Sint Maarten
Introduction
Background
Although sighted by Christopher COLUMBUS in 1493 and claimed for Spain, it was the Dutch who occupied the island in 1631 and began exploiting its salt deposits. The Spanish retook the island in 1633, but the Dutch continued to assert their claims. The Spanish finally relinquished the island of Saint Martin to the French and Dutch, who divided it between themselves in 1648. The establishment of cotton, tobacco, and sugar plantations dramatically expanded African slavery on the island in the 18th and 19th centuries; the practice was not abolished in the Dutch half until 1863. The island's economy declined until 1939 when it became a free port; the tourism industry was dramatically expanded beginning in the 1950s. In 1954, Sint Maarten and several other Dutch Caribbean possessions became part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands as the Netherlands Antilles. In a 2000 referendum, the citizens of Sint Maarten voted to become a self-governing country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, effective October 2010. On 6 September 2017, Hurricane Irma hit Saint Martin/Sint Maarten, causing extensive damage to roads, communications, electrical power, and housing. The UN estimated the storm destroyed or damaged 90% of the buildings, and Princess Juliana International Airport was heavily damaged and closed to commercial air traffic for five weeks.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
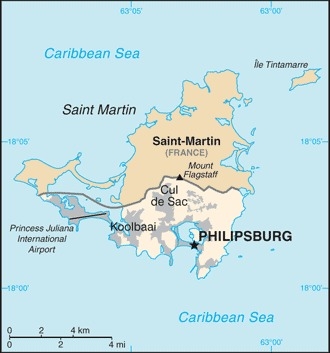
Caribbean, located in the Leeward Islands (northern) group; Dutch part of the island of Saint Martin in the Caribbean Sea; Sint Maarten lies east of the US Virgin Islands
Geographic coordinates
18 4 N, 63 4 W
Map references
Central America and the Caribbean
Area
total: 34 sq km
land: 34 sq km
water: 0 sq km
note: Dutch part of the island of Saint Martin
Area - comparative
one-fifth the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries
total: 16 km
border countries (1): Saint Martin (France) 16 km
Coastline
58.9 km (for entire island)
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical marine climate, ameliorated by northeast trade winds, results in moderate temperatures; average rainfall of 150 cm/year; hurricane season stretches from July to November
Terrain
low, hilly terrain, volcanic origin
Elevation
highest point: Mount Flagstaff 383 m
lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m
Natural resources
fish, salt
Population distribution
most populous areas are Lower Prince's Quarter (north of Philipsburg), followed closely by Cul de Sac
Natural hazards
subject to hurricanes from July to November
Geography - note
the northern border is shared with the French overseas collectivity of Saint Martin; together, these two entities make up the smallest landmass in the world shared by two self-governing states
People and Society
Ethnic groups
Saint Maarten 29.9%, Dominican Republic 10.2%, Haiti 7.8%, Jamaica 6.6%, Saint Martin 5.9%, Guyana 5%, Dominica 4.4%, Curacao 4.1%, Aruba 3.4%, Saint Kitts and Nevis 2.8%, India 2.6%, Netherlands 2.2%, US 1.6%, Suriname 1.4%, Saint Lucia 1.3%, Anguilla 1.1%, other 8%, unspecified 1.7% (2011 est.)
note: data represent population by country of birth
Languages
English (official) 67.5%, Spanish 12.9%, Creole 8.2%, Dutch (official) 4.2%, Papiamento (a Spanish-Portuguese-Dutch-English dialect) 2.2%, French 1.5%, other 3.5% (2001 est.)
Religions
Protestant 41.9% (Pentecostal 14.7%, Methodist 10.0%, Seventh Day Adventist 6.6%, Baptist 4.7%, Anglican 3.1%, other Protestant 2.8%), Roman Catholic 33.1%, Hindu 5.2%, Christian 4.1%, Jehovah's Witness 1.7%, Evangelical 1.4%, Muslim/Jewish 1.1%, other 1.3% (includes Buddhist, Sikh, Rastafarian), none 7.9%, no response 2.4% (2011 est.)
Age structure
0-14 years: 18.64% (male 4,242/female 3,932)
15-24 years: 13.26% (male 2,967/female 2,849)
25-54 years: 39.08% (male 8,417/female 8,717)
55-64 years: 17.47% (male 3,638/female 4,020)
65 years and over: 11.55% (male 2,385/female 2,680) (2020 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: NA
youth dependency ratio: NA
elderly dependency ratio: NA
potential support ratio: NA
Median age
total: 41.1 years
male: 39.6 years
female: 42.7 years (2020 est.)
