Bosnia and Herzegovina
Introduction
Background
Bosnia and Herzegovina declared sovereignty in October 1991 and independence from the former Yugoslavia on 3 March 1992 after a referendum boycotted by ethnic Serbs. The Bosnian Serbs - supported by neighboring Serbia and Montenegro - responded with armed resistance aimed at partitioning the republic along ethnic lines and joining Serb-held areas to form a "Greater Serbia." In March 1994, Bosniaks and Croats reduced the number of warring factions from three to two by signing an agreement creating a joint Bosniak-Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. On 21 November 1995, in Dayton, Ohio, the warring parties initialed a peace agreement that ended three years of interethnic civil strife (the final agreement was signed in Paris on 14 December 1995).
The Dayton Peace Accords retained Bosnia and Herzegovina's international boundaries and created a multiethnic and democratic government charged with conducting foreign, diplomatic, and fiscal policy. Also recognized was a second tier of government composed of two entities roughly equal in size: the predominantly Bosniak-Bosnian Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the predominantly Bosnian Serb-led Republika Srpska (RS). The Federation and RS governments are responsible for overseeing most government functions. Additionally, the Dayton Accords established the Office of the High Representative to oversee the implementation of the civilian aspects of the agreement. The Peace Implementation Council at its conference in Bonn in 1997 also gave the High Representative the authority to impose legislation and remove officials, the so-called "Bonn Powers." An original NATO-led international peacekeeping force (IFOR) of 60,000 troops assembled in 1995 was succeeded over time by a smaller, NATO-led Stabilization Force (SFOR). In 2004, European Union peacekeeping troops (EUFOR) replaced SFOR. Currently, EUFOR deploys around 600 troops in theater in a security assistance and training capacity.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
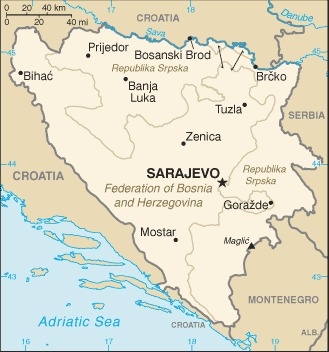
Location
Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea and Croatia
Geographic coordinates
44 00 N, 18 00 E
Map references
Europe
Land boundaries
total: 1,543 km
border countries (3): Croatia 956 km, Montenegro 242 km, Serbia 345 km
Coastline
20 km
Climate
hot summers and cold winters; areas of high elevation have short, cool summers and long, severe winters; mild, rainy winters along coast
Terrain
mountains and valleys
Elevation
highest point: Maglic 2,386 m
lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 500 m
Natural resources
coal, iron ore, antimony, bauxite, copper, lead, zinc, chromite, cobalt, manganese, nickel, clay, gypsum, salt, sand, timber, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land: 42.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 19.7% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 2% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 20.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 42.8% (2018 est.)
other: 15% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
30 sq km (2012)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Black Sea) Danube (795,656 sq km)
Population distribution
the northern and central areas of the country are the most densely populated
Natural hazards
destructive earthquakes
Geography - note
within Bosnia and Herzegovina's recognized borders, the country is divided into a joint Bosniak/Croat Federation (about 51% of the territory) and the Bosnian Serb-led Republika Srpska or RS (about 49% of the territory); the region called Herzegovina is contiguous to Croatia and Montenegro, and traditionally has been settled by an ethnic Croat majority in the west and an ethnic Serb majority in the east
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Bosnian(s), Herzegovinian(s)
adjective: Bosnian, Herzegovinian
Ethnic groups
Bosniak 50.1%, Serb 30.8%, Croat 15.4%, other 2.7%, not declared/no answer 1% (2013 est.)
note: Republika Srpska authorities dispute the methodology and refuse to recognize the results; Bosniak has replaced Muslim as an ethnic term in part to avoid confusion with the religious term Muslim - an adherent of Islam
Languages
Bosnian (official) 52.9%, Serbian (official) 30.8%, Croatian (official) 14.6%, other 1.6%, no answer 0.2% (2013 est.)
