Burundi
Introduction
Background
Established in the 1600s, the Burundi Kingdom has had borders similar to those of modern Burundi since the 1800s. Burundi’s two major ethnic groups, the majority Hutu and minority Tutsi, share a common language and culture and largely lived in peaceful cohabitation under Tutsi monarchs in pre-colonial Burundi. Regional, class, and clan distinctions contributed to social status in the Burundi Kingdom, yielding a complex class structure. German colonial rule in the late 19th and early 20th centuries and Belgian rule after World War I preserved Burundi’s monarchy. Seeking to simplify administration, Belgian colonial officials reduced the number of chiefdoms and eliminated most Hutu chiefs from positions of power. In 1961, the Burundian Tutsi king’s oldest son, Louis Rwagasore was murdered by a competing political faction shortly before he was set to become prime minister, triggering increased political competition that contributed to later instability. Burundi gained its independence from Belgium in 1962 as the Kingdom of Burundi.
Revolution in neighboring Rwanda stoked ethnic polarization as the Tutsi increasingly feared violence and loss of political power. A failed Hutu-led coup in 1965 triggered a purge of Hutu officials and set the stage for Tutsi officers to overthrow the monarchy in 1966 and establish a Tutsi-dominated republic. A Hutu rebellion in 1972 that resulted in the death of several thousand Tutsi civilians sparked a brutal crackdown on Hutu civilians by the Tutsi-led military, which ultimately killed 100,000-200,000 people. International pressure led to a new constitution in 1992 and democratic elections in June 1993. Burundi's first democratically elected president, Hutu Melchior NDADAYE, was assassinated in October 1993 after only 100 days in office by Tutsi military officers fearing Hutu domination, sparking a civil war. His successor, Cyprien NTARYAMIRA, died when the Rwandan president’s plane he was traveling on was shot down in April 1994, which triggered the Rwandan genocide and further entrenched ethnic conflict in Burundi. The internationally brokered Arusha Agreement, signed in 2000, and subsequent ceasefire agreements with armed movements ended the 1993-2005 civil war. Burundi’s second democratic elections were held in 2005, resulting in the election of Pierre NKURUNZIZA as president. He was reelected in 2010 and again in 2015 after a controversial court decision allowed him to circumvent a term limit. President Evariste NDAYISHIMIYE - from NKURUNZIZA’s ruling party - was elected in 2020.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
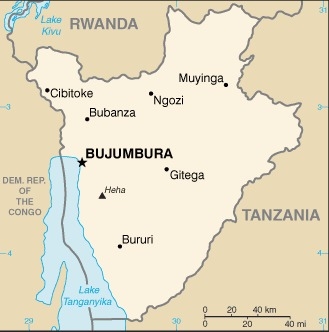
Central Africa, east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, west of Tanzania
Geographic coordinates
3 30 S, 30 00 E
Map references
Africa
Land boundaries
total: 1,140 km
border countries (3): Democratic Republic of the Congo 236 km, Rwanda 315 km, Tanzania 589 km
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
Climate
equatorial; high plateau with considerable altitude variation (772 m to 2,670 m above sea level); average annual temperature varies with altitude from 23 to 17 degrees Celsius but is generally moderate as the average altitude is about 1,700 m; average annual rainfall is about 150 cm; two wet seasons (February to May and September to November), and two dry seasons (June to August and December to January)
Terrain
hilly and mountainous, dropping to a plateau in east, some plains
Elevation
highest point: Heha 2,670 m
lowest point: Lake Tanganyika 772 m
mean elevation: 1,504 m
Natural resources
nickel, uranium, rare earth oxides, peat, cobalt, copper, platinum, vanadium, arable land, hydropower, niobium, tantalum, gold, tin, tungsten, kaolin, limestone
Land use
agricultural land: 73.3% (2018 est.)
arable land: 38.9% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 15.6% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 18.8% (2018 est.)
forest: 6.6% (2018 est.)
other: 20.1% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
230 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Congo (3,730,881 sq km), (Mediterranean Sea) Nile (3,254,853 sq km)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Tanganyika (shared with Democratic Republic of Congo, Tanzania, and Zambia) - 32,000 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Nile (shared with Egypt, Sudan, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, and Tanzania) - 6,650 km;
Population distribution
one of Africa's most densely populated countries; concentrations tend to be in the north and along the northern shore of Lake Tanganyika in the west; most people live on farms near areas of fertile volcanic soil as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards
flooding; landslides; drought
Geography - note
landlocked; straddles crest of the Nile-Congo watershed; the Kagera, which drains into Lake Victoria, is the most remote headstream of the White Nile
People and Society
Population
12,241,065 (July 2021 est.)