Population distribution
most populous areas are Lower Prince's Quarter (north of Philipsburg), followed closely by Cul de Sac
Urbanization
urban population: 100% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.16% annual rate of change (2020-25 est. est.)
Major urban areas - population
1,327 PHILIPSBURG (capital) (2011)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.08 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.9 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.89 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
Infant mortality rate
total: 8.16 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 7.28 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 79.03 years
male: 76.67 years
female: 81.51 years (2021 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: total: 95.1% of population
unimproved: total: 4.9% of population (2017 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved: total: 98.8% of population
unimproved: total: 1.2% of population (2017)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 12 years
male: 12 years
female: 12 years (2014)
Environment
Environment - current issues
scarcity of potable water (increasing percentage provided by desalination); inadequate solid waste management; pollution from construction, chemical runoff, and sewage harms reefs
Climate
tropical marine climate, ameliorated by northeast trade winds, results in moderate temperatures; average rainfall of 150 cm/year; hurricane season stretches from July to November
Urbanization
urban population: 100% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 1.16% annual rate of change (2020-25 est. est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Country of Sint Maarten
conventional short form: Sint Maarten
local long form: Land Sint Maarten (Dutch); Country of Sint Maarten (English)
local short form: Sint Maarten (Dutch and English)
former: Netherlands Antilles; Curacao and Dependencies
etymology: explorer Christopher COLUMBUS named the island after Saint MARTIN of Tours because the 11 November 1493 day of discovery was the saint's feast day
Government type
parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy
Dependency status
constituent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands; full autonomy in internal affairs granted in 2010; Dutch Government responsible for defense and foreign affairs
Capital
name: Philipsburg
geographic coordinates: 18 1 N, 63 2 W
time difference: UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: founded and named in 1763 by John PHILIPS, a Scottish captain in the Dutch navy
Administrative divisions
none (part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands)
note: Sint Maarten is one of four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands; the other three are the Netherlands, Aruba, and Curacao
Independence
none (part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands)
National holiday
King's Day (birthday of King WILLEM-ALEXANDER), 27 April (1967); note - King's or Queen's Day are observed on the ruling monarch's birthday; celebrated on 26 April if 27 April is a Sunday; local holiday Sint Maarten's Day, 11 November (1985), commemorates the discovery of the island by COLUMBUS on Saint Martin's Day, 11 November 1493; celebrated on both halves of the island
Constitution
history: previous 1947, 1955; latest adopted 21 July 2010, entered into force 10 October 2010 (regulates governance of Sint Maarten but is subordinate to the Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands)
amendments: proposals initiated by the Government or by Parliament; passage requires at least a two-thirds majority of the Parliament membership; passage of amendments relating to fundamental rights, authorities of the governor and of Parliament must include the "views" of the Kingdom of the Netherlands Government prior to ratification by Parliament
Legal system
based on Dutch civil law system with some English common law influence
Citizenship
see the Netherlands
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: King WILLEM-ALEXANDER of the Netherlands (since 30 April 2013); represented by Governor General Eugene HOLIDAY (since 10 October 2010)
head of government: Interim Prime Minister Silveria JACOBS (since 16 January 2020)
cabinet: Cabinet nominated by the prime minister and appointed by the governor-general
elections/appointments: the monarch is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch for a 6-year term; following parliamentary elections, the leader of the majority party usually elected prime minister by Parliament
note - on 16 January 2020, Governor Eugene HOLIDAY appoints Silveria JACOBS as formateur of a new government
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Parliament of Sint Maarten (15 seats; members directly elected by proportional representation vote to serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held 9 January 2020 (next to be held in 2024)
election results: percent of vote by party - NA 35.2%, UP 24.2%, US Party 13.2%, PFP 10.6%, UD 8.7%, other 8.1%; seats by party - NA 6, UP 4, PFP 2, US Party 2, UD 1
Judicial branch
highest courts: Joint Court of Justice of Aruba, Curacao, Sint Maarten, and of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba or "Joint Court of Justice" (consists of the presiding judge, other members, and their substitutes); final appeals heard by the Supreme Court (in The Hague, Netherlands); note - prior to 2010, the Joint Court of Justice was the Common Court of Justice of the Netherlands Antilles and Aruba
judge selection and term of office: Joint Court judges appointed by the monarch serve for life
subordinate courts: Courts in First Instance
Political parties and leaders
National Alliance or NA [William MARLIN]
