Introduction
Background
In 1783, the Sunni Al-Khalifa family took power in Bahrain. In order to secure these holdings, it entered into a series of treaties with the UK during the 19th century that made Bahrain a British protectorate. The archipelago attained its independence in 1971. A steady decline in oil production and reserves since 1970 prompted Bahrain to take steps to diversify its economy, in the process developing petroleum processing and refining, aluminum production, and hospitality and retail sectors. It has also endeavored to become a leading regional banking center, especially with respect to Islamic finance. Bahrain's small size, central location among Gulf countries, economic dependence on Saudi Arabia, and proximity to Iran require it to play a delicate balancing act in foreign affairs among its larger neighbors. Its foreign policy activities usually fall in line with Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
The Sunni royal family has long struggled to manage relations with its large Shia-majority population. In early 2011, amid Arab uprisings elsewhere in the region, the Bahraini Government confronted similar pro-democracy and reform protests at home with police and military action, including deploying Gulf Cooperation Council security forces to Bahrain. Failed political talks prompted opposition political societies to boycott 2014 legislative and municipal council elections. In 2018, a law preventing members of political societies dissolved by the courts from participating in elections effectively sidelined the majority of opposition figures from taking part in national elections. As a result, most members of parliament are independents. Ongoing dissatisfaction with the political status quo continues to factor into sporadic clashes between demonstrators and security forces. On 15 September 2020, Bahrain and the United Arab Emirates signed peace agreements (the Abraham Accords) with Israel – brokered by the US – in Washington DC. Bahrain and the UAE thus became the third and fourth Middle Eastern countries, along with Egypt and Jordan, to recognize Israel.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
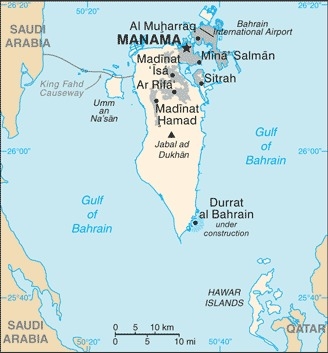
Middle East, archipelago in the Persian Gulf, east of Saudi Arabia
Geographic coordinates
26 00 N, 50 33 E
Map references
Middle East
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
161 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
continental shelf: extending to boundaries to be determined
Climate
arid; mild, pleasant winters; very hot, humid summers
Terrain
mostly low desert plain rising gently to low central escarpment
Elevation
highest point: Jabal ad Dukhan 135 m
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
Natural resources
oil, associated and nonassociated natural gas, fish, pearls
Land use
agricultural land: 11.3% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 3.9% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 5.3% (2018 est.)
forest: 0.7% (2018 est.)
other: 88% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
40 sq km (2012)
Major aquifers
Arabian Aquifer System
Population distribution
smallest population of the Gulf States, but urbanization rate exceeds 90%; largest settlement concentration is found on the far northern end of the island in and around Manamah and Al Muharraq
Natural hazards
periodic droughts; dust storms
Geography - note
close to primary Middle Eastern petroleum sources; strategic location in Persian Gulf, through which much of the Western world's petroleum must transit to reach open ocean
People and Society
Population
1,526,929 (July 2021 est.)
note: immigrants make up approximately 45% of the total population, according to UN data (2019)
Nationality
noun: Bahraini(s)
adjective: Bahraini
Ethnic groups
Bahraini 46%, Asian 45.5%, other Arab 4.7%, African 1.6%, European 1%, other 1.2% (includes Gulf Co-operative country nationals, North and South Americans, and Oceanians) (2010 est.)
Languages
Arabic (official), English, Farsi, Urdu
major-language sample(s):
كتاب حقائق العالم، المصدر الذي لا يمكن الاستغناء عنه للمعلومات الأساسية (Arabic)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Age structure
0-14 years: 18.45% (male 141,039/female 136,687)
15-24 years: 15.16% (male 129,310/female 98,817)
25-54 years: 56.14% (male 550,135/female 294,778)
55-64 years: 6.89% (male 64,761/female 38,870)
65 years and over: 3.36% (male 25,799/female 24,807) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 26.5
youth dependency ratio: 23.1
elderly dependency ratio: 3.4
potential support ratio: 29.8 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 32.9 years
male: 34.4 years
female: 30.3 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
smallest population of the Gulf States, but urbanization rate exceeds 90%; largest settlement concentration is found on the far northern end of the island in and around Manamah and Al Muharraq
Urbanization
urban population: 89.6% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.99% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
664,000 MANAMA (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.31 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.87 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.67 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 1.04 male(s)/female
total population: 1.53 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
14 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137Infant mortality rate
total: 10.54 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 12.31 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 8.71 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 79.67 years
male: 77.39 years
female: 82.02 years (2021 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: total: 100% of population
unimproved: total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
4.1% (2018)
Physicians density
0.93 physicians/1,000 population (2015)
Hospital bed density
1.7 beds/1,000 population (2017)
Sanitation facility access
improved: total: 100% of population
unimproved: total: 0% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
<.1% (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS
<500 (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<100 (2017 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 97.5%
male: 99.9%
female: 94.9% (2018)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 16 years
male: 16 years
female: 17 years (2019)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 5.3%
male: 2.6%
female: 12.2% (2012 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
desertification resulting from the degradation of limited arable land, periods of drought, and dust storms; coastal degradation (damage to coastlines, coral reefs, and sea vegetation) resulting from oil spills and other discharges from large tankers, oil refineries, and distribution stations; lack of freshwater resources (groundwater and seawater are the only sources for all water needs); lowered water table leaves aquifers vulnerable to saline contamination; desalinization provides some 90% of the country's freshwater
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 69.04 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 31.69 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 15.47 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
arid; mild, pleasant winters; very hot, humid summers
Land use
agricultural land: 11.3% (2018 est.)
