Pitcairn Islands
Introduction
Background
Polynesians were the first inhabitants of the Pitcairn Islands, but the islands were uninhabited by the time they were discovered by Europeans in 1606. Pitcairn Island was rediscovered by British explorer Philip CARTERET in 1767, although he incorrectly plotted the coordinates. In 1789, Fletcher CHRISTIAN led a mutiny on the HMS Bounty and after several months of searching for Pitcairn Island, he landed on it with eight other mutineers and their Tahitian companions. They lived in isolation and evaded detection by English authorities until 1808, by which point only one man, 10 women, and 23 children remained. In 1831, with the population growing too big for the island - there were 87 people - the British attempted to move all the islanders to Tahiti, but they were soon returned to Pitcairn Island. The island became an official British colony in 1838 and in 1856, the British again determined that the population of 193 was too high and relocated all of the residents to Norfolk Island. Several families returned in 1858 and 1864, bringing the island’s population to 43, and almost all of the island’s current population are descendants of these returnees. In 1887, the entire population converted to the Seventh-Day Adventist faith.
The UK annexed the nearby islands of Henderson, Oeno, and Ducie in 1902 and incorporated them into the Pitcairn Islands colony in 1938, although all three are uninhabited. The population peaked at 233 in 1937 as outmigration, primarily to New Zealand, has thinned the population. Only two children were born between 1986 and 2012, and in 2005, a couple became the first new outsiders to obtain citizenship in more than a century. (The current population is below 50.) Since 2013, the Pitcairn Islands has tried to attract new migrants but has had no applicants because it requires prospective migrants to front significant sums of money and prohibits employment during a two-year trial period, at which point the local council can deny long-term resident status.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
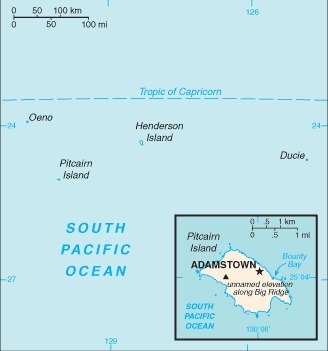
Location
Oceania, islands in the South Pacific Ocean, about midway between Peru and New Zealand
Geographic coordinates
25 04 S, 130 06 W
Map references
Oceania
Area - comparative
about three-tenths the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Coastline
51 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; hot and humid; modified by southeast trade winds; rainy season (November to March)
Terrain
rugged volcanic formation; rocky coastline with cliffs
Elevation
highest point: Palwala Valley Point on Big Ridge 347 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
Natural resources
miro trees (used for handicrafts), fish, note, manganese, iron, copper, gold, silver, and zinc have been discovered offshore
Land use
agricultural land: 0% (2011 est.)
forest: 74.5% (2018 est.)
other: 25.5% (2018 est.)
Irrigated land
0 sq km (2012)
Population distribution
less than 50 inhabitants on Pitcairn Island, most reside near the village of Adamstown
Natural hazards
occasional tropical cyclones (especially November to March), but generally only heavy tropical storms; landslides
Geography - note
Britain's most isolated dependency; only the larger island of Pitcairn is inhabited but it has no port or natural harbor; supplies must be transported by rowed longboat from larger ships stationed offshore
People and Society
Nationality
noun: Pitcairn Islander(s)
adjective: Pitcairn Islander
Ethnic groups
descendants of the Bounty mutineers and their Tahitian wives
Languages
English (official), Pitkern (mixture of an 18th century English dialect and a Tahitian dialect)
Religions
Seventh Day Adventist 100%
Age structure
0-14 years: NA
15-24 years: NA
25-54 years: NA
55-64 years: NA
65 years and over: NA
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: NA
youth dependency ratio: NA
elderly dependency ratio: NA
potential support ratio: NA
Population distribution
less than 50 inhabitants on Pitcairn Island, most reside near the village of Adamstown
Urbanization
urban population: 0% of total population (2012)
rate of urbanization: NA
Infant mortality rate
total: NA (2018)
male: NA
female: NA
Life expectancy at birth
total population: NA
male: NA
female: NA (2021 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: NA
unimproved: urban: NA
rural: NA
total: NA
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: malaria
Environment
Environment - current issues
deforestation (only a small portion of the original forest remains because of burning and clearing for settlement)
Climate
tropical; hot and humid; modified by southeast trade winds; rainy season (November to March)
Land use
agricultural land: 0% (2011 est.)
forest: 74.5% (2018 est.)