Party for Progress or PFP [Melissa GUMBS]
Sint Maarten Christian Party or SMCP [Wycliffe SMITH]
United Democrats Party or UD [Theodore HEYLIGER]
United Peoples Party or UP [NA]
United Sint Maarten Party or US Party [Frans RICHARDSON]
International organization participation
Caricom (observer), ILO, Interpol, UNESCO (associate), UPU, WMO
Diplomatic representation in the US
none (represented by the Kingdom of the Netherlands)
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: the US does not have an embassy in Sint Maarten; the Consul General to Curacao is accredited to Sint Maarten
Flag description
two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and blue with a white isosceles triangle based on the hoist side; the center of the triangle displays the Sint Maarten coat of arms; the arms consist of an orange-bordered blue shield prominently displaying the white court house in Philipsburg, as well as a bouquet of yellow sage (the national flower) in the upper left, and the silhouette of a Dutch-French friendship monument in the upper right; the shield is surmounted by a yellow rising sun in front of which is a brown pelican in flight; a yellow scroll below the shield bears the motto: SEMPER PROGREDIENS (Always Progressing); the three main colors are identical to those on the Dutch flag
note: the flag somewhat resembles that of the Philippines but with the main red and blue bands reversed; the banner more closely evokes the wartime Philippine flag
National symbol(s)
brown pelican, yellow sage (flower); national colors: red, white, blue
National anthem
name: O Sweet Saint Martin's Land
lyrics/music: Gerard KEMPS
note: the song, written in 1958, is used as an unofficial anthem for the entire island (both French and Dutch sides); as a collectivity of France, in addition to the local anthem, "La Marseillaise" is official on the French side (see France); as a constituent part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, in addition to the local anthem, "Het Wilhelmus" is official on the Dutch side (see Netherlands)
Economy
Economic overview
The economy of Sint Maarten centers around tourism with nearly four-fifths of the labor force engaged in this sector. Nearly 1.8 million visitors came to the island by cruise ship and roughly 500,000 visitors arrived through Princess Juliana International Airport in 2013. Cruise ships and yachts also call on Sint Maarten's numerous ports and harbors. Limited agriculture and local fishing means that almost all food must be imported. Energy resources and manufactured goods are also imported. Sint Maarten had the highest per capita income among the five islands that formerly comprised the Netherlands Antilles.
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$1.44 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
$1.436 billion (2018 est.)
$1.538 billion (2017 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
3.6% (2014 est.)
4.1% (2013 est.)
1.9% (2012 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$35,300 note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
$35,342 (2018 est.)
$37,914 (2017 est.)
note: data are in 2015 US dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)
$304.1 million (2014 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 0.4% (2008 est.)
industry: 18.3% (2008 est.)
services: 81.3% (2008 est.)
Industries
tourism, light industry
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 1.1%
industry: 15.2%
services: 83.7% (2008 est.)
Exports
$1.09 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$800 million note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Imports
$1.23 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2019 est.)
$1.22 billion note: data are in current year dollars (2018 est.)
Exchange rates
Netherlands Antillean guilders (ANG) per US dollar -
1.79 (2017 est.)
1.79 (2016 est.)
1.79 (2015 est.)
1.79 (2014 est.)
1.79 (2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2020)
Refined petroleum products - consumption
10,600 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161Communications
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 68,840 (2017)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 196 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: generally adequate facilities; growth sectors include mobile telephone and data segments; effective competition; LTE expansion; tourism and telecom sector contribute greatly to the GDP (2018)
domestic: extensive interisland microwave radio relay links; 196 per 100 mobile-cellular teledensity (2019)
international: country code - 1-721; landing points for SMPR-1 and the ECFS submarine cables providing connectivity to the Caribbean; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2019)
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Internet country code
.sx; note - IANA has designated .sx for Sint Maarten, but has not yet assigned it to a sponsoring organization
Transportation
Airports - with paved runways
total: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2019)
note: Princess Juliana International Airport (SXM) was severely damaged on 6 September 2017 by hurricane Irma, but resumed commercial operations on 10 October 2017
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Philipsburg
oil terminal(s): Coles Bay oil terminal
Military and Security
Military and security forces
no regular military forces; Police Department for local law enforcement, supported by the Royal Netherlands Marechaussee (Gendarmerie), the Dutch Caribbean Police Force (Korps Politie Caribisch Nederland, KPCN), and the Dutch Caribbean Coast Guard (DCCG or Kustwacht Caribisch Gebied (KWCARIB))
Military - note
defense is the responsibility of the Kingdom of the Netherlands