arable land: 2.1% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 3.9% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 5.3% (2018 est.)
forest: 0.7% (2018 est.)
other: 88% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 89.6% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.99% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 951,943 tons (2016 est.)
municipal solid waste recycled annually: 76,155 tons (2012 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 8% (2012 est.)
Major aquifers
Arabian Aquifer System
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 275.6 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 14.1 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 144.7 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
116 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Kingdom of Bahrain
conventional short form: Bahrain
local long form: Mamlakat al Bahrayn
local short form: Al Bahrayn
former: Dilmun, Tylos, Awal, Mishmahig, Bahrayn, State of Bahrain
etymology: the name means "the two seas" in Arabic and refers to the water bodies surrounding the archipelago
Government type
constitutional monarchy
Capital
name: Manama
geographic coordinates: 26 14 N, 50 34 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: name derives from the Arabic "al-manama" meaning "place of rest" or "place of dreams"
Administrative divisions
4 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazah); Asimah (Capital), Janubiyah (Southern), Muharraq, Shamaliyah (Northern)
note: each governorate administered by an appointed governor
Independence
15 August 1971 (from the UK)
National holiday
National Day, 16 December (1971); note - 15 August 1971 was the date of independence from the UK, 16 December 1971 was the date of independence from British protection
Constitution
history: adopted 14 February 2002
amendments: proposed by the king or by at least 15 members of either chamber of the National Assembly followed by submission to an Assembly committee for review and, if approved, submitted to the government for restatement as drafts; passage requires a two-thirds majority vote by the membership of both chambers and validation by the king; constitutional articles on the state religion (Islam), state language (Arabic), and the monarchy and "inherited rule" cannot be amended; amended 2012, 2017
Legal system
mixed legal system of Islamic (sharia) law, English common law, Egyptian civil, criminal, and commercial codes; customary law
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Bahrain
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 25 years; 15 years for Arab nationals
Suffrage
20 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: King HAMAD bin Isa Al-Khalifa (since 6 March 1999)
head of government: Prime minister SALMAN bin Hamad Al-Khalifa (since 11 November 2020); first deputy prime minister (vacant); Deputy Prime Ministers MUHAMMAD bin Mubarak Al-Khalifa (since September 2005), Jawad bin Salim al-ARAIDH, ALI bin Khalifa bin Salman Al-Khalifa (since 11 December 2006), KHALID bin Abdallah Al-Khalifa (since November 2010); note - KHALIFA ibn Salman Al Khalifa, who served as prime minister since Bahrain's independence in 1971, died on 11 November 2020
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the monarch
elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; prime minister appointed by the monarch
Legislative branch
description: bicameral National Assembly consists of:
Consultative Council or Majlis al-Shura (40 seats; members appointed by the king)
Council of Representatives or Majlis al-Nuwab (40 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by absolute majority vote in 2 rounds if needed; members serve 4-year renewable terms)
elections:
Consultative Council - last appointments on 12 December 2018 (next NA)
Council of Representatives - first round for 9 members held on 24 November 2018; second round for remaining 31 members held on 1 December 2018 (next to be held in 2022)
election results:
Consultative Council - composition - men 31, women 9, percent of women 22.5%
Council of Representatives (for 2018 election) - percent of vote by society - NA; seats by society - Islamic Al-Asalah (Sunni Salafi) 3, Minbar al-Taqadumi (Communist) 2, National Unity Gathering (Sunni progovernment) 1, National Islamic Minbar (Sunni Muslim Brotherhood) 1, independent 33; composition - men 34, women 6, percent of women 15%; note - total National Assembly percent of women 19%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Court of Cassation (consists of the chairman and 3 judges); Supreme Court of Appeal (consists of the chairman and 3 judges); Constitutional Court (consists of the president and 6 members); High Sharia Court of Appeal (court sittings include the president and at least one judge)
judge selection and term of office: Court of Cassation judges appointed by royal decree and serve for a specified tenure; Constitutional Court president and members appointed by the Higher Judicial Council, a body chaired by the monarch and includes judges from the Court of Cassation, sharia law courts, and Civil High Courts of Appeal; members serve 9-year terms; High Sharia Court of Appeal member appointments by royal decree for a specified tenure
subordinate courts: Civil High Courts of Appeal; middle and lower civil courts; High Sharia Court of Appeal; Senior Sharia Court; Administrative Courts of Appeal; military courts
note: the judiciary of Bahrain is divided into civil law courts and sharia law courts; sharia courts (involving personal status and family law) are further divided into Sunni Muslim and Shia Muslim; the Courts are supervised by the Supreme Judicial Council.