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
Nationality
noun: Burundian(s)
adjective: Burundian
Ethnic groups
Hutu, Tutsi, Twa (Pygmy)
Languages
Kirundi only 29.7% (official); French only .3% (official); Swahili only .2%; English only .1% (official); Kirundi and French 8.4%; Kirundi, French, and English 2.4%, other language combinations 2%, unspecified 56.9% (2008 est.)
major-language sample(s):
Igitabo Mpuzamakungu c'ibimenyetso bifatika, isoko ntabanduka ku nkuru z'urufatiro. (Kirundi)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
note: data represent languages read and written by people 10 years of age or older; spoken Kirundi is nearly universal
Religions
Roman Catholic 58.6%, Protestant 35.3% (includes Adventist 2.7% and other Protestant 32.6%), Muslim 3.4%, other 1.3%, none 1.3% (2016-17 est.)
Demographic profile
Burundi is a densely populated country with a high population growth rate, factors that combined with land scarcity and poverty place a large share of its population at risk of food insecurity. About 90% of the population relies on subsistence agriculture. Subdivision of land to sons, and redistribution to returning refugees, results in smaller, overworked, and less productive plots. Food shortages, poverty, and a lack of clean water contribute to a 60% chronic malnutrition rate among children. A lack of reproductive health services has prevented a significant reduction in Burundi’s maternal mortality and fertility rates, which are both among the world’s highest. With two-thirds of its population under the age of 25 and a birth rate of about 6 children per woman, Burundi’s population will continue to expand rapidly for decades to come, putting additional strain on a poor country.
Historically, migration flows into and out of Burundi have consisted overwhelmingly of refugees from violent conflicts. In the last decade, more than a half million Burundian refugees returned home from neighboring countries, mainly Tanzania. Reintegrating the returnees has been problematic due to their prolonged time in exile, land scarcity, poor infrastructure, poverty, and unemployment. Repatriates and existing residents (including internally displaced persons) compete for limited land and other resources. To further complicate matters, international aid organizations reduced their assistance because they no longer classified Burundi as a post-conflict country. Conditions have deteriorated since renewed violence erupted in April 2015, causing another outpouring of refugees. In addition to refugee out-migration, Burundi has hosted thousands of refugees from neighboring countries, mostly from the Democratic Republic of the Congo and lesser numbers from Rwanda.
Age structure
0-14 years: 43.83% (male 2,618,868/female 2,581,597)
15-24 years: 19.76% (male 1,172,858/female 1,171,966)
25-54 years: 29.18% (male 1,713,985/female 1,748,167)
55-64 years: 4.17% (male 231,088/female 264,131)
65 years and over: 3.06% (male 155,262/female 207,899) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 91
youth dependency ratio: 86.4
elderly dependency ratio: 4.5
potential support ratio: 22 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 17.7 years
male: 17.4 years
female: 18 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
one of Africa's most densely populated countries; concentrations tend to be in the north and along the northern shore of Lake Tanganyika in the west; most people live on farms near areas of fertile volcanic soil as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization
urban population: 14.1% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 5.43% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
1.075 million BUJUMBURA (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.87 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female
total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
21.5 years (2016/17 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-49
Maternal mortality ratio
548 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16Infant mortality rate
total: 38.96 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 43.21 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 34.58 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 67.07 years
male: 64.98 years
female: 69.22 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
28.5% (2016/17)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 97.6% of population
rural: 77.8% of population
total: 80.3% of population
unimproved: urban: -1.1% of population
rural: 22.2% of population
total: 19.7% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
7.7% (2018)
Physicians density
0.1 physicians/1,000 population (2017)
Hospital bed density
0.8 beds/1,000 population (2014)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 85.2% of population
rural: 53.4% of population
total: 57.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 14.8% of population
rural: 46.6% of population
total: 42.6% of population (2017 est.)
