Albania
Introduction
Background
Albania declared its independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1912, but was conquered by Italy in 1939 and occupied by Germany in 1943. Communist partisans took over the country in 1944. Albania allied itself first with the USSR (until 1960), and then with China (to 1978). In the early 1990s, Albania ended 46 years of isolated communist rule and established a multiparty democracy. The transition has proven challenging as successive governments have tried to deal with high unemployment, widespread corruption, dilapidated infrastructure, powerful organized crime networks, and combative political opponents.
Albania has made progress in its democratic development since it first held multiparty elections in 1991, but deficiencies remain. Most of Albania's post-communist elections were marred by claims of electoral fraud; however, international observers judged elections to be largely free and fair since the restoration of political stability following the collapse of pyramid schemes in 1997. Albania joined NATO in April 2009 and in June 2014 became an EU candidate. Albania in April 2017 received a European Commission recommendation to open EU accession negotiations following the passage of historic EU-mandated justice reforms in 2016. Although Albania's economy continues to grow, it has slowed, and the country is still one of the poorest in Europe. A large informal economy and a weak energy and transportation infrastructure remain obstacles.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
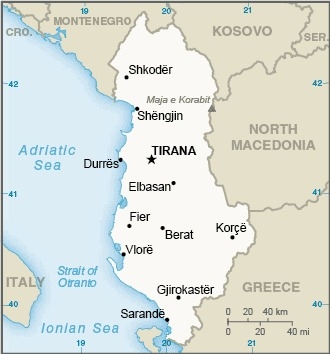
Location
Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea and Ionian Sea, between Greece to the south and Montenegro and Kosovo to the north
Geographic coordinates
41 00 N, 20 00 E
Map references
Europe
Land boundaries
total: 691 km
border countries (4): Greece 212 km, Kosovo 112 km, Macedonia 181 km, Montenegro 186 km
Coastline
362 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Climate
mild temperate; cool, cloudy, wet winters; hot, clear, dry summers; interior is cooler and wetter
Terrain
mostly mountains and hills; small plains along coast
Elevation
highest point: Maja e Korabit (Golem Korab) 2,764 m
lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 708 m
Natural resources
petroleum, natural gas, coal, bauxite, chromite, copper, iron ore, nickel, salt, timber, hydropower, arable land
Land use
agricultural land: 42.8% (2018 est.)
arable land: 22.3% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 17.4% (2018 est.)
forest: 28.8% (2018 est.)
other: 28.2% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
3,537 sq km (2014)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Black Sea) Danube (795,656 sq km)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Scutari (shared with Montenegro) - 400 sq km
note - largest lake in the Balkans
Population distribution
a fairly even distribution, with somewhat higher concentrations of people in the western and central parts of the country
Natural hazards
destructive earthquakes; tsunamis occur along southwestern coast; floods; drought
Geography - note
strategic location along Strait of Otranto (links Adriatic Sea to Ionian Sea and Mediterranean Sea)
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Albanian(s)
adjective: Albanian
Ethnic groups
Albanian 82.6%, Greek 0.9%, other 1% (including Vlach, Romani, Macedonian, Montenegrin, and Egyptian), unspecified 15.5% (2011 est.)
note: data represent population by ethnic and cultural affiliation
Languages
Albanian 98.8% (official - derived from Tosk dialect), Greek 0.5%, other 0.6% (including Macedonian, Romani, Vlach, Turkish, Italian, and Serbo-Croatian), unspecified 0.1% (2011 est.)
major-language sample(s):
Libri i fakteve boterore, burim i pa zevendesueshem per informacione elementare. (Albanian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Muslim 56.7%, Roman Catholic 10%, Orthodox 6.8%, atheist 2.5%, Bektashi (a Sufi order) 2.1%, other 5.7%, unspecified 16.2% (2011 est.)
note: all mosques and churches were closed in 1967 and religious observances prohibited; in November 1990, Albania began allowing private religious practice
Age structure
0-14 years: 17.6% (male 284,636/female 256,474)
15-24 years: 15.39% (male 246,931/female 226,318)
25-54 years: 42.04% (male 622,100/female 670,307)
55-64 years: 11.94% (male 178,419/female 188,783)
65 years and over: 13.03% (male 186,335/female 214,276) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 46.9
youth dependency ratio: 25.3
elderly dependency ratio: 21.6
potential support ratio: 4.6 (2020 est.)
