 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119Electricity - from fossil fuels
35% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
63% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27Electricity - from other renewable sources
2% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135Refined petroleum products - consumption
45,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 56,445 (2019)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2019 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 21,418,681 (2019)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 129.9 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Cambodia’s telecom infrastructure struggles with poor infrastructure and power outages; improvement through competition and foreign investment; fixed-line and fixed/mobile broadband penetration is still low compared to other Asian nations; government and operators preparing for 5G services through Huawei’s infrastructure that will drive mobile broadband through faster speeds; online Internet content subject to government restrictions (2020)
domestic: fixed-line connections stand at about 1 per 100 persons and declining; mobile-cellular usage, aided by competition among service providers, has increased to about 130 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 855; landing points for MCT and AAE-1 via submarine cables providing communication to Asia, the Middle East, Europe and Africa; satellite earth station - 1 Intersputnik (Indian Ocean region) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
mixture of state-owned, joint public-private, and privately owned broadcast media; 27 TV broadcast stations with most operating on multiple channels, including 1 state-operated station broadcasting from multiple locations, 11 stations either jointly operated or privately owned with some broadcasting from several locations; multi-channel cable and satellite systems are available (2019); 84 radio broadcast stations - 1 state-owned broadcaster with multiple stations and a large mixture of public and private broadcasters; one international broadcaster is available (2019) as well as one Chinese joint venture television station with the Ministry of Interior; several television and radio operators broadcast online only (often via Facebook) (2019)
Internet users
total: 8.86 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 78.8% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 713,845 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1.12 (2019 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 6 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 25
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 1,411,059 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 680,000 mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 6
2,438 to 3,047 m: 3
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2019)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 10
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 7
under 914 m: 1 (2013)
Heliports
1 (2013)
Railways
total: 642 km (2014)
narrow gauge: 642 km 1.000-m gauge (2014)
note: under restoration
Roadways
total: 47,263 km (2013)
paved: 12,239 km (2013)
unpaved: 35,024 km (2013)
Merchant marine
total: 245
by type: container ship 2, general cargo 162, oil tanker 18, other 63 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Sihanoukville (Kampong Saom)
river port(s): Phnom Penh (Mekong)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Royal Cambodian Armed Forces: High Command Headquarters, Royal Cambodian Army, Royal Khmer Navy, Royal Cambodian Air Force, Royal Gendarmerie; the National Committee for Maritime Security (performs Coast Guard functions and has representation from military and civilian agencies) (2021)
note - the Cambodian National Police is under the Ministry of Interior
Military expenditures
2.5% of GDP (2020 est.)
2.3% of GDP (2019 est.)
2.2% of GDP (2018)
2.1% of GDP (2017)
2% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; approximately 100,000 total active troops including about 3,000 Navy and 1,000 Air Force; est. 10,000 Gendarmerie (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Royal Cambodian Armed Forces are armed largely with older Chinese and Russian-origin equipment; it has received limited amounts of more modern (mostly second-hand) equipment since 2010 with China as the principal provider (2021)
Military deployments
200 Central African Republic (MINUSCA); 180 Lebanon (UNIFIL); 330 Mali (MINUSMA) (Oct 2021)
Military service age and obligation
18 is the legal minimum age for compulsory and voluntary military service (2021)
Military - note
the Royal Cambodian Armed Forces (RCAF) was re-established in 1993 under the first coalition government from the merger of the Cambodian Government’s military forces (Cambodian People’s Armed Forces) and the two non-communist resistance forces (Sihanoukist National Army, aka National Army for Khmer Independence, and the Khmer People's National Liberation Armed Forces); thousands of communist Khmer Rouge fighters began surrendering by 1994 under a government amnesty program and the last of the Khmer Rouge forces (National Army of Democratic Kampuchea) were demobilized or absorbed into the RCAF in 1999
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Cambodia is concerned about Laos' extensive upstream dam construction; Cambodia and Thailand dispute sections of boundary; in 2011 Thailand and Cambodia resorted to arms in the dispute over the location of the boundary on the precipice surmounted by Preah Vihear Temple ruins, awarded to Cambodia by an International Court of Justice decision in 1962 and part of a UN World Heritage site; Cambodia accuses Vietnam of a wide variety of illicit cross-border activities; progress on a joint development area with Vietnam is hampered by an unresolved dispute over sovereignty of offshore islands
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 57,444 (2020)
Trafficking in persons
current situation: human traffickers exploit Cambodian men, women, and children in forced labor and sex trafficking in Cambodia and abroad, and foreign nationals are trafficked in Cambodia; Cambodian adults and children migrate to other countries in the region or increasingly to the Middle East where traffickers force them to work in agriculture, fishing, construction, manufacturing, and domestic servitude; significant numbers of Cambodian men and boys are subject to forced labor on Thai ships in international waters and may experience physical abuse, nonpayment or underpayment of wages, and confinement at sea for years; brick kiln owners exploit thousands of Cambodians, including children, through debt-based coercion; children from poor families are vulnerable to forced labor, often with the complicity of their parents, in domestic servitude, forced begging, or street vending in Thailand and Vietnam; Cambodian and ethnic Vietnamese women and girls from rural areas move to cities and tourist areas where they are sex trafficked
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List — Cambodia does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking but is making significant efforts to do so; authorities continued to prosecute and convict traffickers and utilized new victim identification and data collection technologies; the government enacted a five-year national action plan to combat human trafficking; however, corruption continued to impede law enforcement efforts, criminal proceedings, and services to victims; some corrupt officials may have profited directly from sex and labor trafficking or accepted bribes to dismiss charges or reduce sentences; insufficient judicial monitoring systems enabled suspected traffickers to flee before trial; authorities failed to issue formal guidance allowing the use of undercover techniques in anti-trafficking investigations (2020)
Illicit drugs
manufacture of methamphetamine expanding due to transnational crime syndicates moving from China to evade the law; drugs destined for Australia, Japan, New Zealand and the Republic of Korea and the rest of East and South-East Asia