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 68.4%
male: 76.3%
female: 61.2% (2017)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 11 years
male: 11 years
female: 11 years (2018)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 2.9%
male: 4.4%
female: 2% (2014 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
soil erosion as a result of overgrazing and the expansion of agriculture into marginal lands; deforestation (little forested land remains because of uncontrolled cutting of trees for fuel); habitat loss threatens wildlife populations
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 35.61 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 0.5 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 1.42 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
equatorial; high plateau with considerable altitude variation (772 m to 2,670 m above sea level); average annual temperature varies with altitude from 23 to 17 degrees Celsius but is generally moderate as the average altitude is about 1,700 m; average annual rainfall is about 150 cm; two wet seasons (February to May and September to November), and two dry seasons (June to August and December to January)
Land use
agricultural land: 73.3% (2018 est.)
arable land: 38.9% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 15.6% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 18.8% (2018 est.)
forest: 6.6% (2018 est.)
other: 20.1% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 14.1% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 5.43% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 10.31% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
Food insecurity
widespread lack of access: due to floods, and lack of rain - about 1 million people are estimated to be severely food insecure in the June−September 2021 period, mainly due to livelihood losses caused by poor rains in northern areas and by floods in western areas bordering Lake Tanganyika; the socio‑economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has put further constraints on livelihoods of vulnerable households. (2021)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1,872,016 tons (2002 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Tanganyika (shared with Democratic Republic of Congo, Tanzania, and Zambia) - 32,000 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Nile (shared with Egypt, Sudan, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, and Tanzania) - 6,650 km;
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Congo (3,730,881 sq km), (Mediterranean Sea) Nile (3,254,853 sq km)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 43.1 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 15 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 222 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
12.536 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Burundi
conventional short form: Burundi
local long form: Republique du Burundi/Republika y'u Burundi
local short form: Burundi
former: Urundi, German East Africa, Ruanda-Urundi, Kingdom of Burundi
etymology: name derived from the pre-colonial Kingdom of Burundi (17th-19th century)
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Gitega (political capital), Bujumbura (commercial capital); note - in January 2019, the Burundian parliament voted to make Gitega the political capital of the country while Bujumbura would remain its economic capital; all branches of the government are expected to have moved from Bujumbura to Gitega by 2022
geographic coordinates: 3 25 S, 29 55 E
time difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the naming origins for both Gitega and Bujumbura are obscure; Bujumbura's name prior to independence in 1962 was Usumbura
Administrative divisions
18 provinces; Bubanza, Bujumbura Mairie, Bujumbura Rural, Bururi, Cankuzo, Cibitoke, Gitega, Karuzi, Kayanza, Kirundo, Makamba, Muramvya, Muyinga, Mwaro, Ngozi, Rumonge, Rutana, Ruyigi
Independence
1 July 1962 (from UN trusteeship under Belgian administration)
National holiday
Independence Day, 1 July (1962)
Constitution
history: several previous, ratified by referendum 28 February 2005
amendments: proposed by the president of the republic after consultation with the government or by absolute majority support of the membership in both houses of Parliament; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Senate membership and at least four-fifths majority vote by the National Assembly; the president can opt to submit amendment bills to a referendum; constitutional articles including those on national unity, the secularity of Burundi, its democratic form of government, and its sovereignty cannot be amended; amended 2018 (amendments extended the presidential term from 5 to 7 years, reintroduced the position of prime minister, and reduced the number of vice presidents from 2 to 1)
Legal system
mixed legal system of Belgian civil law and customary law
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; withdrew from ICCt in October 2017
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Burundi
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Evariste NDAYISHIMIYE (since 18 June 2020); Vice President Prosper BAZOMBANZA (since 24 June 2020); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Evariste NDAYISHIMIYE (since 18 June 2020); Vice President Prosper BAZOMBANZA (since 24 June 2020); Prime Minister Alain-Guillaume BUNYONI (since 24 June 2020)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 7-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 20 May 2020 (next to be held in 2025); vice presidents nominated by the president, endorsed by Parliament; note - a 2018 constitutional referendum effective for the 2020 election, increased the presidential term from 5 to 7 years with a 2-consecutive-term limit, reinstated the position of the prime minister position, and reduced the number of vice presidents from 2 to 1