other: 25.5% (2018 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 0% of total population (2012)
rate of urbanization: NA
Major infectious diseases
degree of risk: high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: malaria
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie, and Oeno Islands
conventional short form: Pitcairn Islands
etymology: named after Midshipman Robert PITCAIRN who first sighted the island in 1767
Government type
parliamentary democracy
Dependency status
overseas territory of the UK
Capital
name: Adamstown
geographic coordinates: 25 04 S, 130 05 W
time difference: UTC-9 (4 hours behind Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: named after John Adams (1767–1829), the last survivor of the Bounty mutineers who settled on Pitcairn Island in January 1790
Administrative divisions
none (overseas territory of the UK)
Independence
none (overseas territory of the UK)
National holiday
Birthday of Queen ELIZABETH II, second Saturday in June (1926); Discovery Day (Pitcairn Day), 2 July (1767)
Constitution
history: several previous; latest drafted 10 February 2010, presented 17 February 2010, effective 4 March 2010
amendments: Reviewed 10 Jun '21; NC
Legal system
local island by-laws
Citizenship
see United Kingdom
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal with three years residency
Executive branch
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by UK High Commissioner to New Zealand and Governor (nonresident) of the Pitcairn Islands Laura CLARK (since 25 January 2018)
head of government: Mayor and Chairman of the Island Council Charlene WARREN-PEU (since 1 January 2020)
cabinet: none
elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor and commissioner appointed by the monarch; island mayor directly elected by majority popular vote for a 3-year term; election last held on 6 November 2019 (next to be held not later than December 2022)
election results: Charlene WARREN-PEU elected mayor and chairman of the Island Council; Island Council vote - NA
Legislative branch
description: unicameral Island Council (10 seats; 4 members directly elected by proportional representation vote, 1 nominated by the elected Council members, 2 appointed by the governor, and 3 ex-officio members - the governor, deputy governor, and commissioner; elected members serve 1-year terms)
elections: last held in November 2017 (next to be held not later than December 2019)
election results: percent of vote - NA; seats - 5 independent; composition - men 5, women 5, percent of women 50%
Judicial branch
highest courts: Pitcairn Court of Appeal (consists of the court president, 2 judges, and the Supreme Court chief justice, an ex-officio member); Pitcairn Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and 2 judges); note - appeals beyond the Pitcairn Court of Appeal are referred to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London)
judge selection and term of office: all judges of both courts appointed by the governor of the Pitcairn Islands on the instructions of the Queen of England through the Secretary of State; all judges can serve until retirement, normally at age 75
subordinate courts: Magistrate's Court
Diplomatic representation in the US
none (overseas territory of the UK)
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: none (overseas territory of the UK)
Flag description
blue with the flag of the UK in the upper hoist-side quadrant and the Pitcairn Islander coat of arms centered on the outer half of the flag; the green, yellow, and blue of the shield represents the island rising from the ocean; the green field features a yellow anchor surmounted by a bible (both the anchor and the bible were items found on the HMS Bounty); sitting on the crest is a Pitcairn Island wheelbarrow from which springs a flowering twig of miro (a local plant)
National anthem
name: We From Pitcairn Island
lyrics/music: unknown/Frederick M. LEHMAN
note: serves as a local anthem; as a territory of the UK, "God Save the Queen" is official (see United Kingdom)
Economy
Economic overview
The inhabitants of this tiny isolated economy exist on fishing, subsistence farming, handicrafts, and postage stamps. The fertile soil of the valleys produces a wide variety of fruits and vegetables, including citrus, sugarcane, watermelons, bananas, yams, and beans. Bartering is an important part of the economy. The major sources of revenue are the sale of postage stamps to collectors and the sale of handicrafts to passing ships.
Agricultural products
honey; wide variety of fruits and vegetables; goats, chickens; fish
Industries
postage stamps, handicrafts, beekeeping, honey
Labor force - by occupation
note: no business community in the usual sense; some public works; subsistence farming and fishing
Budget
revenues: 746,000 (FY04/05)
expenditures: 1.028 million (FY04/05)
Fiscal year
1 April - 31 March
Exports
NA
Exports - partners
South Africa 24%, Canada 20%, Germany 13%, Czechia 8%, El Salvador 5%, Spain 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
leather footwear, gas turbine parts, precious metal ores, clothing and apparel, beef (2019)
Imports
NA
Imports - partners
Ecuador 43%, New Zealand 29% (2019)
Imports - commodities
crude petroleum, refined petroleum, food preparation products, plastics, iron fasteners (2019)
Exchange rates
New Zealand dollars (NZD) per US dollar -
1.416 (2017 est.)
1.4279 (2016 est.)
1.4279 (2015)
1.4279 (2014 est.)
1.2039 (2013 est.)
Communications
Telecommunication systems
general assessment: satellite-based phone services; rural connectivity a challenge; 2G services widespread; demand for mobile broadband due to mobile services providing Internet source; the launch of the Kacific-1 satellite in 2019 will improve telecommunications in the region (2020)
domestic: local phone service with international connections via Internet (2018)
international: country code - 872; satellite earth station - 1 Inmarsat
note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced downturn, particularly in mobile device production; many network operators delayed upgrades to infrastructure; progress towards 5G implementation was postponed or slowed in some countries; consumer spending on telecom services and devices was affected by large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home became evident, and received some support from governments
Broadcast media
satellite TV from Fiji-based Sky Pacific offering a wide range of international channels
Internet users
total: 54
percent of population: 100% (July 2016 est.)
Communications - note
satellite-based local phone service and broadband Internet connections available in all homes
Transportation
Ports and terminals
major seaport(s): Adamstown (on Bounty Bay)
Military and Security
Military - note
defense is the responsibility of the UK