Introduction
Background
Belize was the site of several Mayan city states until their decline at the end of the first millennium A.D. The British and Spanish disputed the region in the 17th and 18th centuries; it formally became the colony of British Honduras in 1862. Territorial disputes between the UK and Guatemala delayed the independence of Belize until 1981. Guatemala refused to recognize the new nation until 1992 and the two countries are involved in an ongoing border dispute. Both nations have voted to send the dispute for final resolution to the International Court of Justice. Tourism has become the mainstay of the economy. Current concerns include the country's heavy foreign debt burden, high crime rates, high unemployment combined with a majority youth population, growing involvement in the Mexican and South American drug trade, and one of the highest HIV/AIDS prevalence rates in Central America.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
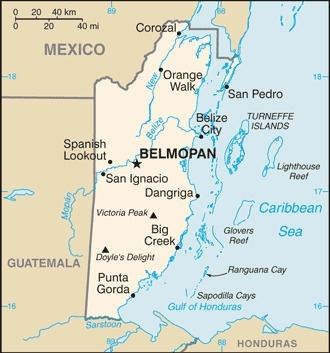
Central America, bordering the Caribbean Sea, between Guatemala and Mexico
Geographic coordinates
17 15 N, 88 45 W
Map references
Central America and the Caribbean
Area - comparative
slightly smaller than Massachusetts
Land boundaries
total: 542 km
border countries (2): Guatemala 266 km, Mexico 276 km
Coastline
386 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm in the north, 3 nm in the south; note - from the mouth of the Sarstoon River to Ranguana Cay, Belize's territorial sea is 3 nm; according to Belize's Maritime Areas Act, 1992, the purpose of this limitation is to provide a framework for negotiating a definitive agreement on territorial differences with Guatemala
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; very hot and humid; rainy season (May to November); dry season (February to May)
Terrain
flat, swampy coastal plain; low mountains in south
Elevation
highest point: Doyle's Delight 1,124 m
lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 173 m
Natural resources
arable land potential, timber, fish, hydropower
Land use
agricultural land: 6.9% (2018 est.)
arable land: 3.3% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.4% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 2.2% (2018 est.)
forest: 60.6% (2018 est.)
other: 32.5% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
35 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
approximately 25% to 30% of the population lives in the former capital, Belize City; over half of the overall population is rural; population density is slightly higher in the north and east
Natural hazards
frequent, devastating hurricanes (June to November) and coastal flooding (especially in south)
Geography - note
only country in Central America without a coastline on the North Pacific Ocean
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Belizean(s)
adjective: Belizean
Ethnic groups
Mestizo 52.9%, Creole 25.9%, Maya 11.3%, Garifuna 6.1%, East Indian 3.9%, Mennonite 3.6%, White 1.2%, Asian 1%, other 1.2%, unknown 0.3% (2010 est.)
note: percentages add up to more than 100% because respondents were able to identify more than one ethnic origin
Languages
English 62.9% (official), Spanish 56.6%, Creole 44.6%, Maya 10.5%, German 3.2%, Garifuna 2.9%, other 1.8%, unknown 0.3%, none 0.2% (cannot speak); note - shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census (2010 est.)
major-language sample(s):
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information. (English)
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
Religions
Roman Catholic 40.1%, Protestant 31.5% (includes Pentecostal 8.4%, Seventh Day Adventist 5.4%, Anglican 4.7%, Mennonite 3.7%, Baptist 3.6%, Methodist 2.9%, Nazarene 2.8%), Jehovah's Witness 1.7%, other 10.5% (includes Baha'i, Buddhist, Hindu, Church of Jesus Christ, Muslim, Rastafarian, Salvation Army), unspecified 0.6%, none 15.5% (2010 est.)