Median age
total: 34.3 years
male: 32.9 years
female: 35.7 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
a fairly even distribution, with somewhat higher concentrations of people in the western and central parts of the country
Urbanization
urban population: 63% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.29% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
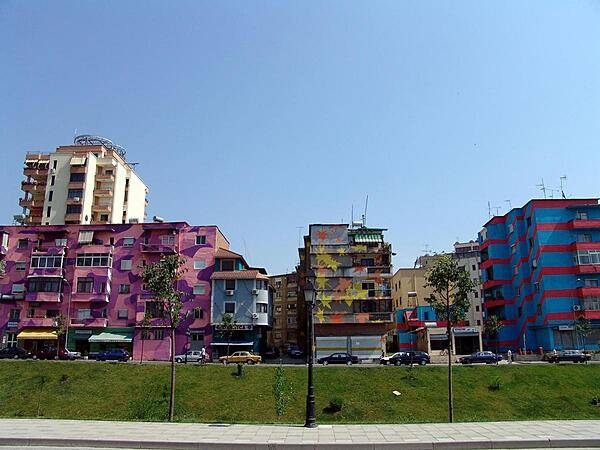
503,000 TIRANA (capital) (2021)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.08 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.11 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.09 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.93 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.87 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
24.8 years (2019 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
15 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136Infant mortality rate
total: 11.1 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 12.15 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 9.96 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 79.23 years
male: 76.55 years
female: 82.12 years (2021 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
46% (2017/18)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: 96.8% of population
rural: 95.3% of population
total: 96.2% of population
unimproved: urban: 4.7% of population
rural: 4.7% of population
total: 3.8% of population (2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure
5.3% (2018)
Physicians density
1.22 physicians/1,000 population (2016)
Hospital bed density
2.9 beds/1,000 population (2013)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 99.5% of population
total: 99.8% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0.5% of population
total: 0.2% of population (2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
<.1 (2020 est.)
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS
1,400 (2020 est.)
note: estimate does not include children
HIV/AIDS - deaths
<100 (2020 est.)
note: estimate does not include children
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 98.1%
male: 98.5%
female: 97.8% (2018)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 15 years
male: 14 years
female: 15 years (2020)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 27%
male: 27.8%
female: 25.9% (2019 est.)
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation; soil erosion; water pollution from industrial and domestic effluents; air pollution from industrial and power plants; loss of biodiversity due to lack of resources for sound environmental management
Environment - international agreements
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Air pollutants
particulate matter emissions: 17.87 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 4.54 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 2.55 megatons (2020 est.)
Climate
mild temperate; cool, cloudy, wet winters; hot, clear, dry summers; interior is cooler and wetter
Land use
agricultural land: 42.8% (2018 est.)
arable land: 22.3% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 3% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 17.4% (2018 est.)
forest: 28.8% (2018 est.)
other: 28.2% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 63% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.29% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
forest revenues: 0.18% of GDP (2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 1,142,964 tons (2015 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Fresh water lake(s): Lake Scutari (shared with Montenegro) - 400 sq km
note - largest lake in the Balkans
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Black Sea) Danube (795,656 sq km)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 283 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 231.8 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 905 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total renewable water resources
30.2 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Albania
conventional short form: Albania
local long form: Republika e Shqiperise
local short form: Shqiperia
former: People's Socialist Republic of Albania
etymology: the English-language country name seems to be derived from the ancient Illyrian tribe of the Albani; the native name "Shqiperia" is derived from the Albanian word "Shqiponje" ("Eagle") and is popularly interpreted to mean "Land of the Eagles"
Government type
parliamentary republic
Capital
name: Tirana (Tirane)
geographic coordinates: 41 19 N, 19 49 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: the name Tirana first appears in a 1418 Venetian document; the origin of the name is unclear, but may derive from Tirkan Fortress, whose ruins survive on the slopes of Dajti mountain and which overlooks the city
Administrative divisions
12 counties (qarqe, singular - qark); Berat, Diber, Durres, Elbasan, Fier, Gjirokaster, Korce, Kukes, Lezhe, Shkoder, Tirane, Vlore
Independence
28 November 1912 (from the Ottoman Empire)
National holiday
Independence Day, 28 November (1912), also known as Flag Day
Constitution
history: several previous; latest approved by the Assembly 21 October 1998, adopted by referendum 22 November 1998, promulgated 28 November 1998