Political parties and leaders
note: political parties are prohibited, but political societies were legalized under a July 2005 law
International organization participation
ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, CICA, FAO, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Abdulla bin Rashid AL KHALIFA (since 21 July 2017)
chancery: 3502 International Drive NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 342-1111
FAX: [1] (202) 362-2192
email address and website:
ambsecretary@bahrainembassy.org
mofa.gov.bh
consulate(s) general: New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Maggie NARDI (since August 2019)
embassy: Building 979, Road 3119 (next to Al-Ahli Sports Club), Block 331, Zinj District, P.O. Box 26431, Manama
mailing address: 6210 Manama Place, Washington DC 20521-6210
telephone: [973] 17-242700
FAX: [973] 17-272594
email address and website:
ManamaConsular@state.gov
https://bh.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
red, the traditional color for flags of Persian Gulf states, with a white serrated band (five white points) on the hoist side; the five points represent the five pillars of Islam
note: until 2002, the flag had eight white points, but this was reduced to five to avoid confusion with the Qatari flag
National symbol(s)
a red field surmounted by a white serrated band with five white points; national colors: red, white
National anthem
name: "Bahrainona" (Our Bahrain)
lyrics/music: unknown
note: adopted 1971; although Mohamed Sudqi AYYASH wrote the original lyrics, they were changed in 2002 following the transformation of Bahrain from an emirate to a kingdom
Economy
Economic overview
Oil and natural gas play a dominant role in Bahrain’s economy. Despite the Government’s past efforts to diversify the economy, oil still comprises 85% of Bahraini budget revenues. In the last few years lower world energy prices have generated sizable budget deficits - about 10% of GDP in 2017 alone. Bahrain has few options for covering these deficits, with low foreign assets and fewer oil resources compared to its GCC neighbors. The three major US credit agencies downgraded Bahrain’s sovereign debt rating to "junk" status in 2016, citing persistently low oil prices and the government’s high debt levels. Nevertheless, Bahrain was able to raise about $4 billion by issuing foreign currency denominated debt in 2017.
Other major economic activities are production of aluminum - Bahrain's second biggest export after oil and gas –finance, and construction. Bahrain continues to seek new natural gas supplies as feedstock to support its expanding petrochemical and aluminum industries. In April 2018 Bahrain announced it had found a significant oil field off the country’s west coast, but is still assessing how much of the oil can be extracted profitably.
In addition to addressing its current fiscal woes, Bahraini authorities face the long-term challenge of boosting Bahrain’s regional competitiveness — especially regarding industry, finance, and tourism — and reconciling revenue constraints with popular pressure to maintain generous state subsidies and a large public sector. Since 2015, the government lifted subsidies on meat, diesel, kerosene, and gasoline and has begun to phase in higher prices for electricity and water. As part of its diversification plans, Bahrain implemented a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the US in August 2006, the first FTA between the US and a Gulf state. It plans to introduce a Value Added Tax (VAT) by the end of 2018.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$69.65 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$73.95 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$72.51 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
2.49% (2019 est.)
13.89% (2018 est.)
3.85% (2017 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$40,900 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$45,100 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$46,200 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$38.472 billion (2019 est.)
Credit ratings
Fitch rating: B+ (2020)
Moody's rating: B2 (2018)
Standard & Poors rating: B+ (2017)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 0.3% (2017 est.)
industry: 39.3% (2017 est.)
services: 60.4% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 45.8% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 15.5% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 26.1% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.4% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 80.2% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -67.9% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
mutton, dates, milk, poultry, tomatoes, fruit, sheep offals, sheep skins, eggs, pumpkins
Industries
petroleum processing and refining, aluminum smelting, iron pelletization, fertilizers, Islamic and offshore banking, insurance, ship repairing, tourism
Labor force
831,600 (2017 est.)
note: excludes unemployed; 44% of the population in the 15-64 age group is non-national
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 1%
industry: 32%
services: 67% (2004 est.)