Demographic profile
Migration continues to transform Belize's population. About 16% of Belizeans live abroad, while immigrants constitute approximately 15% of Belize's population. Belizeans seeking job and educational opportunities have preferred to emigrate to the United States rather than former colonizer Great Britain because of the United States' closer proximity and stronger trade ties with Belize. Belizeans also emigrate to Canada, Mexico, and English-speaking Caribbean countries. The emigration of a large share of Creoles (Afro-Belizeans) and the influx of Central American immigrants, mainly Guatemalans, Salvadorans, and Hondurans, has changed Belize's ethnic composition. Mestizos have become the largest ethnic group, and Belize now has more native Spanish speakers than English or Creole speakers, despite English being the official language. In addition, Central American immigrants are establishing new communities in rural areas, which contrasts with the urbanization trend seen in neighboring countries. Recently, Chinese, European, and North American immigrants have become more frequent.
Immigration accounts for an increasing share of Belize's population growth rate, which is steadily falling due to fertility decline. Belize's declining birth rate and its increased life expectancy are creating an aging population. As the elderly population grows and nuclear families replace extended households, Belize's government will be challenged to balance a rising demand for pensions, social services, and healthcare for its senior citizens with the need to reduce poverty and social inequality and to improve sanitation.
Age structure
0-14 years: 32.57% (male 66,454/female 63,700)
15-24 years: 19% (male 39,238/female 36,683)
25-54 years: 37.72% (male 73,440/female 77,300)
55-64 years: 6.18% (male 12,235/female 12,444)
65 years and over: 4.53% (male 8,781/female 9,323) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 52
youth dependency ratio: 44.4
elderly dependency ratio: 7.6
potential support ratio: 13.1 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 23.9 years
male: 23 years
female: 24.8 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
approximately 25% to 30% of the population lives in the former capital, Belize City; over half of the overall population is rural; population density is slightly higher in the north and east
Urbanization
urban population: 46.2% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 2.3% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
23,000 BELMOPAN (capital) (2018)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.95 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.94 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
36 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104Infant mortality rate
total: 11.4 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 12.64 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 10.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 75.56 years
male: 73.96 years
female: 77.24 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
51.4% (2015/16)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 98.6% of population
total: 99.2% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 1.4% of population
total: 0.8% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
5.7% (2018)
Physicians density
1.12 physicians/1,000 population (2017)
Hospital bed density
1 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 98.8% of population
rural: 95.3% of population
total: 96.9% of population
unimproved: urban: 1.2% of population
rural: 4.7% of population
total: 3.1% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<200 (2020 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 13 years
male: 13 years
female: 13 years (2020)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 19.3%
male: 12.7%
female: 28.5% (2019 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation; water pollution, including pollution of Belize's Barrier Reef System, from sewage, industrial effluents, agricultural runoff; inability to properly dispose of solid waste
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 21.23 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 0.57 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 0.55 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
tropical; very hot and humid; rainy season (May to November); dry season (February to May)
Land use
agricultural land: 6.9% (2018 est.)
arable land: 3.3% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.4% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 2.2% (2018 est.)
forest: 60.6% (2018 est.)