amendments: proposed by at least one-fifth of the Assembly membership; passage requires at least a two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly; referendum required only if approved by two-thirds of the Assembly; amendments approved by referendum effective upon declaration by the president of the republic; amended several times, last in 2020
Legal system
civil law system except in the northern rural areas where customary law known as the "Code of Leke" is still present
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Albania
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President of the Republic Ilir META (since 24 July 2017)
head of government: Prime Minister Edi RAMA (since 10 September 2013); Deputy Prime Minister Arben AHMETAJ (since 18 September 2021)
cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the prime minister, nominated by the president, and approved by the Assembly
elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by the Assembly for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); a candidate needs three-fifths majority vote of the Assembly in 1 of 3 rounds or a simple majority in 2 additional rounds to become president; election last held in 4 rounds on 19, 20, 27, and 28 April 2017 (next election to be held in 2022); prime minister appointed by the president on the proposal of the majority party or coalition of parties in the Assembly
election results: Ilir META elected president; Assembly vote - 87 - 2 in fourth round
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Assembly or Kuvendi (140 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote to serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 25 April 2021 (next to be held in 2025)
election results: percent of vote by party/coalition - PS 48.7%, PD-Alliance for Change 39.4%, LSI 6.8%, PSD 2.3%, other 2.8%; seats by party/coalition - PS 74, PD-Alliance for Change 59, LSI 4, PSD 3; composition -men 93, women 47, percent of women 33.6%%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of 19 judges, including the chief justice); Constitutional Court (consists of 9 judges, including the chairman)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the High Judicial Council with the consent of the president to serve single 9-year terms; Supreme Court chairman is elected for a single 3-year term by the court members; appointments of Constitutional Court judges are rotated among the president, Parliament, and Supreme Court from a list of pre-qualified candidates (each institution selects 3 judges), to serve single 9-year terms; candidates are pre-qualified by a randomly selected body of experienced judges and prosecutors; Constitutional Court chairman is elected by the court members for a single, renewable 3-year term
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; Courts of First Instance; specialized courts: Court for Corruption and Organized Crime, Appeals Court for Corruption and Organized Crime (responsible for corruption, organized crime, and crimes of high officials)
Political parties and leaders
Alliance for Change (electoral coalition led by PD)
Democratic Party or PD [Lulzim BASHA]
Party for Justice, Integration and Unity or PDIU [Shpetim IDRIZI] (part of the Alliance for Change; formerly part of APMI)
Social Democratic Party or PSD [Tom DOSHI]
Socialist Movement for Integration or LSI [Monika KRYEMADHI]
Socialist Party or PS [Edi RAMA]
International organization participation
BSEC, CD, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, EITI (compliant country), FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, OAS (observer), OIC, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, SELEC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Floreta LULI-FABER (since 18 May 2015)
chancery: 2100 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 223-4942
FAX: [1] (202) 628-7342
email address and website:
embassy.washington@mfa.gov.al
http://www.ambasadat.gov.al/usa/en
consulate(s) general: New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Yuri KIM (since 27 January 2020)
embassy: Rruga Stavro Vinjau, No. 14, Tirana
mailing address: 9510 Tirana Place, Washington DC 20521-9510
telephone: [355] 4 2247-285
FAX: [355] 4 2232-222
email address and website:
ACSTirana@state.gov
https://al.usembassy.gov/
Flag description
red with a black two-headed eagle in the center; the design is claimed to be that of 15th-century hero Georgi Kastrioti SKANDERBEG, who led a successful uprising against the Ottoman Turks that resulted in a short-lived independence for some Albanian regions (1443-78); an unsubstantiated explanation for the eagle symbol is the tradition that Albanians see themselves as descendants of the eagle; they refer to themselves as "Shqiptare," which translates as "sons of the eagle"
National symbol(s)
black double-headed eagle; national colors: red, black
National anthem
name: "Hymni i Flamurit" (Hymn to the Flag)
lyrics/music: Aleksander Stavre DRENOVA/Ciprian PORUMBESCU
note: adopted 1912
Economy
Economic overview
Albania, a formerly closed, centrally planned state, is a developing country with a modern open-market economy. Albania managed to weather the first waves of the global financial crisis but, the negative effects of the crisis caused a significant economic slowdown. Since 2014, Albania’s economy has steadily improved and economic growth reached 3.8% in 2017. However, close trade, remittance, and banking sector ties with Greece and Italy make Albania vulnerable to spillover effects of possible debt crises and weak growth in the euro zone.