major-language sample(s):
Knjiga svjetskih činjenica, neophodan izvor osnovnih informacija. (Bosnian/Montenegrin)
Knjiga svetskih činjenica, neophodan izvor osnovnih informacija. (Serbian)
Knjiga svjetskih činjenica, nužan izvor osnovnih informacija. (Croatian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Muslim 50.7%, Orthodox 30.7%, Roman Catholic 15.2%, atheist 0.8%, agnostic 0.3%, other 1.2%, undeclared/no answer 1.1% (2013 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 13.18% (male 261,430/female 244,242)
15-24 years: 10.83% (male 214,319/female 201,214)
25-54 years: 44.52% (male 859,509/female 848,071)
55-64 years: 15.24% (male 284,415/female 300,168)
65 years and over: 16.22% (male 249,624/female 372,594) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 48
youth dependency ratio: 21.5
elderly dependency ratio: 26.5
potential support ratio: 3.8 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 43.3 years
male: 41.6 years
female: 44.8 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
the northern and central areas of the country are the most densely populated
Urbanization
urban population: 49.4% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 0.61% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
344,000 SARAJEVO (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.67 male(s)/female
total population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
27.7 years (2019 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
10 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143Infant mortality rate
total: 5.32 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 5.44 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 5.19 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 77.74 years
male: 74.76 years
female: 80.93 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
45.8% (2011/12)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 99.9% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 99.9% of population
unimproved: urban: 0.1% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0.1% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
8.9% (2018)
Physicians density
2.16 physicians/1,000 population (2015)
Hospital bed density
3.5 beds/1,000 population (2014)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 98.9% of population
rural: 92.1% of population
total: 95.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 1.1% of population
rural: 7.9% of population
total: 4.5% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
<.1% (2018)
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS
<500 (2018)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<100 (2018)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 98.5%
male: 99.5%
female: 97.5% (2015)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 14 years
male: 14 years
female: 15 years (2014)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 36.6%
male: 32.5%
female: 42.8% (2020 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
air pollution; deforestation and illegal logging; inadequate wastewater treatment and flood management facilities; sites for disposing of urban waste are limited; land mines left over from the 1992-95 civil strife are a hazard in some areas
Environment - international agreements
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 27.25 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 21.85 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 2.92 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
hot summers and cold winters; areas of high elevation have short, cool summers and long, severe winters; mild, rainy winters along coast
Land use
agricultural land: 42.2% (2018 est.)
arable land: 19.7% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 2% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 20.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 42.8% (2018 est.)
other: 15% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 49.4% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 0.61% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.49% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1,248,718 tons (2015 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 12 tons (2015 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 0% (2015 est.)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Black Sea) Danube (795,656 sq km)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 360.8 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 71.8 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
37.5 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Bosnia and Herzegovina
local long form: none
local short form: Bosna i Hercegovina
former: People's Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina
abbreviation: BiH
etymology: the larger northern territory is named for the Bosna River; the smaller southern section takes its name from the German word "herzog," meaning "duke," and the ending "-ovina," meaning "land," forming the combination denoting "dukedom"
Government type
parliamentary republic
Capital
name: Sarajevo
geographic coordinates: 43 52 N, 18 25 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: the name derives from the Turkish noun "saray," meaning "palace" or "mansion," and the term "ova," signifying "plain(s)," to give a meaning of "palace plains" or "the plains about the palace"
Administrative divisions
3 first-order administrative divisions - Brcko District (Brcko Distrikt) (ethnically mixed), Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Federacija Bosne i Hercegovine) (predominantly Bosniak-Croat), Republika Srpska (predominantly Serb)
