Country Summary


Introduction
Background
A Rwandan kingdom dominated the region from the mid-18th century onward, with Tutsi rulers conquering others militarily and centralizing power. German colonial rule began in 1898, but Belgian forces captured Rwanda in 1916 during World War I. Rwandan independence came in 1962. Conflict between Tutsi and Hutu ethnic groups continued for decades. Rwanda held its first local elections in 1999 and its first presidential and legislative elections in 2003.
Geography
Area
total: 26,338 sq km
land: 24,668 sq km
water: 1,670 sq km
Climate
temperate; two rainy seasons (February to April, November to January); mild in mountains with frost and snow possible
Natural resources
gold, cassiterite (tin ore), wolframite (tungsten ore), methane, hydropower, arable land
People and Society
Population
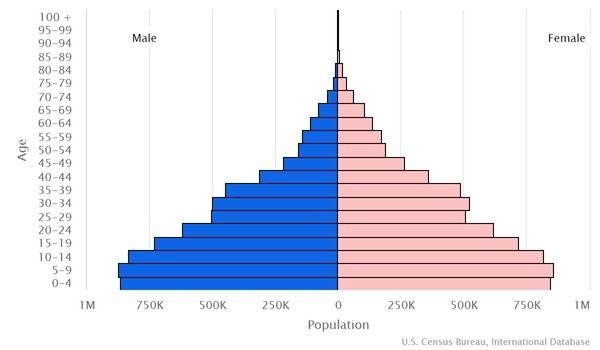
13,173,730 (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Hutu, Tutsi, Twa (Pygmy)
Languages
Kinyarwanda (official, universal Bantu vernacular) 93.2%, French (official) <0.1, English (official) <0.1, Swahili/Kiswahili (official, used in commercial centers) <0.1, more than one language, other 6.3%, unspecified 0.3% (2002 est.)
Religions
Protestant 57.7% (includes Adventist 12.6%), Roman Catholic 38.2%, Muslim 2.1%, other 1% (includes traditional, Jehovah's Witness), none 1.1% (2019-20 est.)
Population growth rate
1.74% (2022 est.)
Government
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Kigali
Executive branch
chief of state: President Paul KAGAME (since 22 April 2000)
head of government: Prime Minister Edouard NGIRENTE (since 30 August 2017)
Legislative branch
description: bicameral Parliament consists of:
Senate or Senat (26 seats; 12 members indirectly elected by local councils, 8 appointed by the president, 4 appointed by the Political Organizations Forum - a body of registered political parties, and 2 selected by institutions of higher learning; members serve 8-year terms)
Chamber of Deputies or Chambre des Deputes (80 seats; 53 members directly elected by proportional representation vote, 24 women selected by special interest groups, and 3 selected by youth and disability organizations; members serve 5-year terms)
Economy
Economic overview
fast-growing Sub-Saharan economy; major public investments; trade and tourism hit hard by COVID-19; increasing poverty after 2 decades of declines; Ugandan competition for regional influence; major coffee exporter; contested GDP figures
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$27.18 billion (2020 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$2,100 (2020 est.)
Agricultural products
bananas, sweet potatoes, cassava, potatoes, plantains, beans, maize, gourds, milk, taro
Industries
cement, agricultural products, small-scale beverages, soap, furniture, shoes, plastic goods, textiles, cigarettes
Exports
$2.25 billion (2019 est.)
Exports - partners
United Arab Emirates 35%, Democratic Republic of the Congo 28%, Uganda 5% (2019)
Exports - commodities
gold, refined petroleum, coffee, tea, tin (2019)
Imports
$3.74 billion (2019 est.)
Imports - partners
China 17%, Kenya 10%, Tanzania 9%, United Arab Emirates 9%, India 7%, Saudi Arabia 5% (2019)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, gold, raw sugar, packaged medicines, broadcasting equipment (2019)
Exchange rates
Rwandan francs (RWF) per US dollar -
Page last updated: Sunday, July 31, 2022