Remittances, a significant catalyst for economic growth, declined from 12-15% of GDP before the 2008 financial crisis to 5.8% of GDP in 2015, mostly from Albanians residing in Greece and Italy. The agricultural sector, which accounts for more than 40% of employment but less than one quarter of GDP, is limited primarily to small family operations and subsistence farming, because of a lack of modern equipment, unclear property rights, and the prevalence of small, inefficient plots of land. Complex tax codes and licensing requirements, a weak judicial system, endemic corruption, poor enforcement of contracts and property issues, and antiquated infrastructure contribute to Albania's poor business environment making attracting foreign investment difficult. Since 2015, Albania has launched an ambitious program to increase tax compliance and bring more businesses into the formal economy. In July 2016, Albania passed constitutional amendments reforming the judicial system in order to strengthen the rule of law and to reduce deeply entrenched corruption.
Albania’s electricity supply is uneven despite upgraded transmission capacities with neighboring countries. However, the government has recently taken steps to stem non-technical losses and has begun to upgrade the distribution grid. Better enforcement of electricity contracts has improved the financial viability of the sector, decreasing its reliance on budget support. Also, with help from international donors, the government is taking steps to improve the poor road and rail networks, a long standing barrier to sustained economic growth.
Inward foreign direct investment has increased significantly in recent years as the government has embarked on an ambitious program to improve the business climate through fiscal and legislative reforms. The government is focused on the simplification of licensing requirements and tax codes, and it entered into a new arrangement with the IMF for additional financial and technical support. Albania’s three-year IMF program, an extended fund facility arrangement, was successfully concluded in February 2017. The Albanian Government has strengthened tax collection amid moderate public wage and pension increases in an effort to reduce its budget deficit. The country continues to face high public debt, exceeding its former statutory limit of 60% of GDP in 2013 and reaching 72% in 2016.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$37.73 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$39.02 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$38.19 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
Real GDP growth rate
2.24% (2019 est.)
4.07% (2018 est.)
3.8% (2017 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$13,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$13,700 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$13,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$15.273 billion (2019 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
1.4% (2019 est.)
2% (2018 est.)
1.9% (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
Moody's rating: B1 (2007)
Standard & Poors rating: B+ (2016)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 21.7% (2017 est.)
industry: 24.2% (2017 est.)
services: 54.1% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 78.1% (2017 est.)
government consumption: 11.5% (2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 25.2% (2017 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.2% (2017 est.)
exports of goods and services: 31.5% (2017 est.)
imports of goods and services: -46.6% (2017 est.)
Agricultural products
milk, maize, tomatoes, potatoes, watermelons, wheat, grapes, cucumbers, onions, apples
Industries
food; footwear, apparel and clothing; lumber, oil, cement, chemicals, mining, basic metals, hydropower
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 41.4%
industry: 18.3%
services: 40.3% (2017 est.)
Unemployment rate
5.83% (2019 est.)
6.32% (2018 est.)
note: these official rates may not include those working at near-subsistence farming
Population below poverty line
14.3% (2012 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
33.2 (2017 est.)
30 (2008 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 4.1%
highest 10%: 19.6% (2015 est.)
Budget
revenues: 3.614 billion (2017 est.)
expenditures: 3.874 billion (2017 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Current account balance
-$908 million (2017 est.)
-$899 million (2016 est.)
Exports
$3.47 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$4.82 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$4.78 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exports - partners
Italy 45%, Spain 8%, Germany 6%, Greece 5%, France 4%, China 4% (2019)
Exports - commodities
leather footwear and parts, crude petroleum, iron alloys, clothing, electricity, perfumes (2019)
Imports
$5.67 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2020 est.)
$6.93 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$6.85 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports - partners
Italy 28%, Greece 12%, China 11%, Turkey 9%, Germany 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, cars, tanned hides, packaged medical supplies, footwear parts (2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$3.59 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$3.109 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
Debt - external
$9.311 billion (2019 est.)
$9.547 billion (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
leke (ALL) per US dollar -
102.43 (2020 est.)