other: 32.5% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 46.2% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 2.3% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.31% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 101,379 tons (2015 est.)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 11.4 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 21.2 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 68.4 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
21.734 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Belize
former: British Honduras
etymology: may be named for the Belize River, whose name possibly derives from the Maya word "belix," meaning "muddy-watered"
Government type
parliamentary democracy (National Assembly) under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm
Capital
name: Belmopan
geographic coordinates: 17 15 N, 88 46 W
time difference: UTC-6 (1 hour behind Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the decision to move the capital of the country inland to higher and more stable land was made in the 1960s; the name chosen for the new city was formed from the union of two words: "Belize," the name of the longest river in the country, and "Mopan," one of the rivers in the area of the new capital that empties into the Belize River
Administrative divisions
6 districts; Belize, Cayo, Corozal, Orange Walk, Stann Creek, Toledo
Independence
21 September 1981 (from the UK)
National holiday
Battle of St. George's Caye Day (National Day), 10 September (1798); Independence Day, 21 September (1981)
Constitution
history: previous 1954, 1963 (preindependence); latest signed and entered into force 21 September 1981
amendments: proposed and adopted by two-thirds majority vote of the National Assembly House of Representatives except for amendments relating to rights and freedoms, changes to the Assembly, and to elections and judiciary matters, which require at least three-quarters majority vote of the House; both types of amendments require assent of the governor general; amended several times, last in 2017
Legal system
English common law
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor Froyla TZALAM (since 27 May 2021)
head of government: Prime Minister Juan Antonio BRICENO (since 12 November 2020); Deputy Prime Minister Cordel HYDE (since 16 November 2020)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister from among members of the National Assembly
elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the governor general; prime minister recommends the deputy prime minister
Legislative branch
description: bicameral National Assembly consists of:
Senate (14 seats, including the president); members appointed by the governor general - 6 on the advice of the prime minister, 3 on the advice of the leader of the opposition, and 1 each on the advice of the Belize Council of Churches and Evangelical Association of Churches, the Belize Chamber of Commerce and Industry and the Belize Better Business Bureau, non-governmental organizations in good standing, and the National Trade Union Congress and the Civil Society Steering Committee; Senate president elected from among the Senate members or from outside the Senate; members serve 5-year terms
House of Representatives (31 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 5-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last appointed 11 November 2020 (next appointments in November 2025)
House of Representatives - last held on 11 November 2020 (next to be held in November 2025)
election results: Senate - all members appointed; composition - men 9, women 5, percent of women 35.7%
House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - PUP 59.6%, UDP 38.8%, other 1.6%; seats by party - PUP 26, UDP 5; composition - men 27, women 4, percent of women 12.9%; note - total percent of women in the National Assembly 20%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court of Judicature (consists of the Court of Appeal with the court president and 3 justices, and the Supreme Court with the chief justice and 10 justices); note - in 2010, Belize acceded to the Caribbean Court of Justice as the final court of appeal, replacing that of the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in London
judge selection and term of office: Court of Appeal president and justices appointed by the governor-general upon advice of the prime minister after consultation with the National Assembly opposition leader; justices' tenures vary by terms of appointment; Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the governor-general upon the advice of the prime minister and the National Assembly opposition leader; other judges appointed by the governor-general upon the advice of the Judicial and Legal Services Section of the Public Services Commission and with the concurrence of the prime minister after consultation with the National Assembly opposition leader; judges can be appointed beyond age 65 but must retire by age 75; in 2013, the Supreme Court chief justice overturned a constitutional amendment that had restricted Court of Appeal judge appointments to as short as 1 year
subordinate courts: Magistrates' Courts; Family Court
Political parties and leaders
Belize Progressive Party or BPP [Patrick ROGERS] (formed in 2015 from a merger of the People's National Party, elements of the Vision Inspired by the People, and other smaller political groups)
People's United Party or PUP [Johnny BRICENO]
United Democratic Party or UDP [Dean Oliver BARROW]
Vision Inspired by the People or VIP [Hubert ENRIQUEZ]
International organization participation
ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CD, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ITU, LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, SICA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Lynn Raymond YOUNG (since 7 July 2021)
chancery: 2535 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008-2826
telephone: [1] (202) 332-9636
FAX: [1] (202) 332-6888
email address and website:
reception.usa@mfa.gov.bz
https://www.belizeembassyusa.mfa.gov.bz/
consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, New York (consular services temporarily suspended beginning 18 December 2020)
consulate(s): Miami
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d’Affaires Leyla MOSES-ONES(since August 2021)
embassy: Floral Park Road, Belmopan, Cayo
mailing address: 3050 Belmopan Place, Washington DC 20521-3050
telephone: (501) 822-4011
FAX: (501) 822-4012
email address and website:
ACSBelize@state.gov
https://bz.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
royal blue with a narrow red stripe along the top and the bottom edges; centered is a large white disk bearing the coat of arms; the coat of arms features a shield flanked by two workers in front of a mahogany tree with the related motto SUB UMBRA FLOREO (I Flourish in the Shade) on a scroll at the bottom, all encircled by a green garland of 50 mahogany leaves; the colors are those of the two main political parties: blue for the PUP and red for the UDP; various elements of the coat of arms - the figures, the tools, the mahogany tree, and the garland of leaves - recall the logging industry that led to British settlement of Belize
note: Belize's flag is the only national flag that depicts human beings; two British overseas territories, Montserrat and the British Virgin Islands, also depict humans
National symbol(s)
Baird's tapir (a large, browsing, forest-dwelling mammal), keel-billed toucan, Black Orchid; national colors: red, blue
National anthem
name: Land of the Free
lyrics/music: Samuel Alfred HAYNES/Selwyn Walford YOUNG
note: adopted 1981; as a Commonwealth country, in addition to the national anthem, "God Save the Queen" serves as the royal anthem (see United Kingdom)
Economy
Economic overview
Tourism is the number one foreign exchange earner in this small economy, followed by exports of sugar, bananas, citrus, marine products, and crude oil.