Unemployment rate
3.6% (2017 est.)
3.7% (2016 est.)
note: official estimate; actual rate is higher
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
Budget
revenues: 5.854 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 9.407 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$1.6 billion (2017 est.)
-$1.493 billion (2016 est.)
Exports
$30.1 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$26.762 billion (2017 est.)
Exports - partners
United Arab Emirates 31%, Saudi Arabia 12%, Japan 8%, United States 8% (2019)
Exports - commodities
refined petroleum, aluminum and plating, crude petroleum, iron ore, gold (2019)
Imports
$27.19 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
$22.132 billion (2017 est.)
Imports - partners
United Arab Emirates 27%, China 11%, Saudi Arabia 7%, United States 5%, Brazil 5%, Japan 5%, India 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
cars, iron ore, jewelry, gold, gas turbines (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$2.349 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$3.094 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$52.15 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$42.55 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Exchange rates
Bahraini dinars (BHD) per US dollar -
0.37705 (2020 est.)
0.37705 (2019 est.)
0.377 (2018 est.)
0.376 (2014 est.)
0.376 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 5.3%
male: 2.6%
female: 12.2% (2012 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
3.928 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90Electricity - from fossil fuels
100% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156Electricity - from other renewable sources
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174Crude oil - proved reserves
124.6 million bbl (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67Refined petroleum products - production
274,500 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45Refined petroleum products - consumption
61,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94Natural gas - proved reserves
92.03 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 266,659 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 15.67 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 1,748,672 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 102.8 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Bahrain is one of the most technically advanced and connected countries in the world; NGN for increased mobile and Wi-Fi traffic; mobile infrastructure and fiber-optic Internet allows greater Internet penetration and competitive prices; government provides free Internet in schools and public areas, and national broadband with sole control over network; regulator controlled by monarchy; Internet freedom restricted through blocks; well served by satellite and submarine cable access; importer of broadcasting equipment from UAE (2020)
domestic: 17 per 100 fixed-line, 116 per 100 mobile-cellular; modern fiber-optic integrated services; digital network with rapidly expanding mobile-cellular telephones (2020)
international: country code - 973; landing points for the FALCON, Tata TGN-Gulf, GBICS/MENA, and FOG submarine cable network that provides links to Asia, the Middle East, and Africa; tropospheric scatter to Qatar and UAE; microwave radio relay to Saudi Arabia; satellite earth station - 1 (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
state-run Bahrain Radio and Television Corporation (BRTC) operates 5 terrestrial TV networks and several radio stations; satellite TV systems provide access to international broadcasts; 1 private FM station directs broadcasts to Indian listeners; radio and TV broadcasts from countries in the region are available (2019)
Internet users
total: 1.71 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 99.54% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 148,595 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 8.73 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 6 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 42
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 5,877,003 (2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 420.98 million mt-km (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 4
over 3,047 m: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2017)
Heliports
1 (2013)
Pipelines
20 km gas, 54 km oil (2013)
Roadways
total: 4,122 km (2010)
paved: 3,392 km (2010)
unpaved: 730 km (2010)
Merchant marine
total: 205
by type: general cargo 12, oil tanker 4, other 189 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Mina' Salman, Sitrah
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Bahrain Defense Force (BDF): Royal Bahraini Army (includes the Royal Guard), Royal Bahraini Navy, Royal Bahraini Air Force; Ministry of Interior: National Guard, Special Security Forces Command (SSFC), Coast Guard
(2021)
note - the Royal Guard is officially under the command of the Army, but exercises considerable autonomy
Military expenditures
4.2% of GDP (2020 est.)
3.7% of GDP (2019)
4.1% of GDP (2018)
4.3% of GDP (2017)
4.7% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; approximately 10,000 active personnel (7,500 Army; 1,000 Navy; 1,500 Air Force); est. 3,000 National Guard (2021)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the inventory of the Bahrain Defense force is comprised mostly of equipment acquired from the US along with a smaller quantity of material from European suppliers; since 2010, the US is the leading supplier of arms to Bahrain (2020)
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service; 15 years of age for NCOs, technicians, and cadets; no conscription (2019)
Military - note
as of 2021, Bahrain hosted the US Naval Forces Central Command (USNAVCENT; established 1983), which included the US 5th Fleet, several subordinate naval task forces, and the Combined Maritime Forces (established 2002), a coalition of more than 30 nations providing maritime security for regional shipping lanes; in 2018, the UK opened a naval support base in Bahrain
Bahrain has Major Non-NATO Ally (MNNA) status with the US; MNNA is a designation under US law that provides foreign partners with certain benefits in the areas of defense trade and security cooperation; while MNNA status provides military and economic privileges, it does not entail any security commitments
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
al-Ashtar Brigades; Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps/Qods Force
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T