election results: Evariste NDAYISHIMIYE elected president; percent of vote - Evariste NDAYISHIMIYE (CNDD-FDD) 71.5%, Agathon RWASA (CNL) 25.2%, Gaston SINDIMWO (UPRONA) 1.7%, OTHER 1.6%
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliament or Parlement consists of:
Senate or Inama Nkenguzamateka (39 seats in the July 2020 election); 36 members indirectly elected by an electoral college of provincial councils using a three-round voting system, which requires a two-thirds majority vote in the first two rounds and simple majority vote for the two leading candidates in the final round; 3 seats reserved for Twas, and 30% of all votes reserved for women; members serve 5-year terms)
National Assembly or Inama Nshingamateka (123 seats in the May 2020 election; 100 members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote and 23 co-opted members; 60% of seats allocated to Hutu and 40% to Tutsi; 3 seats reserved for Twas; 30% of total seats reserved for women; members serve 5-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last held on 20 July 2020 (next to be held in 2025)
National Assembly - last held on 20 May 2020 (next to be held in 2025)
election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - CNDD-FDD 87.2%, Twa 7.7%, CNL 2.6%, UPRONA 2.6%; seats by party - CNDD-FDD 34, CNL 1, UPRONA 1, Twa 3; composition - men 23, women 16, percent of women 37.2%
National Assembly - percent of vote by party - CNDD-FDD 70.9%, CNL 23.4%, UPRONA 2.5%, other (co-opted Twa) 3.2%; seats by party - CNDD-FDD 86, CNL 32, UPRONA 2, Twa 3; composition - men 76, women 47, percent of women 38.2%; note - total Parliament percent of women 38%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of 9 judges and organized into judicial, administrative, and cassation chambers); Constitutional Court (consists of 7 members)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by the Judicial Service Commission, a 15-member independent body of judicial and legal profession officials), appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate and serve 6-year nonrenewable terms
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; County Courts; Courts of Residence; Martial Court; Court Against Corruption; Commercial Court
Political parties and leaders
Front for Democracy in Burundi-Nyakuri or FRODEBU-Nyakuri [Keffa NIBIZI]
Front for Democracy in Burundi-Sahwanya or FRODEBU-Sahwanya [Pierre Claver NAHIMANA]
National Congress for Liberty or CNL [Agathon RWASA]
National Council for the Defense of Democracy - Front for the Defense of Democracy or CNDD-FDD [Evariste NDAYISHIMIYE]
National Liberation Forces or FNL [Jacques BIGITIMANA]
Union for National Progress (Union pour le Progress Nationale) or UPRONA [Abel GASHATSI]
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, CEMAC, CEPGL, CICA, COMESA, EAC, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Jean de Dieu NDIKUMANA (since 7 July 2021)
chancery: 2233 Wisconsin Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone: [1] (202) 342-2574
FAX: [1] (202) 342-2578
email address and website:
burundiembusadc@gmail.com
https://burundiembassy-usa.com/index.php
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Melanie Harris HIGGINS (since 2 March 2021)
embassy: B.P. 1720, Avenue Des Etats-Unis, Bujumbura
mailing address: 2100 Bujumbura Place, Washington DC 20521-2100
telephone: [257] 22-207-000
FAX: [257] 22-222-926
email address and website:
BujumburaC@state.gov
https://bi.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
divided by a white diagonal cross into red panels (top and bottom) and green panels (hoist side and fly side) with a white disk superimposed at the center bearing three red six-pointed stars outlined in green arranged in a triangular design (one star above, two stars below); green symbolizes hope and optimism, white purity and peace, and red the blood shed in the struggle for independence; the three stars in the disk represent the three major ethnic groups: Hutu, Twa, Tutsi, as well as the three elements in the national motto: unity, work, progress
National symbol(s)
lion; national colors: red, white, green
National anthem
name: "Burundi Bwacu" (Our Beloved Burundi)
lyrics/music: Jean-Baptiste NTAHOKAJA/Marc BARENGAYABO
note: adopted 1962
Economy
Economic overview
Burundi is a landlocked, resource-poor country with an underdeveloped manufacturing sector. Agriculture accounts for over 40% of GDP and employs more than 90% of the population. Burundi's primary exports are coffee and tea, which account for more than half of foreign exchange earnings, but these earnings are subject to fluctuations in weather and international coffee and tea prices, Burundi is heavily dependent on aid from bilateral and multilateral donors, as well as foreign exchange earnings from participation in the African Union Mission to Somalia (AMISOM). Foreign aid represented 48% of Burundi's national income in 2015, one of the highest percentages in Sub-Saharan Africa, but this figure decreased to 33.5% in 2016 due to political turmoil surrounding President NKURUNZIZA’s bid for a third term. Burundi joined the East African Community (EAC) in 2009.