The government's expansionary monetary and fiscal policies, initiated in September 1998, led to GDP growth averaging nearly 4% in 1999-2007, but GPD growth has averaged only 2.1% from 2007-2016, with 2.5% growth estimated for 2017. Belize’s dependence on energy imports makes it susceptible to energy price shocks.
Although Belize has the third highest per capita income in Central America, the average income figure masks a huge income disparity between rich and poor, and a key government objective remains reducing poverty and inequality with the help of international donors. High unemployment, a growing trade deficit and heavy foreign debt burden continue to be major concerns. Belize faces continued pressure from rising sovereign debt, and a growing trade imbalance.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$2.43 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$2.83 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$2.78 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
0.8% (2017 est.)
-0.5% (2016 est.)
3.8% (2015 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$6,100 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$7,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$7,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$1.854 billion (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Moody's rating: Caa3 (2020)
Standard & Poors rating: CCC+ (2020)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 10.3% (2017 est.)
industry: 21.6% (2017 est.)
services: 68% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 75.1% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 15.2% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 22.5% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 1.2% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 49.1% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -63.2% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
sugar care, oranges, bananas, maize, poultry, rice, sorghum, papayas, grapefruit, soybeans
Industries
garment production, food processing, tourism, construction, oil
Labor force
120,500 (2008 est.)
note: shortage of skilled labor and all types of technical personnel
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 10.2%
industry: 18.1%
services: 71.7% (2007 est.)
Population below poverty line
41% (2013 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 553.5 million (2017 est.)
expenditures: 572 million (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
1 April - 31 March
Current account balance
-$143 million (2017 est.)
-$163 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$710 million note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$1.1 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$1.07 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
United Kingdom 27%, United States 24%, Spain 6%, Jamaica 5%, Ireland 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
raw sugar, bananas, fruit juice, fish products, crude petroleum (2019)
Imports
$900 million note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$1.2 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$1.16 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
United States 36%, China 13%, Mexico 12%, Guatemala 10% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, cigarettes, recreational boats, natural gas, cars (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$312.1 million (31 December 2017 est.)
$376.7 million (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$1.315 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$1.338 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Belizean dollars (BZD) per US dollar -
2 (2017 est.)
2 (2016 est.)
2 (2015 est.)
2 (2014 est.)