111.36 (2019 est.)
108.57 (2018 est.)
125.96 (2014 est.)
105.48 (2013 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
total: 27%
male: 27.8%
female: 25.9% (2019 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Electricity - installed generating capacity
2.109 million kW (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112Electricity - from fossil fuels
5% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202Electricity - from nuclear fuels
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33Electricity - from hydroelectric plants
95% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5Electricity - from other renewable sources
0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171Crude oil - proved reserves
168.3 million bbl (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59Refined petroleum products - production
5,638 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103Refined petroleum products - consumption
29,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120Natural gas - proved reserves
821.2 million cu m (1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 223,469 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 7.77 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 2,618,880 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 91 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: Albania’s small telecom market has improved through signatory status of EU accession plan; EU financial aid will build infrastructure and enhance cooperation; operator committed €100 million to upgrade fixed-line infrastructure, supporting broadband services nationally; consistent with the region, fixed-line telephony use and penetration is declining as subscribers prefer mobile solutions; mobile sector is supported through LTE networks; operators have invested in 5G, including the intention to create a corridor with Kosovo; importer of broadcasting equipment from EU neighbors (2021)
domestic: fixed-line 8 per 100, teledensity continues to decline due to heavy use of mobile-cellular telephone services; mobile-cellular telephone use is widespread and generally effective, 91 per 100 for mobile-cellular (2020)
international: country code - 355; submarine cables for the Adria 1 and Italy-Albania provide connectivity to Italy, Croatia, and Greece; a combination submarine cable and land fiber-optic system, provides additional connectivity to Bulgaria, Macedonia, and Turkey; international traffic carried by fiber-optic cable and, when necessary, by microwave radio relay from the Tirana exchange to Italy and Greece (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
Albania has more than 65 TV stations, including several that broadcast nationally; Albanian TV broadcasts are also available to Albanian-speaking populations in neighboring countries; many viewers have access to Italian and Greek TV broadcasts via terrestrial reception; Albania's TV stations have begun a government-mandated conversion from analog to digital broadcast; the government has pledged to provide analog-to-digital converters to low-income families affected by this decision; cable TV service is available; 2 public radio networks and roughly 78 private radio stations; several international broadcasters are available (2019)
Internet users
total: 2 million (2021 est.)
percent of population: 72.24% (2020 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 508,937 (2020)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 17.68 (2020 est.)
Transportation
National air transport system
number of registered air carriers: 2 (2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 5
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 303,137 (2018)
Airports - with paved runways
total: 3 (2020)
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2 (2017)
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2017)
Pipelines
498 km gas (a majority of the network is in disrepair and parts of it are missing), 249 km oil (2015)
Railways
total: 677 km (447 km of major railway lines and 230 km of secondary lines) (2015)
standard gauge: 677 km 1.435-m gauge (2015)
Merchant marine
total: 70
by type: general cargo 47, oil tanker 1, other 22 (2021)
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Durres, Sarande, Shengjin, Vlore
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Republic of Albania Armed Forces (Forcat e Armatosura të Republikës së Shqipërisë (FARSH)): Land Forces, Navy Forces (includes Coast Guard), Air Forces (2021)
Military expenditures
1.3% of GDP (2020 est.)
1.31% of GDP (2019)
1.16% of GDP (2018)
1.11% of GDP (2017)
1.1% of GDP (2016)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; approximately 8,000 total active duty personnel (6,000 Army; 1,500 Navy; 500 Air Force) (2020)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Albanian military was previously equipped with mostly Soviet-era weapons that were sold or destroyed; its inventory now includes a mix of mostly donated and second-hand European and US equipment; since 2010, it has received limited amounts of equipment from France, Germany, and the US (2020)
Military service age and obligation
19 is the legal minimum age for voluntary military service; 18 is the legal minimum age in case of general/partial compulsory mobilization; conscription abolished 2010 (2019)
Military - note
Albania officially became a member of NATO in 2009
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps/Qods Force; Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (ISIS)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix T
Transnational Issues
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 1,031 (2020)
note: 11,827 estimated refugee and migrant arrivals (January 2015-January 2021)
Illicit drugs
active transshipment point for Albanian narco-trafficking organizations moving illicit drugs such as cocaine and heroin from Turkey and countries in South America and Asia throughout Europe; significant source country for cannabis production