Burundi faces several underlying weaknesses – low governmental capacity, corruption, a high poverty rate, poor educational levels, a weak legal system, a poor transportation network, and overburdened utilities – that have prevented the implementation of planned economic reforms. The purchasing power of most Burundians has decreased as wage increases have not kept pace with inflation, which reached approximately 18% in 2017.
Real GDP growth dropped precipitously following political events in 2015 and has yet to recover to pre-conflict levels. Continued resistance by donors and the international community will restrict Burundi’s economic growth as the country deals with a large current account deficit.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$8.69 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$8.67 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$8.51 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
0% (2017 est.)
-1% (2016 est.)
-4% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$700 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$800 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$800 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$3.027 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
-0.6% (2019 est.)
-2.5% (2018 est.)
15.9% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 39.5% (2017 est.)
industry: 16.4% (2017 est.)
services: 44.2% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 83% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 20.8% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 16% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 5.5% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -25.3% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
cassava, bananas, sweet potatoes, plantains, beans, vegetables, potatoes, cashew nuts, maize, taro
Industries
light consumer goods (sugar, shoes, soap, beer); cement, assembly of imported components; public works construction; food processing (fruits)
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 93.6%
industry: 2.3%
services: 4.1% (2002 est.)
Population below poverty line
64.6% (2014 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
38.6 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 4.1%
highest 10%: 28% (2006)
Budget
revenues: 536.7 million (2017 est.)
expenditures: 729.6 million (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$418 million (2017 est.)
-$411 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$290 million note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$283 million (2018 est.)
$315 million (2017 est.)
Exports - partners
United Arab Emirates 50%, Democratic Republic of the Congo 7% (2019)
Exports - commodities
gold, coffee, tea, raw earth metal ores, wheat flours (2019)
Imports
$910 million note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$927 million (2018 est.)
$1.295 billion (2017 est.)
Imports - partners
China 14%, Saudi Arabia 14%, India 9%, Kenya 7%, United Arab Emirates 7%, Tanzania 5%, Zambia 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, packaged medicines, cement, raw sugar, cars (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$97.4 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$95.17 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$610.9 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$622.4 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Burundi francs (BIF) per US dollar -
1,945 (2020 est.)
1,876.25 (2019 est.)
1,800.495 (2018 est.)
1,571.9 (2014 est.)
1,546.7 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 2.9%
male: 4.4%
female: 2% (2014 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 11% (2019)
electrification - urban areas: 66% (2019)
electrification - rural areas: 2% (2019)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
68,000 kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 186Electricity - from fossil fuels
14% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
73% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14Electricity - from other renewable sources
14% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60Refined petroleum products - consumption
1,500 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 18,300 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 6,631,154 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 55.77 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment:
Burundi’s high population density and low telecom penetration rates make it an attractive market for investors; mobile operators have launched 3G and LTE to meet the demand for Internet; mobile subscription remains low; government/World Bank joint project to build a national broadband backbone connecting to submarine cable landings in Kenya and Tanzania; government launched e-health project (2021)
(2020)domestic: telephone density one of the lowest in the world; fixed-line connections stand at well less than 1 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular usage is 58 per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 257; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean); the government, supported by the Word Bank, has backed a joint venture with a number of prominent telecoms to build a national fiber backbone network, offering onward connectivity to submarine cable infrastructure landings in Kenya and Tanzania (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
state-controlled Radio Television Nationale de Burundi (RTNB) operates a TV station and a national radio network; 3 private TV stations and about 10 privately owned radio stations; transmissions of several international broadcasters are available in Bujumbura (2019)
Internet users
total: 1.61 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 2.66% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 4,230 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2020 est.)