Independence
1 March 1992 (from Yugoslavia); note - referendum for independence completed on 1 March 1992; independence declared on 3 March 1992
National holiday
Independence Day, 1 March (1992) and Statehood Day, 25 November (1943) - both observed in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina entity; Victory Day, 9 May (1945) and Dayton Agreement Day, 21 November (1995) - both observed in the Republika Srpska entity
note: there is no national-level holiday
Constitution
history: 14 December 1995 (constitution included as part of the Dayton Peace Accords); note - each of the political entities has its own constitution
amendments: decided by the Parliamentary Assembly, including a two-thirds majority vote of members present in the House of Representatives; the constitutional article on human rights and fundamental freedoms cannot be amended; amended several times, last in 2009
Legal system
civil law system; Constitutional Court review of legislative acts
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Bosnia and Herzegovina
dual citizenship recognized: yes, provided there is a bilateral agreement with the other state
residency requirement for naturalization: 8 years
Suffrage
18 years of age, 16 if employed; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: Chairman of the Presidency Zeljko KOMSIC (chairman since 20 July 2021; presidency member since 20 November 2018 - Croat seat); Sefik DZAFEROVIC (presidency member since 20 November 2018 - Bosniak seat); Milorad DODIK (presidency member since 20 November 2018 - Serb seat)
head of government: Chairman of the Council of Ministers Zoran TEGELTIJA (since 5 December 2019)
cabinet: Council of Ministers nominated by the council chairman, approved by the state-level House of Representatives
elections/appointments: 3-member presidency (1 Bosniak and 1 Croat elected from the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and 1 Serb elected from the Republika Srpska) directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term, but then ineligible for 4 years); the presidency chairpersonship rotates every 8 months with the new member of the presidency elected with the highest number of votes starting the new mandate as chair; election last held on 7 October 2018 (next to be held in October 2022); the chairman of the Council of Ministers appointed by the presidency and confirmed by the state-level House of Representatives
election results:
2018: percent of vote - Milorad DODIK (SNSD) 53.9% - Serb seat; Zeljko KOMSIC (DF) 52.6% - Croat seat; Sefik DZAFEROVIC (SDA) 36.6% - Bosniak seat
2014: percent of vote - Mladen IVANIC (PDP) 48.7% - Serb seat; Dragan COVIC (HDZ-BiH) 52.2% - Croat seat; Bakir IZETBEGOVIC (SDA) 32.9% - Bosniak seat
note: President of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina Marinko CAVARA (since 9 February 2015); Vice Presidents Melika MAHMUTBEGOVIC (since 9 February 2015), Milan DUNOVIC (since 9 February 2015); President of the Republika Srpska Zeljka CVIJANOVIC (since 18 November 2018); Vice Presidents Ramiz SALKIC (since 24 November 2014), Josip JERKOVIC (since 24 November 2014)
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliamentary Assembly or Skupstina consists of:
House of Peoples or Dom Naroda (15 seats - 5 Bosniak, 5 Croat, 5 Serb; members designated by the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina's House of Peoples and the Republika Srpska's National Assembly to serve 4-year terms)
House of Representatives or Predstavnicki Dom (42 seats to include 28 seats allocated to the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and 14 to the Republika Srpska; members directly elected by proportional representation vote to serve 4-year terms); note - the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina has a bicameral legislature that consists of the House of Peoples (58 seats - 17 Bosniak, 17 Croat, 17 Serb, 7 other) and the House of Representatives (98 seats; members directly elected by proportional representation vote to serve 4-year terms); Republika Srpska's unicameral legislature is the National Assembly (83 directly elected delegates serve 4-year terms)
elections: House of Peoples - last held on 18 October 2018 (next to be held in October 2022)
House of Representatives - last held on 7 October 2018 (next to be held in October 2022)
election results: House of Peoples - percent of vote by coalition/party - NA; seats by coalition/party - NA; composition - men 13, women 2, percent of women 13.3%
House of Representatives - percent of vote by coalition/party - SDA 17%, SNSD 16%, SDS/NDP/NS/SRS-VS 9.8%, SDP 9.1%, HDZ-BiH/HSS/HKDU/HSP-AS BiH/HDU BiH 9.1%, DF, 5.8%, PDP 5.1%, DNS 4.2%, SBB BiH 4.2%, NS/HC 2.9%, NB 2.5%, PDA 2.3%, SP 1.9%, A-SDA 1.8%, other 17.4%; seats by coalition/party - SDA 9, SNSD 6, SDP 5, HDZ-BiH/HSS/HKDU/HSP-AS BiH/HDU BiH 5, SDS/NDP/NS/SRS-VS 3, DF 3, PDP 2, SBB BiH 2, NS/HC 2, DNS 1, NB 1 PDA 1, SP 1, A-SDA 1; composition - men 33, women 9, percent of women 21.4%; note - total Parliamentary Assembly percent of women 19.3%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH) Constitutional Court (consists of 9 members); Court of BiH (consists of 44 national judges and 7 international judges organized into 3 divisions - Administrative, Appellate, and Criminal, which includes a War Crimes Chamber)