2 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 19.3%
male: 12.7%
female: 28.5% (2019 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 99.5% (2018)
electrification - urban areas: 98.2% (2018)
electrification - rural areas: 100% (2018)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
198,000 kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165Electricity - from fossil fuels
51% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
27% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73Electricity - from other renewable sources
22% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32Refined petroleum products - consumption
4,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 18,500 (2019)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4.74 (2019 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 254,919 (2019)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 65.3 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Belize’s fixed-line tele-density and mobile penetration is lower than average for the region, due to insufficient competition, underinvestment in services, and lax standards; mobile accounts for 90% of all phones; operator aims to provide cheaper prices and customer retention through investment in broadband to over 80% of premises and LTE infrastructure; operator launched safe cities project to fight crime; government distributed tablets to students to promote e-learning; submarine cable to Ambergris Caye enables FttP service in San Pedro; importer of broadcast equipment from the United States (2020)
domestic: 5 per 100 fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity approaching 65 per 100 persons; mobile sector accounting for over 90% of all phone subscriptions (2019)
international: country code - 501; landing points for the ARCOS and SEUL fiber-optic telecommunications submarine cable that provides links to South and Central America, parts of the Caribbean, and the US; satellite earth station - 8 (Intelsat - 2, unknown - 6) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
8 privately owned TV stations; multi-channel cable TV provides access to foreign stations; about 25 radio stations broadcasting on roughly 50 different frequencies; state-run radio was privatized in 1998 (2019)
Internet users
total: 188,900 (2021 est.)
percent of population: 47.08% (2019 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 29,600 (2019)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 7.58 (2019 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 28
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 1,297,533 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 3.78 million mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 6
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 2
under 914 m: 3 (2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 41
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 11
under 914 m: 29 (2013)
Roadways
total: 3,281 km (2017)
paved: 601 km (2017)
unpaved: 2,680 km (2017)
Merchant marine
total: 813
by type: bulk carrier 54, container ship 1, general cargo 428, oil tanker 70, other 260 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Belize City, Big Creek
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Belize Defense Force (BDF): Army, Air Wing; Belize Coast Guard (independent from the BDF, but under the Ministry of Defense) (2021)
Military expenditures
1.5% of GDP (2020 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2019)
1.2% of GDP (2018)
1.3% of GDP (2017)
1.3% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Belize Defense Force (BDF) has approximately 1,300 active personnel; approximately 300 Belize Coast Guard (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the BDF's inventory is limited and consists mostly of UK- and US-origin equipment (2021)
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service; laws allow for conscription only if volunteers are insufficient; conscription has never been implemented; volunteers typically outnumber available positions by 3:1; initial service obligation 12 years (2021)
Military - note
the BDF was established in 1978 from the disbanded Police Special Force and the Belize Volunteer Guard to assist the resident British forces with the defense of Belize against Guatemala; the BDF traces its history back to the Prince Regent Royal Honduras Militia, a volunteer force established in 1817
the British Army has maintained a presence in Belize since its independence; as of 2021, the presence consisted of a small training support unit that provides jungle training to troops from the UK and international partners
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Guatemala persists in its territorial claim to approximately half of Belize, but agrees to the Line of Adjacency to keep Guatemalan squatters out of Belize's forested interior; both countries agreed in April 2012 to hold simultaneous referenda, scheduled for 6 October 2013, to decide whether to refer the dispute to the ICJ for binding resolution, but this vote was suspended indefinitely; Belize and Mexico are working to solve minor border demarcation discrepancies arising from inaccuracies in the 1898 border treaty
Trafficking in persons
current situation: human traffickers exploit domestic and foreign victims and Belizeans abroad; Belizean and foreign women, men, and girls and LGBTI persons, mainly from Central America, are sex trafficked in bars, nightclubs, hotels, and brothels; men, women, and children from Central America, Mexico, and Asia may migrate voluntarily to Belize seeking work and then are subjected to forced labor in restaurants, shops, domestic work, and agriculture; foreign child sex tourists exploit children in tourist areas
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List — Belize does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking but is making significant efforts to do so; authorities initiated more trafficking investigations, convicted a trafficker, screened for potential trafficking victims during labor inspections, and continued to implement a 2018-2020 national anti-trafficking action plan; anti-trafficking training was provided to the anti-trafficking police unit, immigration officers, prosecutors, judges, prison officials, and social workers; however, the government did not initiate any new trafficking prosecutions and continued to apply victim identification procedures inconsistently; corruption and official complicity in trafficking remained concerns, but no investigations, prosecutions, or convictions of government employees were reported (2020)
Illicit drugs
Belize is a transit country for illegal drugs, mainly cocaine, originating from countries in South America; low domestic drug consumption problem outside of recreational cannabis