Transportation
Airports - with paved runways
total: 1
over 3,047 m: 1 (2019)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 6
914 to 1,523 m: 4
under 914 m: 2 (2013)
Heliports
1 (2012)
Roadways
total: 12,322 km (2016)
paved: 1,500 km (2016)
unpaved: 10,822 km (2016)
Waterways
(mainly on Lake Tanganyika between Bujumbura, Burundi's principal port, and lake ports in Tanzania, Zambia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo) (2011)
Ports and terminals
lake port(s): Bujumbura (Lake Tanganyika)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
National Defense Forces (Forces de Defense Nationale, FDN): Army (includes maritime wing, air wing); Ministry of Public Security: National Police (Police Nationale du Burundi) (2021)
Military expenditures
2.1% of GDP (2020 est.)
1.8% of GDP (2019)
1.9% of GDP (2018)
1.8% of GDP (2017)
2.2% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the National Defense Forces (FDN) have approximately 25,000 active duty troops, the majority of which are ground forces (2020)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the FDN is armed mostly with weapons from Russia and the former Soviet Union, with some Western equipment, largely from France; since 2010, the FDN has received small amounts of mostly second-hand equipment from China, South Africa, and the US (2020)
Military deployments
750 Central African Republic (MINUSCA); 5,400 Somalia (AMISOM) (Feb 2021)
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service; the armed forces law of 31 December 2004 did not specify a minimum age for enlistment, but the government claimed that no one younger than 18 was being recruited (2019)
Military - note
in addition to its foreign deployments, the FDN as of 2021 was focused on internal security missions, particularly against rebel groups opposed to the regime such as National Forces of Liberation (FNL), the Resistance for the Rule of Law-Tabara (aka RED Tabara), and Popular Forces of Burundi (FPB or FOREBU); these groups were based in the neighboring Democratic Republic of Congo and have carried out sporadic attacks in Burundi
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Burundi and Rwanda dispute two sq km (0.8 sq mi) of Sabanerwa, a farmed area in the Rukurazi Valley where the Akanyaru/Kanyaru River shifted its course southward after heavy rains in 1965; cross-border conflicts persist among Tutsi, Hutu, other ethnic groups, associated political rebels, armed gangs, and various government forces in the Great Lakes region
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 42,136 (Democratic Republic of the Congo) (refugees and asylum seekers) (2021)
IDPs: 109,169 (some ethnic Tutsis remain displaced from intercommunal violence that broke out after the 1,993 coup and fighting between government forces and rebel groups; violence since April 2015) (2021)
stateless persons: 974 (2020)
Trafficking in persons
current situation: human traffickers exploit domestic and foreign victims in Burundi and victims from Burundi abroad; traffickers take advantage of Burundians in precarious or desperate situations, including returned refugees; children were reportedly recruited by armed groups and forced to participate in anti-government activities; non-state armed groups allegedly used threats, intimidation, and physical assaults to coerce refugees in a camp in Rwanda to support the Burundian opposition; children and young adults are trafficked by relatives, neighbors, and friends and are subjected to forced labor in agriculture, mining, informal commerce, charcoal production, and fishing; some girls and young women are forced into domestic servitude and sex trafficking in restaurants and bars around Lake Tanganyika; women and girls who go to the Middle East for domestic service jobs report physical and sexual abuse
tier rating: Tier 3 — Burundi does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; the government worked with an international organization to provide training to immigration officials, identified victims of trafficking abroad, and conducted public awareness campaigns with an international organization; however, authorities did not convict any traffickers for the fifth consecutive year and did not investigate, prosecute, or convict officials allegedly complicit in human trafficking; the government did not have standard operating procedures to identify and refer victims to services and did not have adequate protection services for victims; authorities continued to lack a clear understanding of trafficking despite the government providing training to immigration officials (2020)