judge selection and term of office: BiH Constitutional Court judges - 4 selected by the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina House of Representatives, 2 selected by the Republika Srpska's National Assembly, and 3 non-Bosnian judges selected by the president of the European Court of Human Rights; Court of BiH president and national judges appointed by the High Judicial and Prosecutorial Council; Court of BiH president appointed for renewable 6-year term; other national judges appointed to serve until age 70; international judges recommended by the president of the Court of BiH and appointed by the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina; international judges appointed to serve until age 70
subordinate courts: the Federation has 10 cantonal courts plus a number of municipal courts; the Republika Srpska has a supreme court, 5 district courts, and a number of municipal courts
Political parties and leaders
Alliance for a Better Future of BiH or SBB BiH [Fahrudin RADONCIC]
Alliance of Independent Social Democrats or SNSD [Milorad DODIK]
Alternative Party for Democratic Activity or A-SDA [Nermin OGRESEVIC] (merged with Independent Bosnian Herzegovinian List to form NES)
Croat Peasants' Party or HSS [Mario KARAMATIC]
Croatian Christian Democratic Union of Bosnia and Herzegovina or HKDU [Ivan MUSA]
Croatian Democratic Union of Bosnia and Herzegovina or HDU-BiH [Miro GRABOVAC-TITAN]
Croatian Democratic Union of Bosnia and Herzegovina or HDZ-BiH [Dragan COVIC]
Croatian Democratic Union 1990 or HDZ-1990 [Ilija CVITANOVIC]
Croatian Party of Rights dr. Ante Starcevic or HSP-AS Bih [Stanko PRIMORAC]
Democratic Alliance or DEMOS [Nedeljko CUBRILOVIC]
Democratic Front of DF [Zeljko KOMSIC]
Democratic Peoples' Alliance or DNS [Nenad NESIC]
Independent Bloc or NB [Senad SEPIC]
Movement for Democratic Action or PDA [Mirsad KUKIC]
People and Justice Party or NiP [elmedin KONAKOVIC]
People's European Union of Bosnia and Herzegovina or NES [Nermin OGRESEVIC]
Progressive Srpska or NS [Goran DORDIC]
Our Party or NS/HC [Edin FORTO]
Party for Democratic Action or SDA [Bakir IZETBEGOVIC]
Party of Democratic Progress or PDP [Branislav BORENOVIC]
People's Democratic Movement or NDP [Dragan CAVIC]
Serb Democratic Party or SDS [Mirko SAROVIC]
Serb Radical Party-Dr. Vojislav Seselj or SRS-VS [Vojislav SESELJ] (merged with PDP)
Social Democratic Party or SDP [Nermin NIKSIC]
Socialist Party or SP [Petar DOKIC]
United Srpska or US [Nenad STEVANDIC]
International organization participation
BIS, CD, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, NAM (observer), OAS (observer), OIC (observer), OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PFP, SELEC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Bojan VUJIC (since 16 September 2019)
chancery: 2109 E Street NW, Washington, DC 20037
telephone: [1] (202) 337-1500
FAX: [1] (202) 337-1502
email address and website:
consularaffairs@bhembassy; info@bhembassy.org
http://www.bhembassy.org/index.html
consulate(s) general: Chicago, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Eric NELSON (since 19 February 2019)
embassy: 1 Robert C. Frasure Street, 71000 Sarajevo
mailing address: 7130 Sarajevo Place, Washington DC 20521-7130
telephone: [387] (33) 704-000
FAX: [387] (33) 659-722
email address and website:
sarajevoACS@state.gov
https://ba.usembassy.gov/
branch office(s): Banja Luka, Mostar
Flag description
a wide blue vertical band on the fly side with a yellow isosceles triangle abutting the band and the top of the flag; the remainder of the flag is blue with seven full five-pointed white stars and two half stars top and bottom along the hypotenuse of the triangle; the triangle approximates the shape of the country and its three points stand for the constituent peoples - Bosniaks, Croats, and Serbs; the stars represent Europe and are meant to be continuous (thus the half stars at top and bottom); the colors (white, blue, and yellow) are often associated with neutrality and peace, and traditionally are linked with Bosnia
note: one of several flags where a prominent component of the design reflects the shape of the country; other such flags are those of Brazil, Eritrea, and Vanuatu
National symbol(s)
golden lily; national colors: blue, yellow, white
National anthem
name: "Drzavna himna Bosne i Hercegovine" (The National Anthem of Bosnia and Herzegovina)
lyrics/music: none officially; Dusan SESTIC and Benjamin ISOVIC/Dusan SESTIC
note: music adopted 1999; lyrics proposed in 2009 and others in 2016 were not approved; a parliamentary committee launched a new initiative for lyrics in February 2018
Economy
Economic overview
Bosnia and Herzegovina has a transitional economy with limited market reforms. The economy relies heavily on the export of metals, energy, textiles, and furniture as well as on remittances and foreign aid. A highly decentralized government hampers economic policy coordination and reform, while excessive bureaucracy and a segmented market discourage foreign investment. The economy is among the least competitive in the region. Foreign banks, primarily from Austria and Italy, control much of the banking sector, though the largest bank is a private domestic one. The konvertibilna marka (convertible mark) - the national currency introduced in 1998 - is pegged to the euro through a currency board arrangement, which has maintained confidence in the currency and has facilitated reliable trade links with European partners. Bosnia and Herzegovina became a full member of the Central European Free Trade Agreement in September 2007. In 2016, Bosnia began a three-year IMF loan program, but it has struggled to meet the economic reform benchmarks required to receive all funding installments.
Bosnia and Herzegovina's private sector is growing slowly, but foreign investment dropped sharply after 2007 and remains low. High unemployment remains the most serious macroeconomic problem. Successful implementation of a value-added tax in 2006 provided a steady source of revenue for the government and helped rein in gray-market activity, though public perceptions of government corruption and misuse of taxpayer money has encouraged a large informal economy to persist. National-level statistics have improved over time, but a large share of economic activity remains unofficial and unrecorded.
Bosnia and Herzegovina's top economic priorities are: acceleration of integration into the EU; strengthening the fiscal system; public administration reform; World Trade Organization membership; and securing economic growth by fostering a dynamic, competitive private sector.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$47.05 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$49.17 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$47.82 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
3% (2017 est.)
3.2% (2016 est.)
3.1% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$14,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$14,900 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$14,400 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$20.078 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
1.2% (2017 est.)
-1.1% (2016 est.)
Credit ratings
Moody's rating: B3 (2012)
Standard & Poors rating: B (2011)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 6.8% (2017 est.)
industry: 28.9% (2017 est.)
services: 64.3% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 77.4% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 20% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 16.6% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 2.3% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 38.7% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -55.1% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
maize, milk, vegetables, potatoes, wheat, plums/sloes, apples, barley, cabbages, poultry
Industries
steel, coal, iron ore, lead, zinc, manganese, bauxite, aluminum, motor vehicle assembly, textiles, tobacco products, wooden furniture, ammunition, domestic appliances, oil refining
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 18%
industry: 30.4%
services: 51.7% (2017 est.)
Unemployment rate
33.28% (2019 est.)
35.97% (2018 est.)
note: official rate; actual rate is lower as many technically unemployed persons work in the gray economy
Population below poverty line
16.9% (2015 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
33 (2011 est.)
33.1 (2007)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2.9%
highest 10%: 25.8% (2011 est.)
Budget
revenues: 7.993 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 7.607 billion (2017 est.)
Public debt
39.5% of GDP (2017 est.)
44.1% of GDP (2016 est.)
note: data cover general government debt and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions.
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$873 million (2017 est.)
-$821 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$6.81 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$8.17 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$8.57 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
Germany 14%, Italy 12%, Croatia 11%, Serbia 11%, Austria 9%, Slovenia 8% (2019)
Exports - commodities
electricity, seating, leather shoes, furniture, insulated wiring (2019)
Imports
$9.71 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$11.15 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$11.55 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
Croatia 15%, Serbia 13%, Germany 10%, Italy 9%, Slovenia 7%, China 6% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, cars, packaged medicines, coal, electricity (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$6.474 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$5.137 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$10.87 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$10.64 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
konvertibilna markas (BAM) per US dollar -
1.729 (2017 est.)
1.7674 (2016 est.)
1.7674 (2015 est.)
1.7626 (2014 est.)
1.4718 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 36.6%
male: 32.5%
female: 42.8% (2020 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
4.676 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83Electricity - from fossil fuels
49% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
51% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35Electricity - from other renewable sources
1% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147Refined petroleum products - consumption
32,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 706,135 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 5.12 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 3,509,674 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 107 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment:
Bosnia-Herzegovina aims for national LTE coverage through integration with European Union (EU); roaming agreements with EU and Balkan neighbors; fixed-line broadband is underdeveloped, investments in mobile upgrades facilitate broadband connectivity to a greater extent than in Europe; DSL and cable are the main platforms for fixed-line connectivity while fiber broadband has a small market presence; operators support broadband in rural areas where fixed-line infrastructure is insufficient; LTE services under test licenses; 5G awaits market maturity; importer of broadcasting equipment from China
(2021)domestic: fixed-line teledensity roughly 24 per 100 persons and mobile-cellular subscribership has been increasing rapidly and stands at roughly 112 telephones per 100 persons (2019)
international: country code - 387; no satellite earth stations
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
3 public TV broadcasters: Radio and TV of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Federation TV (operating 2 networks), and Republika Srpska Radio-TV; a local commercial network of 5 TV stations; 3 private, near-national TV stations and dozens of small independent TV broadcasting stations; 3 large public radio broadcasters and many private radio stations
Internet users
total: 2.32 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 73.21% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 770,624 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 23.49 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 1 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 1
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 7,070 (2015)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 87 mt-km (2015)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 7
2,438 to 3,047 m: 4
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
under 914 m: 2 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 17
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 5
under 914 m: 11 (2013)
Heliports
6 (2013)
Pipelines
147 km gas, 9 km oil (2013)
Railways
total: 965 km (2014)
standard gauge: 965 km 1.435-m gauge (565 km electrified) (2014)
Roadways
total: 22,926 km (2010)
paved: 19,426 km (4,652 km of interurban roads) (2010)
unpaved: 3,500 km (2010)
Waterways
(Sava River on northern border; open to shipping but use limited) (2011)
Ports and terminals
river port(s): Bosanska Gradiska, Bosanski Brod, Bosanski Samac, Brcko, Orasje (Sava River)
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Oruzanih Snaga Bosne i Hercegovine, OSBiH): Operations Command (includes Army, Air, and Air Defense units), Support Command (2021)
Military expenditures
0.9% of GDP (2021 est.)
0.9% of GDP (2020)
0.9% of GDP (2019)
0.9% of GDP (2018)
0.9% of GDP (2017)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina have approximately 9,000 active duty personnel (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the inventory for the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina includes mainly Soviet-era weapons systems with a small and varied mix of older European and US equipment (2021)
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service; mandatory retirement at age 35 or after 15 years of service for E-1 through E-4, mandatory retirement at age 50 and 30 years of service for E-5 through E-9, mandatory retirement at age 55 and 30 years of service for all officers; conscription abolished in 2005 (2019)
Military - note
the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina are comprised of the former Bosnian-Croat Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Vojska Federacije Bosne i Hercegovin, VF) and the Bosnian-Serb Republic of Serbia Army (Vojska Republike Srpske, VRS); the two forces were unified under the 2003 Law on Defense, which also established the country’s Ministry of Defense
Bosnia and Herzegovina joined NATO’s Partnership for Peace (PfP) program in 2007 and was invited to join NATO’s Membership Action Plan in 2010; as of 2021, NATO maintained a military headquarters in Sarajevo with the mission of assisting Bosnia and Herzegovina with the PfP program and promoting closer integration with NATO, as well as providing logistics and other support to the European Union Force deployed there
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps/Qods Force
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Serbia delimited about half of the boundary with Bosnia and Herzegovina, but sections along the Drina River remain in dispute
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees (country of origin): 5,112 (Croatia) (2020)
IDPs: 99,000 (Bosnian Croats, Serbs, and Bosniaks displaced by inter-ethnic violence, human rights violations, and armed conflict during the 1992-95 war) (2020)
stateless persons: 66 (2020)
note: 85,765 estimated refugee and migrant arrivals (January 2015-December 2021)
Trafficking in persons
current situation: human traffickers exploit domestic and foreign victims in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Bosnians and Herzegovinians abroad; Bosnian and foreign women and girls are sex trafficked within the country; Bosnians are also exploited through forced labor in construction and other industries in neighboring Balkan countries and throughout Europe; thousands of migrants and refugees smuggled through Bosnia and Herzegovina are vulnerable to trafficking, especially women and unaccompanied minors; Romani children are victims of forced begging, sex trafficking, and domestic servitude
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List — Bosnia and Herzegovina does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking but is making significant efforts to do so; because the government devoted sufficient resources to a written plan that, if implemented, would constitute significant efforts to meet minimum standards, Bosnia and Herzegovina was granted a waiver from being downgraded to Tier 3; the government adopted a national strategy in January 2020; the State Prosecutor’s Office appointed a prosecutor to the anti-trafficking strike force, the only mechanism to coordinate law enforcement efforts across entities on trafficking cases; the government identified more trafficking victims and revised the structure and guidelines of regional coordinating teams to increase effectiveness; however, the lack of an approved state budget delayed funding for anti-trafficking efforts; law enforcement continued to regularly investigate trafficking under lesser offenses, while judges continued to issue sentences below the minimum penalty; the government continued to penalize victims and did not disburse annual funds to NGOs for victim protection (2020)
Illicit drugs
drug trafficking groups are major players in the procurement and transportation of large quantities of cocaine destined for European markets